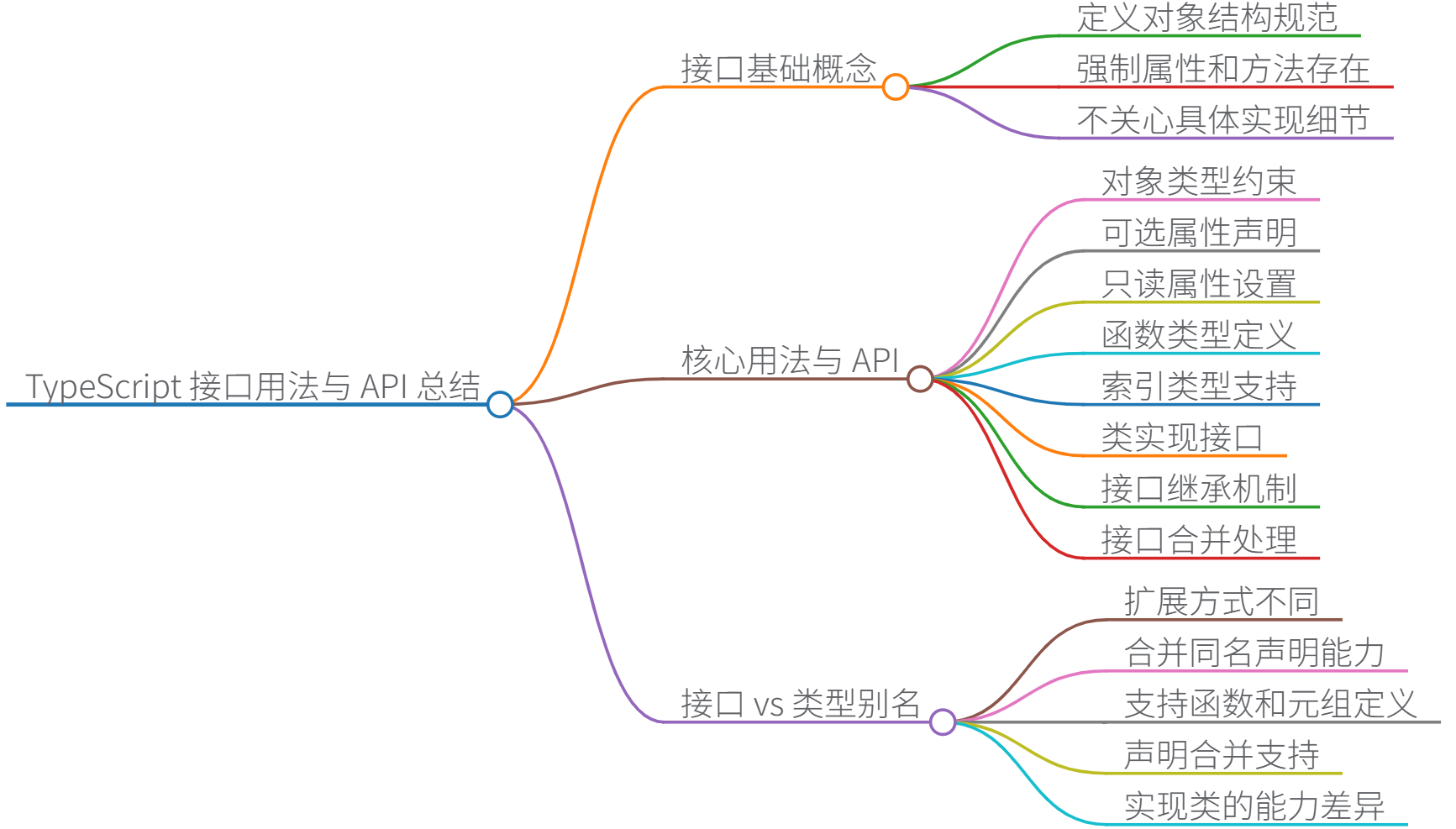
一、接口基礎概念
????????接口(interface)是 TypeScript 的核心類型系統工具,用于定義對象的結構規范。它不關心具體實現細節,只強制要求符合接口定義的對象必須包含指定屬性和方法。例如:
interface Person {name: string;age: number;greet(): void;
}
二、核心用法與 API
1.對象類型約束
最基礎用法是聲明對象形狀:
interface User {id: number;username: string;
}
const admin: User = { id: 1, username: "admin" }; // ? 符合接口
2.可選屬性
通過 ? 聲明非必需屬性:
interface Config {url: string;timeout?: number; // 可選
}
3.只讀屬性
用 readonly 防止修改:
interface Point {readonly x: number;readonly y: number;
}
4.函數類型
定義函數簽名:
interface SearchFunc {(source: string, keyword: string): boolean;
}
const mySearch: SearchFunc = (src, kw) => src.includes(kw);
5.索引類型
支持動態鍵值對(數字/字符串索引):
// 數字索引
interface NumMap {[index: number]: string;
}
const arr: NumMap = ["TS", "JS"]; // arr[0]="TS"// 字符串索引
interface StrMap {[key: string]: number;
}
const dict: StrMap = { "A": 65, "B": 66 }; // dict["A"]=65
6.類實現接口
強制類滿足特定契約(面向對象):
interface ClockInterface {currentTime: Date;setTime(d: Date): void;
}class Clock implements ClockInterface {currentTime: Date = new Date();setTime(d: Date) { this.currentTime = d; }
}
7.接口繼承
支持單繼承或多繼承:
interface Shape { color: string; }
interface Circle extends Shape { radius: number; }const c: Circle = { color: "red", radius: 10 }; // ?
8.接口合并
同名接口自動合并(擴展第三方庫常用):
interface Box { width: number; }
interface Box { height: number; }
// 合并后: { width: number; height: number; }
三、接口 vs 類型別名(type)
| 特性 | interface | type |
|---|---|---|
| 擴展方式 | 繼承(extends) | 交叉類型(&) |
| 合并同名聲明 | ? 自動合并 | ? 報錯 |
| 函數/元組定義 | ? 支持 | ? 支持 |
| 聲明合并 | ? | ? |
| 實現類 | ??implements | ? 僅對象類型 |
最佳實踐:優先使用
interface定義對象結構,用type處理聯合類型或復雜類型運算。
四、高級技巧
1.混合類型
組合函數和對象屬性:
interface Counter {(start: number): void;interval: number;reset(): void;
}
2.索引簽名約束
限制索引值類型必須匹配特定屬性:
interface Foo {[key: string]: number;bar: number; // ?// baz: string; ? 違反索引簽名
}
五、常見錯誤解決方案
屬性缺失錯誤 → 檢查是否遺漏必需屬性或誤用可選屬性
類型不匹配錯誤 → 確認屬性類型是否精確符合接口定義
索引簽名沖突 → 確保所有顯式屬性符合索引簽名類型
接口的核心價值在于 定義契約 而非實現,這是構建可維護大型項目的關鍵。












:Linux原生線程庫相關接口)




 ——易格斯igus)
采集系統(二):門診發藥后端)
