目錄
OrangepiPro初體驗
前述:
一、硬件準備
二、安裝CANN工具鏈(虛擬機)
三、配置模型轉換環境(虛擬機)
1.安裝miniconda 。
2.創建環境。
3.安裝依賴包
四、轉換模型
1. 查看設備號(開發板)
2. 使用ATC命令轉換onnx模型為om模型(虛擬機)
補:使用ATC命令時遇到問題
五、模型推理(開發板)
1. 在板端安裝CANN
2. 安裝Mindx,用于推理。
3. 使用conda創建虛擬環境- python=3.9
4. python推理代碼。
六、效果展示(開發板)
七、總結
OrangepiPro初體驗
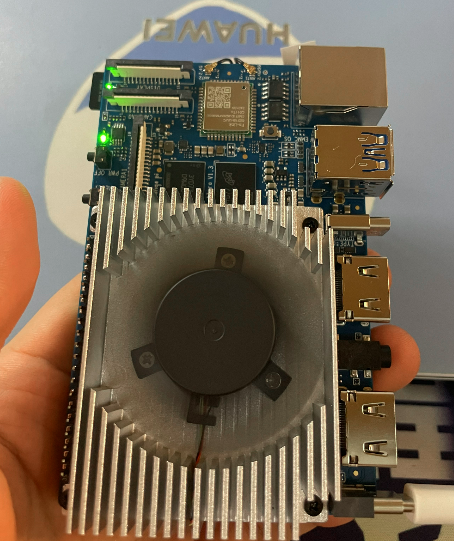
?? 終于!懷著激動的心情拿到了期待已久的開發板,迫不及待趕緊拆箱,映入眼簾的只有一個字:酷!正如下面幾個大字所寫:為AI而生。該開發板搭載華為昇騰AI處理器。能覆蓋生態開發板者的主流應用場景,讓用戶實踐各種創新場景,并為其提供配套的軟硬件。豐富的接口更是賦予了Orange Pi AIpro強大的可拓展性。包括兩個HDMI輸出、GPIO接口、Type-C電源接口、支持SATA/NVMe SSD 2280的M.2插槽、TF插槽、千兆網口、兩個USB3.0、一個USB Type-C 3.0、一個Micro USB、兩個MIPI攝像頭、一個MIPI屏等,預留電池接口。在操作系統方面,Orange Pi AIpro可運行Ubuntu、openEuler操作系統,滿足大多數AI算法原型驗證、推理應用開發的需求。實物如下:


前述:
?? 本文將不再介紹獲取ip、連接wifi、vnc等操作,詳情查看OrangpiPro官方手冊即可。官方地址。
?? 作者認為后續的進一步學習或開發都應該建立在有基本了解的前提下,所以本文的宗旨就是帶剛入門的初級開發者實現模型部署的完整流程。且本文內容還涉及在部署模型時所遇到的問題及其解決方法。每一步都有詳細的步驟,避免踩坑。對剛入門進行學習的開發者來說,簡直是不要太友好。相信根據本文部署完成后,會對流程有一些較為清楚的認識,對以后其他模型部署以及學習會有很大的幫助。創造不易,且看且珍惜。
一、硬件準備
Ubuntu22.04_x86系統(虛擬機)
OrangepiPro開發板
二、安裝CANN工具鏈(虛擬機)
??異構計算架構CANN是華為針對AI場景推出的異構計算架構,向上支持多種AI框架,包括MindSpore、PyTorch、TensorFlow等,向下服務AI處理器與編程,發揮承上啟下的關鍵作用,是提升昇騰AI處理器計算效率的關鍵平臺。所以CANN工具鏈是我們必備工具鏈。打開ubuntu的瀏覽器:資源下載地址。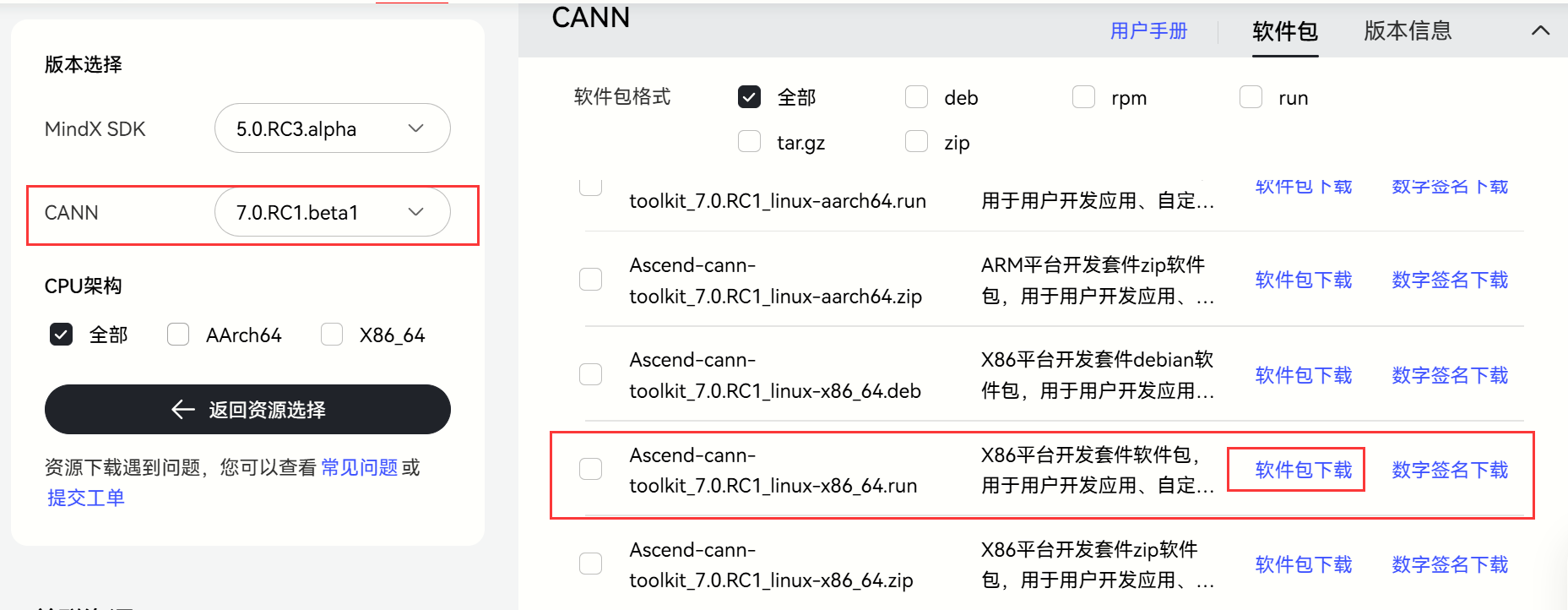
下載完成后,自動保存在Downloads目錄下,如下所示:
?? 這里我已經給軟件包添加了執行權限,如果初次下載請使用添加可執行權限。后續使用安裝命令進行安裝。安裝命令:?./Ascend-cann-toolkit_7.0.RC1_linux-x86_64.run --install?。安裝完成后,配置環境變量。使用命令:vi ~/.bashrc。將下述命令粘貼到文件里,這樣就可以永久有效使用了,而不是只對當前命令窗口有效。
source /home/qjl/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/set_env.sh
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/qjl/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/7.0.RC1/x86_64-linux/devlib/x86_64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
?? 添加成功后,使用source ~/.bashrc命令來刷新使得文件配置生效。此時我們就可以使用atc命令來轉換模型咯!如下,出現下面內容說明我們atc命令可以使用。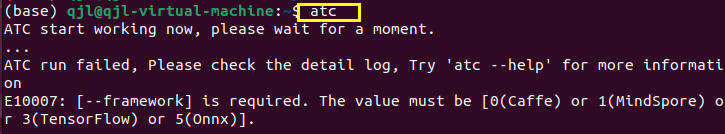
三、配置模型轉換環境(虛擬機)
1.安裝miniconda 。
//linux_x86架構下的conda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py37_4.12.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda3-py37_4.12.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
2.創建環境。
?? 這里使用conda來創建環境,這里我創建的為python 3.9版本。創建環境流程這里就不多贅述,具體詳情查看創建環境教程。
3.安裝依賴包
pip install attrs numpy decorator sympy cffi pyyaml pathlib2 psutil protobuf scipy requests absl-py wheel typing_extensions -i https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/repository/pypi/simple
這里安裝完成后,如果哪些包出現依賴問題,則單獨裝一下該包即可。
四、轉換模型
1. 查看設備號(開發板)
?? 使用命令:npu-smi info,查看設備號這個操作是在開發板上進行的,上面的操作都是在ubuntu上進行的(當然也可以在開發板上進行,只不過本文演示是在ubuntu_x86)。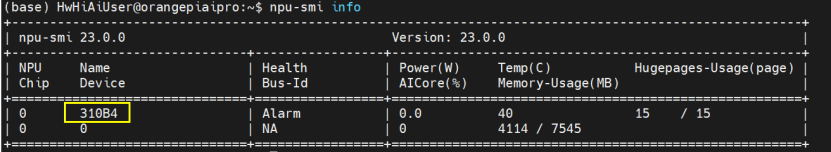
2. 使用ATC命令轉換onnx模型為om模型(虛擬機)
atc --model=/home/qjl/cup.onnx --framework=5 --output=/home/qjl/cup --soc_version=Ascend310B4
該命令的具體參數這里不多介紹,詳情請查看官方手冊即可。
我們使用完命令后,等待幾分鐘轉換好om模型。此時大功告成!廢話不多說,立馬部署到開發板上!
補:使用ATC命令時遇到問題
問題一: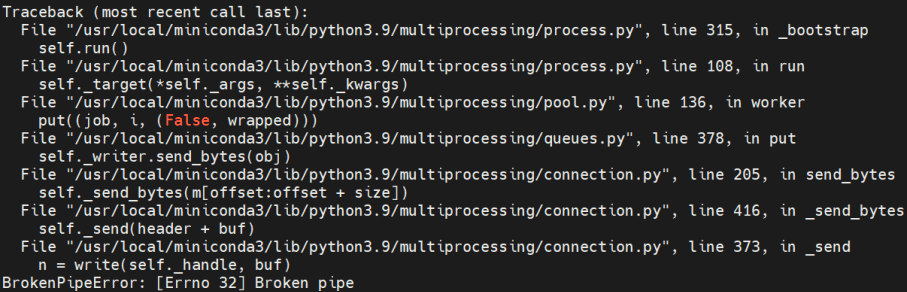
?? 這個情況說明內存崩潰。這個問題原以為是因為訓練模型的時候num_worker數量太大導致的問題,于是修改num_worker=0重新訓練模型,將模型導入linux中轉換時還是出現該錯誤,一時不知如何是好。但最終還是找到解決辦法,將下面命令導入環境變量。設置最大核心數即可。編譯過程僅使用一個核心,為了避免由于使用過多核心導致的資源競爭或內存不足問題。
export TE_PARALLEL_COMPILER=1
export MAX_COMPILE_CORE_NUMBER=1
這里和上面設置環境變量一樣,可以設置到~/.bashrc中,使其永久生效。
問題二: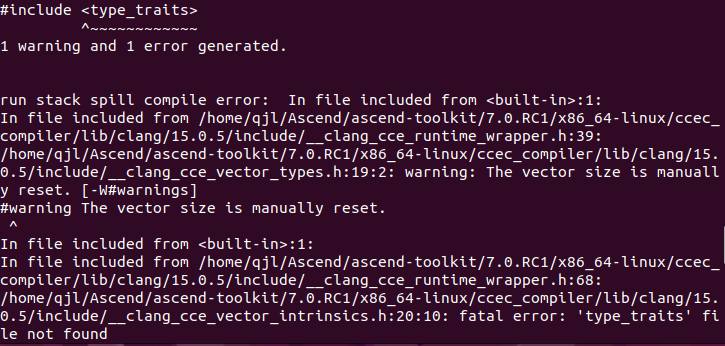
?? 找不到<type_traits>(C++庫),這是因為缺失C++庫導致的。于是我搜索本地gcc及g++庫,結果發現還沒有安裝編譯器,如下所示。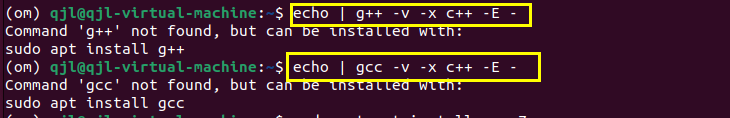
?? 既然這樣,我們使用命令:sudo apt install build-essential,來安裝編譯工具包。這個工具包里包含了編譯時所需要的各種工具以及相應的庫文件。安裝完成以后,我們就可以使用之前的命令進行模型轉換咯~
五、模型推理(開發板)
1. 在板端安裝CANN
?? 使用命令?./Ascend-cann-toolkit_7.0.RC1_linux-aarch64.run --install進行安裝。安裝完成后,和在linux_x86端一樣設置環境變量等操作,這里不再贅述。
2. 安裝Mindx,用于推理。
注意:這里只有當安裝好CANN后再進行安裝Mindx!
?? 下載好以后,執行?./Ascend-mindxsdk-mxvision_6.0.RC1_linux-aarch64.run --install進行安裝。
?? 安裝完成后vi ~/.bashrc,添加source /home/HwHiAiUser/Mindx/mxVision/set_env.sh。添加完成后使用source ~/.bashrc使得文件生效。
3. 使用conda創建虛擬環境- python=3.9
//arm架構下的conda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py37_4.9.2-Linux-aarch64.sh
bash Miniconda3-py37_4.9.2-Linux-aarch64.sh
(1)安裝opencv:pip install opencv-python
(2)安裝numpy:pip install numpy
(3)安裝torch以及torchvision。下載好whl文件安裝即可。點擊:下載地址。如果缺少哪個包就再pip安裝一下即可。
(4)安裝mindx包。
進入Mindx安裝目錄,路徑如下。找到whl文件使用pip進行安裝即可。
4. python推理代碼。
(1)后處理代碼(公用)
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):# Resize image to a 32-pixel-multiple rectangle https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]if isinstance(new_shape, int):new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)r = min(r, 1.0)# Compute paddingratio = r, r # width, height ratiosnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh paddingif auto: # minimum rectangledw, dh = np.mod(dw, 64), np.mod(dh, 64) # wh paddingelif scaleFill: # stretchdw, dh = 0.0, 0.0new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratiosdw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sidesdh /= 2if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeimg = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add borderreturn img, ratio, (dw, dh)def non_max_suppression(prediction,conf_thres=0.25,iou_thres=0.45,classes=None,agnostic=False,multi_label=False,labels=(),max_det=300,nm=0, # number of masks
):"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detectionsReturns:list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]"""if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference outputdevice = prediction.devicemps = 'mps' in device.type # Apple MPSif mps: # MPS not fully supported yet, convert tensors to CPU before NMSprediction = prediction.cpu()bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch sizenc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classesxc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates# Checksassert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'# Settings# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and heightmax_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and heightmax_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()time_limit = 0.5 + 0.05 * bs # seconds to quit aftermulti_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)t = time.time()mi = 5 + nc # mask start indexoutput = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bsfor xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference# Apply constraints# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-heightx = x[xc[xi]] # confidence# Cat apriori labels if autolabellingif labels and len(labels[xi]):lb = labels[xi]v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5), device=x.device)v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # boxv[:, 4] = 1.0 # confv[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # clsx = torch.cat((x, v), 0)# If none remain process next imageif not x.shape[0]:continue# Compute confx[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf# Box/Maskbox = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)mask = x[:, mi:] # zero columns if no masks# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)if multi_label:i, j = (x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).Tx = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 5 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)else: # best class onlyconf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True)x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]# Filter by classif classes is not None:x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]# Check shapen = x.shape[0] # number of boxesif not n: # no boxescontinueelif n > max_nms: # excess boxesx = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidenceelse:x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)] # sort by confidence# Batched NMSc = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classesboxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scoresi = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMSif i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detectionsi = i[:max_det]output[xi] = x[i]if mps:output[xi] = output[xi].to(device)if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:print(f'WARNING ?? NMS time limit {time_limit:.3f}s exceeded')break # time limit exceededreturn outputdef xywh2xyxy(x):# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-righty = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left xy[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left yy[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right xy[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right yreturn ydef get_labels_from_txt(path):labels_dict = dict()with open(path) as f:for cat_id, label in enumerate(f.readlines()):labels_dict[cat_id] = label.strip()return labels_dictdef scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shapeif ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shapegain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / newpad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh paddingelse:gain = ratio_pad[0][0]pad = ratio_pad[1]coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x paddingcoords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y paddingcoords[:, :4] /= gainclip_coords(coords, img0_shape)return coordsdef clip_coords(boxes, shape):# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individuallyboxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2else: # np.array (faster grouped)boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2def nms(box_out, conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.5):try:boxout = non_max_suppression(box_out, conf_thres=conf_thres, iou_thres=iou_thres, multi_label=True)except:boxout = non_max_suppression(box_out, conf_thres=conf_thres, iou_thres=iou_thres)return boxout
(2)圖片推理:將模型文件和圖片、以及推理代碼放在一個目錄下。運行該文件即可。
# coding=utf-8
import cv2 # 圖片處理三方庫,用于對圖片進行前后處理
import numpy as np # 用于對多維數組進行計算
import torch # 深度學習運算框架,此處主要用來處理數據
import time
import torchvision
from mindx.sdk import Tensor # mxVision 中的 Tensor 數據結構
from mindx.sdk import base # mxVision 推理接口def draw_bbox(bbox, img0, color, wt, names):det_result_str = ''for idx, class_id in enumerate(bbox[:, 5]):if float(bbox[idx][4] < float(0.05)):continueimg0 = cv2.rectangle(img0, (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1])), (int(bbox[idx][2]), int(bbox[idx][3])), color, wt)img0 = cv2.putText(img0, str(idx) + ' ' + names[int(class_id)], (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] + 16)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)img0 = cv2.putText(img0, '{:.4f}'.format(bbox[idx][4]), (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] + 32)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)det_result_str += '{} {} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(names[bbox[idx][5]], str(bbox[idx][4]), bbox[idx][0], bbox[idx][1], bbox[idx][2], bbox[idx][3])return img0if __name__ == '__main__':# 初始化資源和變量base.mx_init() # 初始化 mxVision 資源DEVICE_ID = 0 # 設備idmodel_path = 'best.om' # 模型路徑image_path = 'image.jpg' # 測試圖片路徑# 數據前處理img_bgr = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # 讀入圖片img, scale_ratio, pad_size = letterbox(img_bgr, new_shape=[640, 640]) # 對圖像進行縮放與填充,保持長寬比img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, HWC to CHWimg = np.expand_dims(img, 0).astype(np.float32) # 將形狀轉換為 channel first (1, 3, 640, 640),即擴展第一維為 batchsizeimg = np.ascontiguousarray(img) / 255.0 # 轉換為內存連續存儲的數組img = Tensor(img) # 將numpy轉為轉為Tensor類# 模型推理, 得到模型輸出model = base.model(modelPath=model_path, deviceId=DEVICE_ID) # 初始化 base.model 類output = model.infer([img])[0] # 執行推理。輸入數據類型:List[base.Tensor], 返回模型推理輸出的 List[base.Tensor]# 后處理output.to_host() # 將 Tensor 數據轉移到內存output = np.array(output) # 將數據轉為 numpy array 類型boxout = nms(torch.tensor(output), conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.5) # 利用非極大值抑制處理模型輸出,conf_thres 為置信度閾值,iou_thres 為iou閾值pred_all = boxout[0].numpy() # 轉換為numpy數組scale_coords([640, 640], pred_all[:, :4], img_bgr.shape, ratio_pad=(scale_ratio, pad_size)) # 將推理結果縮放到原始圖片大小labels_dict = get_labels_from_txt('./coco_names.txt') # 得到類別信息,返回序號與類別對應的字典img_dw = draw_bbox(pred_all, img_bgr, (0, 255, 0), 2, labels_dict) # 畫出檢測框、類別、概率# 保存圖片到文件cv2.imwrite('result.png', img_dw)print('save infer result success'
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import time
import torchvision
from mindx.sdk import Tensor
from mindx.sdk import base# 這里包括你已經提供的所有函數
# letterbox, non_max_suppression, xywh2xyxy, get_labels_from_txt, scale_coords, clip_coords, nmsdef draw_bbox(bbox, img0, color, wt, names):det_result_str = ''for idx, class_id in enumerate(bbox[:, 5]):if float(bbox[idx][4] < float(0.05)):continueimg0 = cv2.rectangle(img0, (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1])), (int(bbox[idx][2]), int(bbox[idx][3])), color, wt)img0 = cv2.putText(img0, str(idx) + ' ' + names[int(class_id)], (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] - 10)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)img0 = cv2.putText(img0, '{:.2f}'.format(bbox[idx][4]), (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] - 30)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)det_result_str += '{} {} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(names[bbox[idx][5]], str(bbox[idx][4]), bbox[idx][0], bbox[idx][1], bbox[idx][2], bbox[idx][3])return img0def process_frame(frame, model, labels_dict, scale_ratio, pad_size, input_shape=(640, 640)):img, _, _ = letterbox(frame, new_shape=input_shape)img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, HWC to CHWimg = np.expand_dims(img, 0).astype(np.float32) # batch size 1img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) / 255.0img = Tensor(img)output = model.infer([img])[0]output.to_host()output = np.array(output)boxout = nms(torch.tensor(output), conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.5)pred_all = boxout[0].numpy()scale_coords(input_shape, pred_all[:, :4], frame.shape, ratio_pad=(scale_ratio, pad_size))img_with_boxes = draw_bbox(pred_all, frame, (0, 255, 0), 2, labels_dict)return img_with_boxesif __name__ == '__main__':# 初始化資源和變量base.mx_init()DEVICE_ID = 0model_path = 'best.om'video_path = 'video.mp4'output_video_path = 'result_video.mp4'# 初始化視頻讀取與寫入cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_video_path, fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height))# 讀取類別標簽labels_dict = get_labels_from_txt('./coco_names.txt')# 加載模型model = base.model(modelPath=model_path, deviceId=DEVICE_ID)while cap.isOpened():ret, frame = cap.read()if not ret:break# 數據前處理img_bgr = frameimg, scale_ratio, pad_size = letterbox(img_bgr, new_shape=[640, 640])# 處理幀processed_frame = process_frame(frame, model, labels_dict, scale_ratio, pad_size)# 寫入處理后的幀out.write(processed_frame)# 釋放資源cap.release()out.release()print('Video processing complete. Saved to', output_video_path)遇到問題:
?? 我們在運行推理代碼時出現上述問題,原因是因為我們torch和torchvision的版本有點高,只需要降低版本即可。如使用torch==1.10.0 torchvision==0.11.0即可。當然這里不影響我們最后的結果,所以覺得煩的小伙伴可以降低版本,該問題就解決了。
六、效果展示(開發板)

圖片推理結果: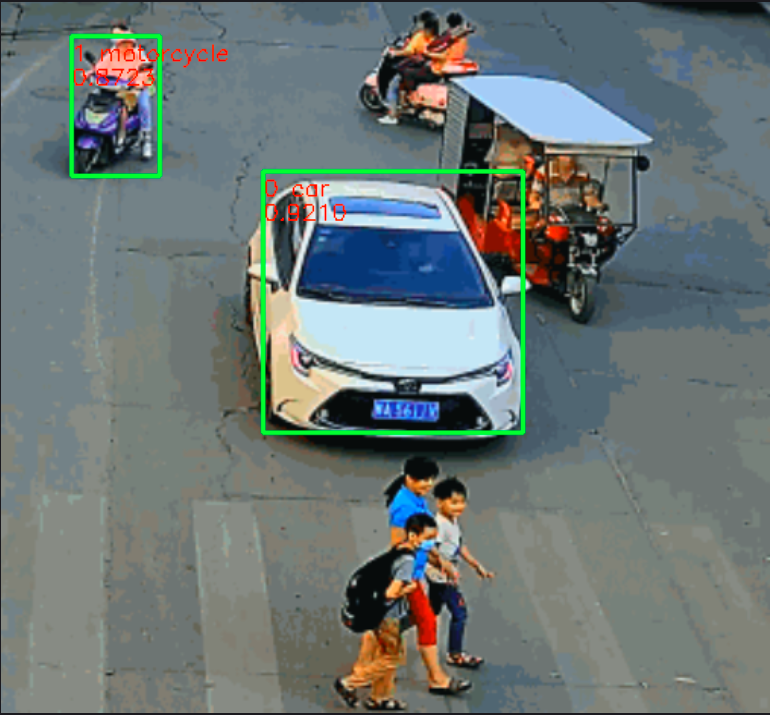
視頻推理結果:
七、總結
??這里我們使用自訓練的車輛數據集模型,部署到開發板上可見效果很好,這里我們就完成了從0到1的全部流程,中間也遇到很多問題,也是通過查閱大量資料來解決的問題,這也是必備的學習方法之一。本人也是處于學習階段,所以有錯誤的地方,希望各位積極指正,我們一起加油。




元素定位工具appium-inspector)










數據處理)



