目錄
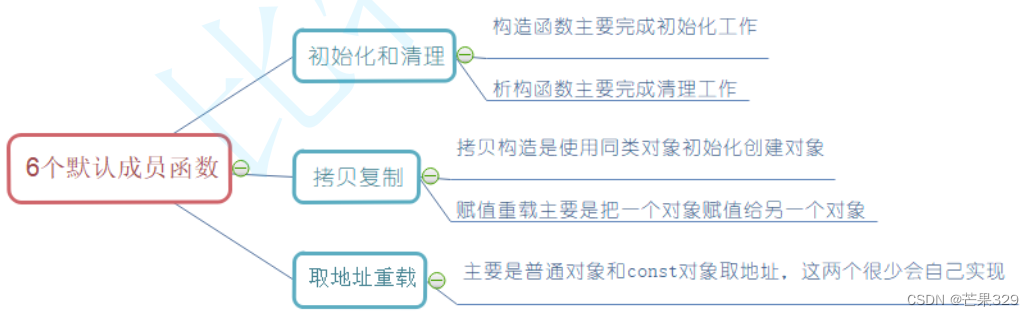
- 類的6個默認成員函數
- 構造函數
- 自己寫的構造函數
- 默認生成的構造函數
- 析構函數
- 概念
- 特征
- 拷貝構造函數
- 特征
- 運算符重載
- == 、 >、 <=
- +=
- +
- 賦值重載
- Date類的完善
- 構造函數的完善
- 用+復用+=
類的6個默認成員函數
默認成員函數:不寫編譯器也會默認生成一份
構造函數
自己寫的構造函數
構造函數是特殊的成員函數,需要注意的是,構造函數雖然名稱叫構造,但是構造函數的主要任
務并不是開空間創建對象,而是初始化對象。
其特征如下:
- 函數名與類名相同。
- 無返回值,不需要寫void。
- 對象實例化時編譯器自動調用對應的構造函數。
- 構造函數可以重載。
- . 如果類中沒有顯式定義構造函數,則C++編譯器會自動生成一個無參的默認構造函數,一旦
用戶顯式定義編譯器將不再生成。 - 關于編譯器生成的默認成員函數,很多童鞋會有疑惑:不實現構造函數的情況下,編譯器會
生成默認的構造函數。但是看起來默認構造函數又沒什么用?d對象調用了編譯器生成的默
認構造函數,但是d對象_year/_month/_day,依舊是隨機值。也就說在這里編譯器生成的
默認構造函數并沒有什么用??
解答:C++把類型分成內置類型(基本類型)和自定義類型。內置類型就是語言提供的數據類
型,如:int/char…,自定義類型就是我們使用class/struct/union等自己定義的類型,看看
下面的程序,就會發現編譯器生成默認的構造函數會對自定類型成員_t調用的它的默認成員
函數。 - 無參的構造函數和全缺省的構造函數都稱為默認構造函數,并且默認構造函數只能有一個。
注意:無參構造函數、全缺省構造函數、我們沒寫編譯器默認生成的構造函數,都可以認為
是默認構造函數。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(){_day = 1;_month = 1;_year = 1;}Date(int day, int month, int year){_day = day;_month = month;_year = year;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2(2023, 1, 24);d1.Print();d2.Print();return 0;
}
對于沒有參數的初始化對象時,不能寫成下面那樣,因為無法與函數聲明區分
Date d1()
也可以用缺省函數,下面兩個函數構成函數重載,但是無參調用的時候會產生歧義
//Date()
// {
// _day = 1;
// _month = 1;
// _year = 1;
// }Date(int day = 1, int month = 1, int year = 1){_day = day;_month = month;_year = year;}
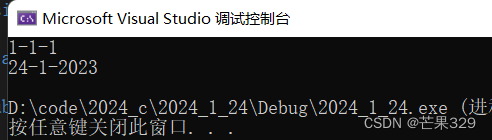
默認生成的構造函數
默認構造函數:編譯器默認生成的、無參的構造函數、全缺省的構造函數(可以不傳參的都叫默認構造),這三個函數不能同時存在,因為會存在調用歧義。
如果不寫構造函數,有沒有構造函數
默認生成的,但此時是隨機值
class Date
{
public:void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _day;int _month;int _year;
};int main()
{Date d1;d1.Print();return 0;
}
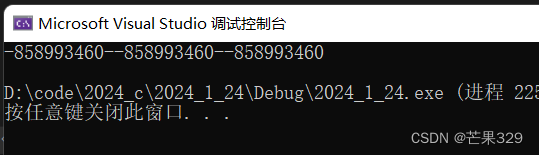
對于棧的初始函數來說,初始化的也是隨機值
class Stack
{
public:private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};int main()
{Stack s1;return 0;
}
但對于像MyQueue的構造函數就初始化了
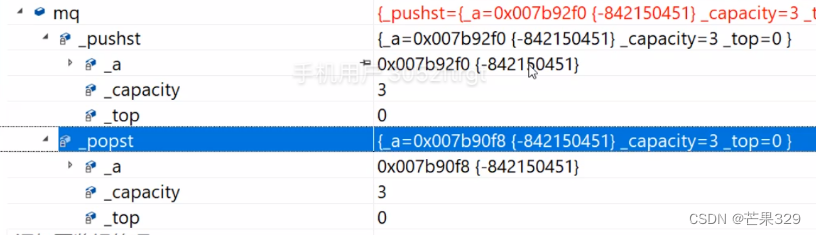
規則
內置類型:int/double/…指針,eg:Date* p是內置類型
自定義類型: class struct…
默認生成的構造函數,對于內置類型成員不做處理(看編譯器,建議當成不處理),自定義類型會取調用它的默認構造(調用無參的默認構造,如果自定義類型沒有默認構造 - 初始化列表,類和對象下講)
對于這個缺陷C++11提供如下解決方法,下面這個寫法還是聲明,給的缺省值

析構函數
概念
析構函數:與構造函數功能相反,析構函數不是完成對對象本身的銷毀,局部對象銷毀工作是由
編譯器完成的。而對象在銷毀時會自動調用析構函數,完成對象中資源的清理工作。
特征
析構函數是特殊的成員函數,其特征如下:
- 析構函數名是在類名前加上字符 ~。
- 無參數無返回值類型。
- 一個類只能有一個析構函數。若未顯式定義,系統會自動生成默認的析構函數。注意:析構
函數不能重載 - 對象生命周期結束時,C++編譯系統系統自動調用析構函數。
- 編譯器生成的默認析構函數,對自定類型成員調用它的析構函數。
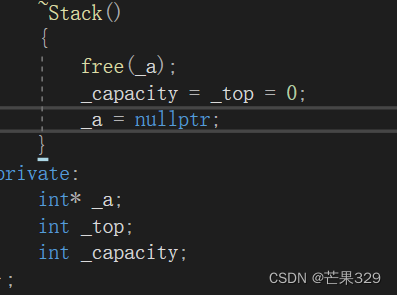
- 如果類中沒有申請資源時,析構函數可以不寫,直接使用編譯器生成的默認析構函數,比如
Date類;有資源申請時,一定要寫,否則會造成資源泄漏,比如Stack類
日期類不需要寫析構,棧需要寫析構
class Date
{
public:Date(int day = 1, int month = 1, int year = 1){_day = day;_month = month;_year = year;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}~Date(){cout << "~Date()" << endl;}
private:int _day = 1;int _month = 1;int _year = 1;
};int main()
{Date d1;d1.Print();return 0;
}

拷貝構造函數
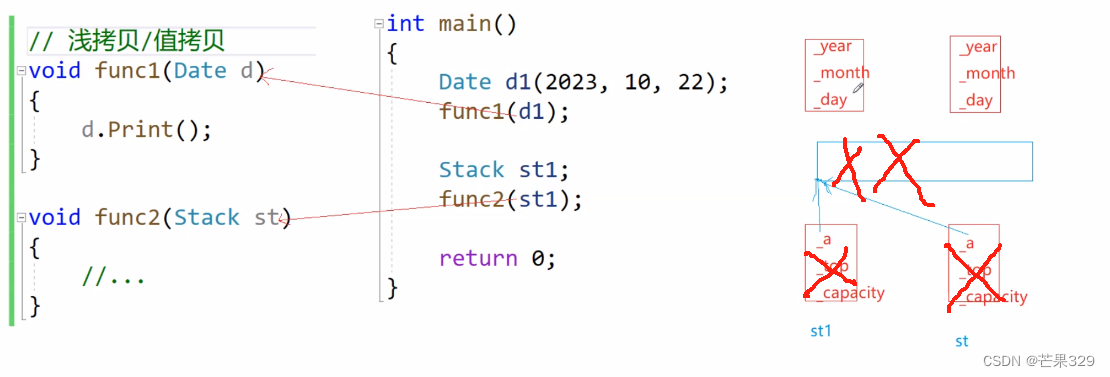
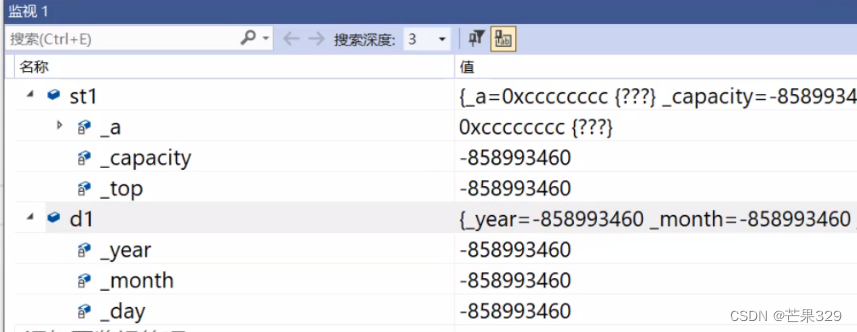
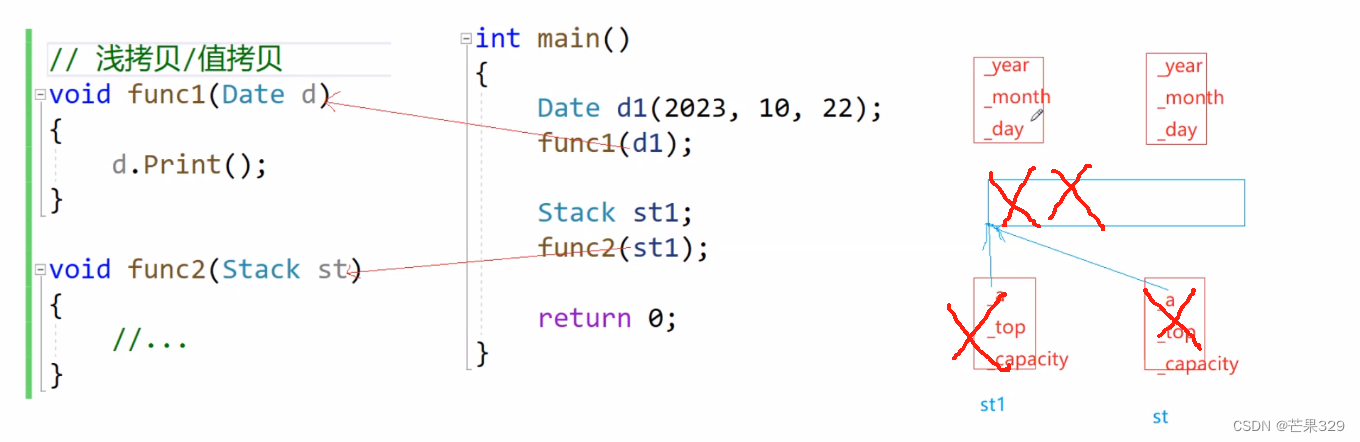
淺拷貝時,st和st1對象會導致對同一塊空間的重復釋放
解決方法:自定義類型對象拷貝時,調用一個函數,這個函數就叫拷貝構造 - 深拷貝。
(1)傳參的時候
(2)初始化構造的時候Date d2(d1)
特征
- 拷貝構造函數是構造函數的一個重載形式。
- 拷貝構造函數的參數只有一個且必須是類類型對象的引用,使用傳值方式編譯器直接報錯,
因為會引發無窮遞歸調用。.0 - 默認生成的拷貝構造函數:對內置類型會完成值拷貝,自定義對象回去調用它的拷貝對象。
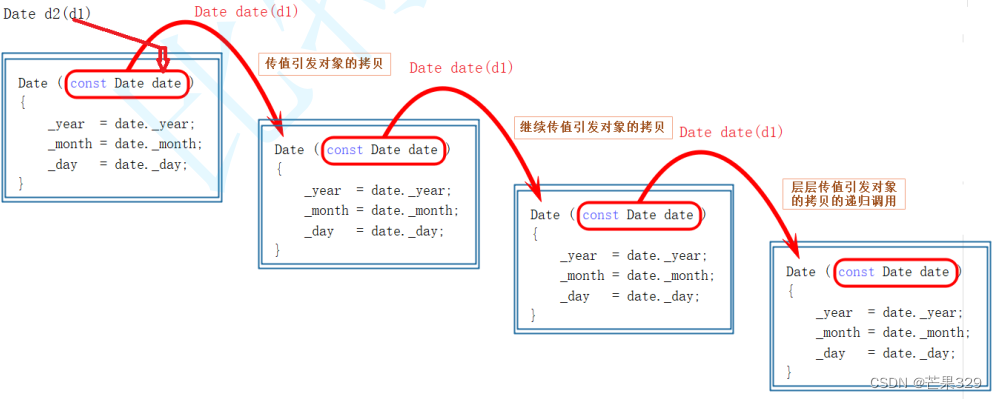
像下面所示,st1與st中的_a是指向同一塊空間,當這兩個對象被釋放時,會對_a所指的這段空間釋放兩次,從而造成錯誤,拷貝構造主要是解決這個問題的– 深拷貝。

class Stack
{
public:Stack(){//...}Stack(const Stack& stt){_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * stt._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_a, stt._a, sizeof(int) * stt._top);_top = stt._top;_capacity = stt._capacity;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;}
private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};
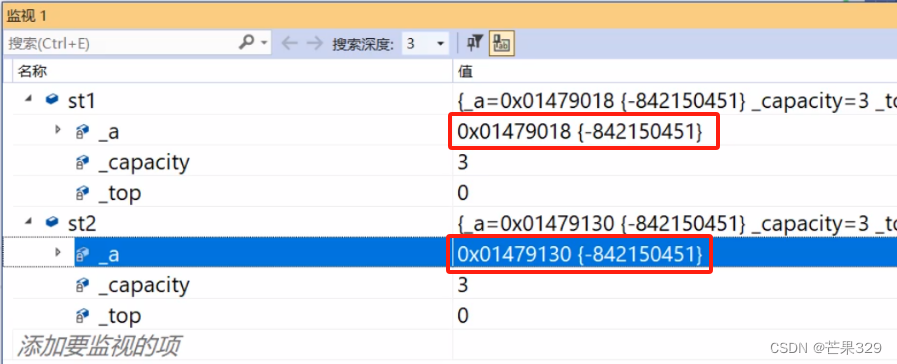
1、被拷貝的對象前面加const,防止意外的改變
運算符重載
對于+、-、*、/、>、<等等,內置類型可以直接使用,自定義類型無法使用
解決方法:(1)寫一個函數 (2)使用運算符重載
運算符重載:operator+運算符 ,使用方法:直接使用運算符
函數重載:允許參數不同的同名函數存在
運算符重載:自定義類型可以直接使用運算符
== 、 >、 <=
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}public:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
bool operator==(Date x, Date y)
{return x._year == y._year && x._month == y._month && x._day == y._day;
}
bool operator>(Date x, Date y)
{if (x._year > y._year)return true;else if (x._year == y._year && x._month > y._month)return true;else if (x._year == y._year && x._month == y._month && x._day > y._day)return true;return false;
}
bool operator<=(Date x, Date y)
{return ~(x > y);
}int main()
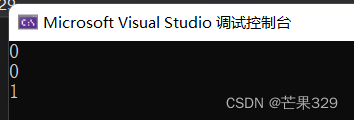
{Date d1(2001, 3, 29);Date d2(2024, 3, 1);cout << (d1 > d2) << endl;cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;cout << (d1 <= d2) << endl;return 0;
}
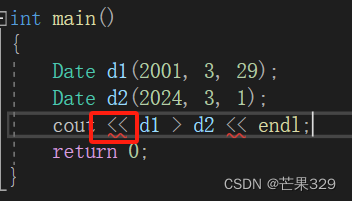
報錯的原因:因為流提取運算符的優先級大于>,因此加個括號就沒事了
**此時程序的缺陷 :
1、運算符重載函數的參數那,調用了拷貝構造 --> 用&
2、為了在函數里訪問類的成員變量,把成員變量設置 成了公有 --> 在類里面設置一些訪問成員的函數;將運算符重載函數放到類里面
**
缺陷1修改
bool operator==(const Date& x, const Date& y)
{return x._year == y._year && x._month == y._month && x._day == y._day;
}
bool operator>(const Date& x, const Date& y)
{if (x._year > y._year)return true;else if (x._year == y._year && x._month > y._month)return true;else if (x._year == y._year && x._month == y._month && x._day > y._day)return true;return false;
}
bool operator<=(const Date& x, const Date& y)
{return ~(x > y);
}
缺陷2修改
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}bool operator==(const Date& y){return _year == y._year && _month == y._month && _day == y._day;}bool operator>(const Date& y){if (_year > y._year)return true;else if (_year == y._year && _month > y._month)return true;else if (_year == y._year && _month == y._month && _day > y._day)return true;return false;}bool operator<=(const Date& y){return ~(*this > y);}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
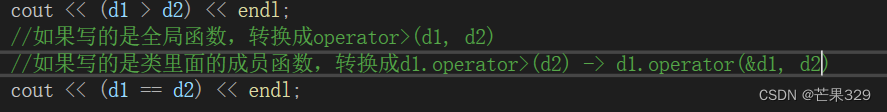
也可以d1.operator>(d2)這樣顯示的調用
這個類還可以些哪些運算符重載,這個取決于哪些運算符對于這個類是有意義的
eg:日期-日期、日期+=天數、日期+天數
+=
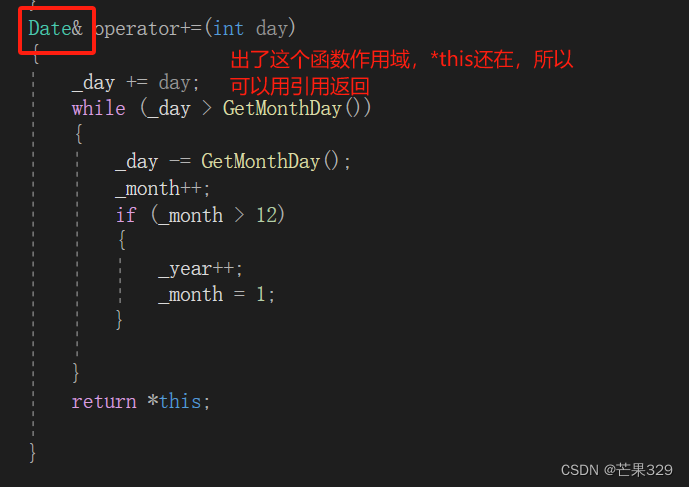
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && day >= 1);int arr[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};if (month == 2 && (((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || year % 400 == 0))return 29;return arr[month];}Date& operator+=(int day){_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay()){_day -= GetMonthDay();_month++;if (_month > 12){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}
細節
根據內置類型的定義,+=是有返回值的,因此自定義類型也應該有返回值
+
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && day >= 1);int arr[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};if (month == 2 && (((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || year % 400 == 0))return 29;return arr[month];}
Date operator+(int day){Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month > 12){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}
賦值重載
operator= 我們不寫,編譯器回生成默認的operator=。跟拷貝構造的行為類似,內置類型值拷貝,自定義類型調用他的賦值
Date、MyQueue可以不用寫,默認生成的operator=就可以用
賦值重載:(重載運算符)兩個已經存在的對象拷貝
拷貝構造:一個已經存在的對象去拷貝初始化另一個對象
缺省參數不能同時出現在聲明與定義里面,只能在聲明中定義
Date& operator=(const Date& y);Date& Date::operator=(const Date& y)
{if (this != &y){_year = y._year;_month = y._month;_day = y._day;}return *this;
}
Date類的完善
構造函數的完善
Date::Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (_year < 1 || _month > 13 || _month < 1 || day < 1 || day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){print();cout << "日期非法" << endl;}
}
用+復用+=
復用1
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{*this = *this + day;return *this;}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month > 12){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;}

復用2
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month > 12){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;}

復用2要比復用1效率更高




)














