文章目錄
- 一. 線程創建(start)
- (一)繼承Thread類,重寫run
- (二)繼承Runnable類,重寫run
- (三)Thread匿名內部類重寫
- (四)Runnable匿名內部類重寫
- (五)lambda表達式
- 二. 線程的關鍵屬性
- (一)線程名稱
- (二)線程是否為后臺線程
- 1. 前臺線程
- 2. 后臺線程
- 3. 查看是否是后臺線程(isDaemon)
- 4. 設置后臺線程(setDaemon)代碼及效果圖
- (三)線程是否存活
- 1. 是否存活isAlive
- 2. 代碼及效果圖
- 三. 線程終止(interrupt)
- (一)Java提供的API
- 1. 用法
- 2. 代碼及效果圖
- (二)手動設置條件
- 1. 用法
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- 四. 線程等待(join)
- (一)定義
- (二)代碼及其效果圖
- 五. 獲取線程引用(currentThread)
- (一)用法
- (二)代碼及其效果圖
- 六. 線程休眠(sleep)
- (一)定義
- (二)代碼
- 七. 線程狀態
- (一)NEW
- 1. 定義
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- (二)TERMINATED
- 1. 定義
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- (三)RUNNABLE
- 1. 定義
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- (四)TIMED_WAITING
- 1. 定義
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- (五)WAITING
- 1. 定義
- 2. 代碼及其效果圖
- (六)BLOCKED&LOCK
- (①)
- (②)
- (③)
一. 線程創建(start)
(一)繼承Thread類,重寫run
class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Thread!!!");try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}public class demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new MyThread();thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println("main!!!");Thread.sleep(100);}}
}
(二)繼承Runnable類,重寫run
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Thread!");}}
}public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println("main!");}}
}
(三)Thread匿名內部類重寫
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-11* Time: 20:06*/
public class demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Thread~~");try {Thread.sleep(0);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}};thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println("main~~");Thread.sleep(0);}}
}(四)Runnable匿名內部類重寫
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-11* Time: 20:14*/
public class demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("thread~");try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}};Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println("main~");Thread.sleep(100);}}
}(五)lambda表達式
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {System.out.println("thread!");try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"阿然");thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println("main!");Thread.sleep(10);}}
}
二. 線程的關鍵屬性
(一)線程名稱
線程名字,我們可以通過setName方法來設置線程的名字,方便后期調試
通過getName方法可以獲取線程名稱
(二)線程是否為后臺線程
1. 前臺線程
當前臺線程還在運行時,即使其他所有線程都運行完,進程也不停止,要等待前臺線程結束,進程才結束
2. 后臺線程
當所有前臺線程運行完畢時,即使后臺線程還有任務沒有完成,也會終止進程
3. 查看是否是后臺線程(isDaemon)
是否是后臺線程通過isDeamon方法來查看
Java中線程創建時默認是前臺線程
4. 設置后臺線程(setDaemon)代碼及效果圖
public class demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {System.out.println("thread~~~");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"thread");thread.setDaemon(true);thread.start();System.out.println(thread.isDaemon());for (int i = 0; i < 1 ; i++) {System.out.println("main");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}

(三)線程是否存活
1. 是否存活isAlive
Java中Thread對象與CPU內核中的線程是一一對應的,但是有可能出現內核的線程已經摧毀了,而Thread對象還存在的情況
可以使用isAlive方法來查看線程是否存活
2. 代碼及效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-11* Time: 20:38*/
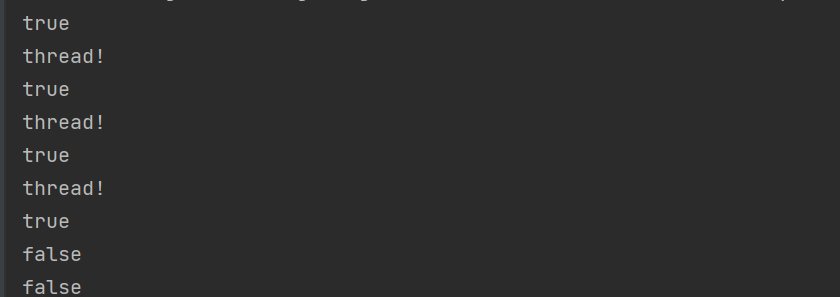
public class demo8 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("thread!");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println(thread.isAlive());Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
三. 線程終止(interrupt)
(一)Java提供的API
1. 用法
1.Java中提供了控制線程結束的方法interrupted與isInterrupted
2. isInterrupted默認是false,在循環中取反使用來運行線程任務
3. 調用interrupt讓isInterrupted置為true
4. 需要注意的是sleep休眠函數會使isInterrupted再次置為false
2. 代碼及效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-11* Time: 20:52*/
public class demo10_interrupt {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {//throw new RuntimeException(e);break;}}System.out.println("進程結束");},"thread");thread.start();Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("main嘗試終止");thread.interrupt();}
}
(二)手動設置條件
1. 用法
1. 手動設置循環關閉條件時,布爾條件需要是成員變量
2. 如果是局部變量那么布爾條件則不能改變,這樣達不到關閉循環從而關閉線程的效果
3. 這是因為每次線程調度切換回該線程時,會從重新棧當中調取變量,如果局部變量則存在銷毀可能,無法調取
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-11* Time: 20:47*/
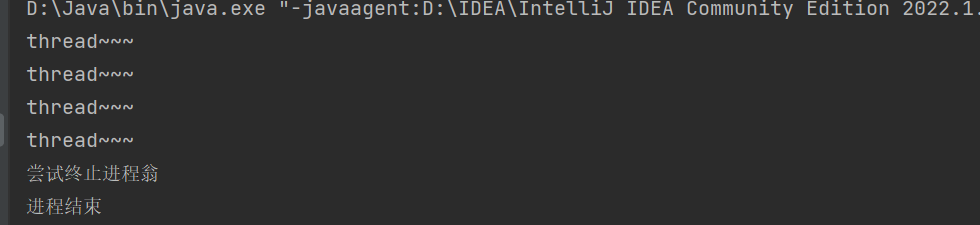
public class demo9 {private static boolean isFinish = false;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (!isFinish) {System.out.println("thread~~~");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("進程結束");},"thread");thread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {Thread.sleep(1000);}System.out.println("嘗試終止進程翁");isFinish = true;}
}
四. 線程等待(join)
(一)定義
1.Java中線程等待函數時join
2. 線程1調用join,線程1就是被等待的線程,要等到線程1結束后才能結束進程
3. join可以設置等待時間,在設定的等待時間結束后,不論線程1是否完成任務,都不再等待,結束進程
4. join會拋出一個InterruptedException異常
(二)代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:08*/
public class demo11_join {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("thread ~");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("thread 線程結束!");});thread.start();thread.join(4000);System.out.println("main 線程結束!");}
}

五. 獲取線程引用(currentThread)
(一)用法
- Java中Thread封裝了獲取當前線程的API,即currentThread方法
- currentThread方法是靜態方法,可以直接用類名Thread調用
(二)代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-13* Time: 21:46*/
public class demo_currentThread {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread main = Thread.currentThread();Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("thread@");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("thread 線程結束");});thread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("main@");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("main 結束");}
}
六. 線程休眠(sleep)
(一)定義
1 Java中休眠方法是sleep
2. sleep方法是靜態方法,可以直接用Thread調用
3. 調用sleep方法會拋出InterruptedException異常
(二)代碼
try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
七. 線程狀態
(一)NEW
1. 定義
線程還未創建的狀態,沒調用start
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:18*/
public class demo12_new {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread();System.out.println(thread.getState());}
}
(二)TERMINATED
1. 定義
線程終止狀態,運行完畢已經結束
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:21*/
public class demo13_TERMINATED {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {}});thread.start();while (true) {System.out.println(thread.getState());Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
(三)RUNNABLE
1. 定義
線程正在運行時狀態
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:28*/
public class demo14_RUNNABLE {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {}});thread.start();System.out.println(thread.getState());}
}
(四)TIMED_WAITING
1. 定義
有時間限制的等待的線程狀態
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:34*/
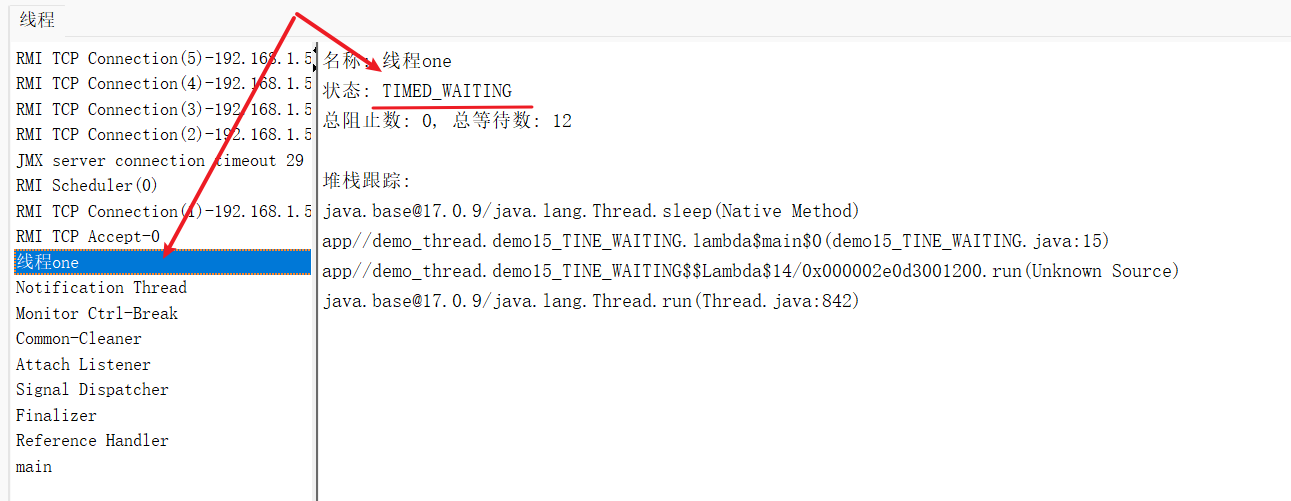
public class demo15_TINE_WAITING {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});thread.start();thread.join(1000*10000);}
}
(五)WAITING
1. 定義
沒有時間限制的等待的線程狀態
2. 代碼及其效果圖
package demo_thread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: 32309* Date: 2025-07-12* Time: 20:39*/
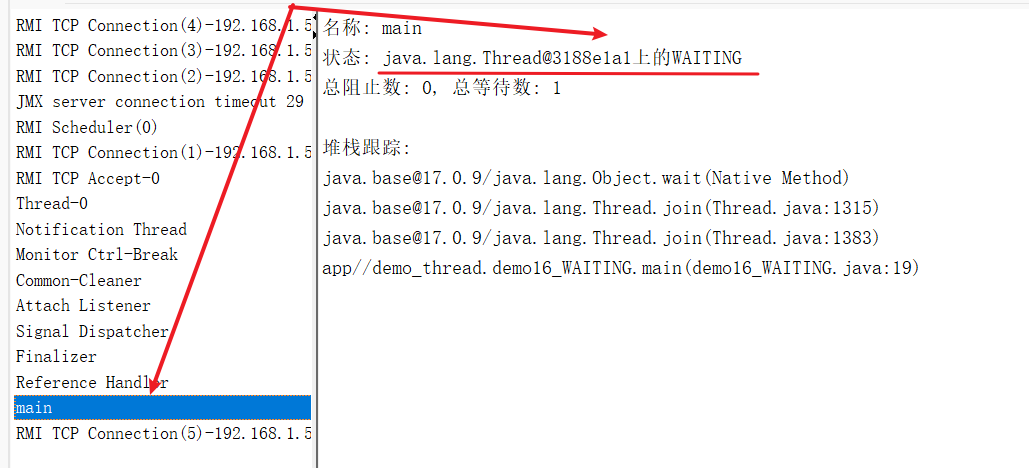
public class demo16_WAITING {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {}});thread.start();thread.join();}
}
(六)BLOCKED&LOCK
阻塞,這里我們只討論的是加鎖后阻塞,提到鎖,不得不談到死鎖,有三種情況:
①:一個線程同時加鎖兩次
②:兩個線程兩把鎖,一個線程獲取到一把鎖之后,再嘗試獲取另一把鎖時,加鎖形成循環,那么就會形成死鎖!
③:N個線程M把鎖,每個線程運轉都需要用到兩把鎖的時候,就會形成循環,造成死鎖阻塞
(①)
觀察下方實例,我們可以發現,用 synchronized 的時候對一個線程多次加鎖,不會觸發阻塞,這說明 synchronized 是可重入鎖!
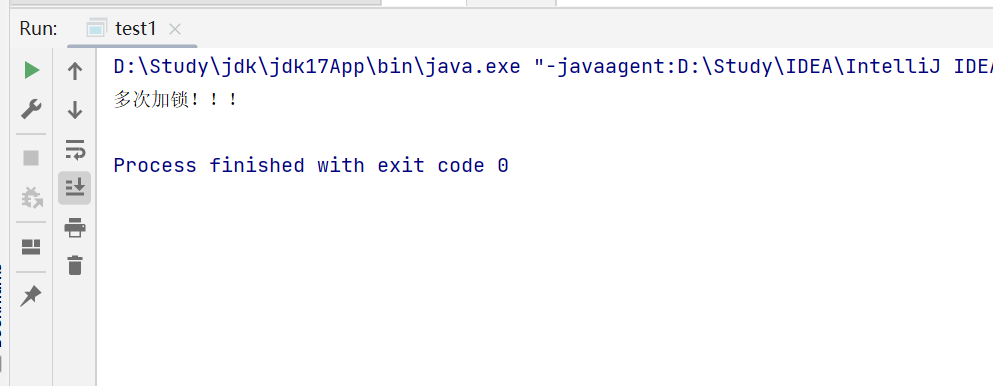
package test;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 9:53* 一個線程多次加鎖*/
public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Object lock = new Object();Thread thread1 = new Thread(() ->{synchronized (lock) {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("多次加鎖!!!");}} });thread1.start();}
}(②)
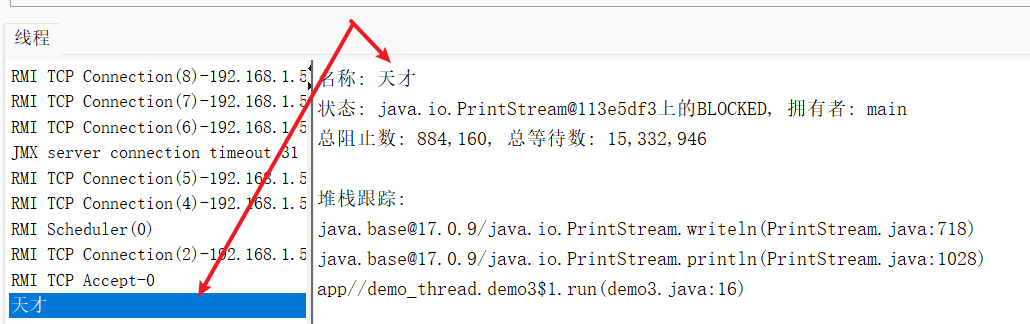
觀察下面的實例可以看出,線程1 對 lock1 加鎖后休眠1s, 再嘗試對第二個 lock2 加鎖時,會產生阻塞, 這是因為 線程2 已經對 lock2 加鎖成功, 又嘗試獲取 lock1 的時候產生了阻塞, 導致 lock2 沒有解鎖, 所以 線程1 嘗試獲取 lock2失敗, 產生阻塞, 相互循環, 形成死鎖
package test;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 10:26*/
public class test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Object lock1 = new Object();Object lock2 = new Object();Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock1) {System.out.println("獲取第一把鎖: lock1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}synchronized (lock2) {System.out.println("嘗試獲取第二把鎖: lock2");}}});Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock2) {System.out.println("獲取第一把鎖: lock2");synchronized (lock1) {System.out.println("嘗試獲取第二把鎖: lock1");}}});thread1.start();thread2.start();}
}(③)
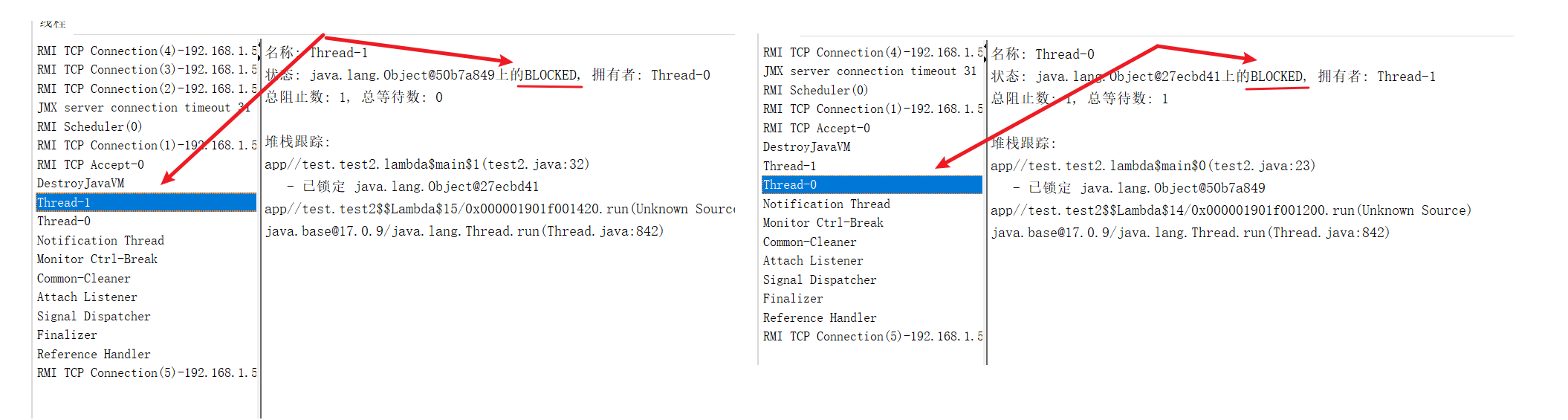
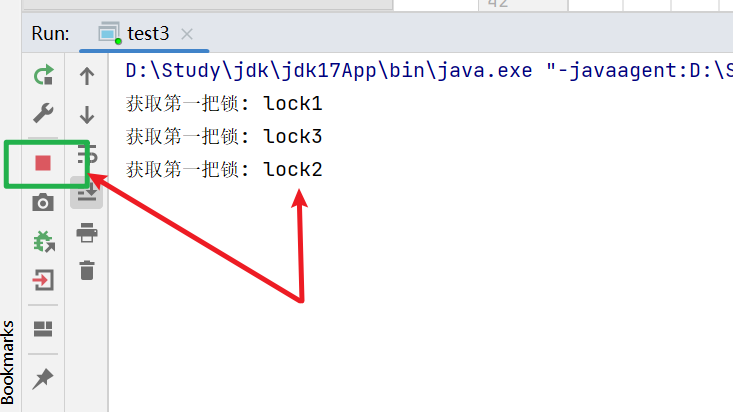
通過下方實例,我們可以看出, N個對象M把鎖, 當每個人都要嵌套兩把鎖才能工作時,就會形成阻塞
package test;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 10:54*/
public class test3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Object lock1 = new Object();Object lock2 = new Object();Object lock3 = new Object();Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock1) {System.out.println("獲取第一把鎖: lock1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}synchronized (lock2) {System.out.println("嘗試獲取第二把鎖: lock2");}}});Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock2) {System.out.println("獲取第一把鎖: lock2");synchronized (lock3) {System.out.println("嘗試獲取第二把鎖: lock3");}}});Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock3) {System.out.println("獲取第一把鎖: lock3");synchronized (lock1) {System.out.println("嘗試獲取第二把鎖: lock1");}}});thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start();}
}














)


)

