前言
Redis中提供多種數據結構:string、list、map、set、zset等,關于上述多種數據類型的底層實現原理,Redis針對不同的數據類型對應的不同使用場景從時間和空間上進行平衡選擇不同的對象編碼方式。本文大致介紹一些Redis對象編碼方式以及在上述五種數據類型上的應用。
一、統一對象結構:redisObject
在Redis中所有的數據都通過redisObject結構體封裝,其核心字段定義如下:
typedef struct redisObject {unsigned type:4; // 數據類型(string/list/hash/set/zset)unsigned encoding:4; // 底層編碼(如int/ziplist/skiplist)unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency* and most significant 16 bits access time). */// 內存淘汰信息int refcount; // 引用計數void *ptr; // 指向實際數據的指針
} robj;通過redisObject結構體中type字段和encoding字段分離,實現對不同的數據類型動態適配合適的編碼方式。用戶使用方式上,無需考慮底層編碼方式只需要按照需求選擇對應數據類型。
二、核心數據類型
1、簡單動態字符串(Simple Dynamic String - SDS)
Redis中描述字符串使用SDS,對比C語言傳統字符串,SDS在獲取字符串長度上有更快的速度優勢,同時保證二進制安全。C語言字符串以'\0'結尾,SDS通過len字段標識字符串長度,因此在存儲二進制數據時保證二進制安全。并且SDS兼容C語言字符串,在buf字段末尾保留'\0',可以兼容部分C語言字符串操作函數。具體實現如下:
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {uint8_t len; /* used */uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {uint16_t len; /* used */uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {uint32_t len; /* used */uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {uint64_t len; /* used */uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];
};-
len :已使用字節長度(字符串實際長度,不包括'\0')
-
alloc:分配的總字節長度(不包括header)
-
flags:SDS類型標識
-
buf[]:柔性數組,存放具體的字符串 + '\0'
2、字典(Dict)
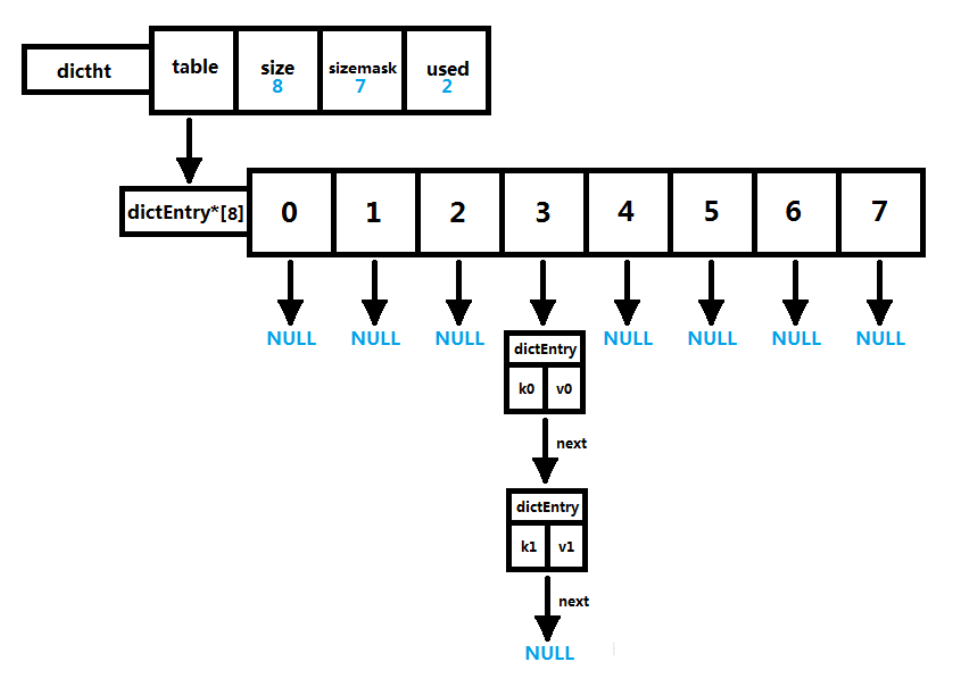
Redis中dict數據類型是使用拉鏈法處理hash沖突的hash表結構。其中關鍵數據結構為:dict、dictht、dictEntry。具體實現以及層級結構如下:
typedef struct dictEntry {void *key; // key值union {void *val;uint64_t u64;int64_t s64;double d;} v; // value值struct dictEntry *next; // 指向下個元素,拉鏈法處理hash沖突
} dictEntry; // 元素
?
typedef struct dictType {uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType; // dict操作函數集合
?
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {dictEntry **table; // 元素數組unsigned long size; // hash表長度unsigned long sizemask; // 用于映射位置的掩碼,值永遠等于 (size - 1),索引值=Hash值&掩碼值unsigned long used; // hash表當前包含的節點數量
} dictht; // 具體hash表結構
?
typedef struct dict {dictType *type; // 該字典對應的特定操作函數 (hash, keyDup, keyCompare, ...)void *privdata; // 上述類型函數對應的可選參數dictht ht[2]; // 兩張hash表,方便rehah操作long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ // rehash標識unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ // 當前運行的迭代器數量
} dict; // hash表3、雙向鏈表(list)
實現結構同數據結構中雙向鏈表。具體實現如下:
typedef struct listNode {struct listNode *prev;struct listNode *next;void *value;
} listNode;
?
typedef struct list {listNode *head;listNode *tail;void *(*dup)(void *ptr);void (*free)(void *ptr);int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);unsigned long len;
} list;4、壓縮列表(ziplist)- Redis 7.0 起替換為 listpack
ziplist結構是一塊連續內存存儲一個字節數組,其中順序存儲多個元素,每個節點元素存儲一個字節數組或者一個整數。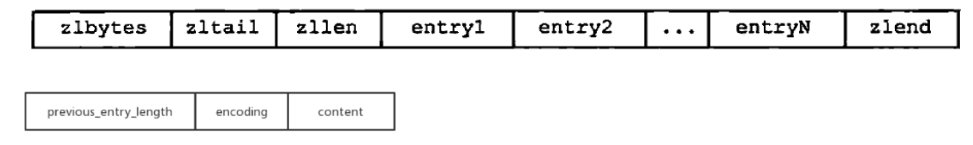
-
zlbytes: 4 字節,列表總字節數(字節長度)。
-
zltail: 4 字節,列表尾節點偏移量。
-
zllen: 2 字節,節點數量 (超過 65535 時需遍歷)。
-
entry: 若干節點。每個節點包含:
-
prevlen: 前一個節點的長度 (1 或 5 字節)。
-
encoding: 內容編碼 (類型和長度,1/2/5 字節)。
-
content: 實際數據。
-
-
zlend: 1 字節,結束標志 0xFF(255)
對于節點的數據結構中prevlen記錄的是前一個節點的長度,此時如果調整當前節點,會影響后面一個節點的prevlen,此時如果是發生的擴展操作,那么可能會導致連續重新分配多個節點。此時該數據結構效率嚴重下降。因此這也是listpack替代它的主要原因。
5、緊湊列表(listpack) - Redis5.0引入,7.0開始列表/哈希/有序集合的ziplist實現替換為listpack
listpack是對ziplist的優化。其結構也是一塊連續內存。與ziplist的主要不同點為在節點元素中ziplist的節點長度信息保存的是前一個節點的長度,而ziplist保存的是自身的長度信息。
6、整數集合(intSet)
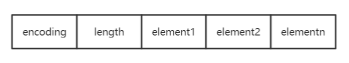
整數集合是一塊連續內存,其元素保存的是一個整數,其中通過encoding字段中標識了當前元素的整數類型,length保存了當前的元素數量,然后后續就挨個保存每個元素。
7、快速列表(quicklist)
快速列表是結合list與ziplist/listpack。list是一個雙向鏈表,ziplist/listpack是一塊連續的內存區域高效的保存數據。list每個節點的值保存一個ziplist/listpack結構。在具體操作時,插入/刪除操作多數集中在list節點內部,即ziplist/listpack中。當節點過大/過小時進行節點分裂/合并操作。
typedef struct quicklistNode {struct quicklistNode *prev;struct quicklistNode *next;unsigned char *zl;unsigned int sz; ? ? ? ? ? ? /* ziplist size in bytes */unsigned int count : 16; ? ? /* count of items in ziplist */unsigned int encoding : 2; ? /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */unsigned int container : 2; ?/* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
?
typedef struct quicklist {quicklistNode *head;quicklistNode *tail;unsigned long count; ? ? ? ?/* total count of all entries in all ziplists */unsigned long len; ? ? ? ? ?/* number of quicklistNodes */int fill : QL_FILL_BITS; ? ? ? ? ? ? ?/* fill factor for individual nodes */unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;8、跳表(skiplist)
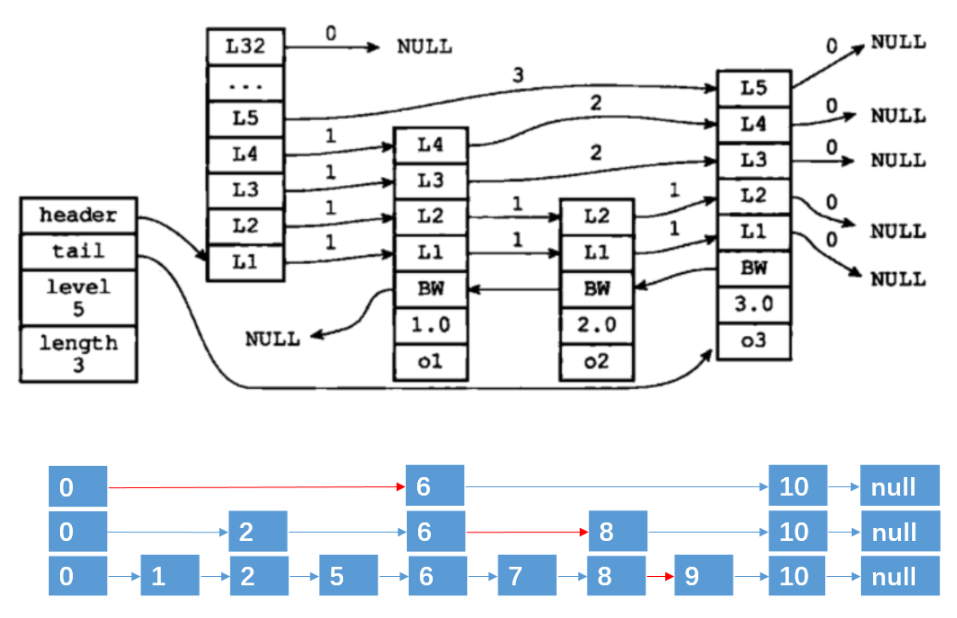
Redis中跳表主要用在zset的實現中。跳表數據結構是對時間和空間上的綜合。跳表是在鏈表基礎上提供更高效的查找效率(O(logN)),并且在實現上更簡單。
?更多資料:0voice · GitHub

-設計模式篇)
)



)


——Time、Vector3、位置位移、角度、旋轉、縮放、看向)

,KL散度)







