Spooky Author Identification | Kaggle
Approaching (Almost) Any NLP Problem on Kaggle (參考)
Spooky Author Identification | Kaggle (My work)
根據三位的一些作品訓練集,三分類測試集是哪個作家寫的概率。
目錄
1. 數據導入&格式display
2. 損失函數的定義
3. 數據準備
4. 兩種向量化編碼 TF-IDF和詞頻統計Count
5. 機器學習分類模型
5.1 邏輯回歸
5.2?樸素貝葉斯模型
5.3 對TF-IDF SVD降維+標準化后 SVM
6. Grid_Search 參數調優
6.1 Grid_Search_SVM
6.2?Grid_Search_貝葉斯
7. GloVe詞向量 + XGboost
8. GloVe詞向量 + 深度學習
8.1 構建embedding_matrix 作為詞嵌入層
8.2 LSTM /?雙頭LSTM /?GRU
8.3 預測+提交
1. 數據導入&格式display
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
train = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/spooky-author-identification/train.zip')
test = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/spooky-author-identification/test.zip')
sample = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/spooky-author-identification/sample_submission.zip')display(train.head())
display(test.head())
display(sample.head())test 數據包含id 和 text內容;train中還多一個標簽 哪個作者寫的。
submission_sample中為 id 以及text為每個作者的概率(每行均為訓練集中每個作者的比例)
2. 損失函數的定義
多類別對數損失函數;僅i屬于類別j時 y=1;即 pij 越大越好
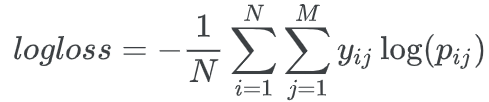
def multiclass_logloss(actual, predicted, eps=1e-15):# 步驟1: 將整數標簽轉換為one-hot編碼if len(actual.shape) == 1:actual2 = np.zeros((actual.shape[0], predicted.shape[1]))for i, val in enumerate(actual):actual2[i, val] = 1 # 對應 y_ij = 1 (當j=真實類別時)actual = actual2# 步驟2: 防止log(0)的情況,將概率裁剪到[eps, 1-eps]范圍clip = np.clip(predicted, eps, 1 - eps) # 對應 p_ij# 步驟3: 計算損失rows = actual.shape[0] # 對應 N (樣本數量)vsota = np.sum(actual * np.log(clip)) # 對應 ΣΣ [y_ij * log(p_ij)]# 步驟4: 最終計算return -1.0 / rows * vsota # 對應 - (1/N) * ΣΣ [y_ij * log(p_ij)]3. 數據準備
target為作者名稱 使用LabelEncoder() 轉換為0 1 2 編碼; 并劃分訓練集測試集
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
lbl_enc = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
y = lbl_enc.fit_transform(train.author.values)
xtrain, xvalid, ytrain, yvalid = train_test_split(train.text.values, y, stratify=y, random_state=42, test_size=0.1, shuffle=True)4. 兩種向量化編碼 TF-IDF和詞頻統計Count
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer, CountVectorizer# TF-IDF特征提取
tfv = TfidfVectorizer(min_df=3, max_features=None, strip_accents='unicode', analyzer='word', token_pattern=r'\w{1,}',ngram_range=(1, 3), use_idf=1, smooth_idf=1, sublinear_tf=1,stop_words='english')# 擬合并轉換數據
tfv.fit(list(xtrain) + list(xvalid)) # 在訓練集+驗證集上學習詞匯表
xtrain_tfv = tfv.transform(xtrain) # 轉換訓練集為TF-IDF矩陣
xvalid_tfv = tfv.transform(xvalid) # 轉換驗證集為TF-IDF矩陣# Count向量化特征提取
ctv = CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', # 按單詞進行分詞token_pattern=r'\w{1,}', # 匹配至少1個字符的單詞ngram_range=(1, 3), # 使用1-gram, 2-gram, 3-gramstop_words='english' # 移除英文停用詞
)# 擬合并轉換數據
ctv.fit(list(xtrain) + list(xvalid)) # 在訓練集+驗證集上學習詞匯表
xtrain_ctv = ctv.transform(xtrain) # 轉換訓練集為詞頻矩陣
xvalid_ctv = ctv.transform(xvalid) # 轉換驗證集為詞頻矩陣print(f"TF-IDF特征維度: {xtrain_tfv.shape}")
print(f"Count特征維度: {xtrain_ctv.shape}")5. 機器學習分類模型
5.1 邏輯回歸
fit + 預測 predict_proba + 之前定義的損失
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Fitting a simple Logistic Regression on TFIDF
clf = LogisticRegression(C=1.0)
clf.fit(xtrain_tfv, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_tfv)print ("logloss: %0.3f " % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))# Fitting a simple Logistic Regression on Counts
clf = LogisticRegression(C=1.0)
clf.fit(xtrain_ctv, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_ctv)print ("logloss: %0.3f " % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))5.2?樸素貝葉斯模型
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
# Fitting a simple Naive Bayes on TFIDF
clf = MultinomialNB()
clf.fit(xtrain_tfv, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_tfv)print ("logloss: %0.3f " % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))# Fitting a simple Naive Bayes on Counts
clf = MultinomialNB()
clf.fit(xtrain_ctv, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_ctv)print ("logloss: %0.3f " % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))5.3 對TF-IDF SVD降維+標準化后 SVM
因為SVM對特征尺度敏感 需要降維+scale 加快收斂
from sklearn import decomposition,preprocessing
from sklearn.svm import SVC# 1. SVD降維
svd = decomposition.TruncatedSVD(n_components=120)
svd.fit(xtrain_tfv)
xtrain_svd = svd.transform(xtrain_tfv)
xvalid_svd = svd.transform(xvalid_tfv)# 2. 數據標準化
scl = preprocessing.StandardScaler()
scl.fit(xtrain_svd)
xtrain_svd_scl = scl.transform(xtrain_svd)
xvalid_svd_scl = scl.transform(xvalid_svd)# 3. SVM訓練和評估
clf = SVC(C=1.0, probability=True, random_state=42)
clf.fit(xtrain_svd_scl, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_svd_scl)print("SVM在SVD降維特征上的logloss: %0.3f" % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))6. Grid_Search 參數調優
需要準備 ?1.estimator模型管道? ? 2.param_grid參數網絡? ? 3.scoring評分器
6.1 Grid_Search_SVM
1. 根據損失函數 創建評分器
from sklearn import metrics, pipeline
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# 1. 創建評分器
mll_scorer = metrics.make_scorer(multiclass_logloss, greater_is_better=False, needs_proba=True)
# 自定義的多類別對數損失函數轉換為scikit-learn的評分器
# greater_is_better=False:logloss越小越好,所以設為False
# needs_proba=True:需要概率預測而不是類別標簽2. 降維+標準化+SVM 三個步驟創建管道
# 2. 創建管道 三個步驟
svd = decomposition.TruncatedSVD()
scl = preprocessing.StandardScaler()
lr_model = LogisticRegression()clf = pipeline.Pipeline([('svd', svd), # 第一步:SVD降維('scl', scl), # 第二步:數據標準化('lr', lr_model) # 第三步:邏輯回歸
])3. 參數網絡? 降維數 / 正則化 類型與大小
# 3. 定義參數網格
param_grid = {'svd__n_components': [120, 180], # SVD組件數'lr__C': [0.1, 1.0, 10], # 正則化強度'lr__penalty': ['l1', 'l2'] # 正則化類型
}4. 執行網格搜索 輸出最優結果
# 4. 網格搜索
model = GridSearchCV(estimator=clf, param_grid=param_grid, scoring=mll_scorer,verbose=10, n_jobs=-1, refit=True, cv=2)# 5. 執行網格搜索
model.fit(xtrain_tfv, ytrain)# 6. 輸出最佳結果
print("Best score: %0.3f" % model.best_score_)
print("Best parameters set:")
best_parameters = model.best_estimator_.get_params()
for param_name in sorted(param_grid.keys()):print("\t%s: %r" % (param_name, best_parameters[param_name]))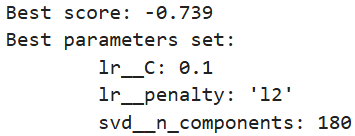
6.2?Grid_Search_貝葉斯
參數:拉普拉斯平滑(Laplace smoothing) 的強度
# GridSearch 三個準備
nb_model = MultinomialNB()clf = pipeline.Pipeline([('nb', nb_model)])param_grid = {'nb__alpha': [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100]}model = GridSearchCV(estimator=clf, param_grid=param_grid, scoring=mll_scorer,verbose=10, n_jobs=-1, refit=True, cv=2)
# 搜索輸出最佳結果
model.fit(xtrain_tfv, ytrain)
print("Best score: %0.3f" % model.best_score_)
print("Best parameters set:")
best_parameters = model.best_estimator_.get_params()
for param_name in sorted(param_grid.keys()):print("\t%s: %r" % (param_name, best_parameters[param_name]))
7. GloVe詞向量 + XGboost
加載為 word->vector 的 embeddings_index = { }
文件中每行第一個詞代表word 后面300維代表向量
# 1. 加載GloVe詞向量
from tqdm import tqdmembeddings_index = {}
with open('/kaggle/input/glove840b300dtxt/glove.840B.300d.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:for line in tqdm(f):values = line.split()word = values[0]# 檢查是否有足夠的數值if len(values) == 301: # 1個詞 + 300個數字try:coefs = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32')embeddings_index[word] = coefsexcept:continueprint('Found %s word vectors.' % len(embeddings_index))將每個句子 tokenize分詞;移除停用詞 只保留字母;
所有詞向量求和,并除以模長得到單位向量,作為句子的詞向量
# 2. 轉換文本為向量
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = stopwords.words('english')
def sent2vec(s):# 1. 文本預處理words = str(s).lower() # 轉換為小寫words = word_tokenize(words) # 分詞:將句子拆分成單詞列表words = [w for w in words if w not in stop_words] # 移除停用詞(如'the', 'is', 'and'等)words = [w for w in words if w.isalpha()] # 只保留純字母單詞(移除數字和標點)# 2. 獲取每個詞的詞向量M = []for w in words:try:M.append(embeddings_index[w]) # 從GloVe詞典中獲取詞的300維向量except:continue # 如果詞不在GloVe詞典中,跳過# 3. 處理空句子情況if len(M) == 0:return np.zeros(300) # 如果沒有有效詞,返回300維零向量# 4. 組合詞向量為句子向量M = np.array(M) # 轉換為numpy數組,形狀為 (n_words, 300)v = M.sum(axis=0) # 對所有詞的向量求和,得到300維向量# 5. 向量歸一化(單位化)norm = np.sqrt((v ** 2).sum()) # 計算向量的模長if norm > 0:v = v / norm # 將向量除以其模長,得到單位向量else:v = np.zeros(300) # 避免除以零return vxtrain_glove = np.array([sent2vec(x) for x in tqdm(xtrain)])
xvalid_glove = np.array([sent2vec(x) for x in tqdm(xvalid)])調用XGboost
import xgboost as xgb
clf = xgb.XGBClassifier(max_depth=7, # 每棵樹的最大深度,控制模型復雜度n_estimators=200, # 樹的數量(弱學習器的數量)colsample_bytree=0.8, # 每棵樹使用的特征比例,防止過擬合subsample=0.8, # 每棵樹使用的樣本比例,防止過擬合n_jobs=10, # 并行線程數,加速訓練learning_rate=0.1, # 學習率,控制每棵樹的貢獻程度random_state=42, # 隨機種子,確保結果可重現verbosity=1 # 輸出訓練信息(替代silent參數)
)
clf.fit(xtrain_glove, ytrain)
predictions = clf.predict_proba(xvalid_glove)print ("logloss: %0.3f " % multiclass_logloss(yvalid, predictions))8. GloVe詞向量 + 深度學習
8.1 構建embedding_matrix 作為詞嵌入層
由于神經網絡擬合概率 將作家0 1 2轉換為獨熱編碼
# y轉換為獨熱編碼
from keras.utils import to_categorical
ytrain_enc = to_categorical(ytrain)
yvalid_enc = to_categorical(yvalid)分詞+相同長度填充;句子 -> 每個詞對應token數值
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
token = Tokenizer(num_words=None)
max_len = 70token.fit_on_texts(list(xtrain) + list(xvalid))
xtrain_seq = token.texts_to_sequences(xtrain)
xvalid_seq = token.texts_to_sequences(xvalid)# zero pad the sequences
xtrain_pad = pad_sequences(xtrain_seq, maxlen=max_len)
xvalid_pad = pad_sequences(xvalid_seq, maxlen=max_len)數值 -> 詞向量 作為embedding
word_index = token.word_index
# create an embedding matrix for the words we have in the dataset
embedding_matrix = np.zeros((len(word_index) + 1, 300))
for word, i in tqdm(word_index.items()):embedding_vector = embeddings_index.get(word)if embedding_vector is not None:embedding_matrix[i] = embedding_vector8.2 LSTM /?雙頭LSTM /?GRU
循環層用 LSTM; Bi-directional LSTM ; GRU?
凍結嵌入層 -> 空間Dropout -> 循環層 -> 全連接Dense層 -> 輸出層三分類
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Embedding, SpatialDropout1D, GRU, Dense, Dropout, Activation, LSTM, Bidirectional
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStoppingmodel = Sequential()# 嵌入層:使用預訓練的GloVe詞向量
model.add(Embedding(len(word_index) + 1, # 詞匯表大小 + 1(為未知詞預留)300, # 詞向量維度(300維)weights=[embedding_matrix], # 預訓練的詞向量矩陣input_length=max_len, # 輸入序列的最大長度trainable=False # 凍結嵌入層,不更新詞向量
))model.add(SpatialDropout1D(0.3))# model.add(LSTM(300, dropout=0.3, recurrent_dropout=0.3)) 若用LSTM
# model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(300, dropout=0.3, recurrent_dropout=0.3))) 若用雙頭LSTM
# 下兩行對應 GRU
model.add(GRU(300, dropout=0.3, recurrent_dropout=0.3, return_sequences=True))
model.add(GRU(300, dropout=0.3, recurrent_dropout=0.3))model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.8))model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.8))# 輸出層:3個神經元(對應3個類別),Softmax激活函數
model.add(Dense(3)) # 3分類問題
model.add(Activation('softmax'))# 編譯模型:使用分類交叉熵損失,Adam優化器
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam',metrics=['accuracy'])# Fit the model with early stopping callback
earlystop = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=3, verbose=0, mode='auto')
model.fit(xtrain_pad, y=ytrain_enc, batch_size=512, epochs=100, verbose=1, validation_data=(xvalid_pad, yvalid_enc), callbacks=[earlystop])8.3 預測+提交
texts_seq = token.texts_to_sequences(test.text.values)
texts_pad = pad_sequences(texts_seq, maxlen=max_len)
y_pred = model.predict(texts_pad)sample[["EAP", "HPL", "MWS"]] = y_pred
sample.to_csv('submission.csv', index=False)![[frontend]WebGL是啥?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[frontend]WebGL是啥?)
![[光學原理與應用-400]:設計 - 深紫外皮秒脈沖激光器 - 元件 - 聲光調制器AOM](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[光學原理與應用-400]:設計 - 深紫外皮秒脈沖激光器 - 元件 - 聲光調制器AOM)







對比)


)




-電機分類)

)