引言
前面幾篇文章都在介紹 Redis 原生命令行客戶端,在實際應用開發中,開發人員更希望使用針對特定編程語言的專用客戶端,通過編程的方式操作 Redis 數據庫。因此,Redis 支持多種編程語言。本文將介紹 如何使用 C++ 語言來操作 Redis。
一、認識 RESP 協議
RESP(Redis serialization protocol)是 Redis 自定義的應用層協議,所有編程語言的 Redis 庫都是基于這個協議開發的。它設計的核心目標是簡單易實現、解析高效,同時兼顧人類可讀性,使得開發者能輕松調試 Redis 通信過程。這里僅做簡單介紹,詳細內容可參考Redis 官方文檔 :Redis 的 RESP 協議
1. RESP 協議的核心特點
- 文本協議:基于 ASCII 字符編碼,協議內容可直接通過肉眼識別(區別于二進制協議),便于調試。
- 類型明確:通過特定前綴字符標識數據類型(如字符串、整數、數組等),解析時無需額外判斷。
- 高效解析:協議格式規則簡單,解析器可通過線性掃描快速處理,幾乎無性能開銷。
- 擴展性強:支持復雜數據結構(如嵌套數組),能滿足 Redis 多樣化命令和返回值的需求。
- 一問一答式:客戶端一次請求,服務器就會回答一次
2. RESP 協議的基本數據類型及格式
RESP 通過首字符區分數據類型,常見類型及格式如下:
| 類型 | 前綴字符 | 格式說明 | 示例 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 簡單字符串 | + | +字符串內容\r\n(不含換行符,用于返回簡單結果,如 “OK”) | +OK\r\n | |
| 錯誤消息 | - | -錯誤類型: 錯誤描述\r\n(用于返回錯誤信息,如命令不存在) | -ERR unknown command 'foo'\r\n | |
| 整數 | : | :整數數值\r\n(用于返回計數、狀態碼等,如 EXISTS 命令的返回值) | :1\r\n(表示存在該鍵) | |
| 批量字符串 | $ | $長度\r\n內容\r\n(用于存儲二進制安全的字符串,長度為 -1 表示空值) | $5\r\nhello\r\n(表示字符串 “hello”) | |
| 數組 | * | *元素數量\r\n元素1\r\n元素2\r\n...(可嵌套數組,用于表示命令或復雜返回值) | *3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$5\r\nmykey\r\n$7\r\nmyvalue\r\n(表示 SET mykey myvalue 命令) |
3.、Redis 命令的傳輸流程(基于 RESP)
Redis 客戶端與服務器的通信均通過 RESP 協議完成,以 SET mykey "hello" 命令為例,流程如下:
-
客戶端發送命令:
命令以數組類型傳輸,數組元素為命令名和參數(均為批量字符串):*3\r\n // 數組包含3個元素(SET、mykey、hello) $3\r\nSET\r\n // 第一個元素:命令名 "SET"(長度3) $5\r\nmykey\r\n // 第二個元素:鍵 "mykey"(長度5) $5\r\nhello\r\n // 第三個元素:值 "hello"(長度5) -
服務器返回結果:
若命令執行成功,返回簡單字符串+OK\r\n;若失敗,返回錯誤消息(如-ERR syntax error\r\n)。
4. RESP 協議的優勢與適用場景
-
優勢:
- 實現簡單:開發者可快速編寫解析器(無需處理復雜的二進制格式)。
- 調試友好:通過
telnet或nc等工具可直接發送 RESP 格式命令與 Redis 交互(如telnet localhost 6379后輸入*2\r\n$4\r\nPING\r\n$0\r\n\r\n測試連接)。 - 兼容性強:支持所有 Redis 命令及返回值類型,包括復雜結構(如
HGETALL返回的鍵值對數組)。
-
適用場景:
- 所有 Redis 客戶端與服務器的通信(如 C++ 的 redisplusplus、Python 的
redis-py、Java 的Jedis等均基于 RESP 實現)。 - 自定義 Redis 客戶端開發(需嚴格遵循 RESP 格式組裝命令和解析響應)。
- 所有 Redis 客戶端與服務器的通信(如 C++ 的 redisplusplus、Python 的
我們實際使用時,不需要按照協議自動組織,只需要使用Redis 官方提供或者大佬們開源的庫就可以,我們接下來將使用 redis-plus-plus 庫,它是 C++ 語言的 Redis庫
二、ubuntu 安裝 redis-plus-plus
1. 安裝 hiredis
hiredis 是 Redis 官方為 c 語言提供的客戶端支持,是redis-plus-plus 必備的依賴庫
通過包管理器來安裝:
sudo apt install libhiredis-dev
2.安裝 redis-plus-plus
只能通過源碼編譯的方式安裝
git clone https://github.com/sewenew/redis-plus-plus.gitcd redis-plus-plusmkdir buildcd buildcmake ..makesudo make installcd ..
依次執行完命令就安裝好了,然后創建的這些目錄我們都可以直接刪除了
三、c++ 操作 Redis
環境安裝好了,我們就可以通過編寫 C++ 代碼來操作 Redis 了
1. c++ redis的第一個程序
hello.cc
#include <sw/redis++/redis++.h>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::unordered_map;
using std::vector;int main()
{// 創建 Redis 對象,需指定 Redis服務器ip地址和端口sw::redis::Redis redis("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");// 調用 ping 方法,讓客戶端發送一個 ping 命令,服務端會返回一個 pongstd::string result = redis.ping();std::cout << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
這段代碼就是創建一個 Redis 對象,然后向 Redis 服務器發送一個 ping 命令,于是 Redis 服務器就會返回一個 pong 。
Makefile編寫
我們需要注意 makefile 編寫中需要指定庫的位置,否則無法編譯
hello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello編譯運行:
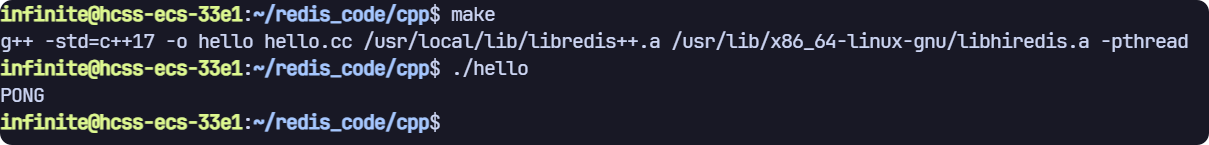
至此,使用 c++ 操作 Redis 的第一個程序就完成了!
2. 使用 c++ 執行 Redis 通用命令
代碼框架
#include <sw/redis++/redis++.h>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>#include <iostream>
#include <string>void test()
{// 每個命令寫在這里// ...
}int main()
{sw::redis::Redis redis("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");return 0;
}首先給出代碼框架,后續測試命令都會新創建一個 test 函數,然后再主函數中調用
Makefile:
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic
hello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthread
generic:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic
get 和 set
set接口

可以看到這些參數和set命令的選項有很大關聯:
- StringView 類型是 redis-plus-plus 提供的只讀字符串,不能修改,這是由于只讀字符產效率更高
- 參數 key 和 參數 val: 都是 StringView 類型
- 參數 ttl:以毫秒為單位的過期時間
- updatetype : 相當于 NX 和 XX
get接口
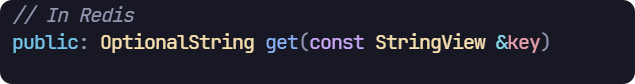
- get的返回值是 OptionalString,這個類型會對 空值 (nil)做特殊處理,c++ 14后也引入了 std::optional_string,具體用法見示例代碼。
// get 和 set
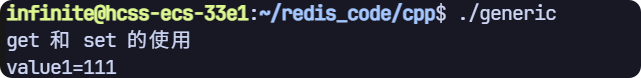
void test1(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "get 和 set 的使用" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 使用 set 設置幾個 keyredis.set("key1", "111");// 使用 get 獲取到 key 對應的 valueauto value1 = redis.get("key1");if (value1){std::cout << "value1=" << value1.value() << std::endl;}// key2 是空值,這里如果不加判斷會拋出異常auto value2 = redis.get("key2");if (value2){std::cout << "value2=" << value2.value() << std::endl;}
}
運行結果(不要忘記在主函數中調用exists):
value2是空值,由于if語句,不會輸出
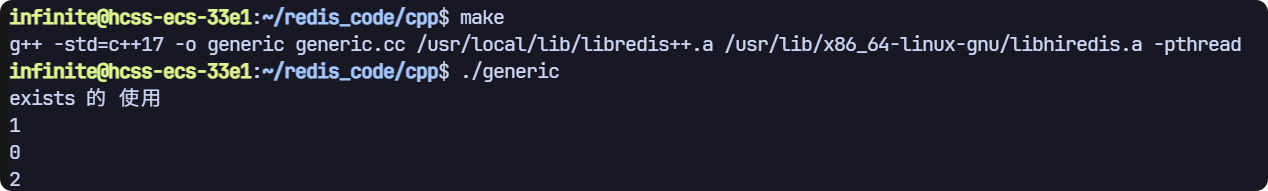
exists

返回類型是 long long,支持查詢多個key,返回存在的個數
generic.cc
// exists 命令
void test2(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "exists 的 使用" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "value1");redis.set("key2", "value2");auto ret = redis.exists("key1");std::cout << ret << std::endl;ret = redis.exists("key3");std::cout << ret << std::endl;ret = redis.exists({"key1", "key2", "key3"});std::cout << ret << std::endl;
}
運行結果(記得在主函數中調用):
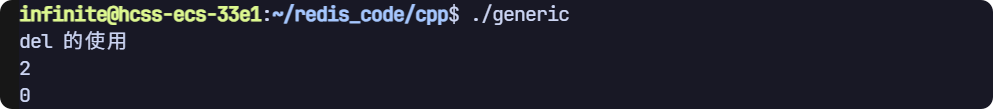
del
返回刪除成功的個數
// del 命令
void test3(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "del 的使用" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "value1");redis.set("key2", "value2");auto ret = redis.del({"key1", "key2", "key3"});std::cout << ret << std::endl;ret = redis.exists({"key1", "key2", "key3"});std::cout << ret << std::endl;
}
運行結果:
keys

- 參數 pattern : 匹配規則
- 參數 output: 插入迭代器,我們可以事先構建一個容器,傳入迭代器,這樣 keys就會把查詢到的元素插入容器中
// keys 命令
void test4(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "keys 的使用" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "value1");redis.set("key2", "value2");redis.set("key3", "value2");redis.set("key4", "value2");redis.set("key5", "value2");// redis 的keys 有兩個參數,第一個是匹配規則// 第二個是 “插入迭代器”,我們可以事先構建一個容器,傳入迭代器// 這樣 keys就會把查詢到的元素插入容器中std::vector<std::string> result;auto it = std::back_inserter(result);redis.keys("*", it);// 打印容器相關內容for (auto &str : result){std::cout << str << std::endl;}
}
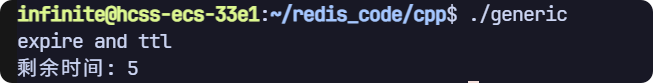
expire 和 ttl
// expire and ttl
void test5(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "expire and ttl" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "111");redis.expire("key1", std::chrono::seconds(10));std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(5));long long ret = redis.ttl("key1");std::cout << "剩余時間: " << ret << std::endl;
}
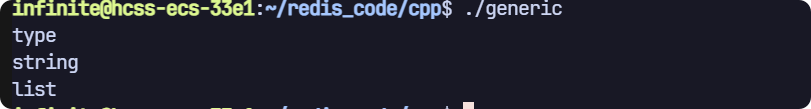
type
返回值是string類型
// type
void test6(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "type" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "111");redis.lpush("key2", "111");std::cout << redis.type("key1") << std::endl;std::cout << redis.type("key2") << std::endl;
}
執行結果:
3. String
代碼框架
#include <sw/redis++/cxx_utils.h>
#include <sw/redis++/redis++.h>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>// mget 和 mset
void test1(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{
}int main()
{sw::redis::Redis redis("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");// test1(redis);// test2(redis);test3(redis);return 0;
}
Makefile:
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic stringhello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadgeneric:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadstring:string.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic string
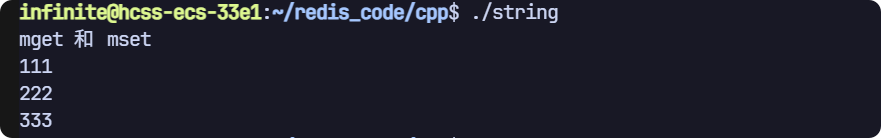
mset 和 mget
支持一次性設置多個值和獲取多個值
// mget 和 mset
void test1(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "mget 和 mset" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 第一種方法,直接使用初始化列表// redis.mset({std::make_pair("key1", "1"), std::make_pair("key2", "2"),// std::make_pair("key3", "3")});// 第二種方法,通過迭代器構造std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>> keys = {{"key1", "111"}, {"key2", "222"}, {"key3", "333"}};redis.mset(keys.begin(), keys.end());std::vector<sw::redis::OptionalString> results;auto it = std::back_inserter(results);redis.mget({"key1", "key2", "key3"}, it);for (auto& str : results){if (str){std::cout << str.value() << std::endl;}}
}
- mset 支持兩種方式設置:
- 一是直接通過初始化列表傳入pair
- 二是構造一個容器,傳入迭代器
- mget 返回值是 OptionalString 也是通過插入迭代器的方式進行實現
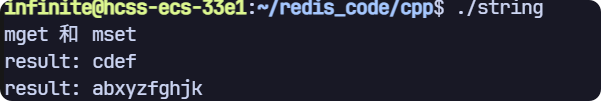
getrange 和 setrange
void test2(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "mget 和 mset" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key", "abcdefghjk");std::string result = redis.getrange("key", 2, 5);std::cout << "result: " << result << std::endl;redis.setrange("key", 2, "xyz");result = redis.getrange("key", 0, -1);std::cout << "result: " << result << std::endl;
}
運行結果:
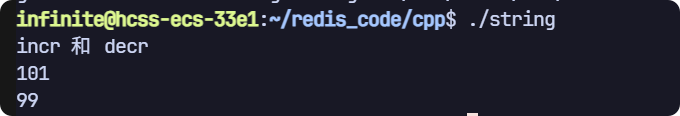
incr 和 decr
// incr decr
void test3(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "incr 和 decr" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.set("key1", "100");redis.set("key2", "100");redis.incr("key1");redis.decr("key2");std::cout << redis.get("key1").value() << std::endl;std::cout << redis.get("key2").value() << std::endl;
}
運行結果:
4. List
代碼框架
#include <sw/redis++/redis++.h>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>int main()
{sw::redis::Redis redis("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");// test1(redis);// test2(redis);test3(redis);return 0;
}
Makefile:
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic string listhello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadgeneric:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadstring:string.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadlist:list.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic string list
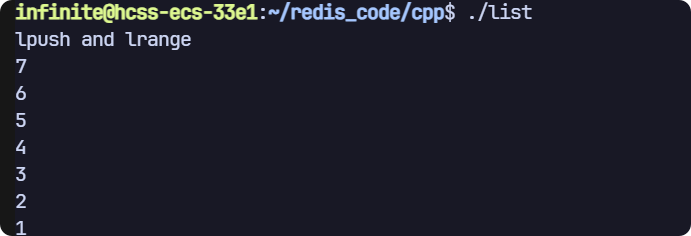
lpush 和 lrange
// lpush 和 lrange
void test1(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "lpush and lrange" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 插入單個元素redis.lpush("key", "1");// 插入一組元素,基于初始化列表redis.lpush("key", {"2", "3", "4"});// 插入一組元素,基于迭代器std::vector<std::string> values = {"5", "6", "7"};redis.lpush("key", values.begin(), values.end());// lrange 獲取結果,需要構造容器,傳入插入迭代器std::vector<std::string> results;auto it = std::back_inserter(results);redis.lrange("key", 0, -1, it);// 打印結果for (auto& result : results){std::cout << result << std::endl;}
}
lpop 和 rpop
// lpop 和 rpop
void test2(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "lpop and rpop" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.rpush("key", {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7"});auto ret = redis.lpop("key");if (ret){std::cout << "lpop: " << ret.value() << std::endl;}ret = redis.rpop("key");if (ret){std::cout << "rpop: " << ret.value() << std::endl;}
}
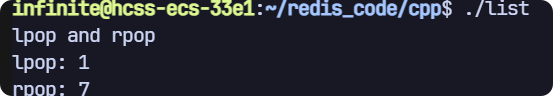
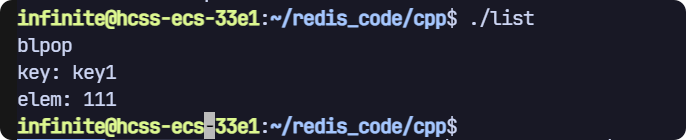
// blpop
void test3(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "blpop" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();auto ret = redis.blpop({"key1", "key2", "key3"});if (ret){std::cout << "key: " << ret.value().first << std::endl;std::cout << "elem: " << ret.value().second << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "元素無效!" << std::endl;}
}
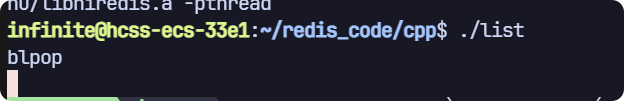
一開始會阻塞住,直到我們往 key1 key2 key3之一插入一個值
5. Set
代碼框架
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic string list sethello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadgeneric:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadstring:string.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadlist:list.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadset:set.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic string list set
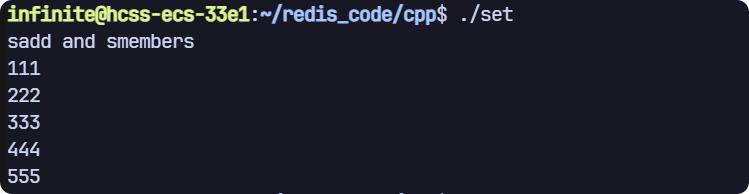
sadd 和 smembers
// sadd smembers
void test1(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "sadd and smembers" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 一次添加一個元素redis.sadd("key", "111");// 一次添加多個元素(使用初始化列表)redis.sadd("key", {"222", "333"});// 一次添加多個元素(使用迭代器)std::vector<std::string> elems = {"444", "555"};redis.sadd("key", elems.begin(), elems.end());// 通過 smembers 獲取返回結果// 1. vector// 2. set// std::vector<std::string> results;// auto it = std::back_inserter(results);std::set<std::string> results;auto it = std::inserter(results, results.end());redis.smembers("key", it);// 打印結果for (auto &res : results){std::cout << res << std::endl;}
}
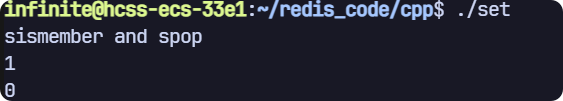
sismember 和 spop
// sismember and spop
void test2(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "sismember and spop" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.sadd("key", {"111", "222", "333"});bool result = redis.sismember("key", "111");std::cout << result << std::endl;redis.spop("key");redis.spop("key");redis.spop("key");result = redis.sismember("key", "111");std::cout << result << std::endl;
}
運行結果:
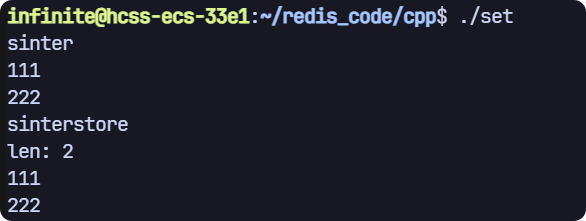
sinter 和 sinterstore
// sinter
void test3(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "sinter" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.sadd("key1", {"111", "222", "333"});redis.sadd("key2", {"111", "222", "444"});std::set<std::string> results;auto it = std::inserter(results, results.end());redis.sinter({"key1", "key2"}, it);for (auto &result : results){std::cout << result << std::endl;}
}// sinterstore
void test4(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "sinterstore" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.sadd("key1", {"111", "222", "333"});redis.sadd("key2", {"111", "222", "444"});long long len = redis.sinterstore("key3", {"key1", "key2"});std::cout << "len: " << len << std::endl;std::set<std::string> results;auto it = std::inserter(results, results.end());redis.smembers("key3", it);// 打印結果for (auto &res : results){std::cout << res << std::endl;}
}
6. Hash
代碼框架
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic string list set hashhello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadgeneric:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadstring:string.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadlist:list.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadset:set.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadhash:hash.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic string list set hashhset 和 hget
// hget and hset
void test1(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "hget and hset" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 插入一個 field-value 對redis.hset("key", "f1", "1");// 插入多個 field-value 對(初始化列表)redis.hset("key", {std::make_pair("f2", "2"), std::make_pair("f3", "3")});// 插入多個 field-value 對(迭代器)std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>> fields = {std::make_pair("f4", "4"), std::make_pair("f5", "5")};auto result = redis.hget("key", "f1");if (result){std::cout << result.value() << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "返回值無效!" << std::endl;}
}
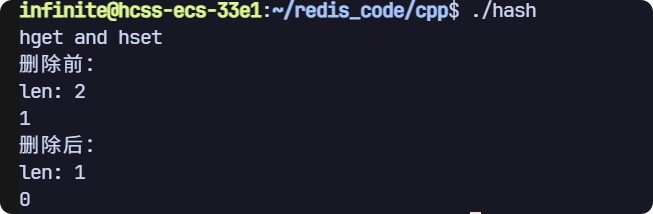
hexists,hdel 和 hlen
// hexists, hlen, hdel
void test2(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "hget and hset" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 插入多個 field-value 對(初始化列表)redis.hset("key", {std::make_pair("f2", "2"), std::make_pair("f3", "3")});std::cout << "刪除前:" << std::endl;long long len = redis.hlen("key");std::cout << "len: " << len << std::endl;bool result = redis.hexists("key", "f2");std::cout << result << std::endl;redis.hdel("key", "f2");std::cout << "刪除后:" << std::endl;len = redis.hlen("key");std::cout << "len: " << len << std::endl;result = redis.hexists("key", "f2");std::cout << result << std::endl;
}
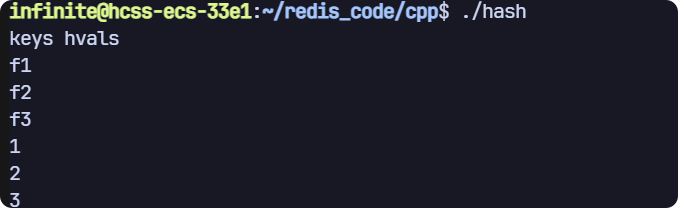
hkeys 和 hvals
// hkeys
// hkeys hvals
void test3(sw::redis::Redis &redis)
{std::cout << "keys hvals" << std::endl;// 清空一下數據庫,避免之前數據的干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 插入多個 field-value 對(初始化列表)redis.hset("key", {std::make_pair("f1", "1"), std::make_pair("f2", "2"),std::make_pair("f3", "3")});std::vector<std::string> fields;auto it = std::back_inserter(fields);redis.hkeys("key", it);for (auto &str : fields){std::cout << str << std::endl;}std::vector<std::string> vals;it = std::back_inserter(vals);redis.hvals("key", it);for (auto &str : vals){std::cout << str << std::endl;}
}
7. Zset
.PHONY:all
all: hello generic string list set hash zsethello:hello.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadgeneric:generic.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadstring:string.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadlist:list.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadset:set.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadhash:hash.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadzset:zset.ccg++ -std=c++17 -o $@ $^ /usr/local/lib/libredis++.a /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhiredis.a -pthreadPHONY:clean
clean:rm -rf hello generic string list set hash zsetzadd 和 zrange
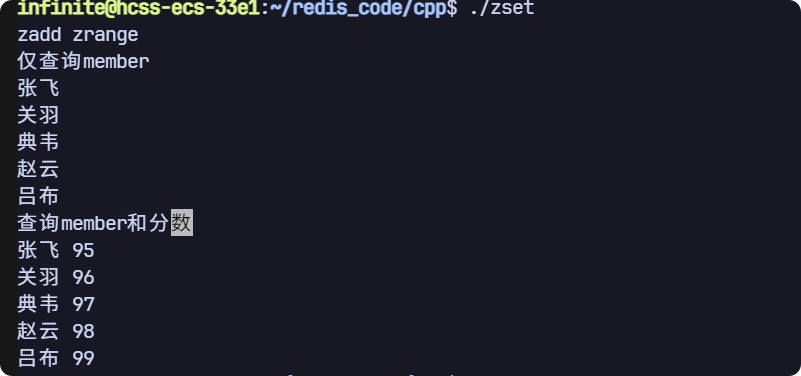
zrange 查詢是否帶分數取決于插入迭代器對應容器的類型:
- 如果插入迭代器對應一個僅包含 string 的類型的容器
- 如果插入迭代器對應容器是
pair<string, double>為元素的容器,則返回分數
// zadd zrange
void test1(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "zadd zrange" << std::endl;// 清空數據庫,防止之前的數據干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();// 三種版本redis.zadd("key", "呂布", 99);redis.zadd("key", {std::make_pair("趙云", 98), std::make_pair("張飛", 95)});std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> members = {std::make_pair("典韋", 97), std::make_pair("關羽", 96)};redis.zadd("key", members.begin(), members.end());// zrange 是否查詢分數要看容器類型// 如果容器僅 string 則 僅查詢member// 如果容器是 pair<string, double>, 則返回member 和 分數std::cout << "僅查詢member" << std::endl;std::vector<std::string> results;auto it = std::back_inserter(results);redis.zrange("key", 0, -1, it);for (auto& s : results){std::cout << s << std::endl;}std::cout << "查詢member和分數" << std::endl;std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> scores;auto it1 = std::back_inserter(scores);redis.zrange("key", 0, -1, it1);for (auto& [member, score] : scores){std::cout << member << " " << score << std::endl;}
}
zcard zrank zscore
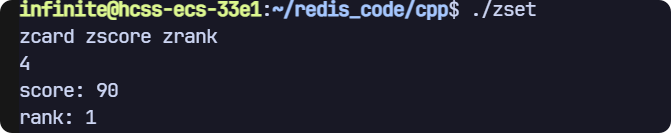
// zcard zscore zrank
void test2(sw::redis::Redis& redis)
{std::cout << "zcard zscore zrank" << std::endl;// 清空數據庫,防止之前的數據干擾,生產環境禁用!redis.flushall();redis.zadd("key", "zhangsan", 90);redis.zadd("key", "lisi", 91);redis.zadd("key", "wangwu", 92);redis.zadd("key", "zhaoliu", 93);long long result = redis.zcard("key");std::cout << result << std::endl;auto score = redis.zscore("key", "zhangsan");if (score){std::cout << "score: " << score.value() << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "score 無效" << std::endl;}auto rank = redis.zrank("key", "lisi");if (score){std::cout << "rank: " << rank.value() << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "rank 無效" << std::endl;}
}




緩存線程池)



)

![[假面騎士] 555淺談](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[假面騎士] 555淺談)
)






)
