Neural Networks
在這個練習中,將實現神經網絡BP算法,練習的內容是手寫數字識別。
Visualizing the data
這次數據還是5000個樣本,每個樣本是一張20*20的灰度圖片
fig, ax_array = plt.subplots(nrows=10, ncols=10, figsize=(6, 4))for row in range(10):for column in range(10):ax_array[row, column].matshow(sample_images[10 * row + column].reshape((20, 20)).T, cmap='gray')ax_array[row, column].axis('off')plt.show()returndata = loadmat("ex4data1.mat")
X = data['X']
y = data['y']m = X.shape[0]
rand_sample_num = np.random.permutation(m)
sample_images = X[rand_sample_num[0:100], :]
display_data(sample_images)
Model representation
這是一個簡單的神經網絡,輸入層、隱藏層、輸出,樣本圖片是20*20,所以輸入層是400個單元,(再加上一個額外偏差單元),第二層隱藏層是25個單元, 輸出層是10個單元。從上面的數據顯示中有兩個變量X 和y。
ex4weights.mat 中提供了訓練好的網絡參數theta1, theta2,
theta1 has size 25 x 401
theta2 has size 10 x 26
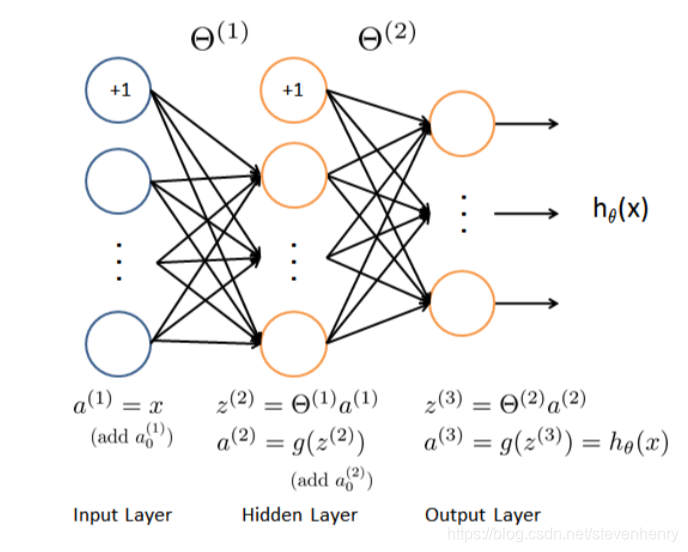
Feedforward and cost function
為了最后的輸出,我們將標簽值也就是數字從0到9, 轉化為one-hot 碼
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
def to_one_hot(y):encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False) # return a array instead of matrixy_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y.reshape(-1,1))return y_onehot
加載數據
X, label_y = load_mat('ex4data1.mat')
X = np.insert(X, 0, 1, axis=1)
y = to_one_hot(label_y)
load weight
def load_weight(path):data = loadmat(path)return data['Theta1'], data['Theta2']t1, t2 = load_weight('ex4weights.mat')
theta 轉化
因為opt.minimize傳參問題,我們這里對theta進行平坦化
# 展開
def unrool(var1, var2):return np.r_[var1.flatten(), var2.flatten()]
# 分開矩陣化
def rool(array):return array[:25*401].reshape(25, 401), array[25*401:].reshape(10, 26)
Feedforward Regularized cost function
這里主要是前饋傳播 和 代價函數的一些邏輯,正則化為了預防高方差問題。
def sigmoid(z):return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))#前饋傳播
def feed_forward(theta, X):theta1, theta2 = rool(theta)a1 = Xz2 = a1.dot(theta1.T)a2 = np.insert(sigmoid(z2), 0, 1, axis=1)z3 = a2.dot(theta2.T)a3 = sigmoid(z3)return a1, z2, a2, z3, a3# a1, z2, a2, z3, h = feed_forward(t1, t2, X)def cost(theta, X, y):a1, z2, a2, z3, h = feed_forward(theta, X)J = -y * np.log(h) - (1-y) * np.log(1 - h)return J# Implement Regularization
def regularized_cost(theta, X, y, l=1):theta1, theta2 = rool(theta)temp_theta1 = theta1[:, 1:]temp_theta2 = theta2[:, 1:]reg = temp_theta1.flatten().T.dot(temp_theta1.flatten()) + temp_theta2.flatten().T.dot(temp_theta2.flatten())regularized_theta = l / (2 * len(X)) * reg return regularized_theta + cost(theta, X, y)
Backprogation
反向傳播算法,是機器學習比較難推理的算法了, 也是最重要的算法,為了得到最優的theta值, 通過進行反向傳播,來不斷跟新theta值, 當然還有一些超參數,如lambda、a 、訓練迭代次數,如果進行adam、Rmsprop等優化學習效率算法,還有有一些其他的超參數。
# random initalization# 梯度
def gradient(theta, X, y):theta1, theta2 = rool(theta)a1, z2, a2, z3, h = feed_forward(theta, X)d3 = h - yd2 = d3.dot(theta2[:, 1:]) * sigmoid_gradient(z2)D2 = d3.T.dot(a2)D1 = d2.T.dot(a1)D = (1 / len(X)) * unrool(D1, D2)return D
Sigmoid gradient
也就是對sigmoid 函數求導
def sigmoid_gradient(z):return sigmoid(z) * (1 - sigmoid(z))
Random initialization
初始化參數,我們一般使用隨機初始化np.random.randn(-2,2),生成高斯分布,再乘以一個小的數,這樣把它初始化為很小的隨機數,
這樣直觀地看就相當于把訓練放在了邏輯回歸的直線部分進行開始,初始化參數還可以盡量避免梯度消失和梯度爆炸的問題。
def random_init(size):return np.random.randn(-2, 2, size) * 0.01
Backporpagation
Regularized Neural Networks
正則化神經網絡
def regularized_gradient(theta, X, y, l=1):a1, z2, a2, z3, h = feed_forward(theta, X)D1, D2 = rool(gradient(theta, X, y))t1[:, 0] = 0t2[:, 0] = 0reg_D1 = D1 + (l / len(X)) * t1reg_D2 = D2 + (l / len(X)) * t2return unrool(reg_D1, reg_D2)
Learning parameters using fmincg
調優參數
def nn_training(X, y):init_theta = random_init(10285) # 25*401 + 10*26res = opt.minimize(fun=regularized_cost,x0=init_theta,args=(X, y, 1),method='TNC',jac=regularized_gradient,options={'maxiter': 400})return resres = nn_training(X, y)
準確率
def accuracy(theta, X, y):
_, _, _, _, h = feed_forward(res.x, X)
y_pred = np.argmax(h, axis=1) + 1
print(classification_report(y, y_pred))
accuracy(res.x, X, label_y)
Visualizing the hidden layer
隱藏層顯示跟輸入層顯示差不多
def plot_hidden(theta):t1, _ = rool(theta)t1 = t1[:, 1:]fig, ax_array = plt.subplots(5, 5, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(6, 6))for r in range(5):for c in range(5):ax_array[r, c].matshow(t1[r * 5 + c].reshape(20, 20), cmap='gray_r')plt.xticks([])plt.yticks([])plt.show()plot_hidden(res.x)
super parameter lambda update
神經網絡是非常強大的模型,可以形成高度復雜的決策邊界。如果沒有正則化,神經網絡就有可能“過度擬合”一個訓練集,從而使它在訓練集上獲得接近100%的準確性,但在以前沒有見過的新例子上則不會。你可以設置較小的正則化λ值和MaxIter參數高的迭代次數為自己看到這個結果。







)

)




)




