scrapy模擬模擬點擊
復雜系統 (Complex Systems)
In our daily life, we encounter many complex systems where individuals are interacting with each other such as the stock market or rush hour traffic. Finding appropriate models for these complex systems may give us a better understanding of their dynamics and allows us to simulate its behaviour under changing conditions. One way of modelling complex systems is by using agent-based models, meaning that we are explicitly simulating individuals and their interactions instead of deriving the dynamics of the system in an aggregate way.
在我們的日常生活中,我們會遇到許多復雜的系統,在這些系統中,人們彼此交互,例如股票市場或交通高峰時間。 為這些復雜的系統找到合適的模型可以使我們對它們的動力學有更好的理解,并使我們能夠模擬在變化條件下的行為。 對復雜系統建模的一種方法是使用基于代理的模型,這意味著我們顯式地模擬個人及其交互,而不是以聚合的方式得出系統動態。
In this post, we want to develop such an agent-based model using python. As an example, we try to model the behaviour of a pandemic. Please note that I am not at all an epidemiologist. The goal of this post is not to build a sophisticated model capable of making real life predictions, but rather to see how we can build a simple agent-based model and study some of the resulting dynamics. Let's start with some basic considerations.
在本文中,我們想使用python開發這種基于代理的模型。 例如,我們嘗試對大流行的行為進行建模。 請注意,我根本不是流行病學家。 這篇文章的目的不是要建立一個能夠做出真實生活預測的復雜模型,而是要了解我們如何建立一個簡單的基于主體的模型并研究由此產生的動力學。 讓我們從一些基本考慮開始。
我們模型的基礎 (Foundations of Our Model)
For our example we assume a non-lethal disease that may spread between individuals which were in contact with each other. The most basic approach is to consider three different groups:
對于我們的示例,我們假設一種非致命性疾病可能會在彼此接觸的個體之間傳播。 最基本的方法是考慮三個不同的組:
Individuals that are not yet infected, called the susceptible group.
尚未感染的個體稱為易感人群。
Individuals that are infected and may spread the disease.
被感染并可能傳播疾病的個體。
Individuals that have recovered from the disease and are now immune.
已從疾病中恢復并且現在已經免疫的個體。
Because of the three involved groups (Susceptible, Infected, Recovered), these models are also called SIR-Models.
由于這三個參與組(Sout usceptible, 我 nfected,R ecovered),這些模型也被稱為SIR-模型。
分析型SIR模型 (Analytical SIR-Model)
We will start with a mathematical SIR-model that will serve us as a benchmark model. In the basic SIR-model, the flow between the three groups is: S -> I -> R . It is a one-way street where in the beginning most individuals are in the S group, eventually cascading via the I group into the R group. At each time step t a certain amount of individuals are traversing from S to I and from I to R, while the total number of individuals N = S+I+R stays constant. We can write these dynamics into a set of differential equations, or, in a bit more understandable form, we can write down by how much each of the groups changes for a certain time step:
我們將從數學SIR模型開始,它將作為基準模型。 在基本的SIR模型中,三組之間的流為: S -> I -> R 這是一條單向街,一開始大多數人都屬于S組,最終通過I組級聯到R組。 在每個時間步t ,一定數量的個體從S遍歷到I ,從I遍歷到R ,而個體的總數N = S + I + R保持不變。 我們可以將這些動力學寫成一組微分方程,或者以一種更易理解的形式,寫下每個組在特定時間步長變化的量:
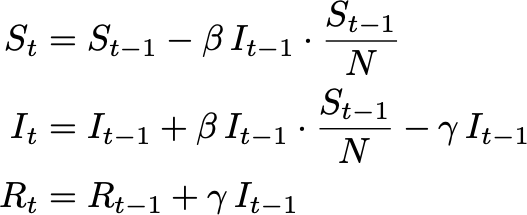
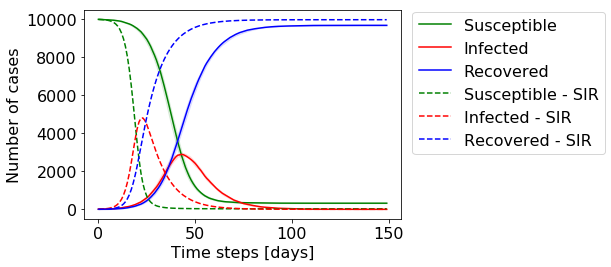
The dynamics are governed by two variables β and γ. While β is the rate with which infectious individuals infect others, γ is the rate at which infectious individuals recover. These dynamics are visualized below for a fixed β and γ:
動力學由兩個變量β和γ控制 。 β是感染性個體感染他人的速度,而γ是感染性個體康復的速度。 對于固定的β和γ,這些動力學如下所示:
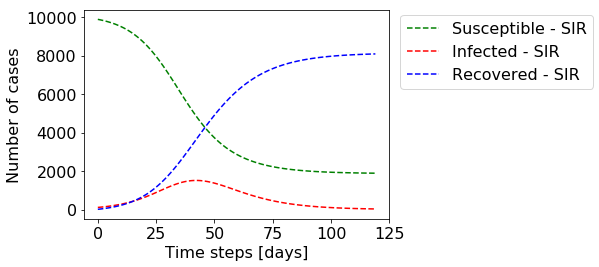
You can see that the number of infected individuals grows fast, peaking around day 40 which is when the number of susceptible individuals drops significantly, slowing down the rate of infections. This is simply because by then a significant amount of individuals already had the disease and cannot be infected anymore. Towards the end, the number of infected individuals drops to zero, eradicating the disease. Note that by then around 20% of the individuals were never infected. This so-called steady-state solution can also be calculated analytically and depends on the parameters β and γ.
您可以看到感染個體的數量快速增長,在第40天左右達到峰值,此時易感染個體的數量顯著下降,從而降低了感染速度。 這僅僅是因為到那時大量的個體已經患有該疾病并且不再被感染。 最終,被感染的人數降至零,從而根除了這種疾病。 請注意,到那時,大約20%的個人從未感染過。 所謂的穩態解也可以解析地計算,并且取決于參數β和γ。
With this simple SIR-model we can already observe some basic dynamics for our problem. However, we are looking at our groups only in an aggregate way. We assume that the individuals are a homogeneous, unstructured set organized into three well defined, perfectly mixed groups. The interactions that are modeled are only on average. Every infected individual infects on each day a fixed number of contacts and a constant fraction of all infected individuals is cured each day. There is no way of implementing complex social interactions of individuals within this model. In order to relax some of these assumptions we will now set up an agent-based model simulating each individual separately.
使用這個簡單的SIR模型,我們已經可以觀察到問題的一些基本動態。 但是,我們僅以匯總方式查看我們的組。 我們假設個體是一個均勻的,無結構的集合,分為三個定義明確,完全混合的組。 建模的交互僅是平均水平 。 每個受感染的個體每天都會感染固定數量的接觸者,并且每天治愈所有受感染個體的一定比例。 在這種模式下,無法實現個人之間復雜的社會互動。 為了放寬這些假設,我們現在將建立一個基于代理的模型,分別模擬每個人。
基于代理的模型 (Agent-Based Model)
Our first goal is to reproduce the results from the analytical SIR-model. As a data structure we want to use pandas dataframes. Let's start with initializing 10'000 agents represented as rows in the dataframe:
我們的首要目標是從分析性SIR模型中復制結果。 作為數據結構,我們要使用pandas數據框。 讓我們從初始化以數據幀中的行表示的1萬個代理開始:

Currently, the dataframe has only one row called state which indicates the health state of the agent. We encode susceptible with 0, infected with 1 and recovered with 2.
當前,數據幀只有一行稱為狀態的行,該行指示代理的運行狀況。 我們將敏感編碼為0,感染1,然后恢復2。
Now we need some function that infects an agent. We want this function to take a list of agents that were in contact with an infected agent. Additionally, we want to give a probability with which these contacts actually get infected. Here some Monte Carlo methods come into play in order to add randomness. The function below does the required job.
現在,我們需要一些感染代理的功能。 我們希望此功能獲取與受感染代理聯系的代理列表。 此外,我們希望提供這些接觸實際上被感染的可能性。 在這里,一些蒙特卡洛方法開始發揮作用,以增加隨機性。 下面的功能完成所需的工作。
def infect(df, contacts, probability=1.0):unique, counts = np.unique(contacts, return_counts=True)roll = np.random.uniform(0,1,len(unique))# accounts for several contacts of the same agentprobability = 1 - np.power(1-probability, counts)change = np.array(roll <= probability).astype(int)state = df.loc[unique,"state"]# If change == 0, state is not updated# If change == 1, change the state only if the agent belongs# to the susceptible group: state 0 -> 1, 1 -> 1, 2 -> 2df.loc[unique,"state"] = state + change*np.maximum((1-state),0)The list of contacts allows to hold the same agent multiple times. We roll a random number between 0 to 1 for each unique agent in the contact list and update the state from susceptible (0) to infected (1) if this roll is below a probability threshold. The last line of the function is updating the state column accordingly.
聯系人列表允許多次保存同一座席。 對于聯系列表中的每個唯一代理,我們在0到1之間滾動一個隨機數,如果此滾動低于概率閾值,則將狀態從易感(0)更新為受感染(1)。 函數的最后一行將相應地更新狀態列。
Similarly, we need a function that recovers infected agents with a certain probability. Here, we use a flat chance of recovery in every time step.
同樣,我們需要一個能夠以一定概率恢復受感染代理的函數。 在這里,我們在每個時間步均使用恢復的機會很小。
def recover(df, probability): roll = np.random.uniform(0,1,len(df[df["state"] == 1]))chance = np.array(roll <= probability).astype(int)df.loc[df["state"] == 1,"state"] = 1 + chanceThe infect and recover functions are called at every time step. For this we create a step function. Here, we are generating the list of random contacts which has a length of a constant time the number of infected agents.
感染和恢復功能在每個時間步都被調用。 為此,我們創建了一個步進函數。 在這里,我們正在生成隨機聯系人列表,該列表的長度是受感染代理程序數量的恒定時間。
def step(df):nInfected = np.sum(df["state"] == 1)contacts = np.random.choice(df.index, _randomContacts * nInfected, replace=True)infect(df, contacts, _chanceOfInfection)recover(df, _chanceOfRecovery)In order to get a feeling for the variations in the outcome of our agent based model we will run the simulation ten times. For each experiment we initialize a set of 10'000 agents with 5 infected patients zero to start with. We then perform 150 time steps.
為了了解基于代理的模型結果的變化,我們將運行十次模擬。 對于每個實驗,我們從5個被感染的患者零開始初始化一組10,000個代理。 然后,我們執行150個時間步。
_nExperiments = 10
_nAgents = 10000
_nSteps = 150_nPatientZero = 5for iExp in range(_nExperiments):df = init(_nAgents, _nPatientZero)for i in tqdm(range(_nSteps)): step(df)基準結果 (Baseline Results)
Visualizing the size of each of the three groups (susceptible, infected and recovered) at each time step, we can see that the dynamics of our agent based model are in agreement with the basic SIR-model.
可視化每個時間步長的三個組(易感,感染和恢復)的大小,我們可以看到基于代理的模型的動力學與基本SIR模型一致。

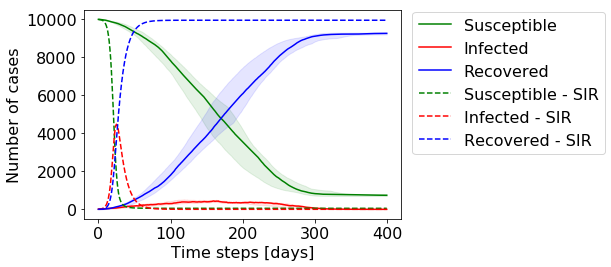
The solid lines show the median of our 10 runs of the simulation, while the shaded area shows the area between the 25%-75% quantile. Even though there is some variance in the central part of the simulation, all models arrive at a very similar endpoint, which equals to the analytical solution.
實線顯示了10次模擬的中位數,而陰影區域顯示了25%-75%分位數之間的面積。 即使模擬的中心部分存在一些差異,但所有模型到達的端點都非常相似,這等于解析解。
Up to now we have not gained much in comparison to the basic SIR-model, but we have setup an agent-based baseline model and verified that it behaves similar. With this setup we can now start to add extra complexity.
到目前為止,與基本SIR模型相比,我們還沒有獲得多少好處,但是我們已經建立了基于代理的基線模型,并驗證了它的行為類似。 通過此設置,我們現在可以開始增加額外的復雜性。
基于空間代理的模型 (Spatial Agent-Based Model)
It is intuitive that the assumption that an infected agent will have contact with a set of completely random agents may not hold true in real life. You would rather expect some social neighborhood, a group of contacts the infected agents acts with on a regular basis. An easy way of simulating this effect is to place the agents on a lattice and let them interact with their nine closest neighbors.
直觀地認為,感染者將與一組完全隨機的代理接觸的假設在現實生活中可能并不成立。 您寧愿期望有一些社交鄰居,也可以是感染者定期與之聯系的一組聯系人。 模擬此效果的一種簡單方法是將代理放置在晶格上,并使它們與9個最近的鄰居進行交互。
Note the prolonged x-axis. You can see that the dynamics are now much slower for the spatial agent based model. I even had to increase the chanceOfInfection significantly, to get it going. The structure that we introduced to the contacts leads to the fact that an infected agent lives in an environment were there are already many agents who are infected as well or have recovered already thus leading to a significant decrease in the spreading of the disease. We can have a look at the spatial distribution of the agents visually in the animation below:
注意延長的x軸。 您可以看到,對于基于空間代理的模型,動力學現在要慢得多。 我什至不得不大幅度增加感染的機會 ,才能使感染持續下去。 我們介紹給聯系人的結構導致這樣一個事實,即被感染的病原體生活在環境中,因為已經有許多病原體也被感染或已經康復,因此導致疾病傳播的顯著減少。 我們可以在下面的動畫中直觀地查看代理的空間分布:
添加隨機聯系人 (Adding Random Contacts)
We saw that when we introduce spatial structure to the social interactions of the agents, the dynamics of the disease are slowed down significantly. What happens when we introduce for every agents an additional random contact besides its nine spatial neighbors?
我們看到,當我們在代理人的社會互動中引入空間結構時,疾病的動力學會大大減慢。 當我們為每個代理引入除其9個空間鄰居之外的其他隨機接觸時,會發生什么情況?

With only one additional random contact the dynamics of the infection are again much faster, quickly breaking the structure we introduced by placing the agents on the lattice.
只需要再進行一次隨機接觸,感染的動力學就會更快得多,通過將藥劑置于晶格上,可以Swift破壞我們引入的結構。
日益復雜 (Increasing Complexity)
We have a working setup that one can now play with by increasing the complexity. One could think of modeling different separate clusters of agents that are only interconnected weakly, or introducing an age structure for the agents reflecting different kinds of interactions for different age groups. Additionally, one could start introducing measures to reduce the chance of infection at a certain time step or reducing the number of contacts.
我們現在可以通過增加復雜性來進行工作。 可以想到的是,對僅相互聯系較弱的代理的不同單獨群集進行建模,或者為代理引入年齡結構,以反映不同年齡組的不同類型的交互。 另外,人們可以開始采取措施以減少在特定時間步的感染機會或減少接觸數量。
性能 (Performance)
One word about the performance of the model. Usually, I like using an object oriented approach for building agent-based models. Modelling the agents as a class makes the simulation and the coding quite intuitive. However, in python the simulation may quickly become relatively slow. By storing the data into pandas dataframes, where one row represents one agent, we are loosing a bit of flexibility, but we can rely on numpy functions doing the major workload, thus making the simulation reasonably fast. The presented examples run with about 50 steps per second on my machine for 100'000 simulated agents, producing the output of the simulation within a few seconds.
關于模型性能的一句話。 通常,我喜歡使用面向對象的方法來構建基于代理的模型。 將代理建模為一個類可以使仿真和編碼變得非常直觀。 但是,在python中,仿真可能很快變得相對緩慢。 通過將數據存儲到熊貓數據幀(其中一行代表一個代理)中,我們失去了一定的靈活性,但是我們可以依靠numpy函數來完成主要工作量,從而使仿真速度相當快。 所提供的示例在我的計算機上以每秒約50步的速度運行,以處理100'000個模擬代理,并在幾秒鐘內產生了模擬輸出。
結論 (Conclusions)
I showed you how to set up a basic agent-based model from scratch. We looked at the example of modelling a spreading disease. As a first step we were validating a minimal version of our model against a known mathematical model. We then started changing parameters in order to investigate changes in the dynamics of the system. By introducing a lattice structure to the agents we observed that the spread of the disease slowed down significantly, but allowing for only one random contact again lead to increasing dynamics. The presented implementation is a flexible setup that allows for an easy implementation of more complex interactions, heterogeneity and structure within the agents. Also, we are capable of studying agents on an individual level, or subgroups of agents within a complex, large scale simulation.
我向您展示了如何從頭開始建立基于代理的基本模型。 我們看了一個模擬傳播疾病的例子。 第一步,我們根據已知的數學模型驗證模型的最小版本。 然后,我們開始更改參數,以調查系統動態的變化。 通過向藥劑中引入晶格結構,我們觀察到疾病的傳播速度顯著減慢,但僅允許一次隨機接觸又導致動力學增加。 提出的實現是一種靈活的設置,可以輕松實現代理中更復雜的交互,異構性和結構。 而且,我們能夠研究單個級別的代理商,或在復雜的大規模模擬中研究代理商的子組。
Feel free to use this setup as a starter and play with it. The full code can be accessed here:
隨意使用此設置作為入門工具并進行嘗試。 完整的代碼可以在這里訪問:
翻譯自: https://towardsdatascience.com/modelling-a-pandemic-eb94025f248f
scrapy模擬模擬點擊
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。 如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/389417.shtml 繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/389417.shtml 英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/389417.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!


















