上文我們通過new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");這段代碼看了下Spring是如何將Xml里面內容注入到Java對象中,并通過context.getBean("jmUser");方式獲得了一個對象實例,而避開使用new 來耦合。今天我們就來看看Spring是如何做到的呢?
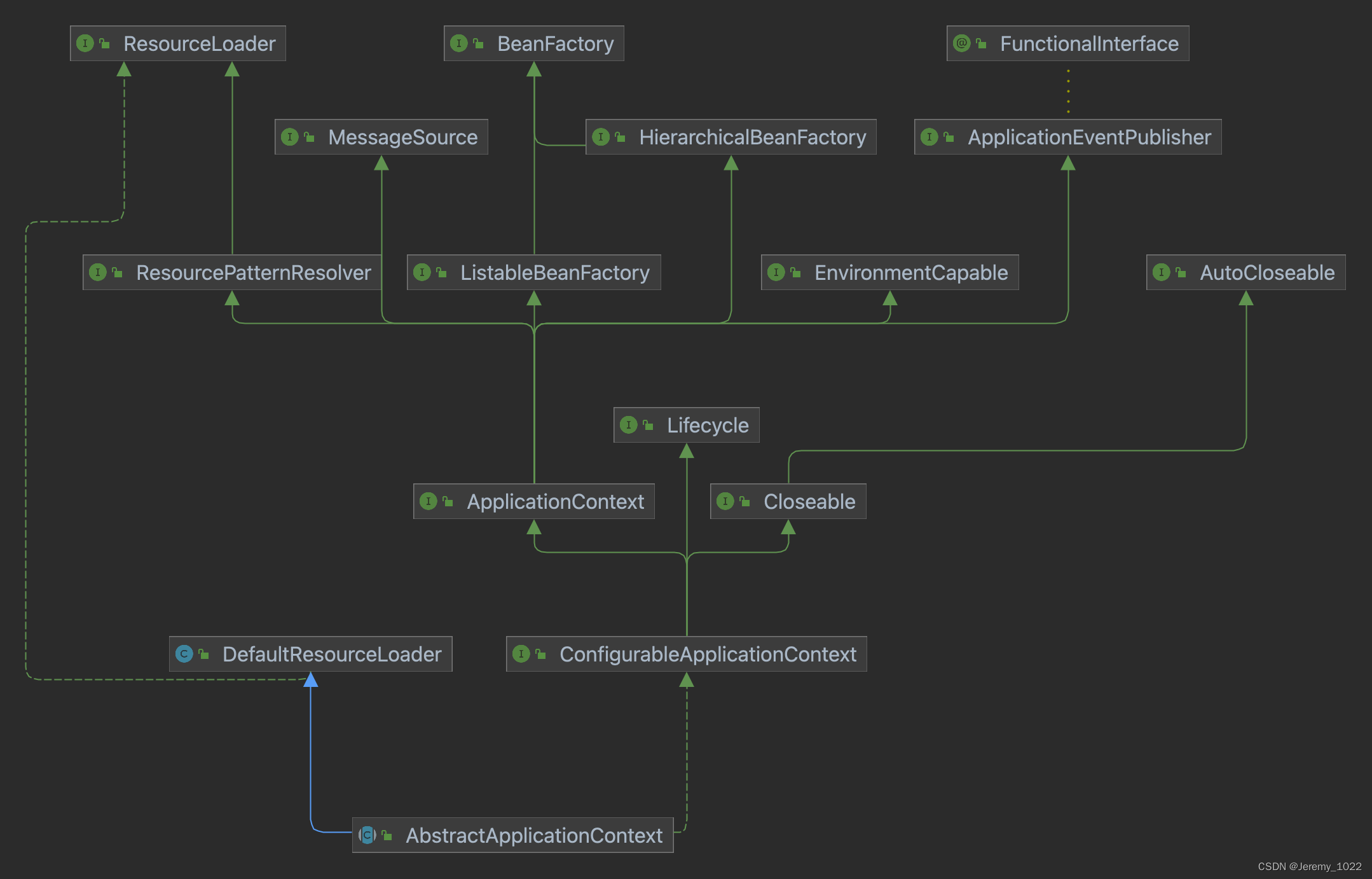 上圖是AbstractApplicationContext的類圖,dedug跟蹤這段代碼
上圖是AbstractApplicationContext的類圖,dedug跟蹤這段代碼
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext構造方法
/*** 根據xml路徑,創建一個ClassPathXmlApplicationContext實例* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,* loading the definitions from the given XML files.* @param configLocations array of resource locations* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.* @param parent the parent context* @throws BeansException if context creation failed* @see #refresh()*/public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)throws BeansException {// 調用父類構造方法,主要是初始化環境變量相關信息,核心代碼在 AbstractApplicationContext 類中super(parent);// 設置配置文件的位置 ApplicationContext的實現可能會使用默認的配置文件位置。setConfigLocations(configLocations);// 默認構造trueif (refresh) {// 進入核心方法refresh();}}1、初始化環境變量相關信息
發現最終進入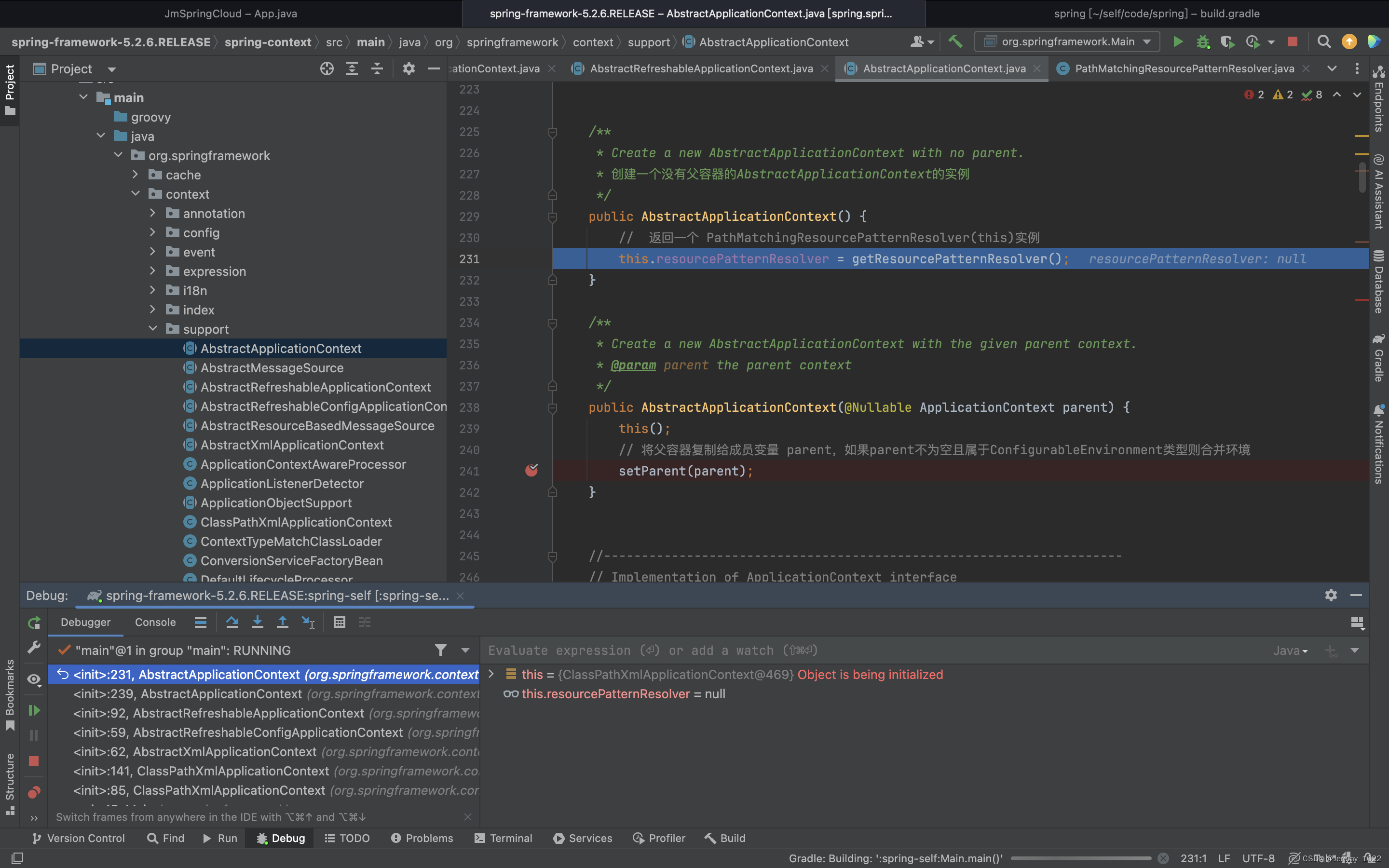
/*** Create a new AbstractApplicationContext with no parent.* 創建一個沒有父容器的AbstractApplicationContext的實例*/public AbstractApplicationContext() {// 返回一個 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this)實例this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();}/*** Create a new AbstractApplicationContext with the given parent context.* @param parent the parent context*/public AbstractApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {this();// 將父容器復制給成員變量 parent,如果parent不為空且屬于ConfigurableEnvironment類型則合并環境setParent(parent);}
2、設置配置文件的位置
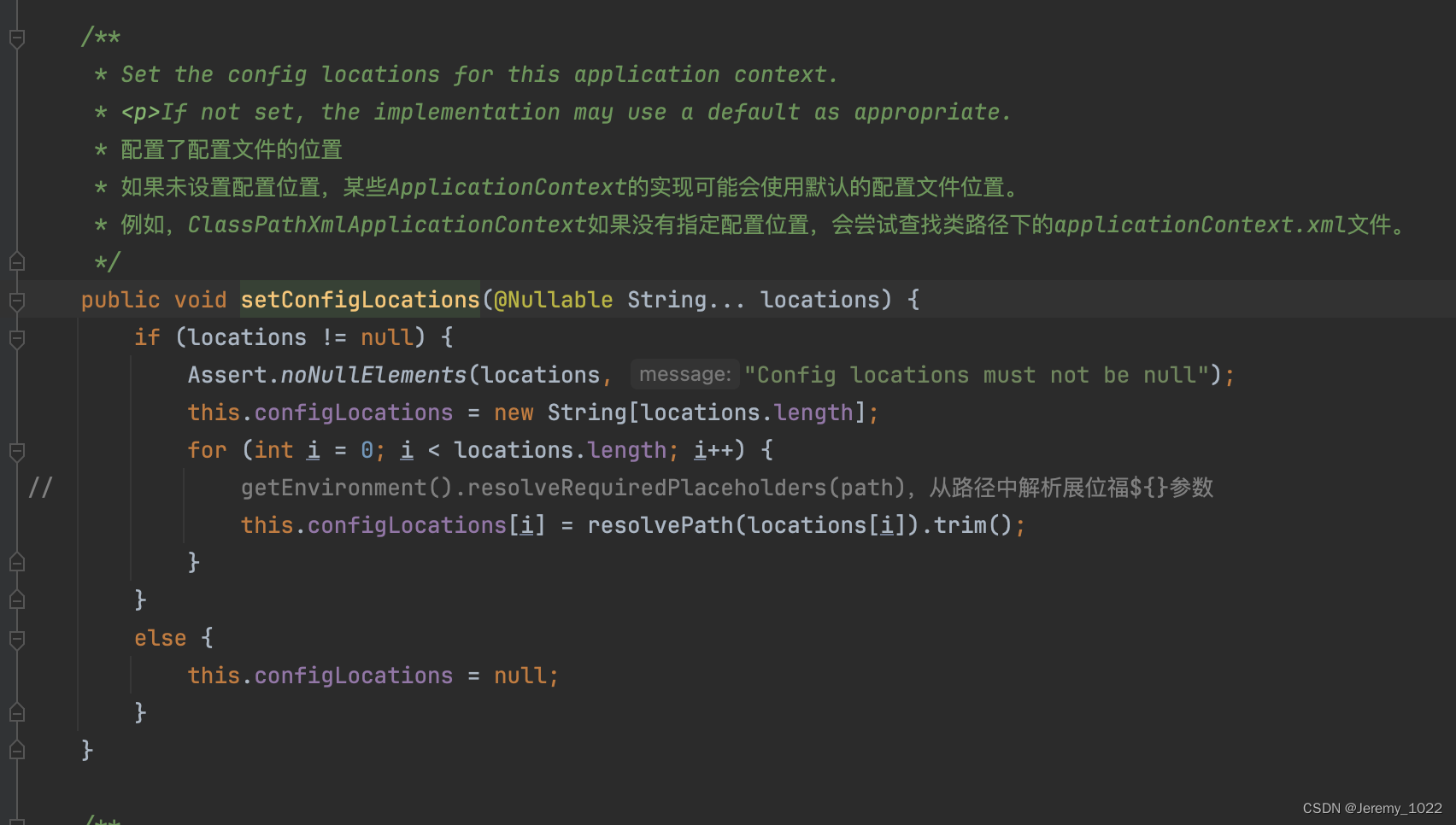
/*** Set the config locations for this application context.* <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate.* 配置了配置文件的位置* 如果未設置配置位置,某些ApplicationContext的實現可能會使用默認的配置文件位置。* 例如,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext如果沒有指定配置位置,會嘗試查找類路徑下的applicationContext.xml文件。*/public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {if (locations != null) {Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
// getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path),從路徑中解析展位福${}參數this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();}}else {this.configLocations = null;}}/*** Resolve the given path, replacing placeholders with corresponding* environment property values if necessary. Applied to config locations.* @param path the original file path* @return the resolved file path* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment#resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String)*/protected String resolvePath(String path) {return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);}public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);}3、進入refresh方法
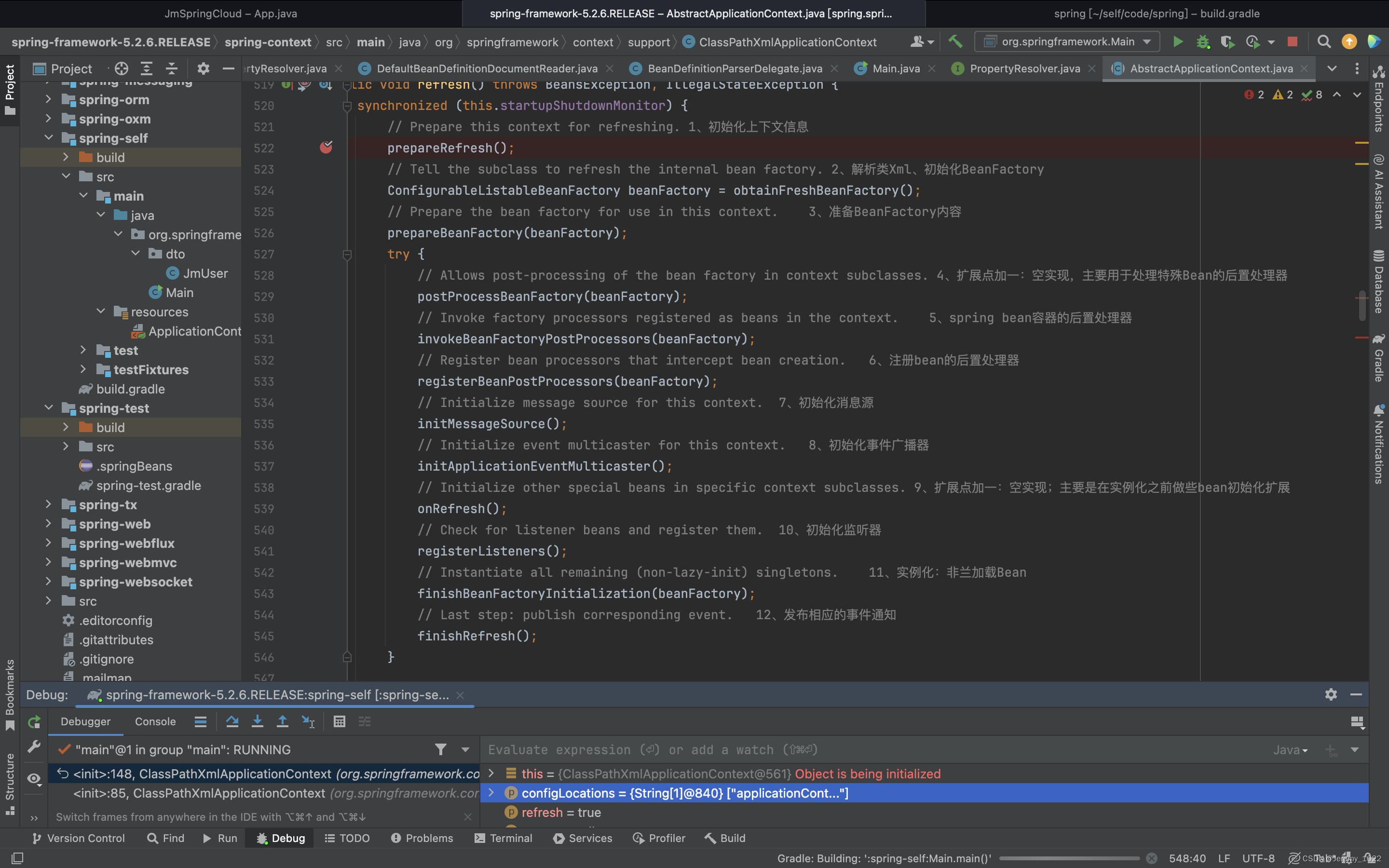
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing. 1、初始化上下文信息prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 2、解析類Xml、初始化BeanFactoryConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 3、準備BeanFactory內容prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 4、擴展點加一:空實現,主要用于處理特殊Bean的后置處理器postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 5、spring bean容器的后置處理器invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 6、注冊bean的后置處理器registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context. 7、初始化消息源initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context. 8、初始化事件廣播器initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 9、擴展點加一:空實現;主要是在實例化之前做些bean初始化擴展onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them. 10、初始化監聽器registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 11、實例化:非蘭加載BeanfinishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event. 12、發布相應的事件通知finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();}}}整個流程可以分為以下幾個主要步驟:
- 初始化上下文環境信息。
- 解析XML配置文件,創建并初始化
BeanFactory。 - 設置BeanFactory的類加載器,注冊一些默認的環境Bean。
- 提供擴展點用于對BeanFactory進行進一步的定制。
- 調用BeanFactory的后置處理器。
- 注冊Bean的后置處理器。
- 初始化消息源,用于國際化支持。
- 初始化事件廣播器,用于發布事件。
- 提供擴展點用于在刷新上下文時做一些特殊的初始化。
- 檢查并注冊監聽器Bean。
- 實例化所有剩余的單例Bean(非懶加載)。
- 發布相應的事件通知,表示上下文刷新完成。
步驟概覽
1. prepareRefresh()
prepareRefresh();prepareRefresh()方法用于初始化上下文環境信息,包括設置啟動時間、活動狀態等基本屬性。它確保在刷新過程中,應用上下文處于正確的狀態。
2. obtainFreshBeanFactory()
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();該方法解析XML配置文件,創建并初始化BeanFactory,并載入Bean定義。它是Spring應用上下文初始化的關鍵步驟之一。
3. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);此步驟設置BeanFactory的類加載器,并注冊一些默認的環境Bean,如類加載器、表達式解析器等。它確保BeanFactory在上下文中能夠正確工作。
4. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);這是一個擴展點,通常為空實現。開發者可以在子類中重寫該方法,對BeanFactory進行進一步的定制,如添加額外的Bean定義或修改現有的Bean定義。
5. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);該方法調用BeanFactory的后置處理器,這些處理器可以在Bean實例化之前對Bean定義進行修改或增加新的Bean定義。
6. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);在此步驟中,Spring注冊Bean的后置處理器,這些處理器會在Bean的創建過程中攔截并進行處理,如執行依賴注入和初始化回調等。
7. initMessageSource()
initMessageSource();該方法初始化消息源,用于支持國際化(i18n)。它允許應用程序根據用戶的語言環境顯示不同的消息。
8. initApplicationEventMulticaster()
initApplicationEventMulticaster();Spring使用事件廣播器來發布和監聽應用程序事件。該方法初始化事件廣播器,確保事件能夠在應用上下文中正確傳播。
9. onRefresh()
onRefresh();這是另一個擴展點,通常為空實現。開發者可以在子類中重寫該方法,在刷新上下文時執行一些特殊的初始化操作。
10. registerListeners()
registerListeners();該方法檢查并注冊監聽器Bean,用于監聽和處理應用程序事件。
11. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);此步驟實例化所有剩余的單例Bean(非懶加載)。它確保所有Bean都已準備就緒,可以在應用程序中使用。
12. finishRefresh()
finishRefresh();最后,Spring發布相應的事件通知,表示上下文刷新已完成。此步驟通常包括發布ContextRefreshedEvent事件,通知所有監聽器上下文已刷新。
總結
本章主要通過斷點源碼,一步步跟蹤到refresh方法,然后整體跟蹤了refresh的具體步驟,每一步大概干了什么內容,后面我們將一個一個方法深入討論,具體做了什么?預留了什么擴展點。我們在開發中怎么去使用這些擴展點。以及后面SpringBoot和SpringCloud是怎樣利用這些擴展點給我么提供開箱即用的功能的。



)






)








