人流量統計系統介紹
Its very important to know about statistics . May you be a from a finance background, may you be data scientist or a data analyst, life is all about mathematics. As per the wiki definition “Statistics is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied.”
了解統計信息非常重要。 可能您是金融背景的人,可能是數據科學家或數據分析師,生活全都與數學有關。 按照Wiki的定義,“統計是一門涉及數據收集,組織,分析,解釋和表示的學科。 在將統計信息應用于科學,工業或社會問題時,通常從統計人口或要研究的統計模型開始。”
Today in this article, we will go through the basics of statistics and in the next few articles we can deep dive.
今天,在本文中,我們將介紹統計學的基礎知識,在接下來的幾篇文章中,我們將深入探討。
Things covered in this article:
本文涵蓋的內容:
· Data type
· 數據類型
· Distributions
·發行
· Sampling and distribution
·抽樣和分配
· Hypothesis testing
· 假設檢驗
Data type:
數據類型:
Roughly we can divide data into 2 types. Categorical and Numerical. Categorical is further divided into Nominal and Ordinal. Numerical is divided into Discrete and continuous.
我們大致可以將數據分為兩種類型。 分類和數值。 分類進一步分為標稱和序數。 數值分為離散和連續。
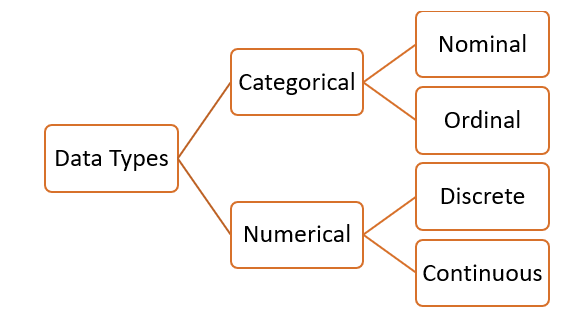
Examples:
例子:
1. What are the names of the students ?[Options — Tony, Harry, Tom, Alex].
1.學生的名字是什么?[選項-托尼,哈里,湯姆,亞歷克斯]。
[ Tony, Harry, Tom, Alex] -> is called the sample space. And these are categorical data. This is Nominal data too because this is used for naming or labeling variables, without any quantitative value.
[Tony,Harry,Tom,Alex]->稱為樣本空間。 這些是分類數據。 這也是名義數據,因為它用于命名或標記變量,沒有任何定量值。
2. Which rating would you give to “XYZ” movie? [Very good, Good, Bad, Worse]
2.您將給“ XYZ”電影哪個等級? [很好,很好,不好,更糟]
This is also categorical data, but ordinal as this has a set order or a scale associated with it.
這也是分類數據,但按序排列,因為它具有設定的順序或與之相關的標度。
3. How many students are there in a class? [ 2,3,4…10……100]
3.班上有多少個學生? [2,3,4…10……100]
This is an example of discrete data as this can take only certain values. We can’t have students as 2.5. So, it can have only certain values.
這是離散數據的示例,因為它只能采用某些值。 我們不能有2.5個學生。 因此,它只能具有某些值。
4. What is the height of the students? [1–10]
4.學生的身高是多少? [1-10]
This is an example of continuous data. The height can take any values like 1.2, 1.87, 1.09 etc. These numbers can have any decimal point and can divide these if we want.
這是連續數據的示例。 高度可以采用任何值,例如1.2、1.87、1.09等。這些數字可以具有任何小數點,并且可以根據需要將它們相除。
Distributions
發行版
How are marks of students distributed?
學生分數如何分配?
Minimum marks : 20
最少分數:20
Maximum marks : 100
最高分數:100
This means that the marks are distributed between 20 to 100. So, this can be represented in the form of a PDF (probability distribution function).
這意味著標記分布在20到100之間。因此,可以用PDF(概率分布函數)的形式表示。
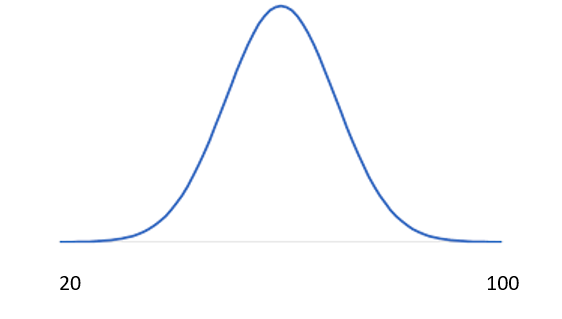
This can be read as — the distribution of the marks of the students (population) are from 20 to 100. All other students will have marks between these two numbers. Or in other words –in terms of probability density function its the probability of selecting someone at random from that population at every given mark. So the probability that someone will have marks around the center ( 60 ) will be more compared to someone having marks as 25 or 95. If I select someone at random, there is highest probability that I would choose a student with marks around 60(the mean ).This curve is called bell curve or a normal distribution curve. The distribution is symmetrical.
可以理解為—學生的分數分布(人口)是20到100。其他所有學生的分數在這兩個數字之間。 換句話說,就概率密度函數而言,它是在每個給定標記處從該人口中隨機選擇某人的概率。 因此,某人在中心(60)周圍有分數的概率要比有25或95的分數高。 如果我隨機選擇某人,則我選擇一個分數在60左右的學生的可能性最大。意思 )。 該曲線稱為鐘形曲線或正態分布曲線。 分布是對稱的 。
Some common terms used in statistics:
統計中使用的一些常用術語:
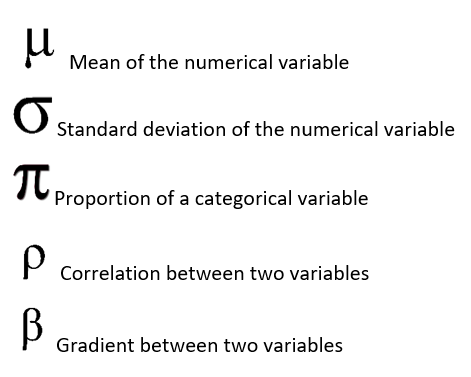
When we take a sample these variables symbols changes. These are X? for mean, S for standard deviation, p for proportion, r for correlation and b for gradient.
當我們取樣時,這些變量符號會發生變化。 這些是平均值的X 1,標準差的S,比例的p,相關性的r和梯度的b。
Hypothesis testing
假設檢驗
Lets understand this with an example.
讓我們用一個例子來理解這一點。
Example: Did dieters lose more fat than the exercisers? We are given certain numbers as below.
例:節食者比運動者失去的脂肪更多嗎? 我們給了某些數字如下。
Diet Only:
僅飲食:
sample mean = 5.9 kg
樣本平均值= 5.9千克
sample standard deviation = 4.1 kg
樣品標準偏差= 4.1千克
sample size = n = 42
樣本量= n = 42
standard error = SEM1 = 4.1/ √42 = 0.633
標準誤差= SEM1 = 4.1 /√42= 0.633
Exercise Only:
僅練習:
sample mean = 4.1 kg
樣本平均值= 4.1千克
sample standard deviation = 3.7 kg
樣品標準偏差= 3.7千克
sample size = n = 47
樣本量= n = 47
standard error = SEM2 = 3.7/ √47 = 0.540
標準誤差= SEM2 = 3.7 /√47= 0.540
measure of variability = [(0.633)2 + (0.540)2] = 0.83
變異性的度量= [(0.633)2 +(0.540)2] = 0.83
Step 1: Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.
步驟1:確定原假設和替代假設。
Null hypothesis: No difference in average fat lost in population for two methods. Population mean difference is zero.
無假設 :兩種方法在人群中平均脂肪損失沒有差異。 總體平均差為零。
Alternative hypothesis: There is a difference in average fat lost in population for two methods. Population mean difference is not zero.
替代假設 :兩種方法在人群中平均損失的脂肪有所不同。 總體平均差異不為零。
Step 2. Collect and summarize data into a test statistic.
步驟2.收集數據并將其匯總到測試統計信息中。
The sample mean difference = 5.9–4.1 = 1.8 kg
樣本平均差異= 5.9–4.1 = 1.8千克
The standard error of the difference is 0.83.
差異的標準誤差為0.83。
So the test statistic: z = (1.8–0)/0.83 = 2.17
因此,檢驗統計量:z =(1.8-0)/0.83 = 2.17
Step 3. Determine the p-value.
步驟3.確定p值。
Recall the alternative hypothesis was two-sided. p-value = 2 × [proportion of bell-shaped curve above 2.17]
回想一下替代假設是兩面的。 p值= 2×[2.17以上的鐘形曲線比例]
proportion is about 2 × 0.015(this value comes from a standard table) = 0.03.
比例約為2×0.015(該值來自標準表)= 0.03。
Step 4. Decide.
步驟4.決定。
The p-value of 0.03 is less than or equal to 0.05, so …
p值0.03小于或等于0.05,因此…
? If really no difference between dieting and exercise as fat loss methods, would see such an extreme result only 3% of the time, or 3 times out of 100.
?如果節食和運動作為減脂方法確實沒有區別,那么僅3%的時間(或100的3倍)就會看到這樣的極端結果。
? Prefer to believe truth does not lie with null hypothesis. We conclude that there is a statistically significant difference between average fat loss for the two methods.
?寧愿相信真理不在于虛無假設。 我們得出的結論是,兩種方法的平均減脂之間存在統計學上的顯著差異。
Congratulations, you did it.
恭喜,您做到了。
For now, thank you all for making it this far. We covered basics of hypothesis tests and the bell curve. We will deep dive into various types of distributions and their terminologies.
現在,謝謝大家所做的一切。 我們介紹了假設檢驗和鐘形曲線的基礎。 我們將深入研究各種發行版本及其術語。
And as always, if there are any question, remarks, or comments feel free to contact me!
和往常一樣,如果有任何問題,評論或意見,請隨時與我聯系!
Reference :
參考:
Statistics How To
統計方法
https://www2.stat.duke.edu/courses
https://www2.stat.duke.edu/courses
翻譯自: https://medium.com/@biswasstar/introduction-of-statistics-53b0f293e0e0
人流量統計系統介紹
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。 如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/389401.shtml 繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/389401.shtml 英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/389401.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!





和下采樣(縮小圖像)(最鄰近插值和雙線性插值的理解和實現))




)







