
🌈 個人主頁:Zfox_
🔥 系列專欄:C++框架/庫

目錄
- 🔥 介紹
- 🔥 ES 安裝
- 🦋 安裝 kibana
- 🦋 ES 客戶端的安裝
- 🔥 ES 核心概念
- 🦋 索引(Index)
- 🦋 類型(Type)
- 🦋 字段(Field)
- 🦋 映射(mapping)
- 🦋 文檔 (document)
- 🔥 Kibana 訪問 es 進行測試
- 通過網頁訪問 kibana
- 🔥 ES 客戶端接口介紹
- 🔥 入門案例
- 🔥 ES 客戶端 API 二次封裝思想
- 🔥 共勉
🔥 介紹
Elasticsearch, 簡稱 ES,它是個開源分布式搜索引擎,它的特點有:分布式,零配置,自動發現,索引自動分片,索引副本機制, restful 風格接口,多數據源,自動搜索負載等。它可以近乎實時的存儲、檢索數據;本身擴展性很好,可以擴展到上百臺服務器,處理 PB 級別的數據。 es 也使用 Java 開發并使用 Lucene 作為其核心來實現所有索引和搜索的功能,但是它的目的是通過簡單的 RESTful API 來隱藏 Lucene 的復雜性,從而讓全文搜索變得簡單。
Elasticsearch 是面向文檔 (document oriented) 的,這意味著它可以存儲整個對象或文檔(document)。然而它不僅僅是存儲,還會索引 (index) 每個文檔的內容使之可以被搜索。在 Elasticsearch 中,你可以對文檔(而非成行成列的數據)進行索引、搜索、排序、過濾。
🔥 ES 安裝
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
# 上邊的添加方式會導致一個 apt-key 的警告,如果不想報警告使用下邊這個
curl -s https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupgring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/icsearch.gpg --import# 添加鏡像源倉庫
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch.list
# 更新軟件包列表
sudo apt update
# 安裝 es
sudo apt-get install elasticsearch=7.17.21
# 啟動 es
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
# 安裝 ik 分詞器插件
sudo /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/7.17.21
# 重啟
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch
# 開機自啟動
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
# 查看 es 服務的狀態
sudo systemctl status elasticsearch.service
# 驗證 es 是否安裝成功
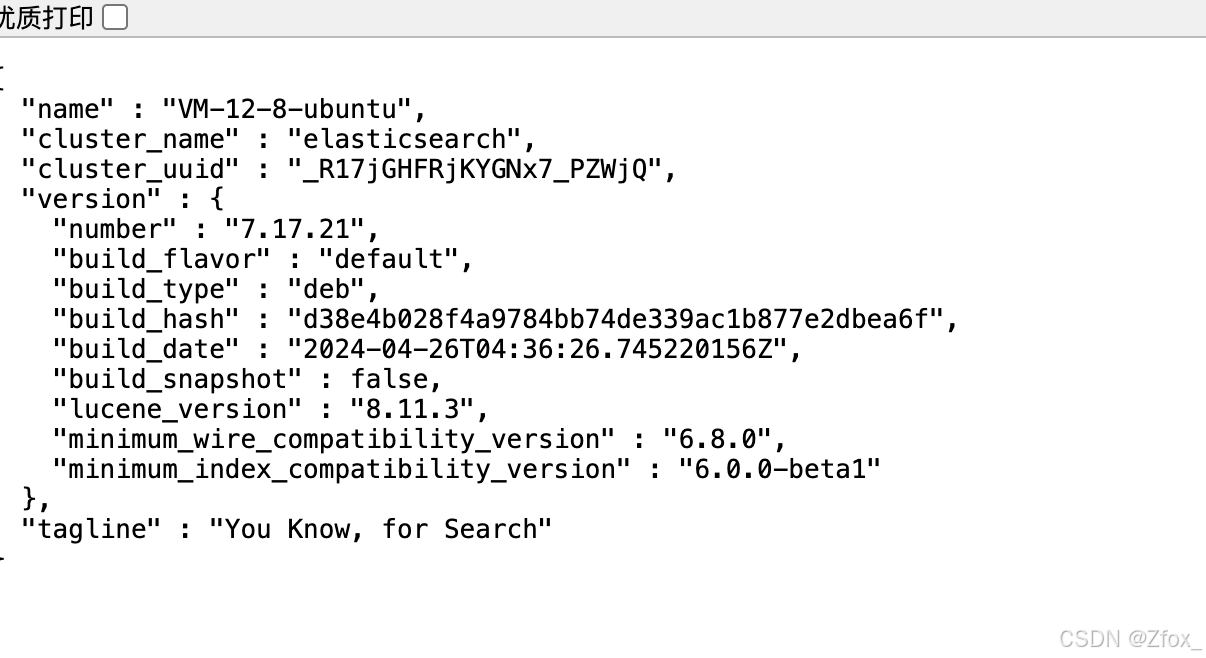
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/"
設置外網訪問:如果新配置完成的話,默認只能在本機進行訪問。
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml# 新增配置
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
瀏覽器訪問 http://xxx.xxx.xx.xx:9200/
🦋 安裝 kibana
使用 apt 命令安裝 Kibana。
sudo apt install kibana配置 Kibana(可選):
根據需要配置 Kibana。配置文件通常位于 /etc/kibana/kibana.yml。可能需要設置如服務器地址、端口、 Elasticsearch URL 等。
sudo vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
例如,你可能需要設置 Elasticsearch 服務的 URL: 大概 32 行左右
elasticsearch.host: "http://localhost:9200"啟動 Kibana 服務:
安裝完成后,啟動 Kibana 服務
sudo systemctl start kibana設置開機自啟(可選):
如果你希望 Kibana 在系統啟動時自動啟動,可以使用以下命令來啟用自啟動
sudo systemctl enable kibana驗證安裝:
使用以下命令檢查 Kibana 服務的狀態
sudo systemctl status kibana訪問 Kibana:
在瀏覽器中訪問 Kibana,通常是 http://<your-ip>:5601
🦋 ES 客戶端的安裝
需要先安裝 MicroHTTPD 庫
不然 make 的時候編譯出錯:這是子模塊 googletest 沒有編譯安裝
sudo apt-get install libmicrohttpd-dev
# 克隆代碼
git clone https://github.com/seznam/elasticlient
# 切換目錄
cd elasticlient
# 更新子模塊
git submodule update --init --recursive
# 編譯代碼
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr ..
make
# 安裝
make install
🔥 ES 核心概念
🦋 索引(Index)
一個索引就是一個擁有幾分相似特征的文檔的集合。比如說,你可以有一個客戶數據的索引,一個產品目錄的索引,還有一個訂單數據的索引。一個索引由一個名字來標識(必須全部是小寫字母的),并且當我們要對應于這個索引中的文檔進行索引、搜索、更新和刪除的時候,都要使用到這個名字。在一個集群中,可以定義任意多的索引。
🦋 類型(Type)
在一個索引中,你可以定義一種或多種類型。一個類型是你的索引的一個邏輯上的分類/分區,其語義完全由你來定。通常,會為具有一組共同字段的文檔定義一個類型。比如說,我們假設你運營一個博客平臺并且將你所有的數據存儲到一個索引中。在這個索引中,你可以為用戶數據定義一個類型,為博客數據定義另一個類型,為評論數據定義另一個類型…
🦋 字段(Field)
字段相當于是數據表的字段,對文檔數據根據不同屬性進行的分類標識。

🦋 映射(mapping)
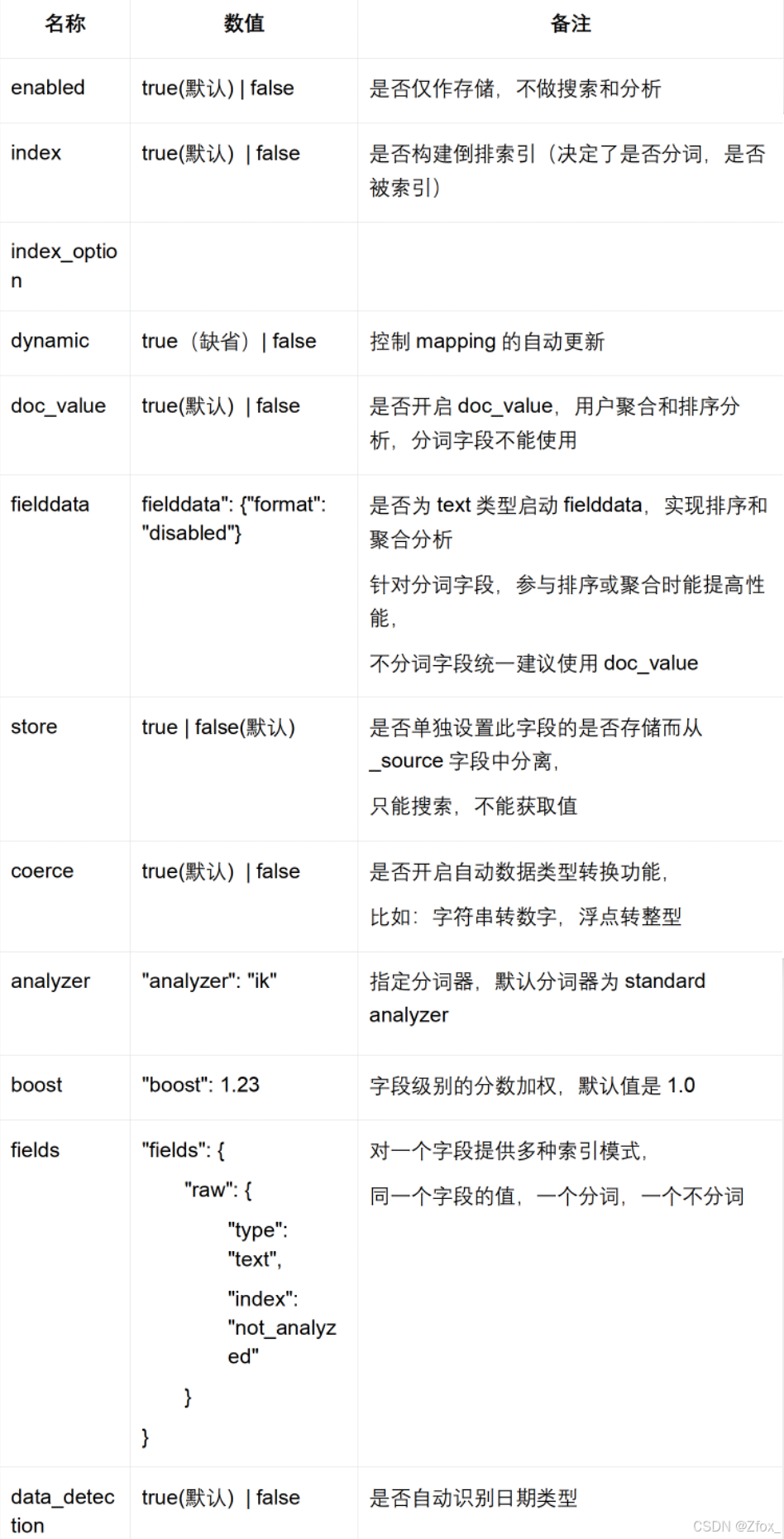
映射是在處理數據的方式和規則方面做一些限制,如某個字段的數據類型、默認值、分析器、是否被索引等等,這些都是映射里面可以設置的,其它就是處理 es 里面數據的一些使用規則設置也叫做映射,按著最優規則處理數據對性能提高很大,因此才需要建立映射,并且需要思考如何建立映射才能對性能更好。
🦋 文檔 (document)
一個文檔是一個可被索引的基礎信息單元。比如,你可以擁有某一個客戶的文檔,某一個產品的一個文檔或者某個訂單的一個文檔。文檔以 JSON(Javascript ObjectNotation)格式來表示,而 JSON 是一個到處存在的互聯網數據交互格式。在一個 index/type 里面,你可以存儲任意多的文檔。一個文檔必須被索引或者賦予一個索引的 type。
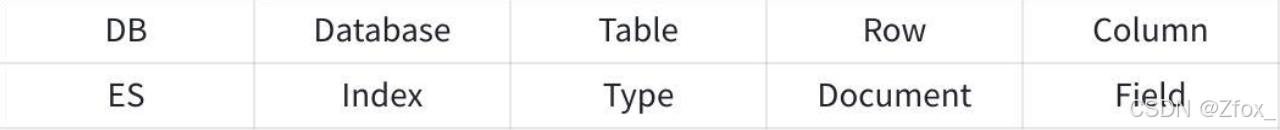
Elasticsearch 與傳統關系型數據庫相比如下:
🔥 Kibana 訪問 es 進行測試
通過網頁訪問 kibana
創建索引庫
POST /user/_doc
{"settings" : {"analysis" : {"analyzer" : {"ik" : {"tokenizer" : "ik_max_word" // 最大粒度分詞 - 你好 你 好 你好}}}},"mappings" : {"dynamic" : true, // 自動更新"properties" : {"nickname" : {"type" : "text", // 字段是文本類型"analyzer" : "ik_max_word" // 使用中文分詞器},"user_id" : {"type" : "keyword", // 是一個文本類型,但是是關鍵字,不進行分詞"analyzer" : "standard" // 使用默認標準分詞器},"phone" : {"type" : "keyword","analyzer" : "standard"},"description" : {"type" : "text","enabled" : false // 僅做存儲,不做搜索},"avatar_id" : {"type" : "keyword","enabled" : false}}}
}
新增數據:
POST /user/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"user_id" : "USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66","nickname" : "昵稱 1","phone" : "手機號 1","description" : "簽名 1","avatar_id" : "頭像 1"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"user_id" : "USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d","nickname" : "昵稱 2","phone" : "手機號 2","description" : "簽名 2","avatar_id" : "頭像 2"}
{"index":{"_id":"3"}}
{"user_id" : "USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869","nickname" : "昵稱 3","phone" : "手機號 3","description" : "簽名 3","avatar_id" : "頭像 3"}
{"index":{"_id":"4"}}
{"user_id" : "USER186ade83-4460d4a6-8c08068f-83127b5d","nickname" : "昵稱 4","phone" : "手機號 4","description" : "簽名 4","avatar_id" : "頭像 4"}
{"index":{"_id":"5"}}
{"user_id" : "USER6f19d074-c33891cf-23bf5a83-57189a19","nickname" : "昵稱 5","phone" : "手機號 5","description" : "簽名 5","avatar_id" : "頭像 5"}
{"index":{"_id":"6"}}
{"user_id" : "USER97605c64-9833ebb7-d0455353-35a59195","nickname" : "昵稱 6","phone" : "手機號 6","description" : "簽名 6","avatar_id" : "頭像 6"}
查看并搜索數據
GET /user/_doc/_search?pretty
{"query" : {"bool" : {"must_not" : [ // 必須不遵循的條件{"terms" : {"user_id.keyword" : ["USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66","USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d","USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869"]}}],"should" : [ // 應該遵循的條件 有任意一個成功就ok{"match" : {"user_id" : "昵稱"}},{"match" : {"nickname" : "昵稱"}},{"match" : {"phone" : "昵稱"}}]}}
}
terms: 完全匹配
match:分詞匹配
過濾條件,是我的好友就過濾掉,在搜索好友進行添加的時候,就可以過濾掉
"user_id.keyword" keyword 不進行分詞
"USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66",
"USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d",
"USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869"
刪除索引:
DELETE /user
POST /user/_doc/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}}
}
🔥 ES 客戶端接口介紹
/*** Perform search on nodes until it is successful. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param body Elasticsearch request body.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response search(const std::string &indexName, 索引名稱 userconst std::string &docType, 索引類型 docconst std::string &body, 請求正文,json字符串const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Get document with specified id from cluster. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param id Id of document which should be retrieved.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response get(const std::string &indexName,const std::string &docType,const std::string &id = std::string(),const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Index new document to cluster. Throws exception if all nodes has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param body Elasticsearch request body.* \param id Id of document which should be indexed. If empty, id will be generated* automatically by Elasticsearch cluster.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/ 創建索引 新增數據cpr::Response index(const std::string &indexName, 索引名稱const std::string &docType, 類型const std::string &id, 自己制定或者es生成數據idconst std::string &body, 請求正文const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Delete document with specified id from cluster. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param id Id of document which should be deleted.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response remove(const std::string &indexName,const std::string &docType,const std::string &id,const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Initialize the Client.* \param hostUrlList Vector of URLs of Elasticsearch nodes in one Elasticsearch cluster.* Each URL in vector should ends by "/".* \param timeout Elastic node connection timeout.*/explicit Client(const std::vector<std::string> &hostUrlList,std::int32_t timeout = 6000);
🔥 入門案例
針對上邊通過 kibana 添加的數據通過客戶端 api 進行一次數據獲取。
#include <elasticlient/client.h>
#include <cpr/cpr.h>
#include <iostream>int main()
{// 1. 構造 ES 客戶端elasticlient::Client client({"http://127.0.0.1:9200/"});// 2. 發起搜索請求try {cpr::Response resp = client.search("user", "_doc", "{\"query\": { \"match_all\": {} }}");// 3. 打印響應狀態碼和響應正文std::cout << resp.status_code << std::endl;std::cout << resp.text << std::endl;} catch (std::exception &e) {std::cout << "請求失敗: " << e.what() << std::endl;return -1;}return 0;
}
🔥 ES 客戶端 API 二次封裝思想
封裝客戶端 api 主要是因為,客戶端只提供了基礎的數據存儲獲取調用功能,無法根據我們的思想完成索引的構建,以及查詢正文的構建,需要使用者自己組織好 json 進行序列化后才能作為正文進行接口的調用。
而封裝的目的就是簡化用戶的操作,將索引的 json 正文構造,以及查詢搜索的正文構造操作給封裝起來,使用者調用接口添加字段就行,不用關心具體的 json 數據格式。
封裝內容:
- 索引構造過程的封裝
- 索引正文構造過程,大部分正文都是固定的,唯一不同的地方是各個字段不同的名稱以及是否只存儲不索引這些選項,因此重點關注以下幾個點即可:
- 字段類型: type : text / keyword (目前只用到這兩個類型)
- 是否索引: enable : true/false
- 索引的話分詞器類型: analyzer : ik_max_word / standard
- 新增文檔構造過程的封裝
- 新增文檔其實在常規下都是單條新增,并非批量新增,因此直接添加字段和值就行
- 文檔搜索構造過程的封裝
- 搜索正文構造過程,我們默認使用條件搜索,我們主要關注的兩個點:
- 應該遵循的條件是什么: should 中有什么
- 條件的匹配方式是什么: match 還是 term/terms,還是 wildcard
- 過濾的條件字段是什么: must_not 中有什么
- 過濾的條件字段匹配方式是什么: match 還是 wildcard,還是 term/terms
整個封裝的過程其實就是對 Json::Value 對象的一個組織的過程,并無太大的難點。
elasticsearch.hpp
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <elasticlient/client.h>
#include <json/json.h>
#include <cpr/cpr.h>
#include "logger.hpp"// 實現字符串的序列化
bool Serialize(const Json::Value &val, std::string &body)
{std::stringstream ss;// 先實例化一個工廠類對象Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;// 再使用工廠類對象來生產派生類std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> sw(swb.newStreamWriter());int ret = sw->write(val, &ss);if(ret != 0){std::cout << "Json Serialize failed!" << std::endl;return false;}body = ss.str();return true;
}// 實現json字符串的反序列化
bool UnSerialize(const std::string &body, Json::Value &val)
{// 實例化工廠類對象Json::CharReaderBuilder crb;std::unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> cr(crb.newCharReader());std::string errs;bool ret = cr->parse(body.c_str(), body.c_str() + body.size(), &val, &errs);if(ret == false){std::cout << "Json UnSerialize failed! " << errs << std::endl;return false;}return true;
}// 構造索引
class ESIndex {
public:ESIndex(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){Json::Value analysis;Json::Value analyzer;Json::Value ik;Json::Value tokenizer;tokenizer["tokenizer"] = "ik_max_word";ik["ik"] = tokenizer;analyzer["analyzer"] = ik;analysis["analysis"] = analyzer;_index["settings"] = analysis;}ESIndex& append(const std::string &key, const std::string &type = "text", const std::string &analyzer = "ik_max_word", bool enabled = true) {Json::Value fields;fields["type"] = type;fields["analyzer"] = analyzer;if (enabled == false) fields["enabled"] = enabled;_propertis[key] = fields;return *this;}bool create(const std::string &index_id = "default_index_id") {Json::Value mappings;mappings["dynamic"] = true;mappings["properties"] = _propertis;_index["mappings"] = mappings;std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(_index, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失敗!");return false;}// 發起搜索請求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->index(_name, _type, index_id, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("創建ES索引 {} 失敗, 響應狀態碼異常: {}", _name, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("創建ES索引 {} 失敗: {}", _name, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _propertis;Json::Value _index;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 添加數據
class ESInsert {
public:ESInsert(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}ESInsert& append(const std::string &key, const std::string &val) {_item[key] = val;return *this;}bool insert(const std::string &id = "") {std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(_item, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失敗!");return false;}// 發起搜索請求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->index(_name, _type, id, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("新增數據 {} 失敗, 響應狀態碼異常: {}", body, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("新增數據 {} 失敗: {}", body, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _item;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 刪除數據
class ESRemove {public:ESRemove(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}bool remove(const std::string &id) {// 發起請求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->remove(_name, _type, id);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("刪除數據 {} 失敗, 響應狀態碼異常: {}", id, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("刪除數據 {} 失敗: {}", id, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 搜索數據
class ESSearch {
public:ESSearch(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}// 必須不遵循的條件ESSearch& append_must_not_terms(const std::string &key, const std::vector<std::string> &vals) {Json::Value fields;for (const auto &val : vals) {fields[key].append(val);}Json::Value terms;terms["terms"] = fields;_must_not.append(terms);return *this;}ESSearch& append_should_match(const std::string &key, const std::string &val) {Json::Value field;field[key] = val;Json::Value match;match["match"] = field;_should.append(match);return *this;}Json::Value search() {Json::Value cond;if (!_must_not.empty()) cond["must_not"] = _must_not; if (!_should.empty()) cond["should"] = _should; Json::Value query;query["bool"] = cond;Json::Value root;root["query"] = query;std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(root, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失敗!");return Json::Value();}cpr::Response resp;// 發起搜索請求try {resp = _client->search(_name, _type, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("檢索數據 {} 失敗, 響應狀態碼異常: {}", body, resp.status_code);return Json::Value();}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("檢索數據 {} 失敗: {}", body, e.what());return Json::Value();}// 反序列化響應正文Json::Value json_res;ret = UnSerialize(resp.text, json_res);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("檢索數據 {} 結果反序列化失敗", resp.text);return Json::Value();}return json_res["hits"]["hits"];}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _must_not; // 必須不遵循的條件Json::Value _should; // 應該遵循的條件std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};
🔥 共勉
😋 以上就是我對 【C++組件】Elasticsearch 安裝及使用 的理解, 覺得這篇博客對你有幫助的,可以點贊收藏關注支持一波~ 😉


)
)







)

)




)

