2074. 反轉偶數長度組的節點
給你一個鏈表的頭節點 head 。
鏈表中的節點 按順序 劃分成若干 非空 組,這些非空組的長度構成一個自然數序列(1, 2, 3, 4, …)。一個組的 長度 就是組中分配到的節點數目。換句話說:
- 節點 1 分配給第一組
- 節點 2 和 3 分配給第二組
- 節點 4、5 和 6 分配給第三組,以此類推
注意,最后一組的長度可能小于或者等于 1 + 倒數第二組的長度 。
反轉 每個 偶數 長度組中的節點,并返回修改后鏈表的頭節點 head 。
示例 1:
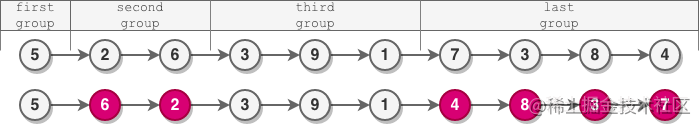
輸入:head = [5,2,6,3,9,1,7,3,8,4]
輸出:[5,6,2,3,9,1,4,8,3,7]
解釋:
- 第一組長度為 1 ,奇數,沒有發生反轉。
- 第二組長度為 2 ,偶數,節點反轉。
- 第三組長度為 3 ,奇數,沒有發生反轉。
- 最后一組長度為 4 ,偶數,節點反轉。
示例 2:
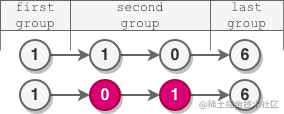
輸入:head = [1,1,0,6]
輸出:[1,0,1,6]
解釋:
- 第一組長度為 1 ,沒有發生反轉。
- 第二組長度為 2 ,節點反轉。
- 最后一組長度為 1 ,沒有發生反轉。
示例 3:
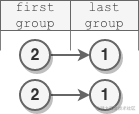
輸入:head = [2,1]
輸出:[2,1]
解釋:
- 第一組長度為 1 ,沒有發生反轉。
- 最后一組長度為 1 ,沒有發生反轉。
示例 4:
輸入:head = [8]
輸出:[8]
解釋:只有一個長度為 1 的組,沒有發生反轉。
提示:
- 鏈表中節點數目范圍是 [1,105][1, 10^5][1,105]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 10510^5105
解題思路
按組遍歷每個鏈表,根據每個組的編號,決定每個組內應該存在多少個鏈表節點,對于偶數長度的節點,先將每個組的所有鏈表節點分隔出來,再將每組節點完成一次鏈表逆置,再重新連接到原鏈表上。
代碼
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *reverse(ListNode *head,ListNode *end,int group){ListNode * pre=head,*cur=head->next;pre->next=end;for (int i = 0; i < group-1&&cur!= nullptr; ++i) {ListNode *next=cur->next;cur->next=pre;pre=cur;cur=next;}return pre;}ListNode *reverseEvenLengthGroups(ListNode *head) {ListNode *cur = head->next,*old=head,*pre=head;int group_no = 2;while (cur!= nullptr) {int res(0);ListNode *temp=cur;for (int i = 0; i < group_no&&temp!= nullptr ; ++i) {temp=temp->next;res++;}if (res%2==0){ListNode *temp=cur;for (int i = 0; i < group_no&&temp!= nullptr ; ++i) {temp=temp->next;}ListNode *next_pre=cur;pre->next=reverse(cur,temp,group_no);pre=next_pre;cur=temp;} elsefor (int i = 0; i < group_no&&cur!= nullptr; ++i) {pre=cur;cur=cur->next;}group_no++;}return old;}
};



:落地微服務架構到直銷系統(事件存儲))






)




![BZOJ.1024.[SCOI2009]生日快樂(記憶化搜索)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BZOJ.1024.[SCOI2009]生日快樂(記憶化搜索))


