力扣100分類
?一、Java基礎代碼模板
1. 基礎輸入輸出模板
import java.util.Scanner;class Solution {public static int linkedListOperation() {// 鏈表操作實現return 0;}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 讀取整數int m = scanner.nextInt(); // 讀取第二個整數scanner.nextLine(); // 清除換行符String str = scanner.nextLine(); // 讀取整行文本System.out.println("輸入的內容是:" + str);}
}
2. Scanner類常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
next() | 讀取下一個字符串(空格分隔) |
nextLine() | 讀取下一行文本 |
nextInt() | 讀取下一個整數 |
nextDouble() | 讀取下一個雙精度浮點數 |
System 輸出? ? ? System.out.print();不換行輸出
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println();換行輸出
二、設計模式實現
單例模式實現
餓漢式單例
1、構造器私有化 private A(){} ==>防止外部通過new創建實例
2、定義一個類變量記住類的一個對象 private static A a = new A(); ==>類內部定義一個靜態成員變量用于保存唯一實例
3、定義一個類方法返回,返回類對象public static A getObject() {return a;} ==>并提供一個公共的靜態方法用于獲取該實例,只會返回同一個a對象,因為第2步中a是類變量,只會開辟一處內存
public class Singleton {// 1. 私有化構造器private Singleton() {}// 2. 類加載時立即創建實例private static final Singleton instance = new Singleton();// 3. 提供全局訪問點public static Singleton getInstance() {return instance;}
}懶漢式單例(線程安全版)
1、構造器私有化 private A(){} ==>防止外部通過new創建實例
2、定義一個靜態成員變量 private static A; 沒有創建對象
3、定義一個類方法返回,返回類對象 public static A getObject(){ if(a==null){a = new A();} return a; } ==>第一次調用方法時才創建對象,每次調用該方法,只會返回同一個a對象
public class Singleton {private static volatile Singleton instance;private Singleton() {}public static Singleton getInstance() {if (instance == null) {synchronized (Singleton.class) {if (instance == null) {instance = new Singleton();}}}return instance;}
}三、集合框架
數組
1、數組長度
int[][] changdu;
int m = changdu.length; ===> changdu[1].length; 行
int n = changdu[0].length; 列2、字符串轉化為字符數組
String str = "Hellow";
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(charArray)); 3、字符串轉為字符串數組
String str = "apple,banana,orange";
String[] strArray = str.split(",");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArray)); 4、數組排序 Arrays.sort();5、數組輸出 int[] nums
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(nums));int[] nums = {1,2,3,4}
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(nums));
int[][] nums = {{1,3},{2,6},{8,10},{15,18}};
System.out.print(Arrays.deepToString(nums));字符串 String
1、字符串長度String str;int n = str.length();2、轉化為數組char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();3、獲取索引位置的字符String char = str.charAt(int index);4、對字符串截取(左閉右開)String sub = str.substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex);動態數組 ArrayList?
1、創建
ArrayList<Integer/String> list = new Arraylist<>(n); n為指定容量
2、添加元素
list.add("apple"); list.add(0,"banana")
3、訪問元素
get(int index); index0f();返回元素首次出現位置
lastIndex0f();返回元素最后一次出現位置
4、刪除元素
remove(int index); 刪除指定位置元素
5、修改元素
list.set(1,"Mango"); 將索引為1的元素修改為“Mango“
6.長度
int n = list.size();動態鏈表 LinkedList 和ArrayList差不多
1、創建
LinkedList<Integer/String> list = new Linkedlist<>(n); n為指定容量
2、添加元素
list.add("apple");
list.add(0,"banana")
list.addFirst();
List.addLast();
3、訪問元素
get(int index);
index0f();返回元素首次出現位置
lastIndex0f();返回元素最后一次出現位置
4、刪除元素
remove(int index); 刪除指定位置元素
5、修改元素
list.set(1,"Mango"); 將索引為1的元素修改為“Mango“
6.長度
int n = list.size(); `哈希 HashMap
1、創建
Map< String , Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
2、添加
map.put("Alice",90);
3、獲取
int score = map.get("Alice");
4、移除
map.remove("Alice");哈希
兩數之和

題目要求:兩數之和,只有一個答案
?思路: 建立Map哈希函數,將值與索引對應,判斷目標值-當前值是否在哈希中,存在則返回 // 無參考意義
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {// 創建一個哈希表來存儲數字及其索引Map<Integer, Integer> numMap = new HashMap<>();// 遍歷數組for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {int complement = target - nums[i]; // 計算目標值與當前數字的差// 如果差值在哈希表中,返回其索引和當前索引if (numMap.containsKey(complement)) {return new int[]{numMap.get(complement), i};}// 否則將當前數字及其索引存入哈希表numMap.put(nums[i], i);}// 如果沒有找到結果,返回空數組(題目假設一定有解,所以實際不會觸發)return new int[]{};}字母異位詞分組

題目要求:字母異位詞分組?將相同字母排列的放在同一個數組內
思路: 創建map哈希:String與List<String>,遍歷字符串數組,對當前的字符串進行排序(字符串--字符串數組排序--字符串)判斷不包含,新建動態數組。都加入map里面
基礎知識:char 是單個字符(比如 'A'、'1'、'中')String 是一串字符組成的“字符串”(比如 "Hello"、"你好世界")
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {Map<String,List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();for(String str:strs){// 字母排序 String - char[] - Stringchar[] chars = str.toCharArray();Arrays.sort(chars); // 返回的是void類型String sortedStr = new String(chars); // 將char[]轉為String// 如果不包含,新建一個ArrayList隊列if(!map.containsKey(sortedStr)){map.put(sortedStr,new ArrayList<>());}// 不管包不包含,都加入map.get(sortedStr).add(str);}// 把map的所有的值放在一個新的ArrayListreturn new ArrayList<>(map.values());}最長連續序列

最長連續序列:數組存在的最長連續序列長度,可間斷,只要存在就行
思路: 先將數值放在Set哈希中,可以去重,然后遍歷numSet先判斷有沒有比當前值小1的數,確認起始值,避免重復計算。再判斷有沒有比當前值大的數,whlie循環。
- Set:只存“唯一元素”,不記錄順序,也不帶鍵值對
- Map:存“鍵值對”(key-value),每個 key 必須唯一,value 可重復
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {// 去重Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();for(int num:nums){numSet.add(num);}int maxLength = 0;for(int num:numSet){int currLength= 1;// 判斷有沒有比當前值小1的數,確認起始值,避免重復計算if(!numSet.contains(num-1)){int currNum = num;// 再判斷有沒有比當前值大的數,whlie循環while (numSet.contains(currNum+1)){currNum++;currLength++;}}maxLength = Math.max(maxLength,currLength);}return maxLength;}雙指針
移動零

將所有的0移動到末尾,保持非0位置相對順序。換個想法,將非0的數移動到前面 不需要交換,直接設置為0。記錄0的位置,與不為0交換
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;int j = 0; // 記錄為0的位置for(int i =0;i<n;i++){if(nums[i] != 0){if(i>j){nums[j] = nums[i];nums[i] = 0;}j++;}}}盛最多水的容器
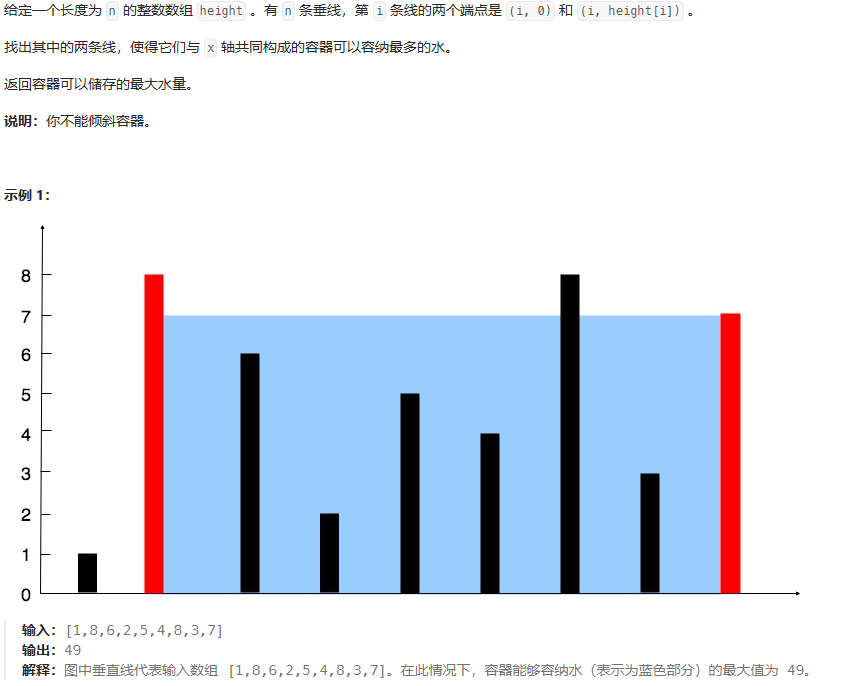
?雙端左右指針,判斷面積。特殊,哪邊小于另一邊,則小邊移動,本質是貪心?
public int maxArea(int[] height) {int n = height.length;int leff = 0;int right = n-1;int maxArea = 0;while (leff <right){int minHeight = Math.min(height[leff],height[right]);int width = right -leff;int curArea = minHeight*width;maxArea = Math.max(maxArea,curArea);if(height[leff]<height[right]){leff++;}else {right--;}}return maxArea;}三數之和
- 處理邊界+重復條件:兩次邊界(整體邊界+if邊界)+兩次重復(if循環單定點重復+while循環左右指針重復)
- 先將數組排序,將三數之和變成二數之和,先確定一個定點,然后用雙端左右指針(左移動,右定點)確定和,判斷指針移動
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();// 處理邊界條件if(nums == null || nums.length <3){return ans; // 初始為空}// 排序,從小到大Arrays.sort(nums);// 定點+雙端左右指針(左移動,右定點)int n = nums.length;for(int i =0;i<n-2;i++){// 處理邊界:當前位置>0,無法合成0if(nums[i] > 0){break;}if(i>0&&nums[i] == nums[i-1]){continue;}// 單次循環int target = -nums[i]; // nums[i]為負數,target肯定為正數int left = i+1; // 左移動int right = n-1; // 右定點while (left < right){int sum = nums[left]+nums[right];if(sum == target){// List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"); 返還為字符串列表ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]));// 去重符合條件兩數之和while (left<right && nums[left] == nums[left+1]){left++;}while (left<right && nums[right] == nums[right-1]){right--;}left++;right--;}else if(sum < target){left++;}else {right--;}}}return ans;}接雨水

接雨水(方塊化) 容器固定,而不是求最大的容器容量
思路:雙端左右指針+最大單邊左右指針+單邊雨水容量
靠高邊,算低邊(移動),底邊:最大-當前。左右高邊相當于外墻
public int trap(int[] height) {// 雙端左右指針+單邊最大左右指針+單邊雨水int left = 0;int right = height.length-1;int leftmax = 0;int rightmax = 0;int total = 0;// 靠高邊,算低邊,底邊:最大-當前while (left <right){// 確認當前最大單邊leftmax = Math.max(leftmax,height[left]);rightmax = Math.max(rightmax,height[right]);// 移動底邊if(height[left] < height[right]){total += leftmax - height[left];left++;}else {total += rightmax - height[right];right--;}}return total;}滑動窗口(定點左右指針):
無重復字符的最長子串(動態窗口)

思路:特點就是Set<Character>? 建立,定點左右指針移動,判斷是否包含在內,如果在內,則去除字符,移動左指針。反之則添加字符
public class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {Set<Character> res = new HashSet<>();int maxlength = 0;int left = 0;for(int right =0;right<s.length();right++){char currentChar = s.charAt(right);if(res.contains(currentChar)){res.remove(s.charAt(left));left++;}res.add(currentChar);maxlength = Math.max(maxlength,right-left+1);}return maxlength;}public static void main(String[] args){Solution solution = new Solution();String s = "abcabcbb";int result = solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s);System.out.print(result);}
}找到字符串中所有字母異位詞(固定窗口)

思路:分別為兩個字符串創建字母表,當相應的位置值相等時,則判斷為異位詞。此位置的定點左右指針為固定窗口值
public class Solution {public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();// 建立一個字母表統計出現次數int[] countP = new int[26];int[] countS = new int[26];for(int i =0;i<p.length();i++){countP[p.charAt(i) - 'a']++;}// 定點左右指針移動for(int right=0;right<s.length();right++){// 統計s字母出現的次數countS[s.charAt(right) - 'a']++;int left = right-p.length()+1;if(left < 0){continue; // 結束此次循環}// 此處只能用equals進行比較if(Arrays.equals(countP,countS)){ans.add(left);}countS[s.charAt(left) - 'a']--;}return ans;}public static void main(String[] args){Solution solution = new Solution();String s = "cbaebabacd";String p = "abc";List<Integer> result = solution.findAnagrams(s,p);System.out.print(result);}
}?滑動窗口最大值(固定窗口)

Deque(雙端隊列):
- 前端:移除超出窗口范圍的舊元素
- 后端:添加新元素并維護遞減順序
peek是查看 poll推出
思路:使用雙端隊列Deque,隊頭和隊尾查看以及移出方便。記在隊列記錄的是索引的值。使用定點左右指針,只有left>=0,才開始記錄隊列的最大值。
- 第一次while循環,如果隊列的隊頭索引<當前左指針索引,那么就移除隊頭,直到大于左指針索引
- 第二次while循環,如果隊列的隊尾索引對應的值<當前右指針對應的值,移除隊尾,直到其值大于右指針對應的值,保存隊列是遞減的,這樣隊列的隊頭就是最大值索引,可以直接出隊。
public class Solution {public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {if( nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k<=0){return new int[0];}int n = nums.length;int[] result = new int[n-k+1];// 存儲的是索引值Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();// 定點左右指針for (int right =0;right<n;right++){int left = right-k+1; // 固定長度// 移除超出窗口范圍的元素while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() < left){deque.pollFirst(); // 出隊隊首}// 移除比當前元素小的元素,保持隊列遞減// 出隊是區間最大元素while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[right]){deque.pollLast(); // 出隊隊尾}deque.addLast(right); //記錄索引位置if(left>=0){result[left] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];}}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {Solution solution = new Solution();int[] nums = {1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};int k = 3;int[] result = solution.maxSlidingWindow(nums, k);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));// 輸出: [3, 3, 5, 5, 6, 7]}
}
子串
和為k的子數組

題目復述:數組中和為k的子數組連續非空序列,
思路:兩次遍歷循環判斷
public class Solution {public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {int maxSum = 0;for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){int sum = 0;for(int j =i;j<nums.length;j++){sum += nums[j];if(sum == k){// 不需要打破當前循環題,萬一下一位是0maxSum++;}}}return maxSum;}public static void main(String[] args) {Solution solution = new Solution();int[] nums = {1,1,1};int k =2;int result = solution.subarraySum(nums,k);System.out.print(result);}
}
最小覆蓋子串(動態窗口)
思路:兩個字符串覆蓋問題,注意這種里面的覆蓋是可以包含其它字母的,求得是最小子串。建立兩個字母表,判斷是否可以覆蓋(cntS字母次數>=cntT字母次數,其他字母)
public class Solution {public String minWindow(String S, String t) {int[] cntS = new int[128];int[] cntT = new int[128];// 記錄t出現的字母次數for(char c:t.toCharArray()){cntT[c]++; // 自動類型轉化,能自動識別字母對應的索引位置}char[] s = S.toCharArray();int m = s.length;// 初始化最大覆蓋長度// 本來應該是0:m-1,但這樣無法判斷s沒有包含t的情況,因此范圍擴大int ansleft = -1;int ansright = m;int left = 0;for(int right =0;right<m;right++){cntS[s[right]]++;// 在覆蓋范圍內的最小值,起始情況while (isCovered(cntS,cntT)){if(right-left<ansright-ansleft){ansleft = left;ansright = right;}cntS[s[left]]--;left++;}}if(ansleft >=0){return S.substring(ansleft,ansright+1);}else {return "";}}private boolean isCovered(int[] cntS,int[] cntT){// cntS的出現的字母肯定要比cntT多// 所以存在cntS字母次數>=cntT字母次數for(int i = 'a';i<='z';i++){if(cntS[i] < cntT[i]){return false;}}for(int i = 'A';i<='Z';i++){if(cntS[i] < cntT[i]){return false;}}return true;}public static void main(String[] args) {Solution solution = new Solution();String s = "ADOBECODEBANC";String t = "ABC";String result = solution.minWindow(s,t);System.out.println(result);}
}
普通數組
最大子數組合(動規)

// 不推薦,時間復雜度太高了public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int n = nums.length;for(int i =0;i<n;i++){int sum = 0;for(int j=i;j<n;j++){sum += nums[j];maxSum = Math.max(maxSum,sum);}}return maxSum;}public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {int maxSum = nums[0];int curSum = nums[0];int n = nums.length;for(int i =0;i<n;i++){// 如果當前值>其累加和,重置位置// 本質是動規curSum = Math.max(nums[i],curSum+nums[i]);maxSum = Math.max(maxSum,curSum);}return maxSum;}輪轉數組(三次翻轉法)

public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length;// 區間范圍壓縮到0:n-1k = k%n;reverse(nums,0,n-1);reverse(nums,0,k-1);reverse(nums,k,n-1);}private void reverse(int[] nums,int left,int right){while (left<right){int temp = nums[left];nums[left] = nums[right];nums[right] = temp;left++;right--;}}除自身以外數組的乘積(正/倒乘法)
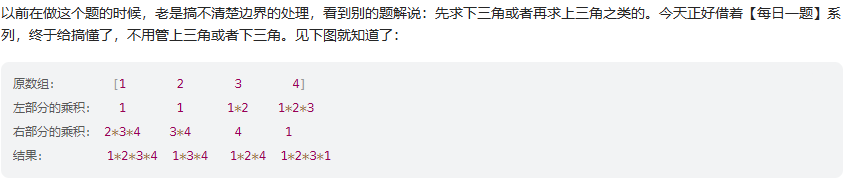
思路:移一位乘法
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;int[] ans = new int[n];ans[n-1] = 1;// 0:n-1區間 倒乘法:當前值=后面相乘for(int i = n-2;i>=0;i--){ans[i] = ans[i+1]*nums[i+1];}// 正乘法:當前值 = 前面相乘int pre = 1;for(int i =0;i<n;i++){ans[i] = ans[i]*pre;pre *= nums[i];}return ans;}
缺失的第一個正數(索引和值對應)

思路:將隊列長度范圍內的索引位置與值對應上,這樣遍歷尋找對應。記得是while循環,直到當前位置值與索引對上或不在范圍跳出循環。

public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;// 另類排序確認范圍內的索引與值對應// 如果沒有,說明最小值為1// 如果有,遍歷找到它for(int i =0;i<n;i++){// 在區間范圍內,將值與索引對應 注意:0不是正數// 記錄當前值大于0且小于隊列長度且當前值不等于當前值位置本來值// 直到當前位置值與索引對上,否有不在范圍跳出循環while(nums[i]>0&&nums[i]<n+1&&nums[nums[i]-1]!=nums[i]){int temp = nums[nums[i]-1];nums[nums[i]-1] = nums[i];nums[i] = temp;}}for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){if(nums[i]!=i+1){return i+1;}}return n+1;}
合并區間(int[][] 列表用法):

基礎知識:對于這種區間帶區間類型int[][] nums,可以這樣考慮for(int[] p : nums) 這里的p代表的單個區間的索引:例如p[0] = 1 p[1] = 3;區間起始位置排序 Array.sort(nums,(p,q) -> p[0]-q[0])Arrays.deepToString(result)
return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]);
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;public class Solution {public static int[][] merge(int[][] nums){// 比較兩個區間起始位置,從小到大排列Arrays.sort(nums,(p,q)->p[0]-q[0]);List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList<>();// 增強型for循環for(int[] p:nums){int m = ans.size();if(m>0 && p[0] <= ans.get(m-1)[1]){ans.get(m-1)[1] = Math.max(ans.get(m-1)[1],p[1]);}else{ans.add(p);}}// List列表轉為數組return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]);}public static void main(String[] args){Solution solution = new Solution();int[][] nums = {{1,3},{2,6},{8,10},{15,18}};int[][] result = solution.merge(nums);System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(result));}}
?動規定義
動態規劃:每一個狀態一定是由上一個狀態推導出來
動歸5部曲
- 確定dp數組(dp table)以及下標的含義
- 確定遞推公式
- dp數組如何初始化
- 確定遍歷順序
- 舉例推導dp數組
單軸
爬樓梯、最小代價爬樓梯
圖型--路徑
不同路徑、不同路徑Ⅱ
爬樓梯
思路:首先確定dp[n]代表的含義是第n個樓層的到達方法,已知一次只能走1~2個臺階,則推導出公式dp[n]=dp[n-1]+dp[n-2]。確定初始條件n>=2,以及dp[0]=1,dp[1]=1
package 動態規劃;public class Solution {public static int climbStairs2(int n){int[] dp = new int[n+1];dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){dp[i] = dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];}return dp[n];}public static void main(String[] args){int n = 1;Solution solution = new Solution();int result = solution.climbStairs2(n);System.out.println(result);}
}
一次可以跨m個臺階,到達n個樓層的多少路徑
package 動態規劃;public class Solution {public static int climbStairs(int m,int n){int[] dp = new int[n + 1];dp[0] = 1; // 初始化:地面有1種方法for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {if (i >= j) {dp[i] += dp[i - j];}}}return dp[n];}public static void main(String[] args){int m = 3;int n = 4;Solution solution = new Solution();int result = solution.climbStairs(m,n);System.out.println(result);}
}楊輝三角
思路:要明白輸出類型List<List<Integer>>,其次發現從第1行開始(存在0行),開始和結尾都是1,可以寫出num.add(1),最后是動規,從j=1開始到i-1結束
給定一個非負整數?numRows,生成「楊輝三角」,的前?numRows?行。
public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows){List<List<Integer>> nums = new ArrayList<>();// 初始化nums.add(List.of(1));for(int i =1;i<numRows;i++){List<Integer> num = new ArrayList<>();num.add(1);for(int j =1;j<i;j++){num.add(nums.get(i-1).get(j-1)+nums.get(i-1).get(j));}num.add(1);nums.add(num);}return nums;}打家截舍
思路:dp[n]代表到達n間房,得到的最大數(注意第n間房可以不偷)。所以其最大值可以是
dp[n]=dp[n-1]或dp[n-2]+nums[n-1](注意nums.length = n,索引最大為n-1)

注意:int[] m = {1,2,3,4};這里是大括號不是中括號
public class Solution {public static int rob(int[] nums){int n = nums.length;if(n == 0){return 0;}int[] dp = new int[n+1];dp[0] = 0;dp[1] = nums[0];for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++) {dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1]);}return dp[n];}public static void main(String[] args){int[] m = {1,2,3,4,5};Solution solution = new Solution();int result = solution.rob(m);System.out.println(result);}
}
完全平方數
思路:dp[n]代表和為n的完全平方數最小數量,dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-j*j]+1),賦值dp[i]最大為i。初始條件dp[0]=0,i-j*j>=0.遍歷順序1<=i<=n,1<=j.

public static int numSquares(int n){int[] dp = new int[n+1];dp[0] = 0;for(int i =1;i<=n;i++){dp[i] = i;for(int j=1;i-j*j>=0;j++){dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-j*j]+1);}}return dp[n];}零錢兌換
思路:dp[n]代表合為n所需要的最小硬幣數,dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-coins[j]]+1)
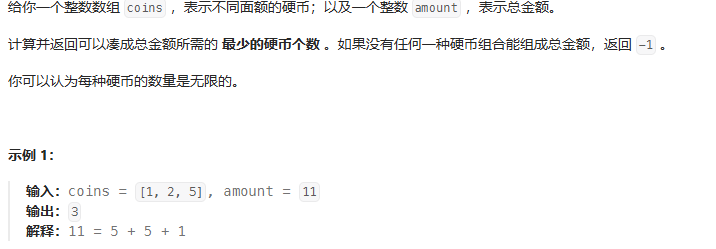
public static int coinChange(int[] coins,int amount){int n = coins.length;int[] dp = new int[amount+1];// dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-coins[j]]+1)for(int i =1;i<=amount;i++){dp[i] = amount+1;for(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(i-coins[j]>=0) {dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);}}}if(dp[amount] == amount+1){return -1;}else {return dp[amount];}}單詞拆分(偏,定點雙指針)
思路:dp[n]代表字符數s是否由字符串列表wordDict拼接而成,定點雙指針,判斷條件
if(dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j,i+1)))

public static boolean wordBreak(String s,List<String> wordDict){Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordDict); // 將字典轉為哈希集合,方便快速查找int n = s.length();boolean[] dp = new boolean[n+1];dp[0] = true;for(int i =0;i<n;i++){for(int j =0;j<=i;j++){// substring 左閉右開if(dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j,i+1))){dp[i+1] = true;break;}}}return dp[n];}最長遞增子序列(定點雙指針)
思路:dp[n]代表在n處,最長子序列的長度。定點雙指針,dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
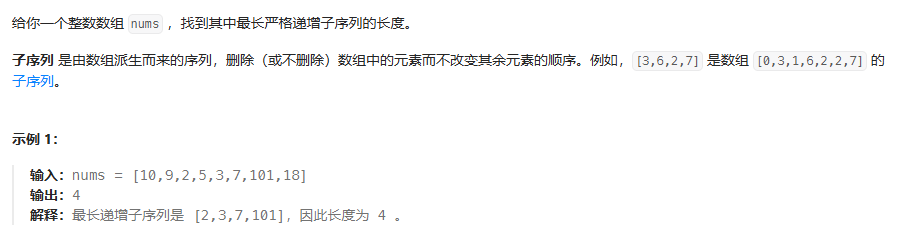
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;if (n == 0) return 0;int[] dp = new int[n]; // dp[i] 表示以 nums[i] 結尾的 LIS 長度int maxLength = 1; // 至少為 1(單個元素)for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {dp[i] = 1; // 初始化為 1(只有自己)for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);}}maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, dp[i]);}return maxLength;}乘積最大數組(非傳統動規)
思路:從數組挑元素這種類型,都要動規自身。這種采用最大,最小變量以及結果變量,如果當前值為負,則互換最大最小值,max = Math.max(num,max*num);? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?min = Math.min(num,min*num);?result = Math.max(result,max);

public static int maxProduct(int[] nums){int n = nums.length;if(n == 0){return 0;}// 維護兩個變量,最大最小int min = nums[0];int max = nums[0];int result = nums[0];for(int i =1;i<n;i++){int num = nums[i];// 當前值為負,交換最大最小值if(num < 0){int temp = max;max = min;min = temp;}max = Math.max(num,max*num);min = Math.min(num,min*num);result = Math.max(result,max);}return result;}分割等和子集
思路:看起來像0-1背包客問題,求目標和,相當于從數組中挑選元素使與之相等,挑選問題要動規自身,由因為dp[i]不能超過其自身i的值==>dp[i]<=i;因此dp[i]要與數組比較最大:dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);dp[j - nums[i]]表示:在j - nums[i]的數值。最后是反向遍歷,保證每個數字只能用一次。


class Solution {public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return false;int n = nums.length;int sum = 0;for(int num : nums) {sum += num;}//總和為奇數,不能平分if(sum % 2 != 0) return false;int target = sum / 2;int[] dp = new int[target + 1];// 此處沒有初始化dp數組,即全部為0for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 反向遍歷保證每個數字只用一次for(int j = target; j >= nums[i]; j--) {//物品 i 的重量是 nums[i],其價值也是 nums[i]dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);}//剪枝一下,每一次完成內層的for-loop,立即檢查是否dp[target] == target,優化時間複雜度(26ms -> 20ms)if(dp[target] == target)return true;}return dp[target] == target;}
}
class Solution {public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;// 如果n為0,1劃分不了if (n < 2) {return false;}//如果sum為奇數,劃分不了int sum = 0, maxNum = 0;for (int num : nums) {sum += num;//求數組里面的最大值maxNum = Math.max(maxNum, num);}if (sum % 2 != 0) {return false;}//判斷數組最大值與sumint target = sum / 2;if (maxNum > target) {return false;}//0-1背包客 倆個數位// 在boolea中,dp沒有設置,全為falseboolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][target + 1];//可以省略 從j = 0開始for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {dp[i][0] = true;}dp[0][nums[0]] = true;// 因為i-1>0,所以 i起始為1for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {int num = nums[i];for (int j = 1; j <= target; j++) {if (j >= num) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] | dp[i - 1][j - num];} else {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];}}if(dp[i][target]){return true;}}return false;//return dp[n - 1][target];}
}最長有效括號
思路:

class Solution {/*** 計算最長有效括號子串的長度(動態規劃解法)* @param str 包含'('和')'的字符串* @return 最長有效括號子串的長度*/public static int longestValidParentheses(String str) {char[] s = str.toCharArray();// dp[i]表示以i位置字符結尾的最長有效括號子串長度int[] dp = new int[s.length];int maxLen = 0; // 記錄全局最大值// 從第1個字符開始遍歷(第0個字符無法形成有效對)for (int i = 1, pre; i < s.length; i++) {// 只有遇到')'才需要處理if (s[i] == ')') {// 計算可能與當前')'匹配的'('位置pre = i - dp[i - 1] - 1;// 檢查pre位置是否是'('if (pre >= 0 && s[pre] == '(') {// 核心狀態轉移方程:// 當前有效長度 = 前一個有效長度 + 2(當前匹配對) + pre前一段的有效長度dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 2 + (pre > 0 ? dp[pre - 1] : 0);// 更新全局最大值maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, dp[i]);}}}return maxLen;}
}
整數拆分(力扣343)
給定一個正整數?n?,將其拆分為?k?個?正整數?的和(?k >= 2?),并使這些整數的乘積最大化。
返回?你可以獲得的最大乘積?。
class Solution {public int integerBreak(int n) {//dp[i] 為正整數 i 拆分后的結果的最大乘積int[] dp = new int[n+1];dp[2] = 1;for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {for(int j = 1; j <= i-j; j++) {// 這里的 j 其實最大值為 i-j,再大只不過是重復而已,//并且,在本題中,我們分析 dp[0], dp[1]都是無意義的,//j 最大到 i-j,就不會用到 dp[0]與dp[1]dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j*(i-j), j*dp[i-j]));// j * (i - j) 是單純的把整數 i 拆分為兩個數 也就是 i,i-j ,再相乘//而j * dp[i - j]是將 i 拆分成兩個以及兩個以上的個數,再相乘。}}return dp[n];}
}不同二叉搜索樹(力扣96)
給你一個整數?n?,求恰由?n?個節點組成且節點值從?1?到?n?互不相同的?二叉搜索樹?有多少種?返回滿足題意的二叉搜索樹的種數。
class Solution {public int numTrees(int n) {//初始化 dp 數組int[] dp = new int[n + 1];//初始化0個節點和1個節點的情況dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {//對于第i個節點,需要考慮1作為根節點直到i作為根節點的情況,所以需要累加//一共i個節點,對于根節點j時,左子樹的節點個數為j-1,右子樹的節點個數為i-jdp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];}}return dp[n];}
}背包理論
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int bagweight = scanner.nextInt();int[] weight = new int[n];int[] value = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {weight[i] = scanner.nextInt();}for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {value[j] = scanner.nextInt();}int[][] dp = new int[n][bagweight + 1];for (int j = weight[0]; j <= bagweight; j++) {dp[0][j] = value[0];}for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j <= bagweight; j++) {if (j < weight[i]) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];} else {dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]);}}}System.out.println(dp[n - 1][bagweight]);}
}分割子集---一維背包客解法
一維度背包客解法本質上來說就是重新覆蓋原有的數組位數
| 你疑惑點 | 解答 |
|---|---|
| “價值”和“重量”都是自身? | 是的,但本題只關心是否能組成目標和,不關心價值累計,所以“價值”可以忽略,數值=重量即可 |

class Solution {public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return false;int n = nums.length;int sum = 0;for(int num : nums) {sum += num;}//總和為奇數,不能平分if(sum % 2 != 0) return false;int target = sum / 2;int[] dp = new int[target + 1];for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for(int j = target; j >= nums[i]; j--) {//物品 i 的重量是 nums[i],其價值也是 nums[i]dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);}//剪枝一下,每一次完成內層的for-loop,立即檢查是否dp[target] == target,優化時間複雜度(26ms -> 20ms)if(dp[target] == target)return true;}return dp[target] == target;}
}代碼輸入輸入模型
class Solution{public static int dangli(){}public static void mian(String[] args){Scanner scanner = new Scanner();int m = scanner.nextInt();int n = sacnner.nextInt();}}多動態
不同路徑
思路:
- 狀態定義:dp[i][j]表示:抵達ij位置的不同路徑、dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
- 初始化 dp[0][j]= 1 dp[i][j] = 1;

class Solution {public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];// 初始化for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++){dp[i][1] = 1;}for(int j =1;j<=n;j++){dp[1][j] = 1;}//計算for(int i=2;i<=m;i++){for(int j =2;j<=n;j++){dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];}}return dp[m][n];}
}最小路徑和
思路:
- 背包客問題 dp[i][j]表示在ij出最小的路徑和
- 公式:dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j])+grid[i][j];
- 初始化 dp[i][0]= dp[i-1][0]+grid[i][0] ?dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1] + grid[0][j]; dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]
class Solution {public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {int m = grid.length; //行數int n = grid[0].length;//列數int[][] dp = new int[m][n];dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];for(int i=1;i<m;i++){dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]+ grid[i][0];}for(int j=1;j<n;j++){dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1]+ grid[0][j];}for(int i=1;i<m;i++){for(int j=1;j<n;j++){dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+grid[i][j];}}return dp[m-1][n-1];}
}最長回文子串
思路:
- 定義狀態:另類動歸 boolean dp[l][r] 這里的lr代表的是定點左右指針 整體表示:l與r區間是否為回文子串
- 公式:dp[l][r]為真的判定條件:(dp[l+1][r-1]為真或l-r<=2單回文和雙回文)且當前s.charAt(r) == s.charAt(l)? ?r-l+1>maxLen
- 初始化: 1<=r<s.length(),0<=l<r

class Solution {public String longestPalindrome(String s) {if (s == null || s.length() < 2) {return s;}int strLen = s.length();int maxStart = 0; //最長回文串的起點int maxEnd = 0; //最長回文串的終點int maxLen = 1; //最長回文串的長度boolean[][] dp = new boolean[strLen][strLen];for (int r = 1; r < strLen; r++) {for (int l = 0; l < r; l++) {if (s.charAt(l) == s.charAt(r) && (r - l <= 2 || dp[l + 1][r - 1])) {dp[l][r] = true;if (r - l + 1 > maxLen) {maxLen = r - l + 1;maxStart = l;maxEnd = r;}}}}return s.substring(maxStart, maxEnd + 1);}}編輯距離
思路:
- 定義狀態:另類遞歸 dp[i][j] 字符串str1與字符串str2最小操作數
- 遞歸公式: ?當str1[i-1] == str2[j-1] ?不需要編輯 dp[i-1][j-1]
- 當str1[i-1] != str2[j-1] ? ?需要編輯(增刪改) min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1])+1
- ?dp[i-1][j] str1刪除元素 ?dp[i][j-1] str2刪除元素==str1增加一個元素 ?dp[i-1][j-1] str1替換元素
- ?初始化: ? dp[i][0] = i; ? ?dp[0][j] = j;?str1 刪除 i個元素變成 str2(為空) ? ?str2 刪除j個元素會變成str1(str1為空)

class Solution {public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {int m = word1.length();int n = word2.length();int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];// 初始化邊界情況for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {dp[i][0] = i;}for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {dp[0][j] = j;}// 動態規劃填表for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {// 計算插入、刪除、替換操作的最小值dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;// 如果字符相等,不需要替換操作if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1]);}}}return dp[m][n];}
}
最長公共子序列
思路:
- 另類動歸 dp[i][j] 表示text1[0:i-1]和text2[0:j-1]的最長公共子序列
- ?遞歸公式: 當text1[i-1] == text2[j-1],說明公共序列長度相等,dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] +1;
- ? ? // ? ? ? ? ?當text1[i-1] != text2[j-1], dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
- ? ? // ? ? ? ? ?這里的思路就是一個定點,一個從頭循環.如果這個定點沒有找到text2循環找到相同的,那么最長序列應該是上一個定點的長度。?找到text2的相同點,但在前面,dp[i][j-1]
- ?初始條件: dp[i][0] = 0; ?dp[0][j] = 0; ==>dp 數組本身初始化就是為 0 因此不需要寫代碼

class Solution {public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {int m = text1.length();int n = text2.length();// DP 數組:dp[i][j] 表示 text1[0...i-1] 和 text2[0...j-1] 的 LCS 長度int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];// 逐個填充 DP 表for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;} else {dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);}}}return dp[m][n];}
}
圖論
島嶼數量

class Solution {public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {int a = 0;for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1') { // 檢查是否為陸地dao(grid, i, j); // 調用DFS,將整個島嶼標記為已訪問a++; // 每發現一個新島嶼,島嶼計數加1}}}return a;}public void dao(char[][] grid, int r, int c) {// 如果超出邊界,或者當前格子不是陸地,則返回if (!inArea(grid, r, c) || grid[r][c] != '1') {return;}// 標記當前格子為已訪問grid[r][c] = '2';// 遞歸遍歷上下左右四個方向dao(grid, r - 1, c); // 上dao(grid, r + 1, c); // 下dao(grid, r, c - 1); // 左dao(grid, r, c + 1); // 右}public boolean inArea(char[][] grid, int r, int c) {// 判斷是否在合法范圍內return 0 <= r && r < grid.length && 0 <= c && c < grid[0].length;}
}
腐爛橘子

class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {int M = grid.length;int N = grid[0].length;Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();int count = 0; // count 表示新鮮橘子的數量for (int r = 0; r < M; r++) {for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {if (grid[r][c] == 1) {count++;} else if (grid[r][c] == 2) {queue.add(new int[]{r, c});}}}int round = 0; // round 表示腐爛的輪數,或者分鐘數while (count > 0 && !queue.isEmpty()) {round++;int n = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int[] orange = queue.poll();int r = orange[0];int c = orange[1];if (r-1 >= 0 && grid[r-1][c] == 1) {grid[r-1][c] = 2;count--;queue.add(new int[]{r-1, c});}if (r+1 < M && grid[r+1][c] == 1) {grid[r+1][c] = 2;count--;queue.add(new int[]{r+1, c});}if (c-1 >= 0 && grid[r][c-1] == 1) {grid[r][c-1] = 2;count--;queue.add(new int[]{r, c-1});}if (c+1 < N && grid[r][c+1] == 1) {grid[r][c+1] = 2;count--;queue.add(new int[]{r, c+1});}}}if (count > 0) {return -1;} else {return round;}
}
}
?鏈表
首先記住鏈表是以節點的形式存在,鏈表循環一般用while,每次循環要根據循環條件來判斷
基礎代碼知識
定義ListNode節點
class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val;this.next = next;}
}創捷節點
ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = pre;創建新的鏈表一般有種形式
鏈表靠節點連接創捷 ==>prev.next = l1;
鏈表靠自己創建節點 ==>prev.next = new ListNode();
鏈表刪除倒數某節點 ==>在自身連接上刪除也可創建新的鏈表
鏈表復制(隨機指針)
鏈表排序判斷while的循環條件==看傳遞參數
多鏈表
&&符號?==>while(l1 != null&&l2 !=null) ==>不需要在循環里面判斷l1和l2是否為空
||符號 ==>while(l1 != null||l2 !=null) ==>需要在循環里面判斷l1和l2是否為空?單鏈表
while(head !=null && head.next !=null) ==> 用于交換節點例子
合并有序鏈表==>額外情況 l1長度!=l2 ==> 續接上去
兩數相加 ==>額外判斷while(l1 != null||l2 !=null||count !=0)
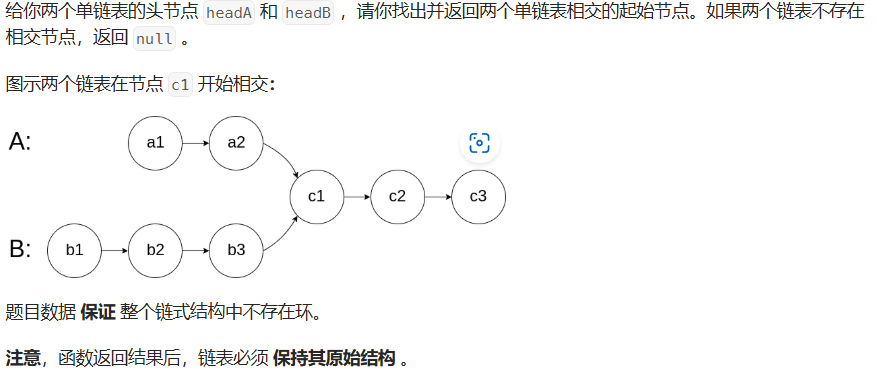
相鄰節點互換==>pre.next = head; 防止出現節點為單數情況相交鏈表
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;ListNode pA = headA,pB = headB;while(pA != pB){if (pA == null) {pA = headB; // 切換到鏈表B的頭部} else {pA = pA.next; // 繼續遍歷鏈表A}if (pB == null) {pB = headA; // 切換到鏈表B的頭部} else {pB = pB.next; // 繼續遍歷鏈表A}}return pA;}
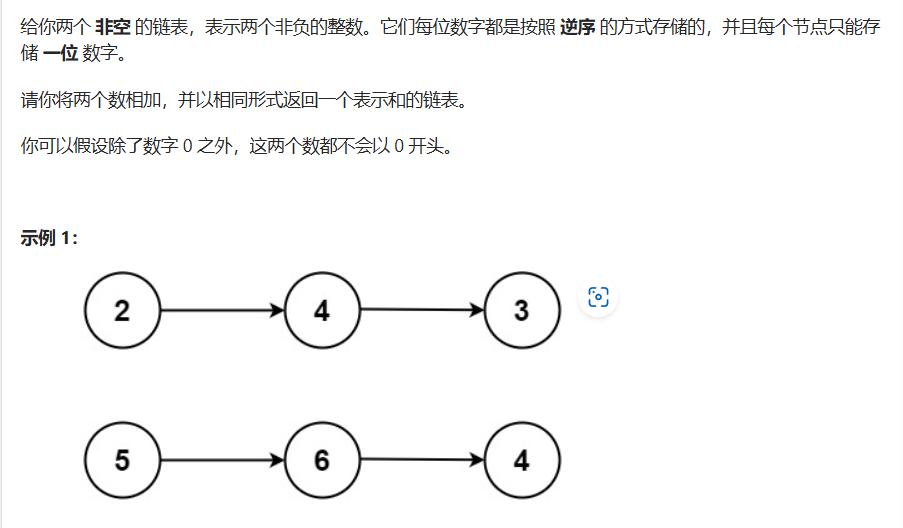
}兩數相加
class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur = dummy;int count = 0;//只要存在l1或l2或count不符合條件,就繼續執行while( l1!=null||l2!=null||count!=0){int sum = count;if(l1 != null){sum += l1.val;l1 = l1.next;}if(l2 != null){sum += l2.val;l2 = l2.next;}count = sum/10;cur.next = new ListNode(sum%10);cur = cur.next;}return dummy.next;}
}合并兩個有序鏈表
class Solution{public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);ListNode prev = pre;while(l1 != null && l2 != null){if(l1.val <= l2.val){prev.next = l1;l1 = l1.next; }else{prev.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}prev = prev.next;}if( l1 == null){prev.next = l2;}else{prev.next = l1;}return pre.next;}
}K個一組鏈表反轉(定點雙指針+單指針循環)
思路:在while條件最后節點end不為null,遍歷到k組最后end節點,斷開連接,虛擬節點連接反轉k組,兩個鏈表表頭連接
? 反轉:創造虛擬節點,當前節點指向虛擬節點(斷開了與下一節點的連接),當前節點轉為下一節點,循環(當前節點不為null)
class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);dummy.next = head;ListNode pre = dummy;ListNode end = dummy;while(end.next != null){for(int i =0;i<k&&end!=null;i++){end = end.next;}if(end == null){break;}ListNode start = pre.next;ListNode start1 = end.next;end.next = null;pre.next = reverse(start);start.next = start1;pre = start;end = start;}return dummy.next;}private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {ListNode pre = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {ListNode temp = curr.next;curr.next = pre; //斷開下一節點連接,指向虛擬節點// 指向下一節點pre = curr;curr = next;}return pre;}}兩兩節點互換(單指針+循環)
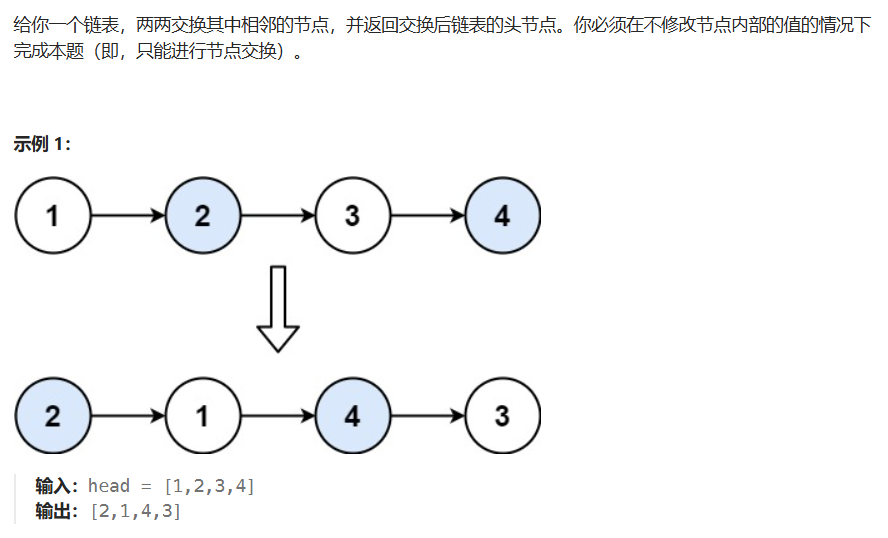
class Solution{public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head){ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);pre.next = head;//防止為空情況發生ListNode prev = pre;while(head !=null && head.next !=null){ListNode first = head;ListNode second = head.next;prev.next = second;first.next = second.next;second.next = first;prev =first;head = first.next;}return pre.next;}}環形鏈表Ⅱ(快慢指針)
思路:快慢指針確定環形是否存在,如果快慢指針重合,那么一定存在。在重合基礎上,慢指針與頭節點一起出發,相遇即為環形節點入口
class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head, fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;//判斷相遇點,是否為環形表if (fast == slow) {//判斷是否為環形鏈路點while (slow != head) {slow = slow.next;head = head.next;}return slow;}}return null;}
}
回文鏈表(轉數組或快慢指針+反轉鏈表)
思路:創建列表存儲節點值,遍歷鏈接節點,取值。使用左右指針判斷說法為回文鏈表
class Solution {public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<Integer>();ListNode currentNode = head;while(currentNode != null){vals.add(currentNode.val);currentNode = currentNode.next;}int left = 0;int right =vals.size()-1;while(left < right){if (!vals.get(left).equals(vals.get(right))) {return false;}left++;right--;}return true;}
}鏈表復制(隨機指針)
class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;}
}
class Solution{public Node copyRandomList(Node head){if(head == null){return null;}Node cur = head;//本質來說創建節點對應關系,牢記是兩個節點//第一個節點是老的,第二個節點是新建的//一個節點包含多個鍵值對==>b+樹類似的==>引申key為節點Map<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();//第一次遍歷,復制節點值while(cur!=null){Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);map.put(cur,newNode);cur = cur.next;}//第二次遍歷,設置節點的next和randomcur = head;//重置cur,恢復起始位置while( cur!= null){Node newNode = map.get(cur);newNode.next = map.get(cur.next);newNode.random = map.get(cur.random);cur = cur.next}return map.get(head);}
}刪除鏈表倒數第n個節點(得鏈表長度跳過)
思路:先得到鏈表的長度,然后遍歷到length-k,之后節點指向跳過此節點,curr.next = curr.next.next
class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;// 構造函數ListNode() {}ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val;this.next = next;}
}class Solution {//思路:確定節點的鏈表長度,循環到那一步直接跳過public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur = dummy;cur.next = head;ListNode temp = head;int length = 0;while(temp != null){temp = temp.next;length++;}for(int i =0;i<length - n;i++){cur = cur.next;}cur.next = cur.next.next;return dummy.next;}public static void main(String[] args) {// 構造鏈表:1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5ListNode head = new ListNode(1,new ListNode(2,new ListNode(3,new ListNode(4,new ListNode(5)))));int n = 2; // 要刪除倒數第2個節點(值為4)Solution solution = new Solution();ListNode result = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n);// 打印刪除后的鏈表while (result != null) {System.out.print(result.val);if (result.next != null) System.out.print(" -> ");result = result.next;}}
}
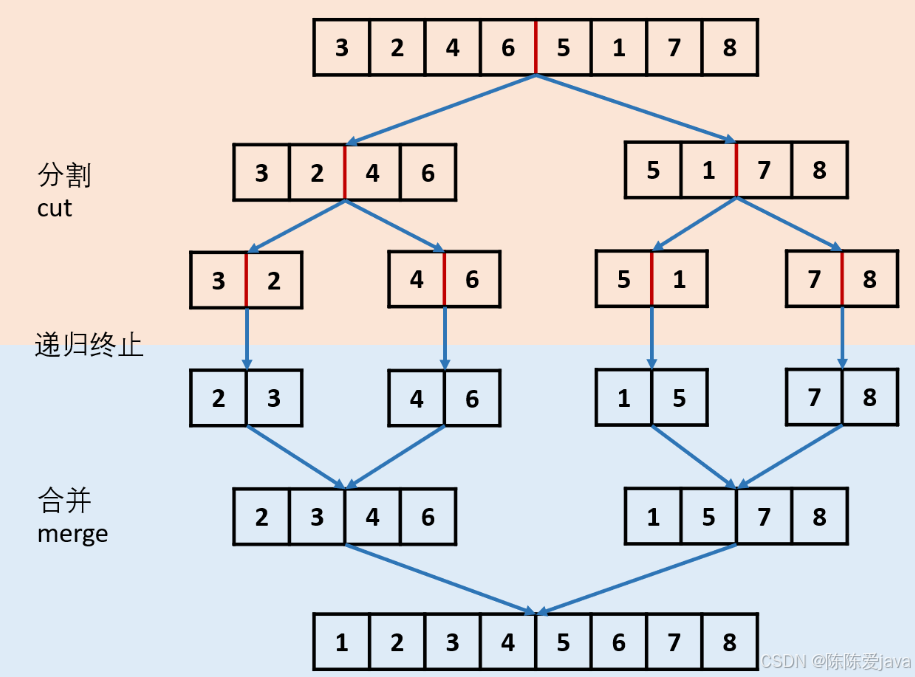
鏈表排序(遞歸法+歸進算法)
思路:先使用快慢指針確定中點位置,然后中點位置斷開連接,分別使用兩個新鏈表遞歸,最后合并鏈表。
快慢指針==>一般用來確定鏈表中點的位置(慢指針)
ListNode fast = head.next,slow = head;
// 快慢指針尋找鏈表的中點
while(fast != null && fast.next != null ){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;
}得出中點位置,斷開連接,為兩個鏈表(無序)==>兩個鏈表(有序)遞歸==>合并兩個有序鏈表
class Solution{public ListNode sortList(ListNode head){//特殊情況if(head == null || head.next == null){return head;}//快慢指針尋找中點,并劃分兩個列表ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while( fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}ListNode tmp = slow.next;//新鏈表頭部slow.next = null;//斷開//列表遞歸排序ListNode left = sortList(head);ListNode right = sortList(tmp);//合并兩個有序列表ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);ListNode prev = pre;while( left!=null && right!=null){if(left.val <= right.val){prev.next = left;left = left.next;}else{prev.next = right;right = right.next;}prev = prev.next;}if(left != null){prev.next = left;}else{prev.next = right;}return pre.next; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 構建鏈表 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3ListNode head = new ListNode(4, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(1, new ListNode(3))));Solution solution = new Solution();ListNode sorted = solution.sortList(head);// 輸出排序后的鏈表while (sorted != null) {System.out.print(sorted.val);if (sorted.next != null) System.out.print(" -> ");sorted = sorted.next;}}
}
鏈表排序(冒泡原鏈表排序)
思路:使用boolean類型作為while的循環條件,以當前節點為主,再次while循環(下個節點不為null),兩兩比較,大于則交換節點值。然后大while循環curr為下一節點
class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
}public class LinkedListBubbleSort {public ListNode bubbleSort(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;boolean swapped = true; // 初始設為true以進入循環while (swapped) {swapped = false; // 重置交換標志ListNode curr = head;while (curr.next != null) {if (curr.val > curr.next.val) {// 交換節點值int temp = curr.val;curr.val = curr.next.val;curr.next.val = temp;swapped = true;}curr = curr.next;}}return head;}public static void main(String[] args) {// 測試代碼與之前相同}
}合成K個升序鏈表
class Solution {// 特殊情況、劃分+合并public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {return null;}return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);}public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {if (left == right) {return lists[left];}int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;ListNode l1 = merge(lists, left, mid);ListNode l2 = merge(lists, mid + 1, right);ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur = dummy;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {if (l1.val < l2.val) {cur.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;} else {cur.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}cur = cur.next;}if (l1 != null) {cur.next = l1;} else {cur.next = l2;}return dummy.next;}
}LRU緩存
思路:定義-->雙向節點,容量,虛擬節點,MAP函數(Interge,Node)
? ? ? ? ? ?方法-->get(int key),put(key,value),getNode,remove,pushFront
雙向鏈表節點問題
//刪除某節點(本質是越過)
x.prev.next = x.next;
x.next.prev = x.prev;
//添加某節點到表頭
x.prev = dummy;
x.next = dummy.next;
x.prev.next = x;
x.next.prev = x;
class LRUCache(Solution) {//雙向鏈表+哈希+哨兵節點private static class Node{int key,value;Node prev,next;Node(int k,int v){this.key = key;this.value = value;}}//創捷全局變量private final int capacity;private final Node dummy = new Node(-1,-1);private final Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap<>();public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;//節點初始化dummy.prev = dummy;dummy.next = dummy;}public int get(int key) {Node node = getNode(key);if(node != null){return node.value;}else{return -1;}}public void put(int key, int value) {Node node = getNode(key);if(node != null){node.value = value;//更新值return;//不需要返回}//否則新建節點node = new Node(key,value); //為空節點賦值map.put(key,node);//添加到哈希表pushFront(node);//移動表頭//判斷是否超容if(map.size() > capacity){Node backNode = dummy.prev;//確定表尾節點map.remove(backNode.key);//去除哈希表尾數據remove(backNode);//鏈表去除尾節點}}//判斷是否存在鏈表,存在更新表頭,否則返回為空public Node getNode(int key){if(!map.containsKey(key)){//contain==>containsKey表示在key里查詢return null;}//更新表頭Node node = map.get(key);//確定對應的節點remove(node); //移除鏈表的節點pushFront(node); //更新為表頭//確認存在,不為空return node; }//輔助函數//移除節點private void remove(Node node){node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}//更新為表頭private void pushFront(Node node){node.prev = dummy;node.next = dummy.next;dummy.next = node;node.next.prev = node;}public static void main(String[] args) {LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2); // 緩存容量 2cache.put(1, 1);cache.put(2, 2);System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 1cache.put(3, 3); // 使 key 2 作廢System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 -1 (未找到)cache.put(4, 4); // 使 key 1 作廢System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 -1 (未找到)System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 3System.out.println(cache.get(4)); // 返回 4}
}定義ListNode節點
class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;// 構造函數ListNode() {}ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val;this.next = next;}
}?二叉樹算法
基礎知識
二叉樹類型:
- 滿二叉樹:節點有兩個子節點,且每一層都填滿
- 完全二叉樹:左順序二叉樹,每一層節點從最左節點依次開始
- 二叉搜索樹:有序二叉樹,節點的左子樹節點<節點值<節點的右子樹節點
- 平衡二叉搜索樹:二叉搜索樹+平衡(左右子樹高度差<=1)
存儲方式:鏈表/數組
遍歷方式:
深度優先遍歷DFS(遞歸法,迭代法):先往深處走,遇到空節點再往回走? 數據結構:棧,先進后出(遞歸法,迭代法)
- 前序遍歷:中左右
- 中序遍歷:左中右
- 后序遍歷:左右中
觀察:前中后,分別對應中的位置不同,其次一左一右;
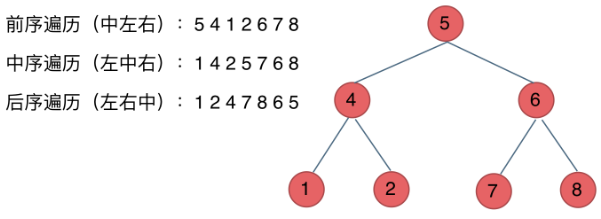
廣度優先遍歷BFS(迭代法):一層一層遍歷 數據結構:隊列 先進先出
- 層次遍歷
節點定義
class TreeNode{int val;TreeNode left,right;TreeNode(){}TreeNode(int val){this.val = val;}TreeNode(int val,TreeNode left,TreeNode right){this.val = val;this.left = left;this.right = right;}}算法思路:
- 確定遞歸函數的參數和返回值:?確定哪些參數是遞歸的過程中需要處理的,那么就在遞歸函數里加上這個參數, 并且還要明確每次遞歸的返回值是什么進而確定遞歸函數的返回類型。
- 確定終止條件:?寫完了遞歸算法, 運行的時候,經常會遇到棧溢出的錯誤,就是沒寫終止條件或者終止條件寫的不對,操作系統也是用一個棧的結構來保存每一層遞歸的信息,如果遞歸沒有終止,操作系統的內存棧必然就會溢出。
- 確定單層遞歸的邏輯:?確定每一層遞歸需要處理的信息。在這里也就會重復調用自己來實現遞歸的過程。
DFS
二叉樹的前中后序遍歷
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root){// 1.遞歸參數和返回值 入參 root 出參 resList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();inorder(root,res);return res;}public void inorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> res){// 2.終止條件 遇到節點if(root == null){return;}// 3.單層遞歸邏輯res.add(root.val); // 前序遍歷inorder(root.left, res);
// res.add(root.val); // 中序遍歷inorder(root.right,res);
// res.add(root.val); // 后序遍歷}二叉樹的最大深度
返還數值的一般都是全局單獨定義
private int ans = 0;public int maxDepth(TreeNode root){// 1.遞歸的入參和出參dfs(root,0);return ans;}public void dfs(TreeNode root,int depth){// 2.終止條件if(root == null){return;}// 3。單層遞歸邏輯depth++;ans = Math.max(ans,depth);dfs(root.left,ans);dfs(root.right,ans);}翻轉二叉樹
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root){dfs(root);return root;}public void dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return;}// 節點互換TreeNode temp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = temp;// 遞歸dfs(root.left);dfs(root.right);}對稱二叉樹
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return true;}else {return dfs(root.left,root.right);}}public boolean dfs(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){if(left == null && right == null){return true;}if(left == null || right == null || left.val!=right.val){return false;}return dfs(left.right,right.left) && dfs(left.left,right.right);}二叉樹直徑
思路:
private int ans;public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root){dfs(root);return ans;}private int dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return -1;}int leftLen = dfs(root.left)+1;int rightLen = dfs(root.right)+1;ans = Math.max(ans,leftLen+rightLen);return Math.max(leftLen,rightLen);}有序數組轉二叉搜索樹(前序遍歷)
思路:
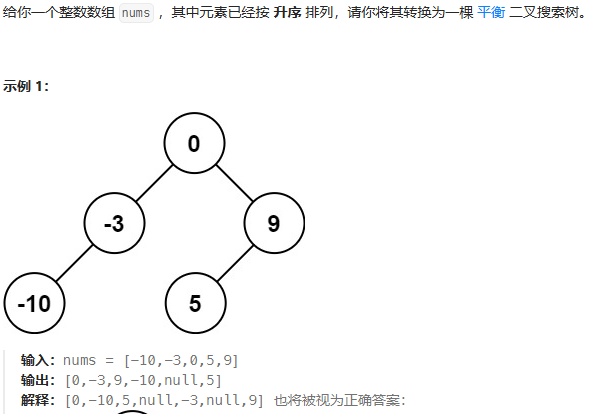
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums){return dfs(nums,0,nums.length-1);}public TreeNode dfs(int[] nums,int left,int right){if(left > right){return null;}int mid = left+(right-left)/2;TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);root.left = dfs(nums,left,mid-1);root.right = dfs(nums,mid+1,right);return root;}驗證二叉搜索樹
思路:
class Solution {public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {return dfs(root, null, null); // 初始時無邊界限制}private boolean dfs(TreeNode node, Integer min, Integer max) {if (node == null) {return true;}// 檢查當前節點值是否在 (min, max) 范圍內if ((min != null && node.val <= min) || (max != null && node.val >= max)) {return false;}// 遞歸檢查左子樹(最大值限制為當前節點值)// 遞歸檢查右子樹(最小值限制為當前節點值)return dfs(node.left, min, node.val) && dfs(node.right, node.val, max);}
}二叉搜索樹第k小的樹
思路:將二叉樹轉化為數組,并對數組排序,遍歷數組到k-1(從0索引)位置;
k--與--k前者先比較后減 后者先減后比較
應該是利用搜索樹特性
class Solution {// 用一個列表按順序存儲遍歷到的節點值List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {// 直接中序遍歷整棵樹,把結果存起來inOrderTraversal(root);// 因為中序遍歷結果是升序的,所以第k小的就是列表里第k-1個位置的數return res.get(k - 1);}// 標準的中序遍歷函數private void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) {return;}// 1. 先遍歷左子樹inOrderTraversal(node.left);// 2. 再訪問當前節點(把值加到列表里)res.add(node.val);// 3. 最后遍歷右子樹inOrderTraversal(node.right);}
}路徑和Ⅲ
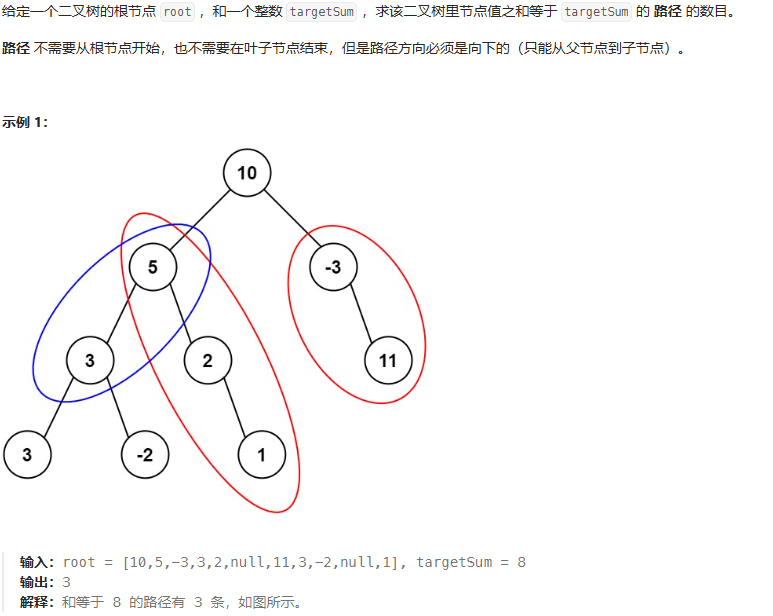
思路:把每個節點都當作根節點,根節點向下遞歸尋找符合條件的單邊和
雙遞歸
class Solution {public int pathSum(TreeNode root, long targetSum) {if(root == null){return 0;}int ret = rootSum(root,targetSum);ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);return ret;}public int rootSum(TreeNode root ,long targetSum){int ret = 0;if(root == null){return 0;}int sum = root.val;if(sum == targetSum){ret++;}ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - sum);ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - sum);return ret;}}二叉樹最近公共先祖
思路:確認節點的左右單邊是否包含p或q節點,包含則返回該節點,否則返回為空。
因為單邊找不到只能向下繼續遞歸,可已經走到頭了,沒有節點了,所以其左右子節點為空返回。

class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root,TreeNode p,TreeNode q){return dfs(root,p,q);}public TreeNode dfs(TreeNode node, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){// 隱含了如果找不到對應的p,q節點就返還為空// 因為找不到,就會向下繼續左右子節點,但二者或單者不存在,因此就返還為空if(node == null){return null;}// 確定p,q所在的節點if(node.val == q.val || node.val == p.val){return node;}TreeNode left = dfs(node.left,p,q);TreeNode right = dfs(node.right,p,q);// 返還公共祖先if( left != null && right != null){return node;}// 返還單邊值if(left != null){return left;}else {return right;}}
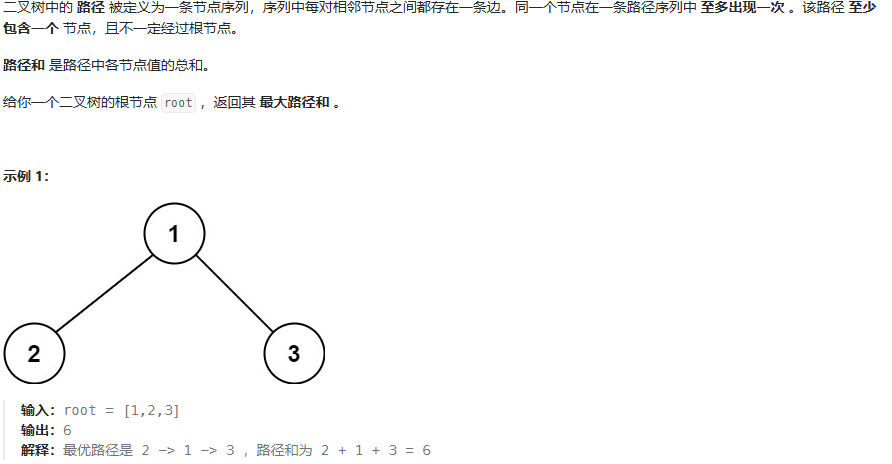
}二叉樹最大路徑和
思路:最大路徑和,返還的是int 類型的數,可以定義一個全局變量。確認單邊最大值,要與0比較,防止出現負數。當前節點左右單邊的最大路徑,返回最大左右單邊值+當前節點值。
class Solution {public int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root){dfs(root);return max;}public int dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return 0;}// 遞歸計算左右子樹的最大貢獻值(如果為負則舍棄)int left = Math.max(0,dfs(root.left));int right = Math.max(0,dfs(root.right));// 更新全局最大值(當前節點 + 左右子樹)int currentMax = root.val+left+right;max = Math.max(max,currentMax);// 返回當前節點的最大貢獻值(只能選擇左或右子樹的一條路徑)return root.val+Math.max(left,right);}
}BFS
適用場景:「層序遍歷」、「最短路徑」
// 二叉樹的層序遍歷
void bfs(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int n = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 變量 i 無實際意義,只是為了循環 n 次TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null) {queue.add(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.add(node.right);}}}
}二叉樹層序遍歷
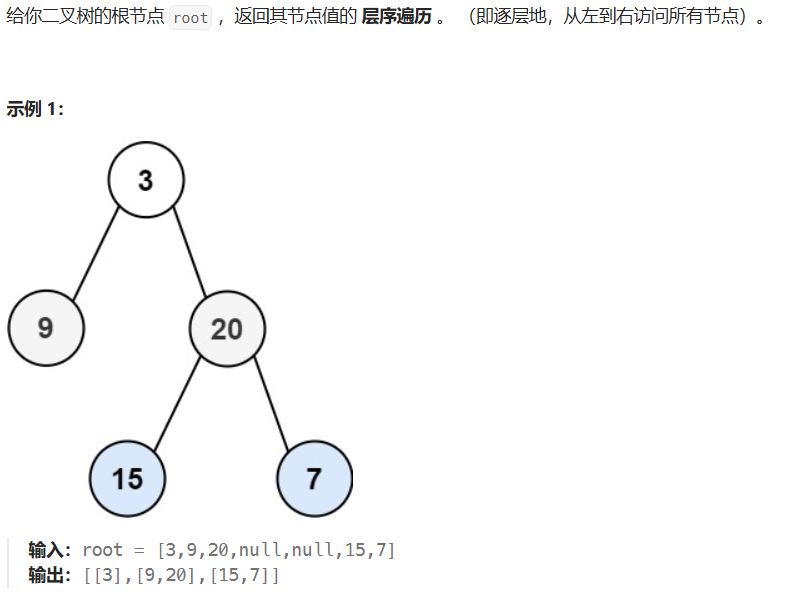
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root){List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();if(root != null){queue.add(root);}while (!queue.isEmpty()){int n = queue.size();List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();for(int i =0;i<n;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();level.add(node.val);if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}res.add(level);}return res;}
二叉樹最短路徑
回溯算法
全排列
思路:
回溯 定義 | 入參類型:int[] nums,int nums.length,int depth,boolean[] used(初始化為false),List<Integer> path ?出參類型:因為還要再寫一個調用dfs所有定義一個全局出參變量 |
終止 條件 | depth == length res.add(new ArrayList(path)) |
回溯 遍歷 | 遞歸遍歷:遍歷nums的每個元素,將當前元素添加到path,并將其對應的used改為true,dfs遞歸 回溯撤銷:當前元素對應的為false,移除元素 |
理解 | [1,2,3]變成[1,3,2]的過程 第一次循環(i=1),遞歸到第二次循環(i=2,因為used(i=1)=true),遞歸到第三次循環(i=3,因為used(i=2)=true),第四次遞歸,無循環depth == len,res.add();開始回溯撤銷,第三次循環:used(i=3)=false,繼續回到第二次循環used(i=2)=false,開始i=2 -- >i=3;從1-3-2 |

public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> permute (int[] nums){int length = nums.length;boolean[] used = new boolean[length];List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums,length,0,used);return res;}public void dfs(int[] nums,int len,int depth,boolean[] used){if(depth == len){res.add(new ArrayList(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<len;i++){if(!used[i]){path.add(nums[i]);used[i] = true;dfs(nums,len,depth+1,used);used[i] = false;path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}子集
思路:
思路 | 選中和沒選中回溯遞歸 |
回溯定義 | 入參類型:int[] nums,len,0,path 出參類型:list<list<integer>> res |
終止條件 | depth == len |
回溯遍歷 | 遞歸遍歷:沒有選中dfs(depth+1) 選中dfs(depth+1) path.add(nums[depth]) ?回溯撤銷:path.remove |

List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums){int length = nums.length;dfs(nums,length,0);return res;}public void dfs(int[] nums,int len,int depth){if(depth == len){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}// 沒有選中dfs(nums,len,depth+1);// 選中path.add(nums[depth]);dfs(nums,len,depth+1);path.remove(path.size()-1);}電話號碼的字母組合
思路:
回溯定義 | 入參類型:char[] digitsChars,List<string> ans,0,char[] path 出參類型:list<string> ans |
終止條件 | depth == digitsChars.length ans.add(new string(path)) |
回溯遍歷 | 遞歸遍歷: for(char c:MAPPING[digitChars[depth]-'0'].toCharArray()) 回溯撤銷: 這個不需要回溯,直接覆蓋原本值 |
class Solution{private String MAPPING[] = new String[]{"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits){int n = digits.length();if(n == 0){return List.of();}List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();char[] path = new char[n];char[] digitChars = digits.toCharArray();dfs(digitChars,ans,path,0);return ans;}private void dfs(char[] digitChars, List<String> ans,char[] path,int depth){if(depth == digitChars.length){ans.add(new String(path));return;}for(char c:MAPPING[digitChars[depth]-'0'].toCharArray()){path[depth] = c;dfs(digitChars,ans,path,depth+1);}}}組合總和
思路:
| 思路 | 起始點 向下遍歷 |
| 回溯定義 | 入參類型:res,path,sum,起始點 start,candidates,target 出參類型:res |
| 終止條件 | 此處有點特殊 sum == target 終止并res.add ?? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?sum > target ?只終止 |
| 回溯遍歷 | 遞歸遍歷:從起始點向下遞歸,start<=i<candidates.length? ,?dfs(,i,sum+candidates[i],) 回溯撤銷:path.remove(path.size()-1) |

List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates,int target){if(candidates.length == 0){return List.of();// 是返回系列為null}dfs(0,0,candidates,target);return res;}public void dfs(int sum,int start,int[] candidates,int target){if(sum == target){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}if(sum > target){return;}// 此處之所以是start,是因為向下遍歷,防止重復for(int i = start;i<candidates.length;i++){path.add(candidates[i]);dfs(sum+candidates[i], i, candidates, target);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}分割回文串
思路:
回溯定義 | 全局變量:res,path 入參類型:s,start 出參類型:res |
終止條件 | start == length res.add |
回溯遍歷 | 遞歸遍歷:for(int i =start;i<s.length();i++) ? ? // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 如果是回文子串,繼續向下遞歸 ? ? // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? path.add(s.substring(start,i+1)); ? ? // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? dfs(s,i+1); 回溯撤銷:path.remove(path.size()-1); 回文子串:已知字符串的范圍,從兩邊向內遞歸 ? ? // ? ? ? ? ?s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--) |

public List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {dfs(s,0);return res;}public void dfs(String s,int start){if(start == s.length()){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i =start;i<s.length();i++){if(huiwen(s,start,i)){path.add(s.substring(start,i+1));dfs(s,i+1);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}public boolean huiwen(String s,int left,int right){while (left<right){if(s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)){return false;}}return true;}
?貪心算法
貪心的本質是:選擇每一階段的局部最優,從而達到全局最優
做題的時候,只要想清楚 局部最優 是什么,如果推導出全局最優,其實就夠了。
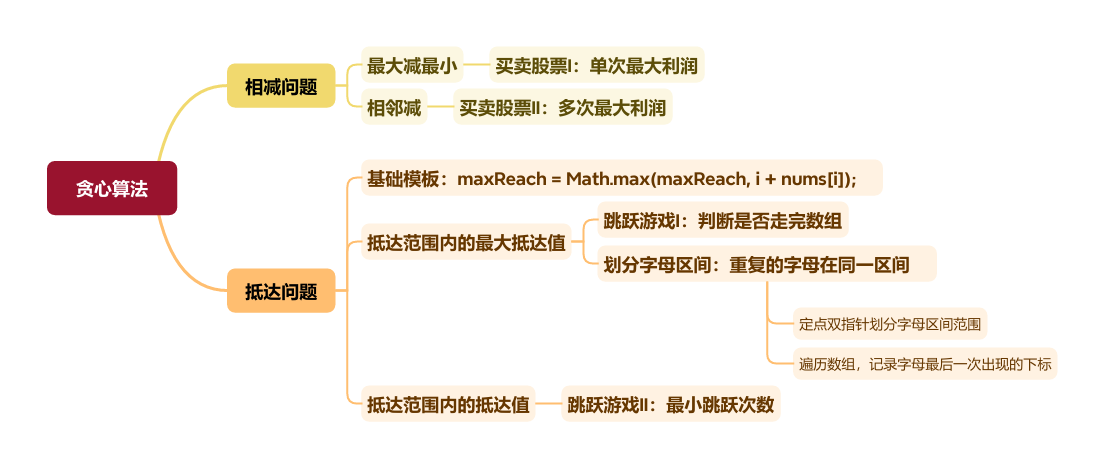
相減問題(怎么相減利潤最大化)
買賣股票的最佳實際
思路:如果第i天賣出股票,則最大利潤為(該天的股價-前面天數中最小的股價),然后與已知的最大利潤比較,如果大于則更新當前最大利潤的值
只要找到一個最低買入價
minPrice,然后在后面找到最大差價。遍歷價格數組,同時維護:
當前最小價格
minPrice當前最大利潤
maxProfit = max(maxProfit, prices[i] - minPrice)

class Solution {public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {// 初始化最大利潤為0,最低價格為第一個價格int maxProfit = 0;int minPrice = 100000;// 遍歷價格數組for (int price : prices) {// 更新最低價格minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, price);// 更新最大利潤maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, price - minPrice);}return maxProfit;}
}
買賣股票的最佳實際Ⅱ
遍歷整個股票交易日價格列表 price,并執行貪心策略:所有上漲交易日都買賣(賺到所有利潤),所有下降交易日都不買賣(永不虧錢)。
- 設 tmp 為第 i-1 日買入與第 i 日賣出賺取的利潤,即 tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1] ;
- 當該天利潤為正 tmp > 0,則將利潤加入總利潤 profit;當利潤為 0 或為負,則直接跳過;
- 遍歷完成后,返回總利潤 profit。
等價于每天都與前一天做交易,賺才去買
class Solution {public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {int profit = 0;for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {int tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];if (tmp > 0) profit += tmp;}return profit;}
}
抵達問題(抵達范圍內是否出現更大的抵達范圍)
跳躍游戲
此處i比較“原本范圍內出現的最大抵達值”,由原本起始點字母出現的最大抵達范圍一直在更新
思路:就是從起點出發,能夠達到的最大點位,如果小于抵達不了則錯誤
- 如果某一個作為 起跳點 的格子可以跳躍的距離是 3,那么表示后面 3 個格子都可以作為 起跳點
- 可以對每一個能作為 起跳點 的格子都嘗試跳一次,把 能跳到最遠的距離 不斷更新
- 如果可以一直跳到最后,就成功了

class Solution {public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {int maxReach = 0; // 記錄能到達的最遠索引int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 如果當前位置 i 已經超出最大可達范圍,則說明無法繼續前進if (i > maxReach) {return false;}// 更新最大可達范圍maxReach = Math.max(maxReach, i + nums[i]);// 如果最大可達范圍已經超過或等于最后一個索引,則返回 trueif (maxReach >= n - 1) {return true;}}return false;}
}
跳躍游戲Ⅱ(判斷跳不跳)
此處i比較“原本出現范圍的最大值”
思路:注意這個肯定是可以抵達到的 所以不需要判斷 i > maxReach 無法抵達情況
可以這樣想:判斷當前節點能夠抵達最大范圍,在這范圍內都要可以跳躍的,只有抵達范圍邊界,才會jumps加1, // 并選取當前節點抵達范圍內的范圍節點最大抵達范圍,如果最大抵達范圍大于nums.length長度,返回jumps
維護兩個變量:
curEnd:當前跳躍可達的最遠邊界。curFarthest:在當前跳躍范圍內能到達的最遠位置。
從左到右遍歷數組(不包含最后一個元素,因為到達最后一個元素就結束):
- 不斷更新
curFarthest = max(curFarthest, i + nums[i])。 - 當
i到達curEnd時,說明當前跳躍范圍已經用完,需要增加一次跳躍次數jumps++,并更新curEnd = curFarthest。
如果 curEnd 已經到達或超過末尾,返回 jumps。
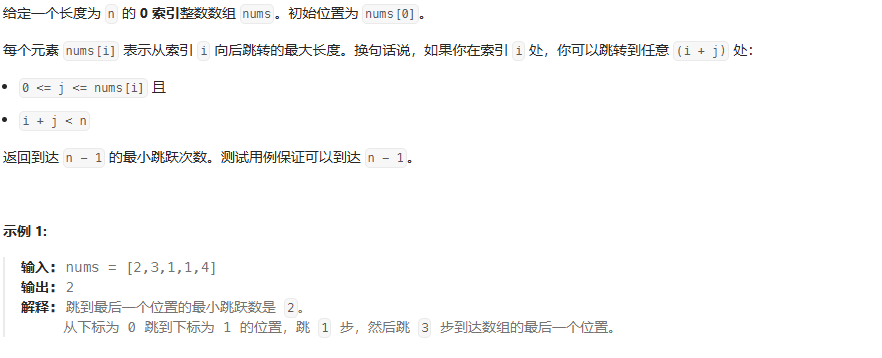
public int jump(int[] nums) {int jumps = 0;int curEnd = 0;int curFarthest = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {curFarthest = Math.max(curFarthest, i + nums[i]);if (i == curEnd) { jumps++;curEnd = curFarthest;if (curEnd >= nums.length - 1) {break;}}}return jumps;
}
劃分字母區間
此處i比較“原本范圍內出現的最大抵達值”,由原本起始點字母出現的最大抵達范圍一直在更新
思路: 重復的字母只能出現在同一區間,那么建立字母表,記錄字母出現的最大下表。就可以將問題轉為抵達問題 // 即使在抵達范圍內的元素出現了更大的抵達值,就直到指針到達該最大抵達值位置

public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String s){char[] sChar = s.toCharArray();int n = s.length();int[] last = new int[26];for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){last[sChar[i] - 'a'] = i;// 每個字母出現的最后下標}List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();int left = 0;int right = 0;for(int i =0;i<n;i++){right = Math.max(right,last[sChar[i]-'a']); // 當前字母可以抵達最大范圍if(i == right){ans.add(right-left+1);left = right+1;}}return ans;}矩陣
堆
數組中第K個最大元素

public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length;// 轉換為找第n-k小的元素(從0開始)return quickselect(nums, 0, n - 1, n - k);}// 使用Hoare分區方案的快速選擇算法private int quickselect(int[] nums, int left, int right, int k) {if (left == right) return nums[k]; // 基線條件// 隨機選擇pivot避免最壞情況int pivotIndex = left + new Random().nextInt(right - left + 1);int pivotValue = nums[pivotIndex];// 分區 每次循環只交換一次// 初始化左右指針int i = left - 1, j = right + 1;while (i < j) {// 從左找到第一個不小于pivot的元素do i++; while (nums[i] < pivotValue); // 先執行循環體,再檢查條件// 從右找到第一個不大于pivot的元素do j--; while (nums[j] > pivotValue);// 交換這兩個元素if (i < j) {int tmp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = tmp;}}// 根據k的位置決定處理哪一部分// j停止的位置就是小于midValue范圍if (k <= j) {return quickselect(nums, left, j, k);} else {return quickselect(nums, j + 1, right, k);}}快排解法(隨機選元素)
private Random rand = new Random();public int findKthLargest (int[] nums,int k){int n = nums.length;return quickSelect(nums,0,n-1,n-k);}private int quickSelect(int[] nums,int left,int right,int targetIndex){int pivotIndex = partiton(nums,left,right);if(pivotIndex == targetIndex){return nums[pivotIndex];}else if(pivotIndex > targetIndex){return quickSelect(nums,left,pivotIndex-1,targetIndex);}else {return quickSelect(nums, pivotIndex+1, right, targetIndex);}}private int partiton(int[] nums,int left,int right){int pivotIndex = left + rand.nextInt(right-left+1); // 隨機選取節點int pivotValue = nums[pivotIndex]; // 該節點值swap(nums,pivotIndex,right); // 將該值放到末尾int storeIndex = left;for(int i = left;i<right;i++){ // 單指針劃分小于/大于pivotValue區間if(nums[i]<pivotValue){swap(nums,storeIndex,i);storeIndex++;}}swap(nums,storeIndex,right); // 再把中位值互換回來return storeIndex;}private void swap(int[] nums,int i,int j){int temp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = temp;}
這個不太行,標準應該是快速排序
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {// 1. 定義桶數組,大小 20001,表示存儲 [-10000, 10000] 范圍內的整數頻率int[] buckets = new int[20001];int n = nums.length;// 2. 統計每個數字出現的次數for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// nums[i] + 10000 是為了將負數映射到 0~20000 的索引范圍buckets[nums[i] + 10000]++;}// 3. 從大到小遍歷桶(即從最大值到最小值)for (int i = 20000; i >= 0; i--) {// 每訪問一個桶,就相當于從最大值開始往下數 k 個k -= buckets[i];if (k <= 0) {// 桶索引還原為原值:i - 10000return i - 10000;}}return 0; // 理論上不會走到這里
}
快速排序
遞歸+分區+互換值
// 分治快排
class QuickSort {public void quickSort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) return; // 遞歸結束條件 索引int pivotIndex = partition(nums, left, right); // 找到 pivot 位置quickSort(nums, left, pivotIndex - 1); // 排序左半部分quickSort(nums, pivotIndex + 1, right); // 排序右半部分}// 分區函數private int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right) {int pivot = nums[right]; // 選取最后一個元素作為 pivotint i = left; // i 指向比 pivot 小的區域的末尾for (int j = left; j < right; j++) {if (nums[j] < pivot) { // 如果當前元素比 pivot 小swap(nums, i, j);i++;}}swap(nums, i, right); // pivot 放到中間return i; // 返回 pivot 位置}// 交換值函數private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {int temp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = temp;}// 測試public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {3, 6, 8, 10, 1, 2, 1};QuickSort qs = new QuickSort();qs.quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);for (int num : arr) {System.out.print(num + " ");}}
}
棧
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();有效括號

class Solution {public boolean isValid(String s) {//特殊情況if(s.isEmpty()){return true;}//創建棧,字符類型Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();for(char c:s.toCharArray()){if(c == '('){stack.push(')');}else if(c == '{'){stack.push('}');}else if(c=='['){stack.push(']');}// 要先判斷是否為空,再判斷出棧else if(stack.empty() || c!=stack.pop()){return false;}}if(stack.empty()){return true;}return false;}
}每日溫度
stack.peek() 返回棧頂元素,但不彈出(空棧會拋出異常)
class Solution {public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {int n = temperatures.length;int[] result = new int[n];Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // 單調遞減棧,存索引for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 如果當前溫度比棧頂索引的溫度高,則計算等待天數while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {int prevIndex = stack.pop();result[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex;}// 當前索引入棧stack.push(i);}return result;}
}
字節面試題
?多線程交替打印0-100
2個線程交替打印0-100
public class Main {private static final Object LOCK = new Object();private static volatile int count = 0;private static final int MAX = 100;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Seq(0));Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Seq(1));thread.start();thread1.start();}static class Seq implements Runnable {private final int index;public Seq(int index) {this.index = index;}@Overridepublic void run() {// Run方法只要執行結束了,線程就結束了while (count < MAX) {// 同步代碼塊,一個時刻只能有一個線程獲取到鎖synchronized (LOCK) {// 獲取到鎖就進來判斷,當前是否輪到該線程打印while (count % 2 != index) {// 不是當前線程打印,那么就讓當前線程去wait,它會自動釋放鎖,所以其他線程可以進來try {LOCK.wait();// 當線程被喚醒時,會嘗試重新進入synchronized代碼塊} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 是當前線程打印, 但count>MAXif (count > MAX) {LOCK.notifyAll();return;}System.out.println("Thread-" + index + ":" + count);count++;LOCK.notifyAll();}}}}
}
public class Main {private static final Object LOCK = new Object();private static volatile int count = 0;private static final int MAX = 100;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Seq(0));Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Seq(1));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Seq(2));thread.start();thread1.start();thread2.start();}static class Seq implements Runnable {private final int index;public Seq(int index) {this.index = index;}@Overridepublic void run() {// Run方法只要執行結束了,線程就結束了while (count < MAX) {// 同步代碼塊,一個時刻只能有一個線程獲取到鎖synchronized (LOCK) {// 獲取到鎖就進來判斷,當前是否輪到該線程打印while (count % 3 != index) {// 不是當前線程打印,那么就讓當前線程去wait,它會自動釋放鎖,所以其他線程可以進來try {LOCK.wait();// 當線程被喚醒時,會嘗試重新進入synchronized代碼塊} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 是當前線程打印, 但count>MAXif (count > MAX) {LOCK.notifyAll();return;}System.out.println("Thread-" + index + ":" + count);count++;LOCK.notifyAll();}}}}
}多線程交替打印ABC
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
// 多線程打印ABC
public class Printer {private final Semaphore semA = new Semaphore(1); // 信號量A設置為1,從A開始打印private final Semaphore semB = new Semaphore(0);private final Semaphore semC = new Semaphore(0);private static int n = 3; // 打印輪次public static void main(String[] args) {Printer printer = new Printer();new Thread(()->printer.print('A',printer.semA,printer.semB)).start();new Thread(()->printer.print('B',printer.semB,printer.semC)).start();new Thread(()->printer.print('C',printer.semC,printer.semA)).start();}public void print(char ch, Semaphore current, Semaphore next) {try {for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {current.acquire(); // 獲取當前信號量System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + ch);next.release(); // 釋放下一個信號量}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}奇偶交換
給定數組,奇數在前,偶數在后
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {public static int[] jiaohuang(int[] nums){if(nums.length<2||nums == null){return nums;}int left = 0;int right = nums.length-1;while (left<right){// 選定偶數while (left<right && nums[left] % 2 !=0){left++;}// 選定奇數while (left<right && nums[right]%2 == 0){right--;}if(left < right){int temp = nums[left];nums[left] = nums[right];nums[right] = temp;left++;right--;}}return nums;}public static void main(String[] args){Solution solution = new Solution();int[] nums = {1,2,3,4};int[] result = solution.jiaohuang(nums);System.out.print(Arrays.toString(nums));}
}
字典序的第k小數字

// 字典序:數字的前綴進行排序,如10<9,因為10的前綴是1<9
// 數組{1,2,-,9,10,11,12}-->{1,10,11,12,2,--,9}
// 思路:當前指針+前綴數(非指針概念),當成一個(key,value)形式,cur為key,value = 前綴數
// 如果當前指針<目標指針,while循環,
// 計算當前數的節點數(如1-201,那么在1和2之間隔著10-19,100-199:節點數為1+10+10*10)
// 如果 當前指針 + 當前前綴節點 <=k,即不在k的范圍內,那么當前指針(下個前綴節點) = 當前指針 + 當前前綴節點,前綴數++
// else,在k的范圍內,那么當前指針 = cur指針+1,前綴數*10更加細分
//(其實這里有點無限迭代的意思,判斷在10-19區間還是繼續細分在100-109~190-199區間,但n是固定的,有限迭代)
public int findKthNumber(int n, int k) {long cur = 1; // 當前指針對應long prix = 1; // 當前前綴數,可以把當成一個(key,value)形式,cur為key,value = 前綴數while (cur < k){long prixNum = getCount(prix,n);// 當前前綴節點數量// k不在當前前綴數if(cur+prixNum <= k){cur+=prixNum; // 下個指針 = 當前指針+節點數prix++; // 前綴數++}else {cur++; // 在當前前綴循環,從1變成10,指針從索引0(1)到索引1(10)prix*=10; // 前綴細分}}return (int)prix;}// 當前前綴下的所有子節點數總和=下一個前綴的起點-當前前綴的起點public long getCount(long prix,long n){long count = 0;// 節點數量long prixNext = prix+1; // 下一個前綴數while (prix <= n){count += Math.min(n-1,prixNext)-prix;prix*=10;prixNext*=10;}return count;}








)
的全流程深度解析)

)






:ChatClient詳解,優雅的流式API設計)
預處理詳解)
)


