目錄
- 一、顯示hello world
- 1.1 圖形化界面
- 1.2 寫代碼
- 二、對象樹
- 三、使用輸入框顯示hello world
- 四、使用按鈕顯示hello world
一、顯示hello world
有兩種方式實現hello world:
- 通過圖形化界面,在界面上創建出一個控件,顯示hello world
- 通過寫代碼的方式,創建控件,顯示hello world
1.1 圖形化界面
點擊widget.ui文件,進入界面設計。左邊找到Label標簽,鼠標點中拖到框框里面,然后寫hello world

注意:框框里面寫了hello world后,在source文件夾的main.cpp和widget.cpp文件內容是沒有變化的,變化的是.ui文件

點擊左下角的三角形按鈕,運行:

同時在右上角發現,多了一個控件:

剛剛我們寫了hello world的內容,ui文件就會在xml中多出來一段代碼,qmake就會在編譯項目的時候,基于這段代碼生成一段C++代碼,然后通過這段C++代碼構建出界面內容(這是自動完成的,不需要手動)
1.2 寫代碼
寫代碼的位置:在widget.cpp文件中
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QLabel>Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget)
{ui->setupUi(this);QLabel* label = new QLabel(this);// QLabel label;label->setText("hello world");
}Widget::~Widget()
{delete ui;
}
- 注意要記得帶上頭文件#include < QLabel>
- QLabel可以在對堆上創建對象,也可以在棧上創建對象,一般用堆更好些
- QLabel對象的小括號中的this表示指明父類(Widget w)
- 對象的方法的setText填入要顯示的文本內容,可以直接用C風格字符串(C格式字符串會隱式構造成QString對象)
由于Qt出現的比較早,當時還沒有C++的標準庫,所以Qt為了自己的開發能夠流暢,也有自己的一套輪子,包括:字符串QString、QVector、QList、QMap等等。但是現在QString和std::string是可以相互轉換的,相比而言,QString稍微好點,因為它內部的已經對于字符編碼做了處理。
運行:

二、對象樹
上面的代碼有一些“問題”,在C++中,我們寫代碼new出來的對象最后都要釋放,否則會內存泄漏,可是這里的代碼并沒有顯示去釋放它。
其實在Qt中,不會產生內存泄漏問題,label對象會在合適的時候被析構釋放,之所以能夠被釋放,是因為這個對象被掛到了對象樹上(與參數的this有關)
這個對象樹是一個N叉樹,會把界面上的各種元素(控件對象)組織起來,然后統一進行釋放,合適的時候:窗口關閉
前面說通過new更好,是為了把這個對象的生命周期交給Qt的對象樹進行管理,如果是棧就不行了,可能存在提起釋放問題(出了作用域對象就銷毀了,導致最后要顯示的內容沒有顯示出來)
驗證堆上能夠自動釋放:
這里我們自定義一個MyLabel類,只要MyLabel類的析構函數執行到了,此時窗口就會銷毀,自動把對象樹上的所有對象銷毀
mylabel.h文件:
#ifndef MYLABEL_H
#define MYLABEL_H#include <QLabel>class MyLabel : public QLabel
{
public:// 構造函數使用QWidget*版本的// 這樣才能確保對象加到對象樹上MyLabel(QWidget* parent);~MyLabel();
};#endif // MYLABEL_H
mylabel.cpp文件:
#include "mylabel.h"
#include <iostream>MyLabel::MyLabel(QWidget* parent):QLabel(parent)
{}MyLabel::~MyLabel()
{std::cout << "mylabel已銷毀" << std::endl;
}
widget.cpp文件:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include "mylabel.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget)
{ui->setupUi(this);MyLabel *mylabel = new MyLabel(this);mylabel->setText("hello world");
}Widget::~Widget()
{delete ui;
}
運行:
出現了亂碼問題。
解決方法:使用Qt提供的qDebug() 工具,可以完成日志打印工作,處理好編碼格式問題
#include "mylabel.h"
#include <iostream>#include <QDebug>MyLabel::MyLabel(QWidget* parent):QLabel(parent)
{}MyLabel::~MyLabel()
{qDebug() << "MyLabel 已銷毀";
}
運行:

后續盡量使用qDebug 來打印輸出信息
三、使用輸入框顯示hello world
使用單行編輯框 QLineEdit 完成
兩種方式:界面和代碼

代碼:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"#include <QLineEdit>Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget)
{ui->setupUi(this);QLineEdit* ld = new QLineEdit(this);ld->setText("hello world");
}Widget::~Widget()
{delete ui;
}

四、使用按鈕顯示hello world

按鈕是可以點擊的,但是需要Qt中的信號槽機制。本質是給按鈕的點擊操作設置一個處理函數,當點擊時,就會執行這個處理函數
代碼:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget)
{ui->setupUi(this);connect(ui->pushButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::handleClick);
}Widget::~Widget()
{delete ui;
}void Widget::handleClick()
{// 當按鈕被點擊時,就把按鈕的內容進行替換if(ui->pushButton->text() == QString("hello world")){ui->pushButton->setText("hello qt");}else {ui->pushButton->setText("hello world");}
}
connect函數:
- ui->pushButton:誰發出信號
- &QPushButton::clicked:發出什么信號,點擊按鈕就會觸發這個信號
- &Widget::handleClick:處理函數
別忘了在widget.h文件聲明處理函數:

運行,點擊按鈕,內容從hello world變成hello qt,再點擊,從hello qt變成hello world

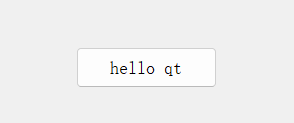
下面用代碼的方式來實現按鈕顯示hello world
代碼:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget)
{ui->setupUi(this);myp = new QPushButton(this);myp->setText("hello world");connect(myp, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::handleClick);
}Widget::~Widget()
{delete ui;
}void Widget::handleClick()
{// 當按鈕被點擊時,就把按鈕的內容進行替換if(myp->text() == QString("hello world")){myp->setText("hello qt");}else {myp->setText("hello world");}
}

運行效果與前面一樣



)

)


EtherCAT/Ethernet/IP/Profinet/ModbusTCP協議互轉工業串口網關)



:原理、算法與應用)



![[react]Next.js之自適應布局和高清屏幕適配解決方案](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[react]Next.js之自適應布局和高清屏幕適配解決方案)


