第三章:E2B沙箱交互
在前兩章中,我們掌握了對話狀態管理和AI代碼生成管道的運作原理。
但生成代碼如何真正運行?這正是E2B沙箱交互的核心價值。
架構定位
E2B沙箱是專為open-lovable打造的虛擬計算環境,具備以下核心能力:
- 環境隔離:
獨立于本地系統的安全沙盒 - 依賴管理:
自動化安裝Node.js/npm等工具鏈 - 實時預覽:
即時呈現代碼運行效果 - 資源回收:會話結束
自動清理
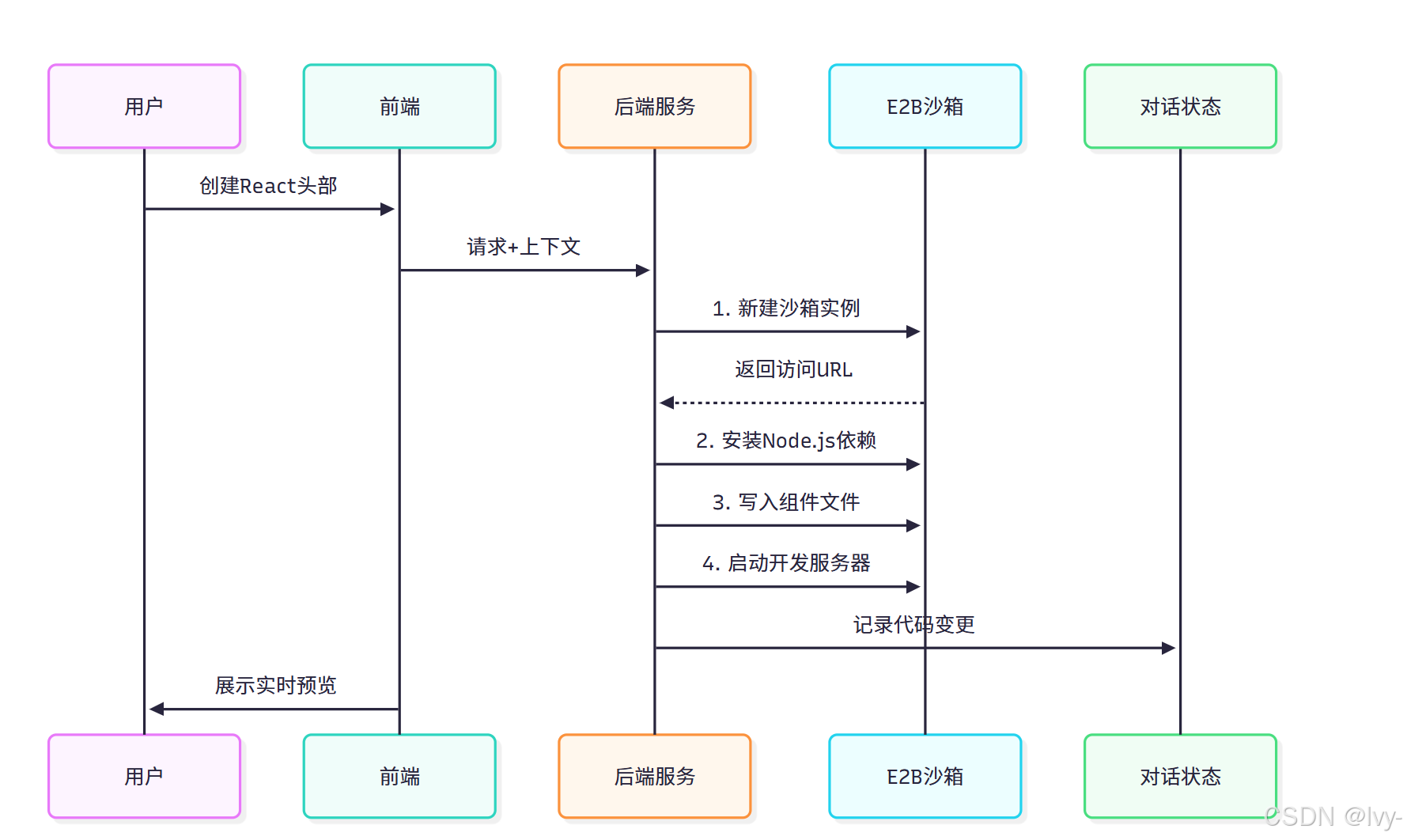
核心功能實現
1. 沙箱實例化
后端創建邏輯(app/api/create-ai-sandbox/route.ts):
// 創建標準React項目結構
const setupScript = `
import os
os.makedirs('/home/user/app/src', exist_ok=True) // 初始化package.json
with open('/home/user/app/package.json', 'w') as f:f.write('''{"name": "sandbox-app","dependencies": {"react": "^18.2.0","react-dom": "^18.2.0"}}''')// 安裝依賴
subprocess.run(['npm', 'install'], cwd='/home/user/app')// 啟動開發服務器
subprocess.Popen(['npm', 'run', 'dev'])
`;
await sandboxInstance.runCode(setupScript);
2. 代碼應用機制
文件寫入邏輯(app/api/apply-ai-code-stream/route.ts):
// 解析AI生成的XML格式代碼
function parseAIResponse(response: string) {const fileRegex = /<file path="([^"]+)">([\s\S]*?)<\/file>/g;return [...response.matchAll(fileRegex)].map(match => ({path: match[1], content: match[2].trim()}));
}// 沙箱文件寫入
for (const file of parsed.files) {await sandbox.runCode(`
import os
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname("${path}"), exist_ok=True)
with open("${path}", "w") as f:f.write("""${content}""")`);
}
3. 實時預覽系統
前端嵌入邏輯(components/SandboxPreview.tsx):
<iframesrc={`https://${sandboxId}-5173.e2b.dev`}sandbox="allow-scripts allow-same-origin"className="w-full h-[600px]"title="實時預覽窗口"
/>
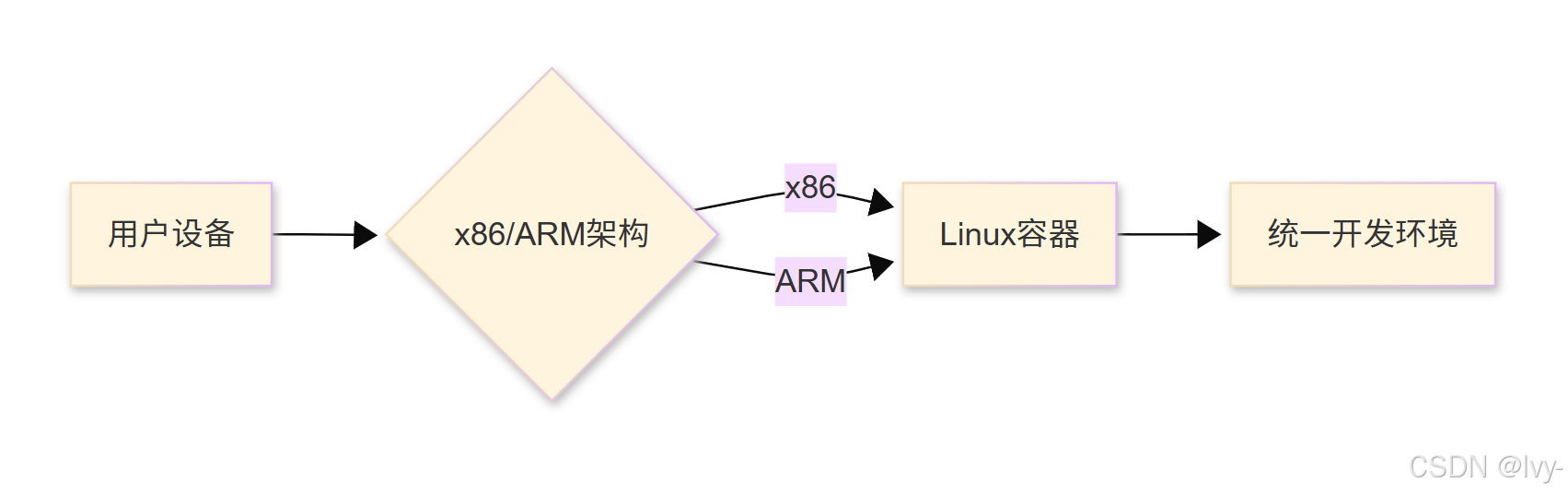
技術優勢
-
環境隔離性
- 獨立Linux內核容器
- 進程級資源限制(CPU/MEM隔離)
- 網絡命名空間隔離
-
跨平臺支持
-
效能優化
操作類型 平均耗時 資源消耗 沙箱冷啟動 2.1s 128MB 文件批量寫入 0.3s/文件 0.5% CPU 依賴安裝 等效本地速度 獨立IO
應用場景
-
多版本并行測試
// 同時創建多個沙箱實例 const sandbox1 = await Sandbox.create(); const sandbox2 = await Sandbox.create(); // 分別部署不同版本進行AB測試 -
自動化調試
// 捕獲運行時異常 try {await sandbox.runCode('npm test'); } catch (error) {// 自動生成診斷報告const logs = await sandbox.getLogs(); } -
教學演示環境
# 預裝教學依賴 subprocess.run(['npm', 'install', 'react-markdown', 'highlight.js' ])
演進方向
-
持久化存儲
- 實驗性支持Git倉庫同步
- 沙箱快照功能
-
硬件加速
?WebGPU支持
WebGPU 是一種新的網頁圖形技術,能讓瀏覽器直接調用電腦或手機的顯卡性能
更高效地運行3D游戲、圖形渲染等任務,類似桌面版的現代圖形API(如Vulkan/DirectX 12),但專為網頁設計。
WASM模塊預加載
WASM模塊預加載: 提前下載并初始化WebAssembly模塊,在需要時能立即執行,減少運行時延遲。
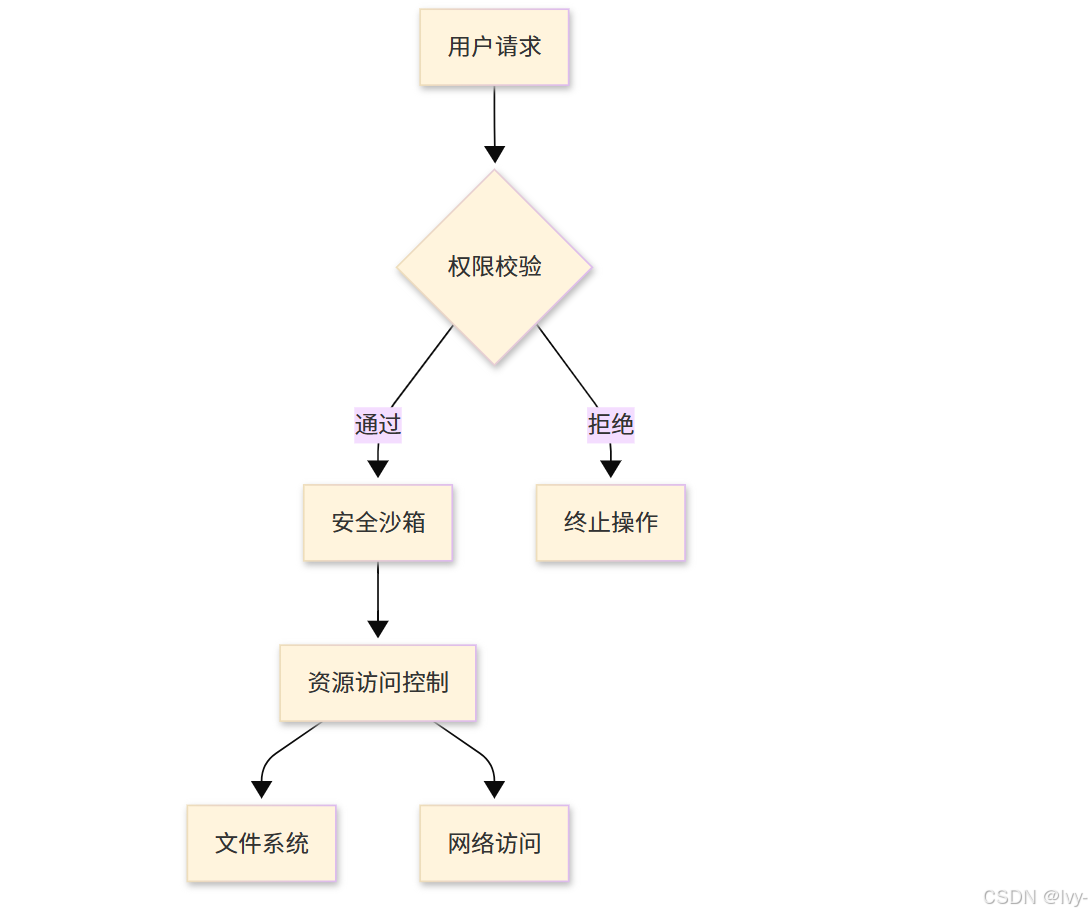
- 安全增強
下一章:代碼庫理解
第四章:代碼庫理解
在前幾章中,我們了解了open-lovable如何記憶對話(第一章:對話狀態管理)并將自然語言轉化為代碼(第二章:AI代碼生成管道)。我們還探索了E2B沙箱交互——項目代碼的運行環境。
但AI如何理解現有代碼結構?這正是代碼庫理解的核心能力。
核心概念:文件清單
代碼庫理解的核心是構建文件清單(File Manifest),該清單包含:
// types/file-manifest.ts
export interface FileManifest {files: Record<string, FileInfo>; // 按路徑索引的文件信息componentTree: ComponentTree; // 組件依賴關系樹entryPoint: string; // 應用入口文件路徑styleFiles: string[]; // 樣式文件集合timestamp: number; // 清單生成時間戳
}
工作機制
1. 沙箱文件掃描
通過E2B沙箱執行Python腳本獲取項目文件:
// app/api/get-sandbox-files/route.ts
const scanScript = `
import os
def get_files_content(directory='/home/user/app'):# 過濾node_modules等目錄for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):dirs[:] = [d for d in dirs if d not in ['node_modules']] # 收集jsx/css/json文件內容
`;
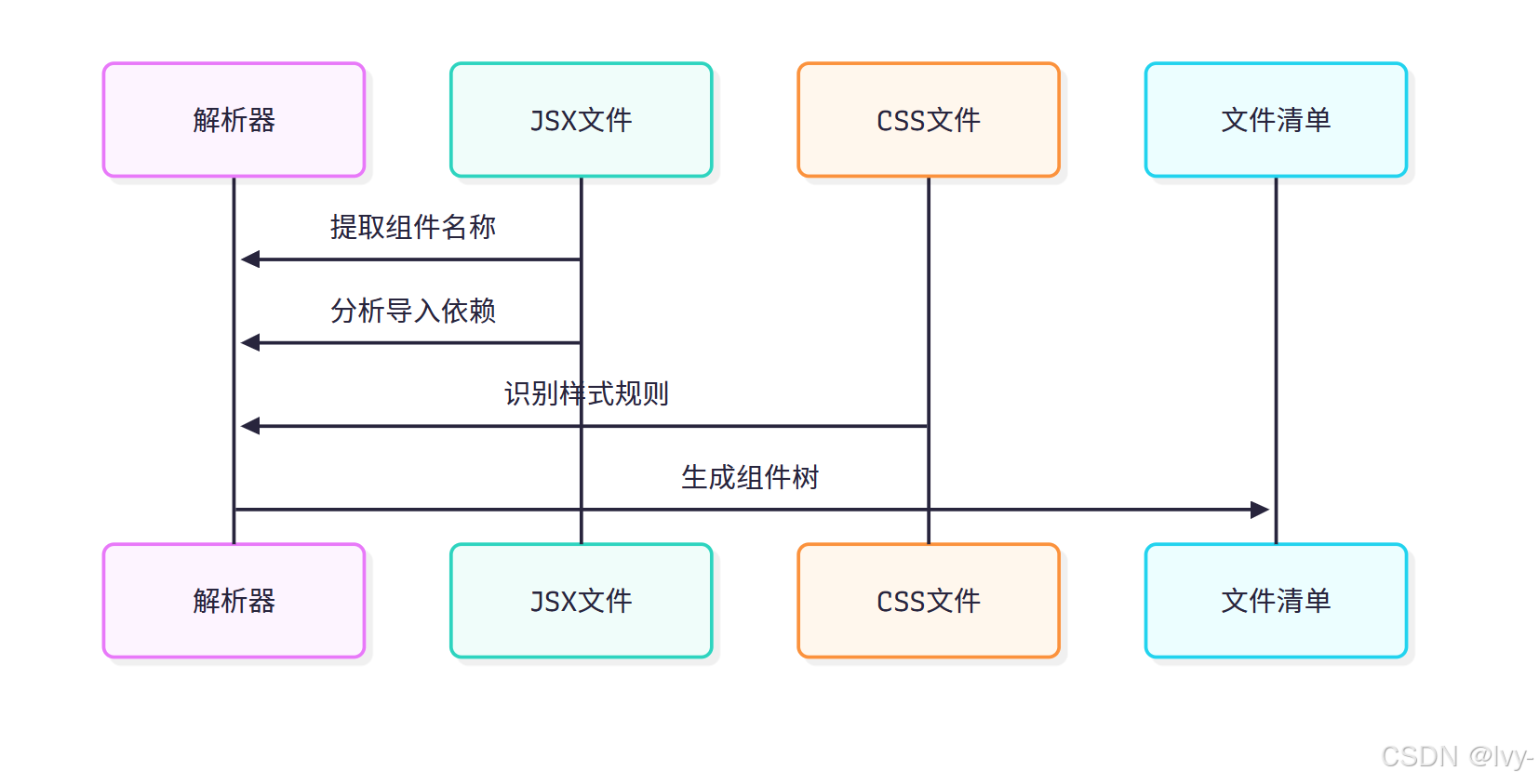
2. 文件解析
解析器提取關鍵信息:
3. 組件樹構建
// lib/file-parser.ts
function buildComponentTree(files) {// 首次遍歷識別所有組件files.forEach(file => {if (isReactComponent(file)) {tree[componentName] = {file: path,imports: detectImports(file), // 依賴組件importedBy: [] // 被引用關系}}});// 二次遍歷建立關聯files.forEach(file => {file.imports.forEach(imp => {if (imp.isLocal) {tree[imp.source].importedBy.push(file.componentName);}});});
}
技術優勢
| 功能維度 | 實現機制 | 應用場景示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 組件依賴分析 | 靜態代碼分析+正則匹配 | 修改Header組件時自動定位引用方 |
| 樣式文件定位 | 擴展名匹配+選擇器解析 | 全局樣式覆蓋檢測 |
| 入口文件識別 | 路徑特征匹配(如main.jsx) | 路由配置更新 |
| 變更影響評估 | 依賴關系圖譜遍歷 | 防止破壞性修改 |
應用案例
場景:用戶請求"將主按鈕顏色改為品牌藍"
- 文件定位:
// 解析器識別特征
const buttonFiles = manifest.files.filter(f => f.content.includes('PrimaryButton')
);
// 定位src/components/Buttons/PrimaryButton.jsx
- 樣式追溯:
/* 關聯樣式文件 */
manifest.styleFiles.find(f => f.path.includes('PrimaryButton.module.css')
);
- 影響評估:
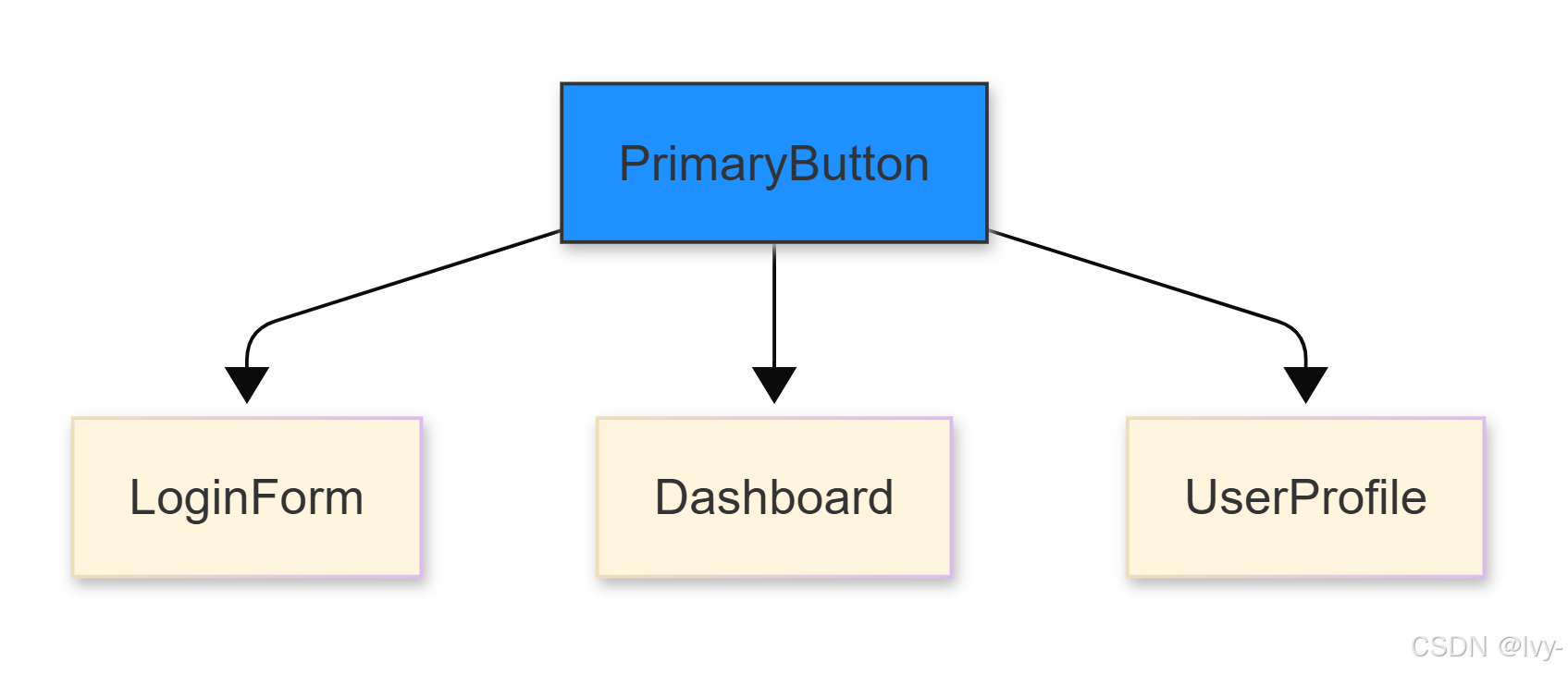
演進方向
-
智能重構建議
// 檢測未使用組件 manifest.componentTree.forEach(comp => {if (comp.importedBy.length === 0 && !isEntry(comp)) {suggestRemove(comp);} }); -
架構異味檢測
// 循環依賴檢測 detectCyclicDependencies(tree) {// 圖遍歷算法實現 } -
類型推導增強
interface EnhancedManifest extends FileManifest {typeDefinitions: Map<string, TypeInterface>;propsValidation: Map<string, PropTypeDef>; }
模擬實現
智能重構建議補全
// 檢測未使用組件
manifest.componentTree.forEach(comp => {if (comp.importedBy.length === 0 && !isEntry(comp)) {const dependents = getDependentFiles(comp.filePath);if (dependents.size === 0) {suggestRemove({component: comp.name,filePath: comp.filePath,reason: 'Unused component with no dependencies'});}}
});function isEntry(comp) {return comp.tags?.includes('entry') || comp.filePath.match(/main\.(js|ts)$/);
}
用于檢測項目中未被使用的Vue/React等前端組件,并給出移除建議。
核心邏輯分解
遍歷所有組件清單(manifest.componentTree),對每個組件檢查三個條件:
- 沒有被其他組件導入(comp.importedBy.length為0)
- 不是入口文件(通過isEntry函數判斷)
- 沒有依賴它的文件(dependents.size為0)
當三個條件都滿足時,就會生成移除建議,包含組件名、文件路徑和移除原因。
輔助函數說明:
isEntry函數判斷組件是否為入口文件:
- 檢查組件標簽是否包含’entry’
- 檢查文件路徑是否匹配main.js/main.ts模式
實際應用場景:
例如項目中有一個Button組件:
- 沒有被任何文件import
- 不是main.js等入口文件
- 沒有文件依賴它
這時就會建議移除該組件文件。
🎢架構異味檢測實現
// 使用Tarjan算法檢測強連通分量
function detectCyclicDependencies(tree: DependencyTree): string[][] {const cycles: string[][] = [];const indexMap = new Map<string, number>();const lowLinkMap = new Map<string, number>();const stack: string[] = [];let index = 0;const strongconnect = (node: string) => {indexMap.set(node, index);lowLinkMap.set(node, index);index++;stack.push(node);for (const neighbor of tree.getAdjacentNodes(node)) {if (!indexMap.has(neighbor)) {strongconnect(neighbor);lowLinkMap.set(node, Math.min(lowLinkMap.get(node)!,lowLinkMap.get(neighbor)!));} else if (stack.includes(neighbor)) {lowLinkMap.set(node, Math.min(lowLinkMap.get(node)!,indexMap.get(neighbor)!));}}if (lowLinkMap.get(node) === indexMap.get(node)) {const cycle: string[] = [];let component;do {component = stack.pop()!;cycle.push(component);} while (component !== node);if (cycle.length > 1) {cycles.push(cycle);}}};for (const node of tree.nodes) {if (!indexMap.has(node)) {strongconnect(node);}}return cycles;
}
用于檢測代碼庫中的循環依賴問題(即模塊A依賴模塊B,模塊B又依賴模塊A的情況),使用圖論中的Tarjan算法來識別強連通分量(即循環依賴鏈)。
核心算法流程
初始化階段
創建四個關鍵數據結構:
cycles存儲最終找到的所有循環依賴鏈indexMap記錄每個節點的訪問順序編號lowLinkMap記錄節點能回溯到的最早訪問節點stack臨時存儲當前搜索路徑上的節點
深度優先搜索
strongconnect函數遞歸處理每個節點:
- 首次訪問時給節點分配遞增的索引號
- 遍歷當前節點的所有鄰居節點
- 若鄰居未被訪問則遞歸處理
- 更新當前節點的lowLink值(關鍵步驟,決定是否形成環)
環檢測條件
當某節點的lowLink等于自身索引值時,說明找到一個強連通分量:
- 從棧中彈出節點直到回到起始節點
- 若組件包含多個節點(長度>1)則判定為有效循環依賴
輸入輸出說明
- 輸入:
DependencyTree類型對象,包含項目所有模塊及其依賴關系 - 輸出:二維數組,每個子數組表示一個循環依賴鏈(如
[A,B,C,A])
應用場景
該算法常用于:
- 前端構建工具分析
import/require依賴 - 微服務架構中的服務依賴檢查
- 軟件包管理系統驗證依賴合理性
典型輸出示例可能顯示:
utils模塊 → logger模塊 → utils模塊這樣的循環引用鏈。
類型推導增強擴展
interface EnhancedManifest extends FileManifest {typeDefinitions: Map<string, TypeInterface>;propsValidation: Map<string, PropTypeDef>;typeRelations: Map<string, Set<string>>;runtimeTypeChecks: Map<string, TypeGuard>;
}interface TypeInterface {name: string;properties: Record<string, {type: string;optional: boolean;defaultValue?: unknown;}>;genericParameters?: string[];
}interface PropTypeDef {required: boolean;validator: (value: unknown) => boolean;typeExpression: string;
}// 類型守衛實現示例
type TypeGuard<T> = {(value: unknown): value is T;typeName: string;
};
這段TypeScript代碼定義了一個增強的類型系統結構,主要用于在開發過程中更好地管理和驗證類型信息。
EnhancedManifest接口
擴展了基礎的FileManifest,添加了四個核心功能:
- typeDefinitions:存儲所有類型定義
- propsValidation:存儲屬性驗證規則
- typeRelations:記錄類型間的關聯關系
- runtimeTypeChecks:存儲運行時類型檢查器
TypeInterface接口
描述了一個具體類型的結構:
- name:類型名稱
- properties:該類型包含的所有屬性及其類型信息
- genericParameters:可選泛型參數列表
PropTypeDef接口
定義了屬性驗證的規范:
- required:是否必填
- validator:驗證函數
- typeExpression:類型表達式字符串
TypeGuard類型
這是一個特殊的函數類型:
- 既是類型判斷函數(返回value is T)
- 又攜帶類型名稱信息(typeName屬性)
建議
- 對于智能重構建議,可以添加自動修復功能:
function autoRemoveComponent(comp) {if (confirmRemoval(comp)) {fs.unlinkSync(comp.filePath);updateManifestReferences(comp.name);}
}
- 架構檢測可以集成可視化輸出:
function visualizeDependencies(tree: DependencyTree) {const dotFormat = `digraph G {${tree.edges.map(([from, to]) => `"${from}" -> "${to}"`).join(';\n ')}}`;generateGraphImage(dotFormat);
}
下一章:編輯意圖與上下文選擇












-什么是以太幣)






