前言
在前一章中,我們設計了強大的注解API。本章將深入探討配置管理系統的設計,學習如何將注解中的聲明式配置轉換為運行時可用的配置對象。
配置管理的核心挑戰
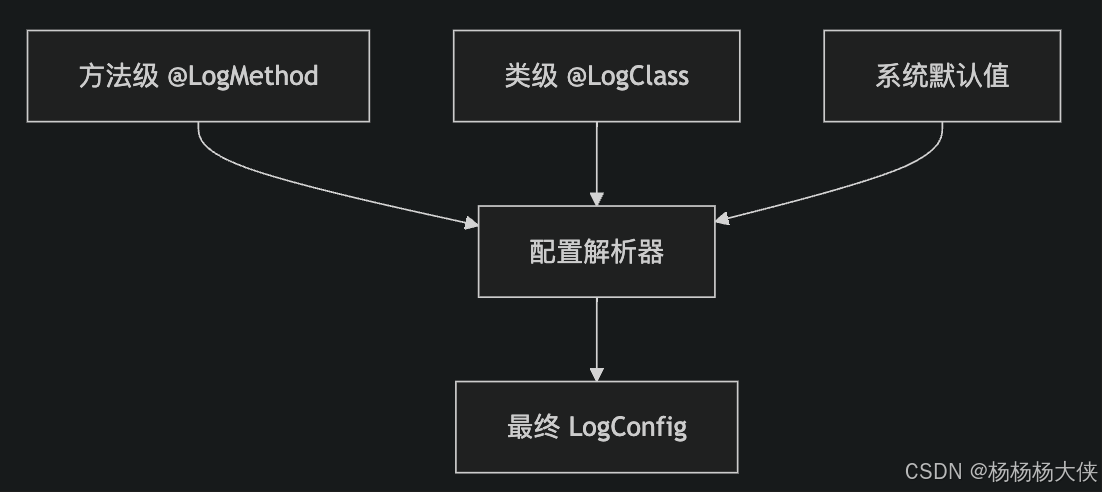
在我們的框架中,配置來源有三個層級:
主要挑戰:
- 🔀 優先級處理:如何正確合并不同層級的配置
- 🎯 類型安全:確保配置值的類型正確性
- ? 性能優化:避免重復解析和計算
- 🛡? 配置驗證:及早發現配置錯誤
LogConfig - 統一配置模型
LogConfig是框架配置管理的核心,承載著從注解解析出來的所有配置信息:
package com.simpleflow.log.config;import com.simpleflow.log.annotation.LogLevel;/*** 日志配置類 - 統一管理所有日志相關的配置項*/
public class LogConfig {// ========== 基礎配置 ==========private LogLevel level;private Boolean logArgs;private Boolean logResult;private Boolean logExecutionTime;private Boolean logException;// ========== 消息模板配置 ==========private String prefix;private String startMessage;private String successMessage;private String errorMessage;// ========== 高級配置 ==========private Boolean enableSpel;private Boolean includeRequestId;private int[] excludeArgs;private String[] sensitiveFields;// ========== 類級專用配置 ==========private String[] includeMethods;private String[] excludeMethods;private Boolean includePrivateMethods;private Boolean includeGetterSetter;/*** 合并配置 - 當前配置的非空值會覆蓋other配置的對應值*/public LogConfig merge(LogConfig other) {if (other == null) {return new LogConfig(this);}LogConfig merged = new LogConfig();// 基礎配置合并(當前配置優先)merged.level = this.level != null ? this.level : other.level;merged.logArgs = this.logArgs != null ? this.logArgs : other.logArgs;merged.logResult = this.logResult != null ? this.logResult : other.logResult;merged.logExecutionTime = this.logExecutionTime != null ? this.logExecutionTime : other.logExecutionTime;merged.logException = this.logException != null ? this.logException : other.logException;// 字符串配置合并merged.prefix = mergeString(this.prefix, other.prefix);merged.startMessage = mergeString(this.startMessage, other.startMessage);merged.successMessage = mergeString(this.successMessage, other.successMessage);merged.errorMessage = mergeString(this.errorMessage, other.errorMessage);// 高級配置合并merged.enableSpel = this.enableSpel != null ? this.enableSpel : other.enableSpel;merged.includeRequestId = this.includeRequestId != null ? this.includeRequestId : other.includeRequestId;// 數組配置合并merged.excludeArgs = mergeIntArray(this.excludeArgs, other.excludeArgs);merged.sensitiveFields = mergeStringArray(this.sensitiveFields, other.sensitiveFields);return merged;}/*** 創建默認配置*/public static LogConfig createDefault() {LogConfig config = new LogConfig();config.level = LogLevel.INFO;config.logArgs = true;config.logResult = true;config.logExecutionTime = true;config.logException = true;config.prefix = "";config.startMessage = "方法開始執行";config.successMessage = "方法執行成功";config.errorMessage = "方法執行異常";config.enableSpel = true;config.includeRequestId = true;config.excludeArgs = new int[0];config.sensitiveFields = new String[0];config.includeMethods = new String[0];config.excludeMethods = new String[0];config.includePrivateMethods = false;config.includeGetterSetter = false;return config;}// 工具方法private String mergeString(String current, String other) {return !isEmpty(current) ? current : other;}private boolean isEmpty(String str) {return str == null || str.trim().isEmpty();}// 省略getter/setter和其他方法...
}
AnnotationConfigResolver - 配置解析器
配置解析器負責將注解轉換為LogConfig對象,并處理配置的合并邏輯:
package com.simpleflow.log.processor;import com.simpleflow.log.annotation.*;
import com.simpleflow.log.config.LogConfig;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;/*** 注解配置解析器*/
public class AnnotationConfigResolver {// 配置緩存,提升性能private final ConcurrentHashMap<Method, LogConfig> methodConfigCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, LogConfig> classConfigCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final LogConfig defaultConfig;public AnnotationConfigResolver() {this.defaultConfig = LogConfig.createDefault();}/*** 解析方法的完整配置* 合并優先級:方法配置 > 類配置 > 默認配置*/public LogConfig resolveMethodConfig(Method method) {if (method == null) {return null;}// 檢查緩存LogConfig cached = methodConfigCache.get(method);if (cached != null) {return cached;}try {// 1. 檢查是否被忽略if (method.isAnnotationPresent(LogIgnore.class)) {methodConfigCache.put(method, null);return null;}// 2. 解析方法級配置LogConfig methodConfig = resolveMethodAnnotation(method);// 3. 解析類級配置LogConfig classConfig = resolveClassConfig(method.getDeclaringClass());// 4. 檢查類級配置是否包含此方法if (classConfig != null && !isMethodIncluded(method, classConfig)) {methodConfigCache.put(method, null);return null;}// 5. 合并配置:方法 > 類 > 默認LogConfig finalConfig = mergeConfigs(methodConfig, classConfig, defaultConfig);// 6. 驗證和緩存結果if (finalConfig != null) {finalConfig.validate();}methodConfigCache.put(method, finalConfig);return finalConfig;} catch (Exception e) {return null;}}/*** 解析類級配置*/public LogConfig resolveClassConfig(Class<?> clazz) {if (clazz == null) {return null;}LogConfig cached = classConfigCache.get(clazz);if (cached != null) {return cached;}LogConfig classConfig = null;if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(LogClass.class)) {LogClass logClass = clazz.getAnnotation(LogClass.class);classConfig = createConfigFromClass(logClass);}classConfigCache.put(clazz, classConfig);return classConfig;}/*** 從@LogMethod注解創建配置*/private LogConfig resolveMethodAnnotation(Method method) {if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(LogMethod.class)) {return null;}LogMethod logMethod = method.getAnnotation(LogMethod.class);LogConfig config = new LogConfig();// 基礎配置config.setLevel(logMethod.level());config.setLogArgs(logMethod.logArgs());config.setLogResult(logMethod.logResult());config.setLogExecutionTime(logMethod.logExecutionTime());config.setLogException(logMethod.logException());// 消息模板config.setPrefix(emptyToNull(logMethod.prefix()));config.setStartMessage(emptyToNull(logMethod.startMessage()));config.setSuccessMessage(emptyToNull(logMethod.successMessage()));config.setErrorMessage(emptyToNull(logMethod.errorMessage()));// 高級配置config.setEnableSpel(logMethod.enableSpel());config.setIncludeRequestId(logMethod.includeRequestId());if (logMethod.excludeArgs().length > 0) {config.setExcludeArgs(logMethod.excludeArgs());}if (logMethod.sensitiveFields().length > 0) {config.setSensitiveFields(logMethod.sensitiveFields());}return config;}/*** 合并多個配置*/private LogConfig mergeConfigs(LogConfig methodConfig, LogConfig classConfig, LogConfig defaultConfig) {LogConfig result = defaultConfig.copy();if (classConfig != null) {result = result.merge(classConfig);}if (methodConfig != null) {result = result.merge(methodConfig);}return (methodConfig != null || classConfig != null) ? result : null;}// 其他工具方法...
}
配置優先級實戰示例
// 示例:配置的繼承和覆蓋
@LogClass(level = LogLevel.WARN, // 類級默認:WARN級別logArgs = true, // 類級默認:記錄參數logResult = false, // 類級默認:不記錄返回值prefix = "用戶服務" // 類級前綴
)
public class UserService {// 繼承類級配置public List<User> findAll() {// 最終配置:level=WARN, logArgs=true, logResult=false, prefix="用戶服務"}// 部分覆蓋類級配置@LogMethod(logResult = true) // 只覆蓋 logResultpublic User findById(Long id) {// 最終配置:level=WARN, logArgs=true, logResult=true, prefix="用戶服務"}// 完全覆蓋類級配置@LogMethod(level = LogLevel.DEBUG,logArgs = false,prefix = "查詢服務")public User findByUsername(String username) {// 最終配置:level=DEBUG, logArgs=false, logResult=false, prefix="查詢服務"}// 忽略日志記錄@LogIgnore(reason = "內部工具方法")private String formatUserInfo(User user) {// 不會記錄任何日志}
}
測試用例
package com.simpleflow.log.processor;import com.simpleflow.log.annotation.*;
import com.simpleflow.log.config.LogConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;class AnnotationConfigResolverTest {private final AnnotationConfigResolver resolver = new AnnotationConfigResolver();@Testvoid testMethodConfigOverridesClassConfig() throws Exception {Method method = TestService.class.getMethod("findById", Long.class);LogConfig config = resolver.resolveMethodConfig(method);assertNotNull(config);assertEquals(LogLevel.INFO, config.getLevel()); // 方法級覆蓋assertTrue(config.getLogResult()); // 方法級覆蓋assertEquals("用戶服務", config.getPrefix()); // 繼承類級}@Testvoid testIgnoredMethod() throws Exception {Method method = TestService.class.getMethod("ignoredMethod");LogConfig config = resolver.resolveMethodConfig(method);assertNull(config); // 被忽略的方法返回null}@LogClass(level = LogLevel.WARN, prefix = "用戶服務", logResult = false)static class TestService {@LogMethod(level = LogLevel.INFO, logResult = true)public User findById(Long id) {return new User();}@LogIgnore(reason = "測試忽略")public void ignoredMethod() {}}static class User {}
}
本章小結
? 完成的任務
- 設計LogConfig:統一的配置模型,支持合并和驗證
- 實現解析器:AnnotationConfigResolver負責注解解析
- 配置優先級:方法 > 類 > 默認的合并策略
- 性能優化:通過緩存提升解析性能
- 測試驗證:編寫測試用例驗證功能
🎯 學習要點
- 配置分層:多層級配置的設計思路
- 合并策略:如何優雅地處理配置優先級
- 緩存機制:提升框架性能的重要手段
- 配置驗證:保證配置有效性的機制
💡 思考題
- 為什么要設計配置緩存機制?
- 如何處理配置的循環依賴問題?
- 配置合并還有哪些策略可以考慮?
🚀 下章預告
下一章我們將進入AOP切面編程的世界,學習如何使用Spring AOP實現無侵入式的日志攔截。我們將實現LogMethodAspect和LogClassAspect,掌握切點表達式和環繞通知的使用技巧。
💡 設計原則: 好的配置管理應該是靈活、高效、易于理解的。通過分層設計和緩存優化,我們既保證了功能的完整性,又確保了良好的性能表現。



)












![[特殊字符] 數據庫知識點總結(SQL Server 方向)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[特殊字符] 數據庫知識點總結(SQL Server 方向))


