REST 服務可用于實現兩個應用之間的通訊,包括 Web 應用中的客戶端和服務器之間,移動應用與后端服務之間,或兩個后端服務之間。
10.1 使用 REST 服務在應用之間交換數據
REST端點是應用程序通過 Web 協議公開服務的方式,因此也稱為 Web 服務。
在 Spring 中,REST 端點仍然是映射到 HTTP 方法和路徑的控制器操作。但對于 REST 服務, Spring MVC 調度器 servlet 不會查找視圖,服務器在 HTTP 響應中直接向客戶端返回控制器操作的返回內容。
REST 端點需注意以下問題:
- 如果控制器的操作需要很長時間才能完成,對端點的 HTTP 調用可能會超時并中斷通信。
- 不建議在一次調用中發送大量數據(例如幾兆字節),可能會導致調用超時并中斷通信。
- 端點上過多的并發調用可能導致應用失敗。
- REST 端點調用可能因為網絡原因而失敗。
總之,要考慮對失效情況的處理。作者推薦了J. J. Geewax的API Design
Patterns (Manning, 2021)一書。
10.2 實現 REST 端點
Spring 在 REST 端點后面使用相同的 Spring MVC 機制。
看一下示例sq-ch10-ex1。本例非常簡單,沒有HTML文件,只有一個控制類HelloController :
@Controller
public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello")@ResponseBodypublic String hello() {return "Hello!";}@GetMapping("/ciao")@ResponseBodypublic String ciao() {return "Ciao!";}
}
注解@Controller和@GetMapping上一章都講過了,唯一新的注解是@ResponseBody。它的作用是告知調度 servlet,控制器的操作不會返回視圖名稱,而是直接在 HTTP 響應中發送數據。
本例和后續示例需要安裝postman:
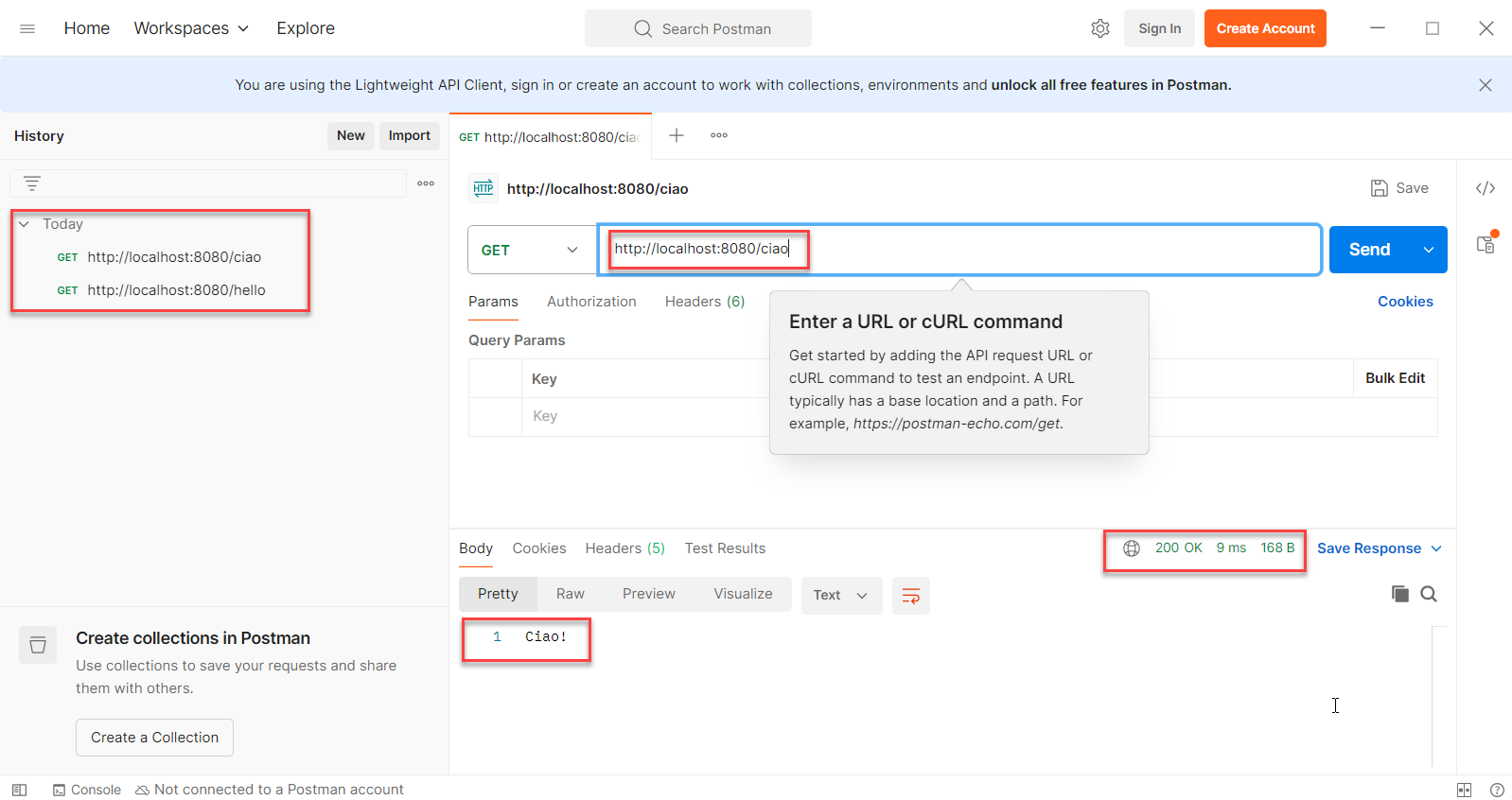
或者也可以命令行工具cURL(Ciao是意大利語的Hello):
$ curl http://localhost:8080/hello
Hello!
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/ciao
Ciao!
示例sq-ch10-ex2和上例的效果完全一樣,只不過使用注解@RestController,他是@Controller 和 @ResponseBody 的組合。
@RestController
public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello() {return "Hello!";}@GetMapping("/ciao")public String ciao() {return "Ciao!";}
}10.3 管理 HTTP 響應
HTTP 響應是指后端應用根據客戶端請求將數據返回給客戶端的方式,包含以下數據:
- 響應頭:響應中的短數據片段(通常不超過幾個字)
- 響應正文:返回的大量數據
- 響應狀態
此處建議閱讀附錄C:HTTP簡介。
10.3.1 將對象作為響應主體發送
示例sq-ch10-ex3和上例非常類似,只不過返回值從字符串變為對象(此對象也稱為DTO,即data transfer object)。
看一下控制類:
@RestController
public class CountryController {@GetMapping("/france")public Country france() {Country c = Country.of("France", 67);return c;}@GetMapping("/all")public List<Country> countries() {Country c1 = Country.of("France", 67);Country c2 = Country.of("Spain", 47);return List.of(c1,c2);}
}
應用運行如下:
$ curl http://localhost:8080/all
[{"name":"France","population":67},{"name":"Spain","population":47}]$ curl http://localhost:8080/france
{"name":"France","population":67}
返回的對象為JSON格式。使用 REST 端點時,JSON 是最常見的對象表示方式(當然你也可以用XML或YAML)。此處建議閱讀附錄D:使用 JSON 格式。
10.3.2 設置響應狀態和標頭
在某些情況下,會要求自定義 HTTP 響應狀態,其最簡單、最常用的方法是使用 ResponseEntity 類。Spring 提供的這個類允許您指定 HTTP 響應的主體、狀態和標頭。詳見示例sq-ch10-ex4。
model類和上例一樣,控制類變為如下:
@RestController
public class CountryController {@GetMapping("/france")public ResponseEntity<Country> france() {Country c = Country.of("France", 67);return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.ACCEPTED).header("continent", "Europe").header("capital", "Paris").header("favorite_food", "cheese and wine").body(c);}
}
程序運行如下:
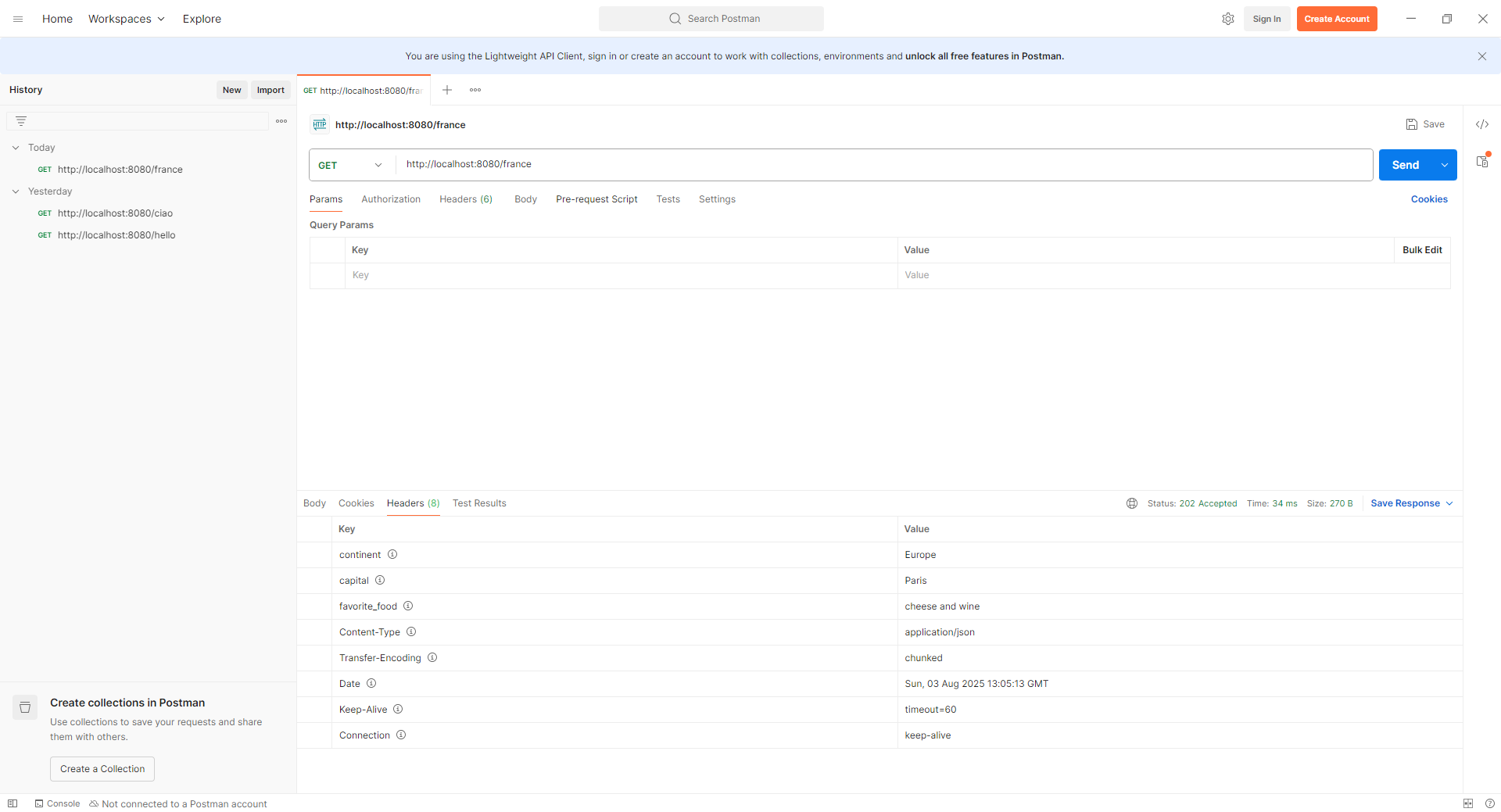
$ curl -v http://localhost:8080/france
* Host localhost:8080 was resolved.
* IPv6: ::1
* IPv4: 127.0.0.1
* Trying [::1]:8080...
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8080
* using HTTP/1.x
> GET /france HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8080
> User-Agent: curl/8.12.1
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 202
< continent: Europe
< capital: Paris
< favorite_food: cheese and wine
< Content-Type: application/json
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
< Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 13:02:47 GMT
<
{"name":"France","population":67}* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
其中202對應HttpStatus.ACCEPTED。
postman運行輸出如下:
10.3.3 在端點級別管理異常
在很多情況下,我們會使用異常來指示特定情況,其中一些與業務邏輯相關。在這種情況下,您可能需要在 HTTP 響應中設置一些詳細信息,以告知客戶端發生的具體情況。管理異常的方法之一是在控制器的操作中捕獲異常,并使用ResponseEntity 類,在發生異常時發送不同的響應配置。
參見示例sq-ch10-ex5。來看一下控制類的主體部分:
@PostMapping("/payment")public ResponseEntity<?> makePayment() {try {PaymentDetails paymentDetails = paymentService.processPayment();return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.ACCEPTED).body(paymentDetails);} catch (NotEnoughMoneyException e) {ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails();errorDetails.setMessage("Not enough money to make the payment.");return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(errorDetails);}}
運行輸出如下:
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/payment
{"message":"Not enough money to make the payment."}
上述錯誤處理方法雖然可行,但在更復雜的應用程序中,將異常管理分離處理會更方便。這樣可以減少重復代碼,因為有時同一個異常可能被多個端點復用。其次,當你需要理解特定情況的工作原理時,知道在一個地方找到所有異常邏輯會更方便。因此,推薦使用 REST 控制器建議,這是一個可以攔截控制器操作拋出的異常并根據攔截到的異常應用自定義邏輯的切面。
在示例sq-ch10-ex6中,控制類PaymentController不再進行異常處理,因此代碼大大簡化:
@RestController
public class PaymentController {private final PaymentService paymentService;public PaymentController(PaymentService paymentService) {this.paymentService = paymentService;}@PostMapping("/payment")public ResponseEntity<PaymentDetails> makePayment() {PaymentDetails paymentDetails = paymentService.processPayment();return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.ACCEPTED).body(paymentDetails);}
}
錯誤處理的工作由advice類ExceptionControllerAdvice 專門負責:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionControllerAdvice {@ExceptionHandler(NotEnoughMoneyException.class)public ResponseEntity<ErrorDetails> exceptionNotEnoughMoneyHandler() {ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails();errorDetails.setMessage("Not enough money to make the payment.");return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(errorDetails);}
}
輸出和上例一樣。
10.4 使用請求主體從客戶端獲取數據
前面已經使用HTTP 請求參數從客戶端到服務器傳輸少量數據,傳輸大量數據則可以用HTTP 請求正文(request body)。
要使用請求正文,只需使用 @RequestBody 注解控制器操作的參數即可。默認情況下,Spring 會假定您使用 JSON 來表示注解的參數,并嘗試將 JSON 字符串解碼為參數類型的實例。如果無法將 JSON 格式的字符串解碼為該類型,應用將返回狀態為“400 Bad Request”的響應。
參見示例sq-ch10-ex7。核心代碼為控制類:
@RestController
public class PaymentController {private static Logger logger =Logger.getLogger(PaymentController.class.getName());@PostMapping("/payment")public ResponseEntity<PaymentDetails> makePayment(@RequestBody PaymentDetails paymentDetails) {logger.info("Received payment " + paymentDetails.getAmount());return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.ACCEPTED).body(paymentDetails);}
}
程序輸出如下:
$ curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8080/payment -d '{"amount": 1000}' -H "Content-Type: application/json"
{"amount":1000.0}
HTTP GET也支持請求正文,詳見RFC 7231。
總結
- 表述性狀態轉移 (REST) Web 服務是在兩個應用程序之間建立通信的一種簡單方法。
- 在 Spring 應用中,Spring MVC 機制支持 REST 端點的實現。您需要使用 @ResponseBody 注解來指定方法直接返回響應主體,或者將 @Controller 注解替換為 @RestController 來實現 REST 端點。如果您不使用上述任何一種注解,調度器 Servlet 將假定控制器的方法返回的是視圖名稱,并嘗試查找該視圖。
- 您可以讓控制器的操作直接返回 HTTP 響應主體,并依賴 Spring 默認的 HTTP 狀態行為。
- 您可以通過讓控制器的操作返回 ResponseEntity 實例來管理 HTTP 狀態和標頭。
- 管理異常的一種方法是直接在控制器的操作級別處理它們。這種方法將處理異常的邏輯與特定的控制器操作耦合在一起。有時,使用這種方法會導致代碼重復,最好避免這種情況。
- 您可以直接在控制器的操作中管理異常,或者使用 REST 控制器建議類來分離控制器的操作拋出異常時執行的邏輯。
- 端點可以通過 HTTP 請求中的請求參數、路徑變量或 HTTP 請求正文從客戶端獲取數據。





![week3-[二維數組]小方塊](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/week3-[二維數組]小方塊)


)
)






![[Git] 如何拉取 GitHub 倉庫的特定子目錄](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Git] 如何拉取 GitHub 倉庫的特定子目錄)

