1、網絡聊天室綜合案例
??????? 客戶端初始代碼:
@Slf4j
public class ChatClient {public static void main(String[] args) {NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();try {Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);bootstrap.group(group);bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);}});Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();channel.closeFuture().sync();} catch (Exception e) {log.error("client error", e);} finally {group.shutdownGracefully();}}
}??????? 服務器初始代碼:
@Slf4j
public class ChatServer {public static void main(String[] args) {NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();try {ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);}});Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();channel.closeFuture().sync();} catch (InterruptedException e) {log.error("server error", e);} finally {boss.shutdownGracefully();worker.shutdownGracefully();}}
}
??????? 1.1、登錄業務
??????? 業務流程:
- 客戶端流水線上新增一個入站處理器,處理登錄邏輯,有連接建立時觸發的channelActive事件(處理登錄邏輯)和channelRead事件(獲取服務器返回登錄的結果)。
- 入站處理器中異步操作,封裝LoginRequestMessage消息請求對象,通過ctx.writeAndFlush發送給服務器,并且觸發該入站處理器之前的所有出站處理器(消息編解碼器,日志打印),然后陷入阻塞等待服務器返回結果
- 服務器創建一個自定義的Handle,專門監聽客戶端的LoginRequestMessage消息請求對象。
- 服務器對登錄信息進行校驗,如果登錄信息正確則臨時保存(將用戶的channel和用戶名綁定)。
- 服務器封裝LoginResponseMessage消息響應對象,通過channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush方法將消息發送給客戶端,并且觸發該入站處理器前的所有出站處理器(消息編解碼器,日志打印)。
- 將自定義的Handle注冊到服務器的流水線上。
- 客戶端channelRead接收到服務器返回的結果,將結果記錄,并且結束阻塞(無論是否登錄成功)
- 客戶端根據結果執行不同的業務邏輯,成功則讓用戶選擇菜單,失敗則斷開連接。
??????? 客戶端,在流水線上新增一個入站處理器,專門處理登錄相關邏輯:
??????? 注意點:
- 使用channelActive,確保該入站處理器是在連接建立時觸發。
- 并非在Netty的主線程中處理登錄相關邏輯,而是新開啟一個線程異步地處理,相應地,線程間的通信使用countDownLatch (判斷是否拿到服務器端的返回結果)和 AtomicBoolean (判斷服務器端返回的結果,是否登錄成功)。
??????? 成員位置:
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
AtomicBoolean loginResult = new AtomicBoolean(false); //編寫登錄邏輯ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {/*** 連接建立時觸發,輸入用戶名和密碼,傳給后端校驗* @param ctx* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {new Thread(() -> {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("請輸入用戶名");String username = sc.nextLine();System.out.println("請輸入密碼");String password = sc.nextLine();LoginRequestMessage requestMessage = new LoginRequestMessage(username, password, null);//發送給后端 后端有一個專門的處理器去處理請求信息并且返回結果ctx.writeAndFlush(requestMessage);try {countDownLatch.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}boolean result = loginResult.get();//登錄成功if (result) {while (true) {System.out.println("==================================");System.out.println("send [username] [content]");System.out.println("gsend [group name] [content]");System.out.println("gcreate [group name] [m1,m2,m3...]");System.out.println("gmembers [group name]");System.out.println("gjoin [group name]");System.out.println("gquit [group name]");System.out.println("quit");System.out.println("==================================");String command = sc.nextLine();String[] s = command.split(" ");switch (s[0]) {case "send":ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChatRequestMessage(username, s[1], s[2]));break;case "gsend":ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupChatRequestMessage(username, s[1], s[2]));break;case "gcreate":Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(s[2].split(",")));set.add(username); // 加入自己ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupCreateRequestMessage(s[1], set));break;case "gmembers":ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupMembersRequestMessage(s[1]));break;case "gjoin":ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupJoinRequestMessage(username, s[1]));break;case "gquit":ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupQuitRequestMessage(username, s[1]));break;case "quit":ctx.channel().close();return;}}} else {//密碼錯誤就關閉連接,觸發 channel.closeFuture().sync();ctx.channel().close();}}, "login").start();}/*** 接受后端返回的登錄校驗結果* @param ctx* @param msg* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {log.debug("登錄結果:{}", msg);//記錄狀態if (msg instanceof LoginResponseMessage) {LoginResponseMessage responseMessage = (LoginResponseMessage) msg;if (responseMessage.isSuccess()) {loginResult.compareAndSet(false, true);}countDownLatch.countDown();}}});??????? 服務器端:
??????? 注意點:
- 自定義一個Handler,繼承SimpleChannelInboundHandler,只關注客戶端發送的登錄請求。
- 登錄成功后,將當前會話信息臨時進行保存。
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
@Slf4j
public class LoginRequesHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<LoginRequestMessage> {@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, LoginRequestMessage loginRequestMessage) throws Exception {String username = loginRequestMessage.getUsername();String password = loginRequestMessage.getPassword();boolean loginSuccess = UserServiceFactory.getUserService().login(username, password);LoginResponseMessage responseMessage = null;if (loginSuccess) {//保存會話信息 key channel value 當前登錄人 zhangsan lisiChannel channel = channelHandlerContext.channel();SessionFactory.getSession().bind(channel, loginRequestMessage.getUsername());responseMessage = new LoginResponseMessage(true, "登錄成功!");log.info("賬號:{}登錄成功,綁定的交換機:{}",username,channel);} else {responseMessage = new LoginResponseMessage(false, "登錄失敗!");}//將結果返回給前端channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(responseMessage);}
}
??????? 將自定義Handler注冊到流水線上:
//接受前端傳遞的用戶名和密碼并校驗,然后返回給前端登錄結果
//指定關注的消息類型為LoginRequestMessage
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoginRequesHandler());????
????????1.2、發送消息(單聊)
??????? 客戶端:
??????? 如果用戶在菜單中選擇send,則觸發單聊功能。
????????
??????? 通過ctx.writeAndFlush發送封裝好的單聊消息請求,并且觸發在這之前的所有出站消息。
ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChatRequestMessage(username, s[1], s[2]));??????? 服務器端:
??????? 注冊一個ChatRequestHandler處理器,繼承SimpleChannelInboundHandler,專門處理客戶端傳遞的單聊請求。
??????? 注意點:
- 發送消息之前需要檢查收件人是否在線,通過用戶名去查詢對應的channel是否存在(如果該用戶已登錄,必定會將自己的用戶名和channel綁定)
- 拿到收件人的channel后,利用收件人的channel向收件人的客戶端發送消息。

???????? 1.3、創建聊天群組
??????? 客戶端:
????????如果用戶在菜單中選擇gcreate,則觸發創建聊天群組功能:
??????? 封裝GroupCreateRequestMessage創建聊天群組請求對象,并且調用ctx.writeAndFlush觸發之前所有的出站處理器。
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupCreateRequestMessage(s[1], set));??????? 服務器端:
??????? 創建一個自定義的Handler,繼承SimpleChannelInboundHandler,專門監聽客戶端的GroupCreateRequestMessage。
??????? 注意點:
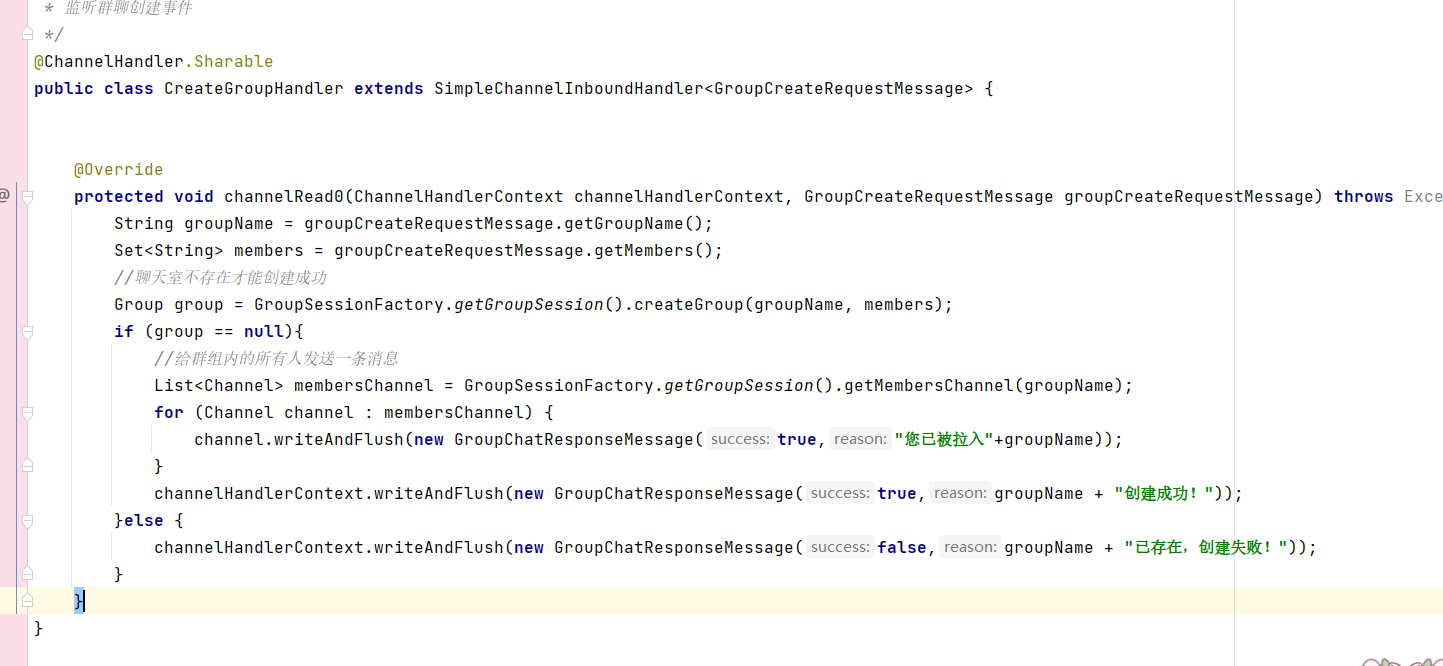
- 首先需要判斷群聊是否存在,如果存在就不能重復創建。
- 創建成功后拿到所有群組成員的channel,向各自的客戶端發送GroupChatResponseMessage消息響應對象。
????????
??????? 1.4、發送消息(群聊)
??????? 客戶端:
?????????如果用戶在菜單中選擇gsend,則觸發創建聊天群組功能:
????????封裝GroupChatRequestMessage創建群聊請求對象,并且調用ctx.writeAndFlush觸發之前所有的出站處理器。?
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupChatRequestMessage(username, s[1], s[2]));??????? 服務器端:
??????? 創建一個Handler繼承SimpleChannelInboundHandler專門監聽GroupChatRequestMessage群聊消息請求。
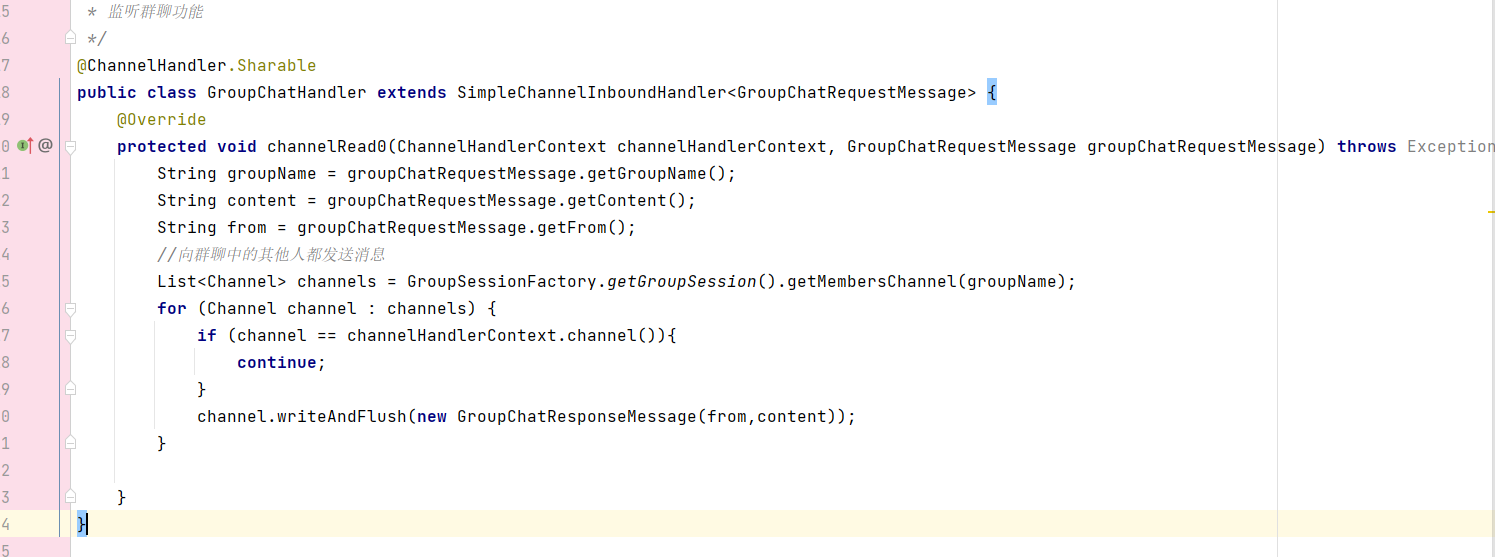
??????
???????? 1.5、心跳消息監測
??????? 有時服務器長時間沒有接收到客戶端發出的消息,可能是因為網絡設備出現故障, 網絡不穩定,應用程序發生阻塞等原因,稱之為連接假死。
??????? 這時我們應該及時地去釋放資源,那么如何去判定是否發生連接假死?如果通過常規的超時機制難以判定,因為連接本身并沒有斷開,但數據無法正常傳輸。
????????可以通過心跳監測機制去實現。客戶端和服務器之間定期互相發送心跳消息,對方在一定時間內收到心跳消息后,會發送一個確認消息,表示連接仍然正常。如果一方在指定時間內未收到對方的心跳消息,就認為連接可能已經中斷或假死。
??????? 心跳機制通常運用于分布式系統和實時通信中,eureka運用的便是心跳檢測機制。
??????? 如果需要在Netty框架中使用心跳消息監測,需要在服務器端的流水線上加入:
- IdleStateHandler:是 Netty 提供的一個處理器,用于檢測連接的空閑狀態,可以分為讀空閑,寫空閑和讀寫空閑。
- ChannelDuplexHandler:是一個入站/出站雙向的處理器,在其中加入userEventTriggered,它是一個自定義的處理器,當IdleStateHandler檢測到空閑事件后,會觸發IdleStateEvent,被userEventTriggered捕獲。
??????? 服務器端關注的是讀空閑。
//空閑檢測ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(5, 0, 0));
// //雙向監測 入站和出站ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {/*** 用戶自定義事件* @param ctx* @param evt* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;if (event.state().equals(IdleState.READER_IDLE)) {log.debug("已經5s未讀取到數據了");ctx.channel().close();}}}});??????? 同時在客戶端中加入,客戶端關注的是寫空閑,如果一定時間內沒有向客戶端發送消息,就發送默認的心跳消息確認雙方都是存活的。
//如果三秒內沒有向服務器寫出數據,就發送心跳消息ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 3, 0));
// 雙向監測 入站和出站ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {/*** 用戶自定義事件* @param ctx* @param evt* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;if (event.state().equals(IdleState.WRITER_IDLE)) {log.debug("已經3s未寫入數據了,發送默認消息");ctx.writeAndFlush(new PingMessage());}}}});??????? 如果超過一定的時間,客戶端沒有向服務器發送消息或心跳,則服務器默認客戶端已經假死,就會斷開連接釋放資源。
????????
??????? 1.6、退出
??????? 退出分為在客戶端選擇quit正常退出,以及異常退出的情況,服務器端為了處理這兩種情況,需要在流水線上加入一個自定義的QuitHandler:
??????? 創建一個自定義的QuitHandler,繼承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter接口,重寫其中的
channelInactive和exceptionCaught方法
// 當連接斷開時觸發 inactive 事件@Overridepublic void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {SessionFactory.getSession().unbind(ctx.channel());log.debug("{} 已經斷開", ctx.channel());}// 當出現異常時觸發@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {SessionFactory.getSession().unbind(ctx.channel());log.debug("{} 已經異常斷開 異常是{}", ctx.channel(), cause.getMessage());}2、擴展序列化算法
??????? 在自定義通訊協議時,消息的傳輸使用到了序列化算法,當時使用的是JDK默認的序列化算法:
??????? 序列化:
// 6. 獲取內容的字節數組
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();??????? 反序列化:
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();??????? 這里介紹一種不需要修改代碼,只需要修改配置文件達成序列化方式切換的思路:
????????application.properties
serializer.algorithm=JSON??????? 創建一個接口,定義序列化和反序列化方法的模版:
public interface Serialized {/*** 序列化** @param object 將要序列化的對象* @param <T>* @return 序列化后的byte數組*/<T> byte[] serialized(T object);/*** 反序列化** @param clazz 將要反序列化成的對象的類型* @param bytes 序列化的byte數組* @param <T>* @return 反序列化后的對象*/<T> T deSerialized(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);}??????? 定義一個枚舉類,實現接口,分別編寫使用JDK自帶的方式序列化以及使用JSON序列化的邏輯:
enum Algorithm implements Serialized {JAVA {@Overridepublic <T> byte[] serialized(T object) {try {ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);oos.writeObject(object);return bos.toByteArray();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException("序列化失敗!");}}@Overridepublic <T> T deSerialized(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {try {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));return (T) ois.readObject();} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException("反序列化失敗!");}}},JSON {@Overridepublic <T> byte[] serialized(T object) {Gson gson = new Gson();String str = gson.toJson(object);return str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);}@Overridepublic <T> T deSerialized(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {Gson gson = new Gson();return gson.fromJson(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), clazz);}}}??????? 再定義一個讀取?application.properties 文件的配置類,如果配置文件中未配置,就按照默認的JDK序列化方式實現:
/*** 序列化配置類*/
public class SerializedConfig {static Properties properties;static {//從application.properties配置文件中讀取try (InputStream is = SerializedConfig.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {properties = new Properties();properties.load(is);} catch (IOException e) {throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);}}public static int getServerPort() {//從配置文件中讀取鍵為server.port的值String value = properties.getProperty("server.port");if (value == null) {return 8080;} else {return Integer.parseInt(value);}}public static Serialized.Algorithm getSerializedAlgorithm() {//從配置文件中讀取鍵為serializer.algorithm的值String value = properties.getProperty("serializer.algorithm");if (value == null) {return Serialized.Algorithm.JAVA;} else {return Serialized.Algorithm.valueOf(value);}}}??????? 改造自定義協議類:
??????? 編碼主要有兩處需要修改,一處是設定字節的序列化方式(獲取的是序列化方式 java json 在枚舉類中的位置 0,1):
out.writeByte(SerializedConfig.getSerializedAlgorithm().ordinal());??????? 另一處是將消息序列化的邏輯:
byte[] bytes = SerializedConfig.getSerializedAlgorithm().serialized(msg);??????? 解碼也有兩處需要修改:
??????? 第一處是確定反序列化的算法:
Serialized.Algorithm[] values = Serialized.Algorithm.values();
//確定反序列化算法
Serialized.Algorithm algorithm = values[serializerType];??????? 第二處是確定消息類型,并且解碼:
//確定消息類型
Class<? extends Message> messageClass = Message.getMessageClass(messageType);
Object message = algorithm.deSerialized(messageClass, bytes)



)

)
:嶺回歸、Lasso回歸、彈性網絡回歸構建預測模型)

)







)

