一、條件構造器和常用接口
1.wapper介紹
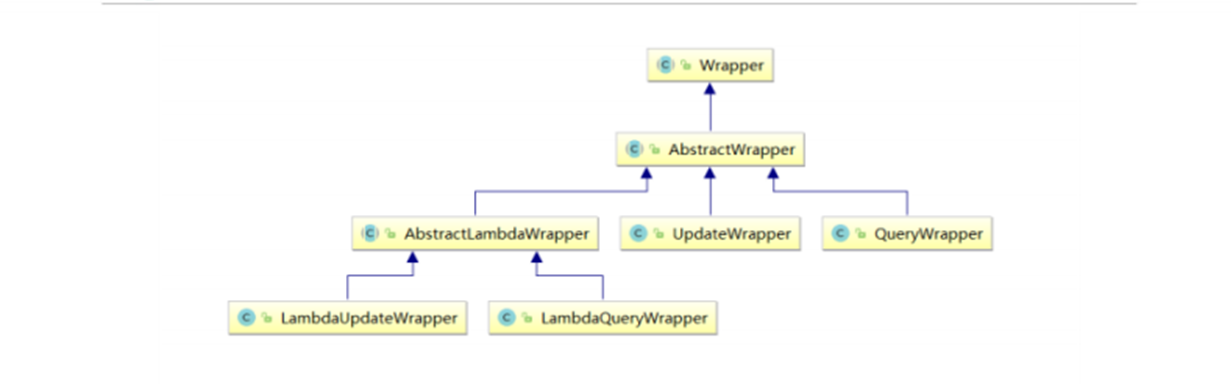
MyBatis-Plus 提供了一套強大的條件構造器(Wrapper),用于構建復雜的數據庫查詢條件。Wrapper 類允許開發者以鏈式調用的方式構造查詢條件,無需編寫繁瑣的 SQL 語句,從而提高開發效率并減少 SQL 注入的風險。
在 MyBatis-Plus 中,Wrapper 類是構建查詢和更新條件的核心工具。以下是主要的 Wrapper 類及其功能:
-
AbstractWrapper:這是一個抽象基類,提供了所有 Wrapper 類共有的方法和屬性。它定義了條件構造的基本邏輯,包括字段(column)、值(value)、操作符(condition)等。所有的 QueryWrapper、UpdateWrapper、LambdaQueryWrapper 和 LambdaUpdateWrapper 都繼承自 AbstractWrapper。
-
QueryWrapper:專門用于構造查詢條件,支持基本的等于、不等于、大于、小于等各種常見操作。它允許你以鏈式調用的方式添加多個查詢條件,并且可以組合使用?
and?和?or?邏輯。 -
UpdateWrapper:用于構造更新條件,可以在更新數據時指定條件。與 QueryWrapper 類似,它也支持鏈式調用和邏輯組合。使用 UpdateWrapper 可以在不創建實體對象的情況下,直接設置更新字段和條件。
-
LambdaQueryWrapper:這是一個基于 Lambda 表達式的查詢條件構造器,它通過 Lambda 表達式來引用實體類的屬性,從而避免了硬編碼字段名。這種方式提高了代碼的可讀性和可維護性,尤其是在字段名可能發生變化的情況下。
-
LambdaUpdateWrapper:類似于 LambdaQueryWrapper,LambdaUpdateWrapper 是基于 Lambda 表達式的更新條件構造器。它允許你使用 Lambda 表達式來指定更新字段和條件,同樣避免了硬編碼字段名的問題。
?2.功能詳解
MyBatis-Plus 的 Wrapper 類是構建復雜查詢和更新條件的關鍵工具。它允許開發者以鏈式調用的方式構造 SQL 的 WHERE 子句,提供了極大的靈活性和便利性。
以下是對 Wrapper 功能的提示和注意事項。
提示:
條件判斷:Wrapper 方法通常接受一個?boolean?類型的參數,用于決定是否將該條件加入到最終的 SQL 中。例如:
queryWrapper.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(name), Entity::getName, name).eq(age != null && age >= 0, Entity::getAge, age);默認行為:如果某個方法沒有顯式提供?boolean?類型的參數,則默認為?true,即條件總是會被加入到 SQL 中。
泛型參數:Wrapper 類是泛型類,其中?Param?通常指的是 Wrapper 的子類實例,如 QueryWrapper、UpdateWrapper 等。
字段引用:在 LambdaWrapper 中,R?代表的是一個函數,用于引用實體類的屬性,例如?Entity::getId。而在普通 Wrapper 中,R?代表的是數據庫字段名。
字段名注意事項:當?R?具體類型為?String?時,表示的是數據庫字段名,而不是實體類數據字段名。如果字段名是數據庫關鍵字,需要使用轉義符包裹。
集合參數:如果方法的參數是?Map?或?List,當它們為空時,對應的 SQL 條件不會被加入到最終的 SQL 中。
學習資源:對于不熟悉的函數式編程概念,可以參考學習資源進行學習。
注意事項:
RPC 調用中的 Wrapper:不支持也不贊成在 RPC 調用中傳輸 Wrapper 對象。Wrapper 對象通常包含大量信息,不適合作為傳輸對象。正確的做法是定義一個 DTO(數據傳輸對象)進行傳輸,然后在被調用方根據 DTO 執行相應的操作。
維護性:避免在 Controller 層使用 Map 接收值,這種做法雖然開發時方便,但會給后續的維護帶來困難。
問題反饋:不接受任何關于 RPC 傳輸 Wrapper 報錯相關的 issue 或 pr。
安全性:?QueryWrapper?UpdateWrapper?字段部分,如有允許?前端傳入 SQL 片段?這可能會導致?SQL 注入風險?需要校驗,更多查看?預防安全漏洞。
3.QueryWrapper
3.1組裝查詢條件
@Test
public void test01(){
//查詢用戶名包含a,年齡在20到30之間,并且郵箱不為null的用戶信息
//SELECT id,username AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM t_user WHERE
is_deleted=0 AND (username LIKE ? AND age BETWEEN ? AND ? AND email IS NOT NULL)
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("username", "a")
.between("age", 20, 30)
.isNotNull("email");
List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.2組裝排序條件
@Test
public void test02(){
//按年齡降序查詢用戶,如果年齡相同則按id升序排列
//SELECT id,username AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM t_user WHERE is_deleted=0 ORDER BY age DESC,id ASC
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.orderByDesc("age")
.orderByAsc("id");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.3組裝刪除條件
@Test
public void test03(){
//刪除email為空的用戶
//DELETE FROM t_user WHERE (email IS NULL)
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.isNull("email");
//條件構造器也可以構建刪除語句的條件
int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
System.out.println("受影響的行數:" + result);
}
3.4條件的優先級
@Test
public void test04() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//將(年齡大于20并且用戶名中包含有a)或郵箱為null的用戶信息修改
//UPDATE t_user SET age=?, email=? WHERE (username LIKE ? AND age > ? OR email IS NULL)
queryWrapper
.like("username", "a")
.gt("age", 20)
.or()
.isNull("email");
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("user@qcby.com");
int result = userMapper.update(user, queryWrapper);
System.out.println("受影響的行數:" + result);
}
@Test
public void test04() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//將用戶名中包含有a并且(年齡大于20或郵箱為null)的用戶信息修改
//UPDATE t_user SET age=?, email=? WHERE (username LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL))
//lambda表達式內的邏輯優先運算
queryWrapper
.like("username", "a")
.and(i -> i.gt("age", 20).or().isNull("email"));
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("user@qcby.com");
int result = userMapper.update(user, queryWrapper);
System.out.println("受影響的行數:" + result);
}
3.5組裝select子句
@Test
public void test05() {
//查詢用戶信息的username和age字段
//SELECT username,age FROM t_user
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("username", "age");
//selectMaps()返回Map集合列表,通常配合select()使用,避免User對象中沒有被查詢到的列值 為null
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper); maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.6實現子查詢
@Test
public void test06() {
//查詢id小于等于3的用戶信息
//SELECT id,username AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM t_user WHERE (id IN (select id from t_user where id <= 3))
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.inSql("id", "select id from t_user where id <= 3"); List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
4.UpdateWrapper
@Test
public void test07() {
//將(年齡大于20或郵箱為null)并且用戶名中包含有a的用戶信息修改
//組裝set子句以及修改條件
UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
//lambda表達式內的邏輯優先運算
updateWrapper
.set("age", 18)
.set("email", "user@qcby.com")
.like("username", "a")
.and(i -> i.gt("age", 20).or().isNull("email"));
//這里必須要創建User對象,否則無法應用自動填充。如果沒有自動填充,可以設置為null
//UPDATE t_user SET username=?, age=?,email=? WHERE (username LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL))
//User user = new User();
//user.setName("張三");
//int result = userMapper.update(user, updateWrapper);
//UPDATE t_user SET age=?,email=? WHERE (username LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL))
int result = userMapper.update(null, updateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}
5.condition
在真正開發的過程中,組裝條件是常見的功能,而這些條件數據來源于用戶輸入,是可選的,因 此我們在組裝這些條件時,必須先判斷用戶是否選擇了這些條件,若選擇則需要組裝該條件,若 沒有選擇則一定不能組裝,以免影響SQL執行的結果
5.1思路一
@Test
public void test08() {
//定義查詢條件,有可能為null(用戶未輸入或未選擇)
String username = null;
Integer ageBegin = 10;
Integer ageEnd = 24;
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//StringUtils.isNotBlank()判斷某字符串是否不為空且長度不為0且不由空白符(whitespace) 構成
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username)){
queryWrapper.like("username","a");
}
if(ageBegin != null){
queryWrapper.ge("age", ageBegin);
}
if(ageEnd != null){
queryWrapper.le("age", ageEnd);
}
//SELECT id,username AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM t_user WHERE (age >= ? AND age <= ?)
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
5.2思路二
上面的實現方案沒有問題,但是代碼比較復雜,我們可以使用帶condition參數的重載方法構建查 詢條件,簡化代碼的編寫
@Test
public void test08UseCondition() {
//定義查詢條件,有可能為null(用戶未輸入或未選擇)
String username = null;
Integer ageBegin = 10;
Integer ageEnd = 24;
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//StringUtils.isNotBlank()判斷某字符串是否不為空且長度不為0且不由空白符(whitespace) 構成
queryWrapper
.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username), "username", "a")
.ge(ageBegin != null, "age", ageBegin)
.le(ageEnd != null, "age", ageEnd);
//SELECT id,username AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM t_user WHERE (age >= ? AND age <= ?)
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
6.LambdaQueryWrapper
@Test
public void test09() {
//定義查詢條件,有可能為null(用戶未輸入)
String username = "a";
Integer ageBegin = 10;
Integer ageEnd = 24;
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//避免使用字符串表示字段,防止運行時錯誤
queryWrapper
.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username), User::getName, username) .ge(ageBegin != null, User::getAge, ageBegin)
.le(ageEnd != null, User::getAge, ageEnd);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
7.LambdaUpdateWrapper
@Test
public void test10() {
//組裝set子句
LambdaUpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>(); updateWrapper
.set(User::getAge, 18)
.set(User::getEmail, "user@qcby.com")
.like(User::getName, "a")
.and(i -> i.lt(User::getAge, 24).or().isNull(User::getEmail)); //lambda 表達式內的邏輯優先運算
User user = new User();
int result = userMapper.update(user, updateWrapper);
System.out.println("受影響的行數:" + result);
}
二、插件
1.分頁插件
MyBatis Plus自帶分頁插件,只要簡單的配置即可實現分頁功能
1.1添加配置類
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.config;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {/*** 配置分頁插件*/@Beanpublic MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();// 添加分頁攔截器(支持MySQL、PostgreSQL等主流數據庫)interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());return interceptor;}
}
1.2測試
@Test
public void testPage(){
//設置分頁參數
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, 5);
userMapper.selectPage(page, null);
//獲取分頁數據
List<User> list = page.getRecords();
list.forEach(System.out::println);
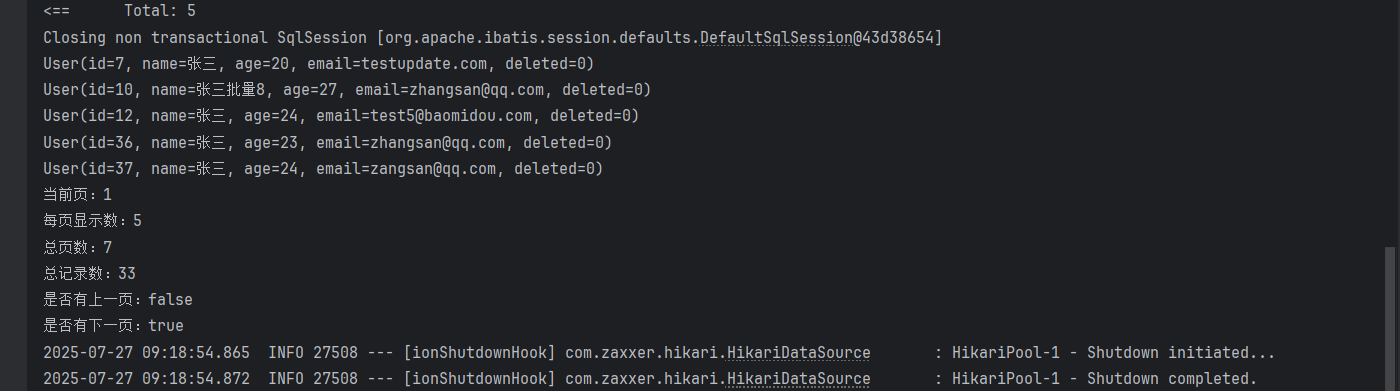
System.out.println("當前頁:"+page.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每頁顯示的條數:"+page.getSize());
System.out.println("總記錄數:"+page.getTotal());
System.out.println("總頁數:"+page.getPages());
System.out.println("是否有上一頁:"+page.hasPrevious());
System.out.println("是否有下一頁:"+page.hasNext());
}
測試結果
2.xml自定義分頁
2.1UserMapper中定義接口方法
/**
* 根據年齡查詢用戶列表,分頁顯示
* @param page 分頁對象 ,xml中可以從里面進行取值 ,傳遞參數 Page 即自動分頁 ,必須放在第一位
* @param age 年齡
* @return */
I
Page<User> selectPageVo(@Param("page") Page<User> page, @Param("age") Integer age);
2.2UserMapper.xml中編寫SQL
<!--SQL片段,記錄基礎字段-->
<sql id="BaseColumns">id,username,age,email</sql><!--IPage<User> selectPageVo(Page<User> page, Integer age);-->
<select id="selectPageVo" resultType="User">
SELECT <include refid="BaseColumns"></include> FROM t_user WHERE age > # {age}
</select>
2.3測試
@Test
public void testSelectPageVo(){
//設置分頁參數
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, 5);
userMapper.selectPageVo(page, 20);
//獲取分頁數據
List<User> list = page.getRecords();
list.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("當前頁:"+page.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每頁顯示的條數:"+page.getSize());
System.out.println("總記錄數:"+page.getTotal());
System.out.println("總頁數:"+page.getPages());
System.out.println("是否有上一頁:"+page.hasPrevious());
System.out.println("是否有下一頁:"+page.hasNext());
}
結果

3.樂觀鎖
3.1場景
一件商品,成本價是80元,售價是100元。老板先是通知小李,說你去把商品價格增加50元。小 李正在玩游戲,耽擱了一個小時。正好一個小時后,老板覺得商品價格增加到150元,價格太
高,可能會影響銷量。又通知小王,你把商品價格降低30元。
此時,小李和小王同時操作商品后臺系統。小李操作的時候,系統先取出商品價格100元;小王? 也在操作,取出的商品價格也是100元。小李將價格加了50元,并將100+50=150元存入了數據? 庫;小王將商品減了30元,并將100-30=70元存入了數據庫。是的,如果沒有鎖,小李的操作就 完全被小王的覆蓋了。
現在商品價格是70元,比成本價低10元。幾分鐘后,這個商品很快出售了1千多件商品,老板虧1 萬多。
3.2樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
上面的故事,如果是樂觀鎖,小王保存價格前,會檢查下價格是否被人修改過了。如果被修改過 了,則重新取出的被修改后的價格,? 150元,這樣他會將120元存入數據庫。
如果是悲觀鎖,小李取出數據后,小王只能等小李操作完之后,才能對價格進行操作,也會保證 最終的價格是120元。
3.3模擬修改沖突
數據庫中增加商品表
CREATE TABLE t_product
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主鍵ID',
NAME VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名稱 ',
price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '價格 ',
VERSION INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '樂觀鎖版本號 ',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
添加數據
INSERT INTO t_product (id, NAME, price) VALUES (1, '外星人筆記本 ', 100);添加實體
package com.qcby.mybatisplus.entity;
import lombok.Data;@Data
public class Product {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer price;
private Integer version;
}
添加mapper
public interface ProductMapper extends BaseMapper<Product> {
}
測試
@Test
public void testConcurrentUpdate() {//1、小李
Product p1 = productMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println("小李取出的價格:" + p1.getPrice());//2、小王
Product p2 = productMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println("小王取出的價格:" + p2.getPrice());
//3、小李將價格加了50元,存入了數據庫
p1.setPrice(p1.getPrice() + 50);
int result1 = productMapper.updateById(p1);
System.out.println("小李修改結果:" + result1);//4、小王將商品減了30元,存入了數據庫
p2.setPrice(p2.getPrice() - 30);
int result2 = productMapper.updateById(p2);
System.out.println("小王修改結果:" + result2);//最后的結果
Product p3 = productMapper.selectById(1L);
//價格覆蓋,最后的結果:70
System.out.println("最后的結果:" + p3.getPrice())
3.4樂觀鎖實現流程
數據庫中添加version字段
取出記錄時,獲取當前version
SELECT id,`name`,price,`version` FROM product WHERE id=1更新時, version + 1,如果where語句中的version版本不對,則更新失敗
UPDATE product SET price=price+50, `version`=`version` + 1 WHERE id=1 AND `version`=13.5Mybatis-Plus實現樂觀鎖
修改實體類
@Datacom.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.Version;
lombok.Data;public class Product {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer price;
@Version
private Integer version;
}
添加樂觀鎖插件配置
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//添加分頁插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new
PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
//添加樂觀鎖插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor()); return interceptor;
}
測試修改沖突
小李查詢商品信息:
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
小王查詢商品信息:
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
小李修改商品價格,自動將version+1
UPDATE t_product SET name=?, price=?, version=? WHERE id=? AND version=?
Parameters: 外星人筆記本(String), 150(Integer), 1(Integer), 1(Long), 0(Integer)
小王修改商品價格,此時version已更新,條件不成立,修改失敗
UPDATE t_product SET name=?, price=?, version=? WHERE id=? AND version=?
Parameters: 外星人筆記本(String), 70(Integer), 1(Integer), 1(Long), 0(Integer)
最終,小王修改失敗,查詢價格: 150
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
優化流程
//樂觀鎖測試@Testpublic void test02(){//小李取數據Product p1 = productMapper.selectById(1L);//小王取數據Product p2 = productMapper.selectById(1L);//小李修改p1.setPrice(p1.getPrice() + 50);int result1 = productMapper.updateById(p1);System.out.println("小李修改結果:" + result1);//小王修改p2.setPrice(p2.getPrice() - 30);int result2 = productMapper.updateById(p2);System.out.println("小王修改結果:" + result2);if(result2 ==0){p2 = productMapper.selectById(1L);p2.setPrice(p2.getPrice() - 30);result2 = productMapper.updateById(p2);}System.out.println("小王修改結果:" + result2);//老板查詢商品價格Product p3 = productMapper.selectById(1L);System.out.println("老板查詢價格:" + p3.getPrice());}結果
![]()
三、通用枚舉
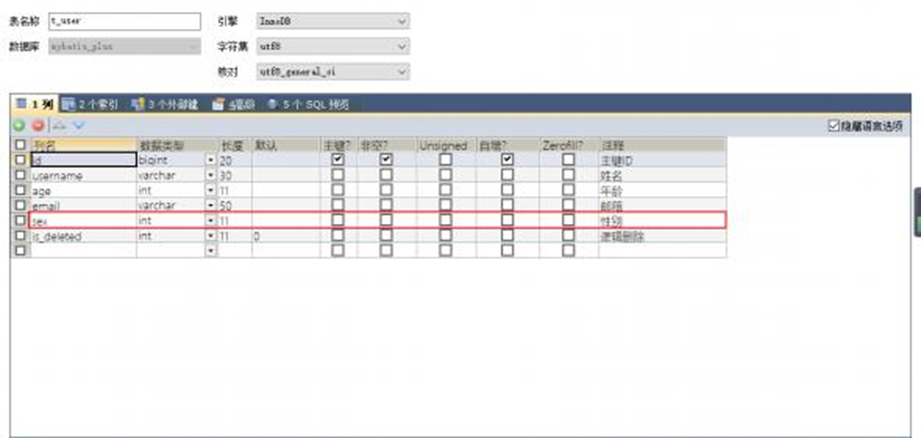
表中的有些字段值是固定的,例如性別(男或女),此時我們可以使用MyBatis-Plus的通用枚舉 來實現
1.數據庫表添加字段sex
2.創建通用枚舉類型
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.enums;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.EnumValue;
import lombok.Getter;@Getter
public enum SexEnum {MALE(1,"男"),FEMALE(2,"女");@EnumValueprivate Integer sex;private String sexname;SexEnum(Integer sex, String sexname){this.sex = sex;this.sexname = sexname;}
}
3.配置掃描通用枚舉
mybatis-plus:configuration:log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplglobal-config:db-config:# 配置MyBatis-Plus操作表的默認前綴table-prefix: t_# 配置MyBatis-Plus的主鍵策略id-type: auto#配置掃面通用枚舉type-enums-package: com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.enums4.測試
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725;import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.entity.User;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.enums.SexEnum;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTest
public class EnumsTest {@Autowiredprivate UserMapper userMapper;@Testpublic void test01(){User user = new User();user.setName("Enum");user.setAge(20);user.setSex(SexEnum.MALE);userMapper.insert(user);}
}
四、代碼生成器
1.引入依賴
<!--代碼生成器--><dependency><groupId>com.baomidou</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.freemarker</groupId><artifactId>freemarker</artifactId><version>2.3.31</version></dependency>?2.快速生成
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.util;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.FastAutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.OutputFile;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.engine.FreemarkerTemplateEngine;import java.util.Collections;public class FastAutoGeneratorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {FastAutoGenerator.create("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true", "root", "lrh123456").globalConfig(builder -> {builder.author("qcby") // 設置作者.enableSwagger() // 開啟 swagger 模式.fileOverride()// 覆蓋已生成文件.outputDir("D:\\code\\springboot\\springbootmybastplus0725\\src\\main\\java");}).packageConfig(builder -> {builder.parent("com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725") // 設置父包名.moduleName("mybatisplus") // 設置父包模塊名.pathInfo(Collections.singletonMap(OutputFile.mapperXml,"D://mybatis_plus"));}).strategyConfig(builder -> {builder.addInclude("t_user") // 設置需要生成的表名.addTablePrefix("t_", "c_");}).templateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine()).execute();}
}
結果
五、多數據源
適用于多種場景:純粹多庫、?? 讀寫分離、??? 一主多從、?? 混合模式等
目前我們就來模擬一個純粹多庫的一個場景,其他場景類似
場景說明
創建兩個庫,
分別為:? mybatis_plus(以前的庫不動)與mybatis_plus_1? (新建),將
mybatis_plus庫的product表移動到mybatis_plus_1庫,這樣每個庫一張表,通過一個測試用例 分別獲取用戶數據與商品數據,如果獲取到說明多庫模擬成功
1.創建數據庫及表
創建數據庫mybatis_plus_1和表product
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis_plus_1` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 */; use `mybatis_plus_1`;
CREATE TABLE product
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主鍵ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名稱 ',
price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '價格 ',
version INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '樂觀鎖版本號 ',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
添加測試數據
INSERT INTO product (id, NAME, price) VALUES (1, '外星人筆記本 ', 100);刪除mybatis_plus庫中的product表
2.引入依賴
<!--多數據源--><dependency><groupId>com.baomidou</groupId><artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.5.0</version></dependency>3.配置多數據源
說明:注釋掉之前的數據庫連接,添加新配置
spring:datasource:dynamic:# 設置默認的數據源或者數據源組 ,默認值即為masterprimary: master# 嚴格匹配數據源 ,默認false.true未匹配到指定數據源時拋異常 ,false使用默認數據源strict: falsedatasource:master:url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=truedriver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverusername: rootpassword: rootslave_1:url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus_1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=truedriver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverusername: rootpassword: root4.創建用戶service
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.entity.User;public interface UserService extends IService<User> {}
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.impl;import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.entity.User;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@DS("master")//指定所操作的數據源
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {
}
6.創建商品service
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.entity.Product;public interface ProductService extends IService<Product> {
}
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.impl;import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.entity.Product;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.mapper.ProductMapper;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@DS("slave_1")
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ProductMapper, Product> implements ProductService {}
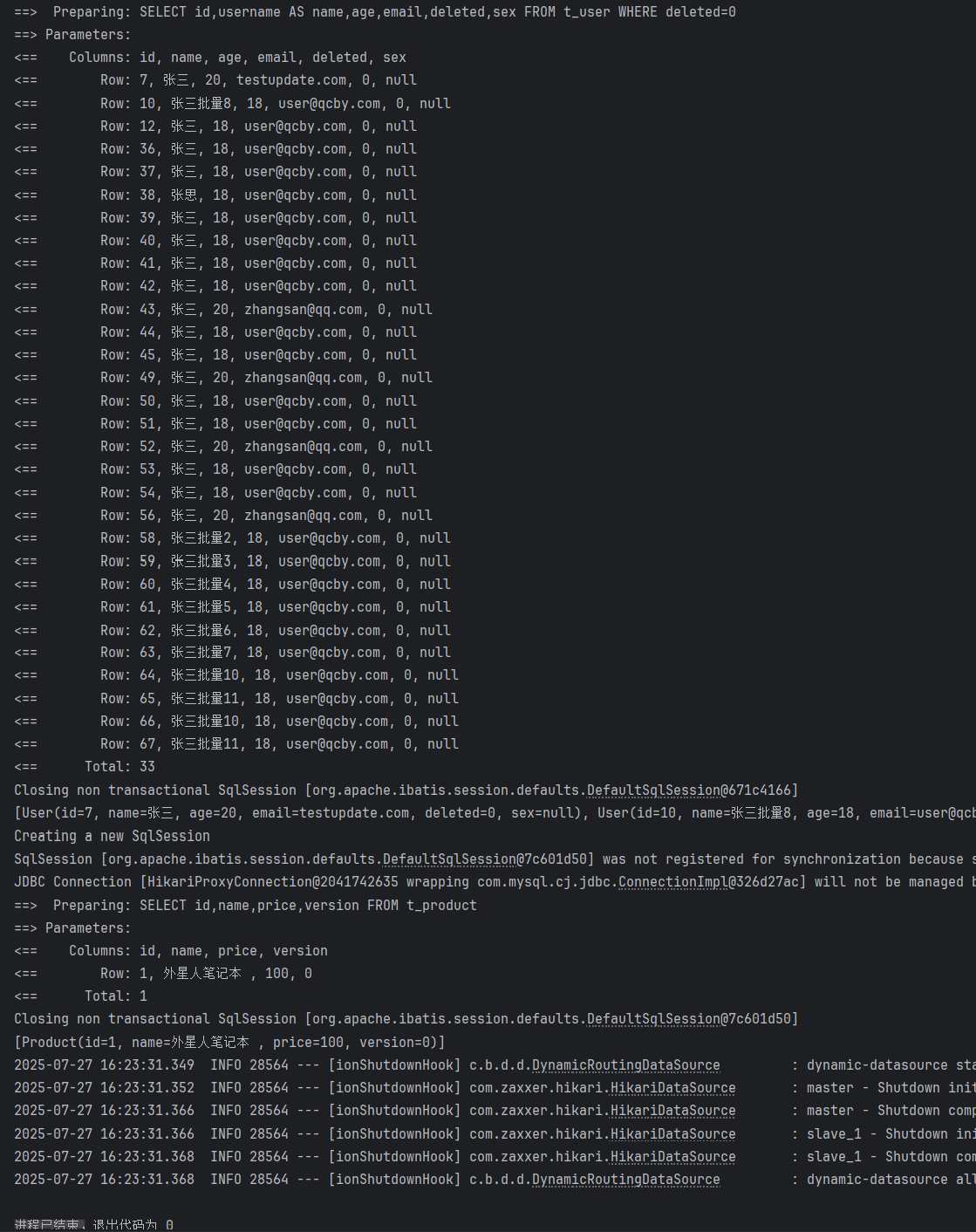
6.測試
package com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725;import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.ProductService;
import com.qcby.springbootmybastplus0725.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTest
public class DynamicTest {@Autowiredprivate ProductService productService;@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Testpublic void test(){System.out.println(userService.list());System.out.println(productService.list());}
}
結果
1、都能順利獲取對象,則測試成功
2、如果我們實現讀寫分離,將寫操作方法加上主庫數據源,讀操作方法加上從庫數據源,自動切 換,是不是就能實現讀寫分離?
六、MyBatisX插件
MyBatis-Plus為我們提供了強大的mapper和service模板,能夠大大的提高開發效率
但是在真正開發過程中,? MyBatis-Plus并不能為我們解決所有問題,例如一些復雜的SQL,多表 聯查,我們就需要自己去編寫代碼和SQL語句,我們該如何快速的解決這個問題呢,這個時候可 以使用MyBatisX插件
MyBatisX一款基于 IDEA 的快速開發插件,為效率而生
MyBatisX插件用法:https://baomidou.com/plugins/


)


)






)|SVM-KKT條件的數學理解)
模型添加教學)




)
