計算機中央處理器cpu
中央處理器(CPU) (Central Processing Unit (CPU))
The CPU is the brain of the computer system. It works as an administrator of a system.
CPU是計算機系統的大腦。 它以系統管理員的身份工作。
All the operations within the system are supervised and controlled by the CPU. It interprets and coordinates the instructions.
系統內的所有操作均由CPU監控。 它解釋和協調指令。
The data and the instructions are temporarily stored in its memory unit. After performing operations, the result of operations can be stored in this memory unit.
數據和指令臨時存儲在其存儲單元中。 執行操作后,操作結果可以存儲在此存儲單元中。
The results of the operations are sent towards the output unit for the user.
操作結果將發送給用戶的輸出單元。
Thus, the CPU controls all internal and external devices, perform arithmetic and logical operations, controls memory usage and control the sequence of operations.
因此,CPU控制所有內部和外部設備,執行算術和邏輯運算,控制內存使用并控制運算順序。
For performing all these operations, the CPU has three subunits:
為了執行所有這些操作,CPU具有三個子單元:
- Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU)
- Control unit
- Memory unit (CPU registers)
算術和邏輯單元(ALU) (Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU))
Arithmetic and logic unit is the subunit of the central processing unit as it is given above.
如上所述,算術和邏輯單元是中央處理單元的子單元。
It performs arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and logic operations like OR, AND, invert, exclusive – OR on binary words. The data stored in the memory unit is transferred to ALU. The ALU performs the operations that are the data is processed and the result is stored in an internal memory unit of the CPU. The result of a final operation is transferred from the memory unit to an output unit.
它對二進制字執行算術運算(例如加法,減法)和邏輯運算(例如OR,AND,取反,異或)。 存儲在存儲單元中的數據將傳輸到ALU。 ALU執行以下操作:處理數據并將結果存儲在CPU的內部存儲單元中。 最終操作的結果從存儲單元傳輸到輸出單元。
Arithmetic and logic operations performed by ALU sets flags to represent certain conditions such as equal to condition, zero condition, greater than the condition and so on. These conditions are checked by program instructions to change the sequence of program executions.
ALU執行的算術和邏輯運算設置標志來表示某些條件,例如等于條件,零條件,大于條件等。 這些條件由程序指令檢查以更改程序執行的順序。
控制單元 (Control Unit)
The control unit controls all the operations which internally take place within the CPU and also the operations of CPU related to input / output devices. The control unit directs the overall functioning of a computer system.
控制單元控制在CPU內部進行的所有操作,以及與輸入/輸出設備有關的CPU的操作。 控制單元指導計算機系統的整體功能。
This unit also checks the correctness of sequence of operations. It fetches instructions in a program from the primary storage unit, interprets them and generates control signals to ensure correct execution of the program. The control signals generated by the control unit direct the overall functioning of the other units of the computer.
本機還檢查操作順序的正確性。 它從主存儲單元中獲取程序中的指令,對其進行解釋并生成控制信號以確保程序正確執行。 由控制單元產生的控制信號指導計算機其他單元的整體功能。
CPU寄存器 (CPU Registers)
A register is a group of flip-flops which can be used to store a word. It is a high-speed temporary storage space for holding data, addresses, and instructions during processing the instructions. Registers are not referenced by their addresses, however, they are directly accessed.
寄存器是一組觸發器,可用于存儲一個字。 它是一個高速臨時存儲空間,用于在處理指令期間保存數據,地址和指令。 寄存器不由其地址引用,但是可以直接訪問它們。
To perform execution of the instructions, the processor contains a number of registers used for temporary storage of data and some special function registers.
為了執行指令,處理器包含許多用于臨時存儲數據的寄存器和一些特殊功能寄存器。
The special function registers include Program Counter (PC), Instruction Register (IR), Memory Address Register (MAR), and Memory Data Register (MDR).
特殊功能寄存器包括程序計數器(PC),指令寄存器(IR),存儲器地址寄存器(MAR)和存儲器數據寄存器(MDR)。
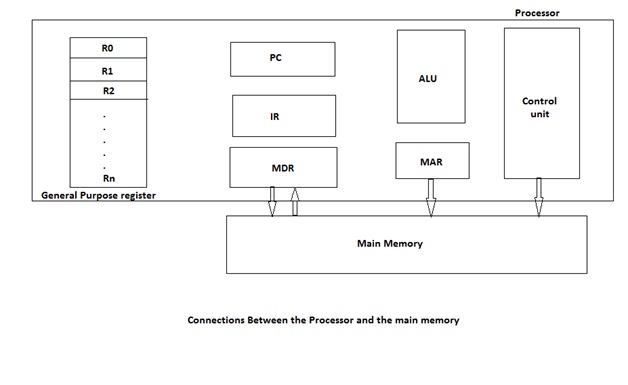
程序計數器(PC) (Program Counter (PC))
A program is a series of instruction stored in the memory. These instructions tell the CPU exactly how to get the desired result.
程序是存儲在存儲器中的一系列指令。 這些指令準確地告訴CPU如何獲得所需的結果。
It is important that these instructions must be executed in a proper order to get the correct result.
必須按照正確的順序執行這些指令,以獲得正確的結果,這一點很重要。
The sequence of instructions executions is monitored by the program counter.
指令執行的順序由程序計數器監視。
It keeps track of which instruction is being executed and what the next instruction will be.
它跟蹤正在執行的指令以及下一條指令。
指令寄存器(IR) (Instruction Register (IR))
It is used to hold the instruction that is currently being executed.
它用于保存當前正在執行的指令。
The contents of IR are available to the control unit, which generate the timing signals that control the various processing elements involved in executing the instruction.
IR的內容可供控制單元使用,控制單元生成控制執行指令所涉及的各種處理元件的定時信號。
內存地址寄存器(MAR)和內存數據寄存器(MDR) (Memory Address Register (MAR) and Memory Data Register (MDR))
These registers are used to handle the data transfer between the main memory and the processor.
這些寄存器用于處理主存儲器和處理器之間的數據傳輸。
The MAR holds the address of the main memory to or from which the data is to be transferred.
MAR保留要向其傳輸數據的主存儲器的地址。
The MDR sometimes also called MBR (Memory Buffer Register) contains the data to be written into or read from the addressed word of the main memory.
MDR有時也稱為MBR(內存緩沖寄存器),包含要寫入主存儲器的尋址字中或從中讀取的數據。
References:
參考文獻:
Basic Operational Concepts
基本操作概念
Instruction cycle
指令周期
Basic Operational Concepts
基本操作概念
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/cso/central-processing-unit.aspx
計算機中央處理器cpu
(專,2020春)(20200831130023).pdf)





vs exit(1)與示例)


)
方法)


方法)





