BeanFactory
BeanFactory和它的子接口們
BeanFactory 接口的所有子接口, 如下圖
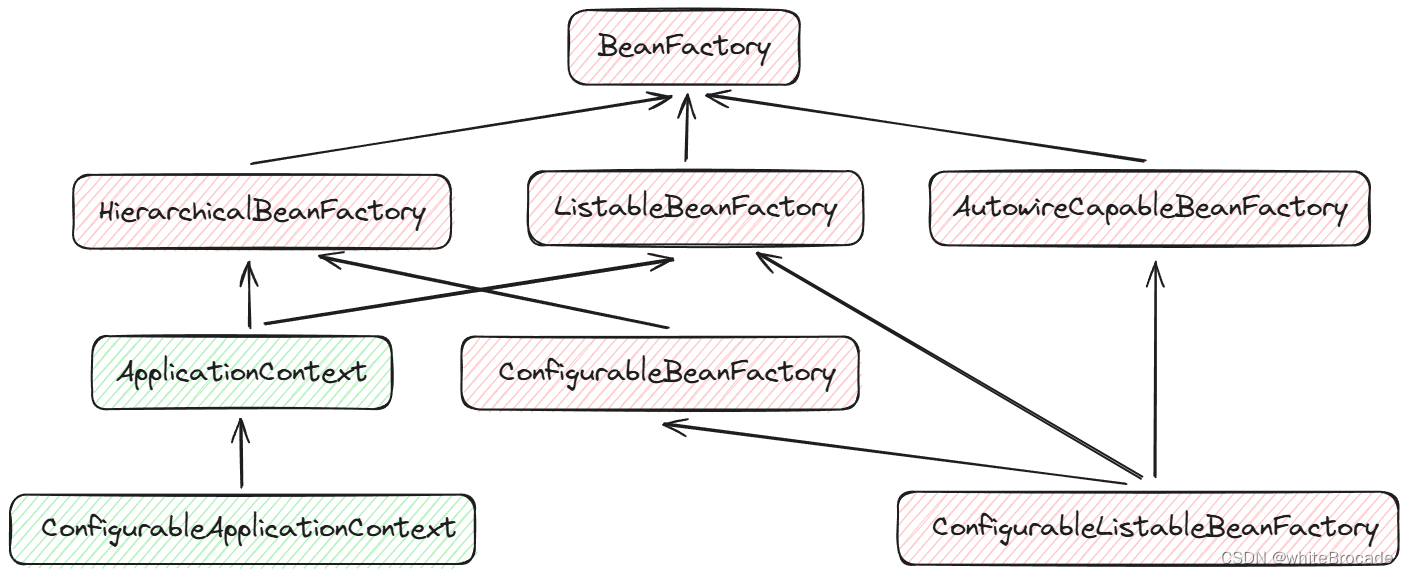
BeanFactory(根容器)-掌握
BeanFactory是根容器
The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container. This is the basic client view of a bean container; further interfaces such as
ListableBeanFactoryandorg.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactoryare available for specific purposes.翻譯:
用于訪問 SpringFramework bean 容器的根接口。這是 bean 容器的基本客戶端視圖。諸如
ListableBeanFactory和org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory之類的擴展接口可用于特定的用途。
- 結論: 解釋
BeanFactory是 SpringFramework 中管理 Bean 的容器, 它是最最基本的根接口, 下面的擴展都是為了實現某些額外的特性(層次性、可搜索性、可配置性等)
BeanFactory中定義的作用域概念
This interface is implemented by objects that hold a number of bean definitions, each uniquely identified by a String name. Depending on the bean definition, the factory will return either an independent instance of a contained object (the Prototype design pattern), or a single shared instance (a superior alternative to the Singleton design pattern, in which the instance is a singleton in the scope of the factory). Which type of instance will be returned depends on the bean factory configuration: the API is the same. Since Spring 2.0, further scopes are available depending on the concrete application context (e.g. “request” and “session” scopes in a web environment).
翻譯:
BeanFactory接口由包含多個 bean 定義的對象實現, 每個 bean 的定義信息均由 "name"進行唯一標識。根據 bean 的定義, SpringFramework 中的工廠會返回所包含對象的獨立實例 ( prototype , 原型模式 ) , 或者返回單個共享實例 ( singleton , 單例模式的替代方案, 其中實例是工廠作用域中的單例 ) 。返回 bean 的實例類型取決于 bean 工廠的配置:API是相同的。從 SpringFramework 2.0 開始, 根據具體的應用程序context ( 例如 Web 環境中的 request 和 session 作用域 ) , 可以使用更多作用域。
- 結論: 解釋了
BeanFactory中設計的作用域概念, 默認情況下,BeanFactory中的 Bean 只有單實例 Bean(singleton) 和原型 Bean(prototype) , 自打 SpringFramework2.0 開始, 出現了 Web 系列的作用域"request"和"session", 后續的又出現了"global session"和"websocket"作用域
BeanFactory集成了環境配置
The point of this approach is that the BeanFactory is a central registry of application components, and centralizes configuration of application components (no more do individual objects need to read properties files, for example). See chapters 4 and 11 of “Expert One-on-One J2EE Design and Development” for a discussion of the benefits of this approach.
翻譯:
這種方法的重點是
BeanFactory是應用程序組件的注冊中心, 并且它集成了應用程序組件的配置(例如不再需要單個對象讀取屬性文件)。有關此方法的好處的討論, 請參見《Expert One-on-One J2EE Design and Development》的第4章和第11章
- 結論: 解釋了
BeanFactory它本身是所有 Bean 的注冊中心, 所有的 Bean 最終都在BeanFactory中創建和保存。另外BeanFactory中還集成了配置信息。通過加載外部的 properties 文件, 借助 SpringFramework 的方式將配置文件的屬性值設置到 Bean 對象中
BeanFactory推薦使用DI而不是DL
Note that it is generally better to rely on Dependency Injection (“push” configuration) to configure application objects through setters or constructors, rather than use any form of “pull” configuration like a BeanFactory lookup. Spring’s Dependency Injection functionality is implemented using this BeanFactory interface and its subinterfaces.
翻譯:
請注意, 通常最好使用依賴注入("推"的配置), 通過setter方法或構造器注入的方式, 配置應用程序對象, 而不是使用任何形式的"拉"的配置(例如借助
BeanFactory進行依賴查找)。 SpringFramework 的 Dependency Injection 功能是使用BeanFactory接口及其子接口實現的
- 結論: SpringFramework 官方在 IOC 的兩種實現上的權衡:推薦使用 DI , 盡可能不要使用 DL。DI 的思想是"推", 它主張把組件需要的依賴"推"到組件的成員上;DL 的思想是"拉", 組件需要哪些依賴需要組件自己去 IOC 容器中"拉取"
BeanFactory支持多種類型的配置源
Normally a BeanFactory will load bean definitions stored in a configuration source (such as an XML document), and use the org.springframework.beans package to configure the beans. However, an implementation could simply return Java objects it creates as necessary directly in Java code. There are no constraints on how the definitions could be stored: LDAP, RDBMS, XML, properties file, etc. Implementations are encouraged to support references amongst beans (Dependency Injection).
翻譯:
通常情況下,
BeanFactory會加載存儲在配置源(例如 XML 文檔)中 bean 的定義, 并使用org.springframework.beans包中的 API 來配置 bean 。然而,BeanFactory的實現可以根據需要直接在 Java 代碼中返回它創建的 Java 對象。bean 定義的存儲方式沒有任何限制, 它可以是 LDAP (輕型文件目錄訪問協議), RDBMS(關系型數據庫系統), XML, properties 文件等。鼓勵實現以支持 Bean 之間的引用(依賴注入)。
- 結論: SpringFramework 可以支持的配置源類型有很多種, 當然咱最常用的還是 xml 和注解驅動啦 ~ 這些配置源中存儲的信息是一些 Bean 的定義(BeanDefinition)
BeanFactory可實現層次性
In contrast to the methods in ListableBeanFactory, all of the operations in this interface will also check parent factories if this is a HierarchicalBeanFactory. If a bean is not found in this factory instance, the immediate parent factory will be asked. Beans in this factory instance are supposed to override beans of the same name in any parent factory.
翻譯:
與
ListableBeanFactory中的方法相比,BeanFactory中的所有操作還將檢查父工廠(如果這是HierarchicalBeanFactory)。如果在BeanFactory實例中沒有找到指定的 bean , 則會向父工廠中搜索查找。BeanFactory實例中的 Bean 應該覆蓋任何父工廠中的同名 Bean 。
- 結論: Spring想告訴我們的是,
BeanFactory本身可以支持父子結構, 這個父子結構的概念和實現由HierarchicalBeanFactory實現, 在BeanFactory中它也只是提了一下
BeanFactory中設有完整的生命周期控制機制
Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:
- BeanNameAware’s setBeanName
- BeanClassLoaderAware’s setBeanClassLoader
- BeanFactoryAware’s setBeanFactory
- EnvironmentAware’s setEnvironment
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware’s setEmbeddedValueResolver
- ResourceLoaderAware’s setResourceLoader (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware’s setApplicationEventPublisher (only applicable when running in an application context)
- MessageSourceAware’s setMessageSource (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationContextAware’s setApplicationContext (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ServletContextAware’s setServletContext (only applicable when running in a web application context)
- postProcessBeforeInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
- InitializingBean’s afterPropertiesSet
- a custom init-method definition
- postProcessAfterInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:
- postProcessBeforeDestruction methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
- DisposableBean’s destroy
- a custom destroy-method definition
翻譯:
BeanFactory接口實現了盡可能支持標準 Bean 的生命周期接口。全套初始化方法及其標準順序為:
- …
在關閉
BeanFactory時, 以下生命周期方法適用:
- …
結論: Bean 的生命周期是在 BeanFactory 中就有設計的, 而且官方文檔也提供了全套的初始化和銷毀流程
總結
總的來說, BeanFactory提供了一下的特性
- BeanFactory是根容器
- 定義的作用域概念
- 集成環境配置
- 支持多種類型的配置源
- 層次性的設計
- 完整的生命周期控制機制
HierarchicalBeanFactory(層次性)-熟悉
Hierarchical翻譯過來就是等級制度的, 分等級的, 很明顯的體現了層次性, 所謂的父子結構就是從這里體現出來的
JavaDoc描述
Sub-interface implemented by bean factories that can be part of a hierarchy.
The corresponding setParentBeanFactory method for bean factories that allow setting the parent in a configurable fashion can be found in the ConfigurableBeanFactory interface翻譯:
由
BeanFactory實現的子接口, 它可以理解為是層次結構的一部分。可以在ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中找到用于BeanFactory的相應setParentBeanFactory方法, 該方法允許以可配置的方式設置父對象。
結論: getParentBeanFactory() , 它就可以獲取到父 BeanFactory 對象
核心方法解析
-
getParentBeanFactory(): 獲取當前BeanFactory的父BeanFactory -
containsLocalBean(): 檢查當前BeanFacotry是否有指定名稱的Bean, 不會往父BeanFactory中進行查找- 即是父容器中有這個Bean, 那么也返回false
-
``containsBean()`: 檢查當前BeanFacotry是否有指定名稱的Bean, 如果沒有, 那么會往父容器中繼續查找
-
getBean(): 從當前BeanFactory開始查找是否存在指定的 Bean , 如果當前找不到就依次向上找父BeanFactory, 直到找到為止返回, 或者都找不到最終拋出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException-
注意這里的說法:如果當前找不到就往上找, 那如果找到了就不往上找了。思考一個問題:如果當前
BeanFactory中有指定的Bean了, 父BeanFactory中可能有嗎?答案是有, 因為即便存在父子關系, 但他們本質上是不同的BeanFactory, 所以有可能找到多個相同的 Bean 。換句話說,
@Scope中聲明的Singleton只是在一個容器中是單實例的, 但有了層次性結構后, 對于整體的多個容器來看, 就不是單實例的了
-
運行示例
Bean類
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Cat {private String name;
}
xml配置
child.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><bean id="dog" class="com.linkedbear.spring.lifecycle.Dog"><constructor-arg index="0" value="childDog"/></bean>
</beans>
parent.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><bean id="pig" class="com.linkedbear.spring.lifecycle.Pig"><constructor-arg index="0" value="parentPig"/></bean>
</beans>
啟動類
public class TestApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 創建子 BeanFactoryConfigurableBeanFactory childContext = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("lifecycle/child.xml"));// 創建父 BeanFactoryConfigurableBeanFactory parentContext = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("lifecycle/parent.xml"));// 設置父子關系childContext.setParentBeanFactory(parentContext);// 控制臺打印結果如下: org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory@8b96fde: defining beans [cat,pig]; root of factory hierarchySystem.out.println("childContext的父容器: " + childContext.getParentBeanFactory());// ------ getBean() 方法 ------Dog childDog = childContext.getBean("dog", Dog.class);// 控制臺打印結果如下: Dog(name=childDog)System.out.println("childContext.getBean(): " + childDog);// 控制臺拋出異常NoSuchBeanDefinitionException, 因為parent.xml中沒有名為dog的Bean// Dog parentDog = parentContext.getBean("dog", Dog.class);System.out.println("------------------");Pig childPig = childContext.getBean("pig", Pig.class);// 控制臺打印結果如下: Pig(name=parentPig), 輸出的是parent.xml中pig, child.xml中并沒有名為pig的Bean, 說明了本地容器沒有這個Bean的時候, getBean()會繼續往父容器找System.out.println("childContext.getBean(): " + childPig);Pig parentPig = parentContext.getBean("pig", Pig.class);// 控制臺打印結果如下: Pig(name=parentPig)System.out.println("parentContext.getBean(): " + parentPig);// 結論: getBean只獲取本地容器中的Bean, 如果本地容器中沒有的這個Bean時, 并不會往父容器查找System.out.println("------------------");// ------ containsLocalBean() 方法 ------boolean childDogContainLocal = childContext.containsLocalBean("dog");// 控制臺打印結果如下: tureSystem.out.println("childContext.containsLocalBean(): " + childDogContainLocal);boolean parentPigContainLocal = parentContext.containsLocalBean("dog");// 控制臺打印結果如下: false, 此時child.xml中沒有pig, 但是父容器parent.xml中有名為pig的Bean, 這里輸出false說明System.out.println("parentContext.containsLocalBean(): " + parentPigContainLocal);System.out.println("------------------");// ------ containsBean() 方法 ------boolean childPigContain = childContext.containsBean("pig");// 控制臺打印結果如下: true, 此時child.xml中沒有pig, 但是父容器parent.xml中有名為pig的Bean, 這里輸出true, 說明了containsBean()在當本地容器沒找到Bean時會往父容器中進行尋找System.out.println("childContext.containsBean(): " + childPigContain);boolean parentPigContain = parentContext.containsBean("pig");// 控制臺打印結果如下: trueSystem.out.println("parentContext.containsBean(): " + parentPigContain);}
}
ListableBeanFactory(可列舉性)-熟悉
Listable翻譯過來就是可列舉的, 那么ListableBeanFactory就可以理解為可列舉的BeanFactory
ListableBeanFactory只列舉當前容器中的Bean
Extension of the BeanFactory interface to be implemented by bean factories that can enumerate all their bean instances, rather than attempting bean lookup by name one by one as requested by clients. BeanFactory implementations that preload all their bean definitions (such as XML-based factories) may implement this interface.
翻譯:
它是
BeanFactory接口的擴展實現, 它可以列舉出所有 bean 實例, 而不是按客戶端調用的要求, 按照名稱一一進行 bean 的依賴查找。具有"預加載其所有 bean 定義信息"的BeanFactory實現(例如基于XML的BeanFactory)可以實現此接口
結論: ListableBeanFactory 只會列舉當前容器的 Bean, 列舉所有Bean可以使用BeanFactoryUtils中的方法獲取
BeanFactory可以具有層次性, 那這樣再列舉所有 Bean 的時候, 就需要斟酌到底是獲取包括父容器在內的所有 Bean , 還是只獲取當前容器中的 Bean , SpringFramework 在斟酌之后選擇了只獲取當前容器中的 Bean , 而如果真的想獲取所有Bean , 可以借助BeanFactoryUtils工具類來實現(工具類中有不少以"IncludingAncestors"結尾的方法, 代表可以一起取父容器)
ListableBeanFactory會有選擇性的列舉
The methods in this interface will just respect bean definitions of this factory. They will ignore any singleton beans that have been registered by other means like org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory’s registerSingleton method, with the exception of getBeanNamesForType and getBeansOfType which will check such manually registered singletons too. Of course, BeanFactory’s getBean does allow transparent access to such special beans as well. However, in typical scenarios, all beans will be defined by external bean definitions anyway, so most applications don’t need to worry about this differentiation.
翻譯:
ListableBeanFactory中的方法將僅遵循當前工廠的bean定義, 它們將忽略通過其他方式(例如ConfigurableBeanFactory的registerSingleton方法)注冊的任何單實例 bean (但getBeanNamesForType和getBeansOfType除外), 它們也會檢查這種手動注冊的單實例 Bean 。當然,BeanFactory的getBean確實也允許透明訪問此類特殊 bean 。在一般情況下, 無論如何所有的 bean 都來自由外部的 bean 定義信息, 因此大多數應用程序不必擔心這種區別。
結論: 作為一個"可迭代"的BeanFactory, 按理來講應該最起碼得把當前容器中的所有Bean都列出來, 結果你又告訴我有些Bean會被忽略掉不給列(比如手動注冊的Bean)
- ListableBeanFactory設計選擇性列舉的目的: 有些組件屬于Spring內部使用的, Spring并不希望開發者平常直接操作它, 類比Win中隱藏受保護的操作系統文件, 默認情況下都是隱藏的, 避免用戶操作(如果動了這些文件, 那么很可能Win就出問題了)
ListableBeanFactory的大部分方法不適合頻繁調用
NOTE: With the exception of getBeanDefinitionCount and containsBeanDefinition, the methods in this interface are not designed for frequent invocation. Implementations may be slow.
翻譯:
注意:除了
getBeanDefinitionCount和containsBeanDefinition之外, 此接口中的方法不適用于頻繁調用, 方法的實現可能執行速度會很慢。
結論: 通常都不需要動不動去翻IOC容器的東西, 頂多是讀完一遍就自己緩存起來. 一般情況下也不會有業務需求會深入到 IOC 容器的底部
AutowireCapableBeanFactory(可自動注入性)-了解
AutowireCapableBeanFactory可以支持外部Bean的自動裝配
Extension of the BeanFactory interface to be implemented by bean factories that are capable of autowiring, provided that they want to expose this functionality for existing bean instances.
翻譯:
它是
BeanFactory接口的擴展實現, 它可以實現自動裝配, 前提是開發者希望為現有的 bean實例公開此功能。
結論: AutowireCapableBeanFactory本身可以支持自動裝配, 而且還可以為現有的一些 Bean 也能支持自動裝配。而這個"現有"的概念, 實際上指的是那些不被Spring管理的 Bean
AutowireCapableBeanFactory用于框架集成
This subinterface of BeanFactory is not meant to be used in normal application code: stick to BeanFactory or ListableBeanFactory for typical use cases.
Integration code for other frameworks can leverage this interface to wire and populate existing bean instances that Spring does not control the lifecycle of. This is particularly useful for WebWork Actions and Tapestry Page objects, for example.
翻譯:
AutowireCapableBeanFactory這個子接口不能在常規的應用程序代碼中使用:一般情況下, 請堅持使用BeanFactory或ListableBeanFactory。 其他框架的集成代碼可以利用此接口來連接和注入SpringFramework 無法控制其生命周期的現有bean實例。例如, 這對于 WebWork 操作和 Tapestry 頁面對象特別有用。
結論: AutowireCapableBeanFactory平常業務代碼不要用, 與其他框架進行集成時才使用。利用此接口來連接和注入 SpringFramework 無法控制其生命周期的現有 bean 實例, 這其實已經把它的作用完整的描述出來了:你要是真想用它, 那也是在跟其它框架集成時, 如果其它框架的一些Bean實例無法讓SpringFramework控制, 但又需要注入一些由SpringFramework管理的對象, 那就可以用它了
- 框架可能會創建自己的Bean實例, 并管理它們的生命周期, 而這些 Bean 實例通常不受 Spring 容器的控制, 因此Spring不會自動地為它們注入依賴或管理它們的生命周期(表明了, 如果這個Bean要注入Spring中管理的Bean, 那么需要將Bean注冊到Spring中)
AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口提供了一個方法autowireBean, 它可以用來手動為這些非 Spring Bean 實例注入依賴。這個方法允許你指定一個 Bean 實例, 以及一個需要注入的屬性名稱。Spring會根據這個屬性的類型, 在其 Bean 定義中查找合適的 Bean, 并將其注入到非 Spring Bean 實例中
場景示例
示例一: 非Spring管理的對象需要注入Spring管理的Bean
// MyAction它不是由Spring管理的類
public class MyAction {// 需要注入MyServiceprivate MyService myService;// setter()注入依賴public void setMyService(MyService myService) {this.myService = myService;}public String execute() {// 使用注入的服務myService.doSomething();return "success";}
}// Spring環境中, 在配置類中使用@Bean配置MyService,
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic MyService myService() {return new MyServiceImpl();}
}// 在非 Spring 環境中, 需要手動注入依賴
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建 Spring 應用contextApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);// 獲取 AutowireCapableBeanFactoryAutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory();// 創建MyAction對象MyAction action = new MyAction();// 手動注入依賴beanFactory.autowireBean(action);// 執行 Struts 動作action.execute();}
}
MyAction需要注入一個MyService實例。雖然 MyService 是由 Spring 容器管理的, 但是 MyAction 實例不是(即是非Spring管理的對象需要注入Spring管理的Bean), 所以我們不能在 MyAction 類中使用 Spring的@Autowired注解來注入MyService。相反, 我們需要在 Spring之外手動注入這個依賴
AutowireCapableBeanFactory不由ApplicationContext實現但可獲取
Note that this interface is not implemented by ApplicationContext facades, as it is hardly ever used by application code. That said, it is available from an application context too, accessible through ApplicationContext’s getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() method.
翻譯:
請注意, 該接口沒有在
ApplicationContext中實現, 因為應用程序代碼幾乎從未使用過此接口。也就是說, 它也可以從應用程序context中獲得:可以通過ApplicationContext的getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()方法進行訪問。
結論: 這個擴展你們一般用不到, 但我給你取的方式, 你們需要的時候自己拿。
AutowireCapableBeanFactory可以借助BeanFactoryAware注入
You may also implement the org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware interface, which exposes the internal BeanFactory even when running in an ApplicationContext, to get access to an AutowireCapableBeanFactory: simply cast the passed-in BeanFactory to AutowireCapableBeanFactory.
翻譯:
您還可以實現
BeanFactoryAware接口, 該接口即使在ApplicationContext中運行時也公開內部BeanFactory, 以訪問AutowireCapableBeanFactory:只需將傳入的BeanFactory強制轉換為AutowireCapableBeanFactory。
結論: 如果你實現了 BeanFactoryAware 接口, Spring 框架會在創建 Bean 的時候自動注入一個 BeanFactory 實例到你的 Bean 中。由于 BeanFactory 是一個接口, 實際注入的對象可能是 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 的實例, 當你需要訪問 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 的特定方法, 你可以將 BeanFactory 強制轉換為 AutowireCapableBeanFactory。, 因為如果你在ApplicationContext中運行, BeanFactory 實際上是 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 的實例
ConfigurableBeanFactory(可配置性)-熟悉
在 SpringFramework 的 BeanFactory 和ApplicationContext 中, 都會有這樣的設計。普通的 BeanFactory 只有 get 相關的操作, 而 Configurable開頭的 BeanFactory 或者 ApplicationContext 就具有了 set 的操作(對權限進行限制劃分)
ConfigurableBeanFactory提供可配置的功能
Configuration interface to be implemented by most bean factories. Provides facilities to configure a bean factory, in addition to the bean factory client methods in the BeanFactory interface.
翻譯:
大多數
BeanFactory的實現類都會實現這個帶配置的接口。除了BeanFactory接口中的基礎獲取方法之外, 還提供了配置BeanFactory的功能。
結論: 表明了ConfigurableBeanFactory帶配置的功能, 可以用這里邊的方法對BeanFactory進行修改, 拓展等
ConfigurableBeanFactory不推薦給開發者使用
This bean factory interface is not meant to be used in normal application code: Stick to BeanFactory or org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory for typical needs. This extended interface is just meant to allow for framework-internal plug’n’play and for special access to bean factory configuration methods.
翻譯:
ConfigurableBeanFactory接口并不希望開發者在應用程序代碼中使用, 而是堅持使用BeanFactory或ListableBeanFactory。此擴展接口僅用于允許在框架內部進行即插即用, 并允許對BeanFactory中的配置方法的特殊訪問。
結論: SpringFramework 不希望開發者用 ConfigurableBeanFactory , 而用最根本的 BeanFactory, 因為程序在運行期間按理不應該對 BeanFactory 再進行頻繁的變動, 此時只應該有讀的動作, 而不應該出現寫的動作
BeanFactory的實現類們
BeanFactory的最核心的實現類取出來, 如下圖
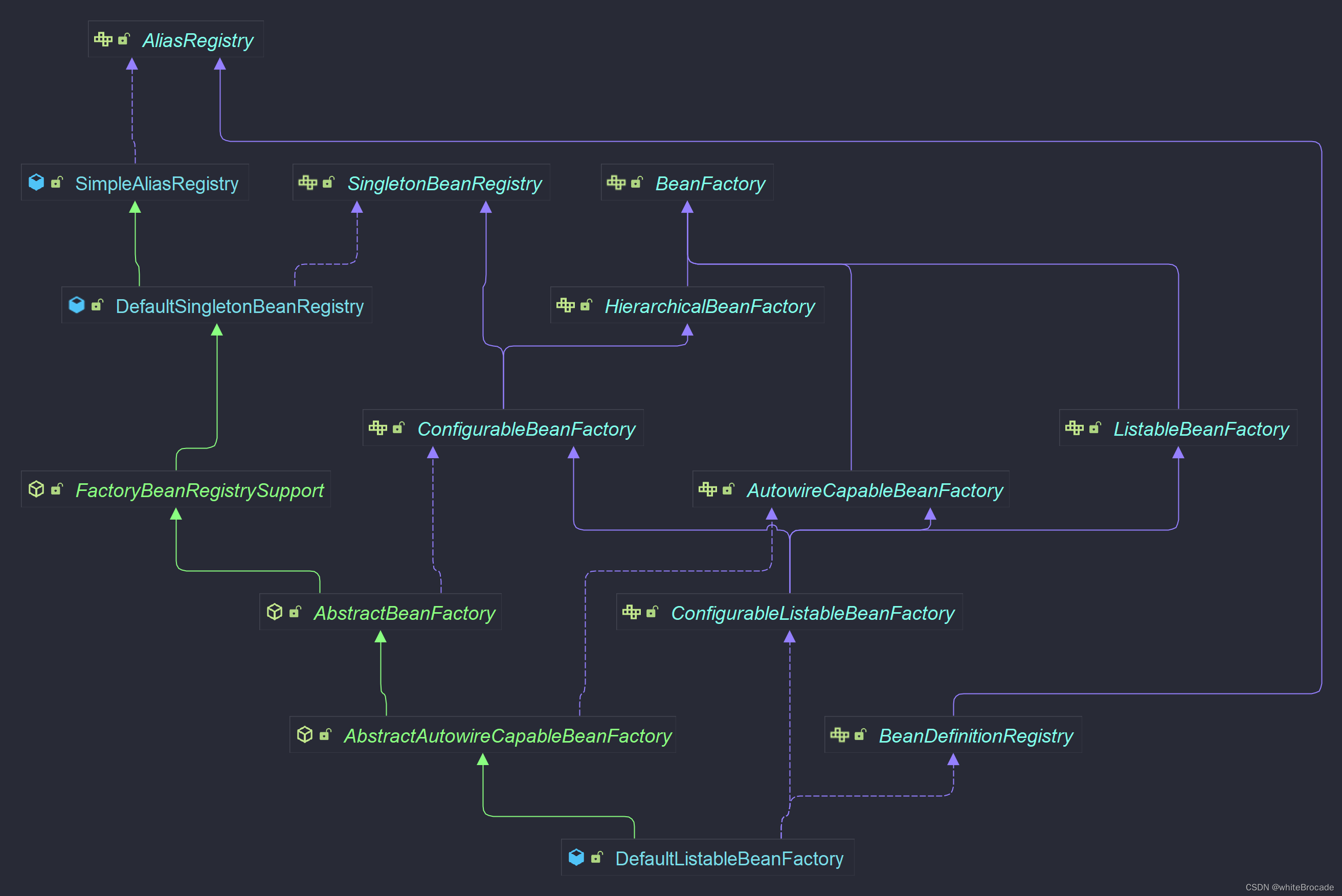
AbstractBeanFactory-熟悉
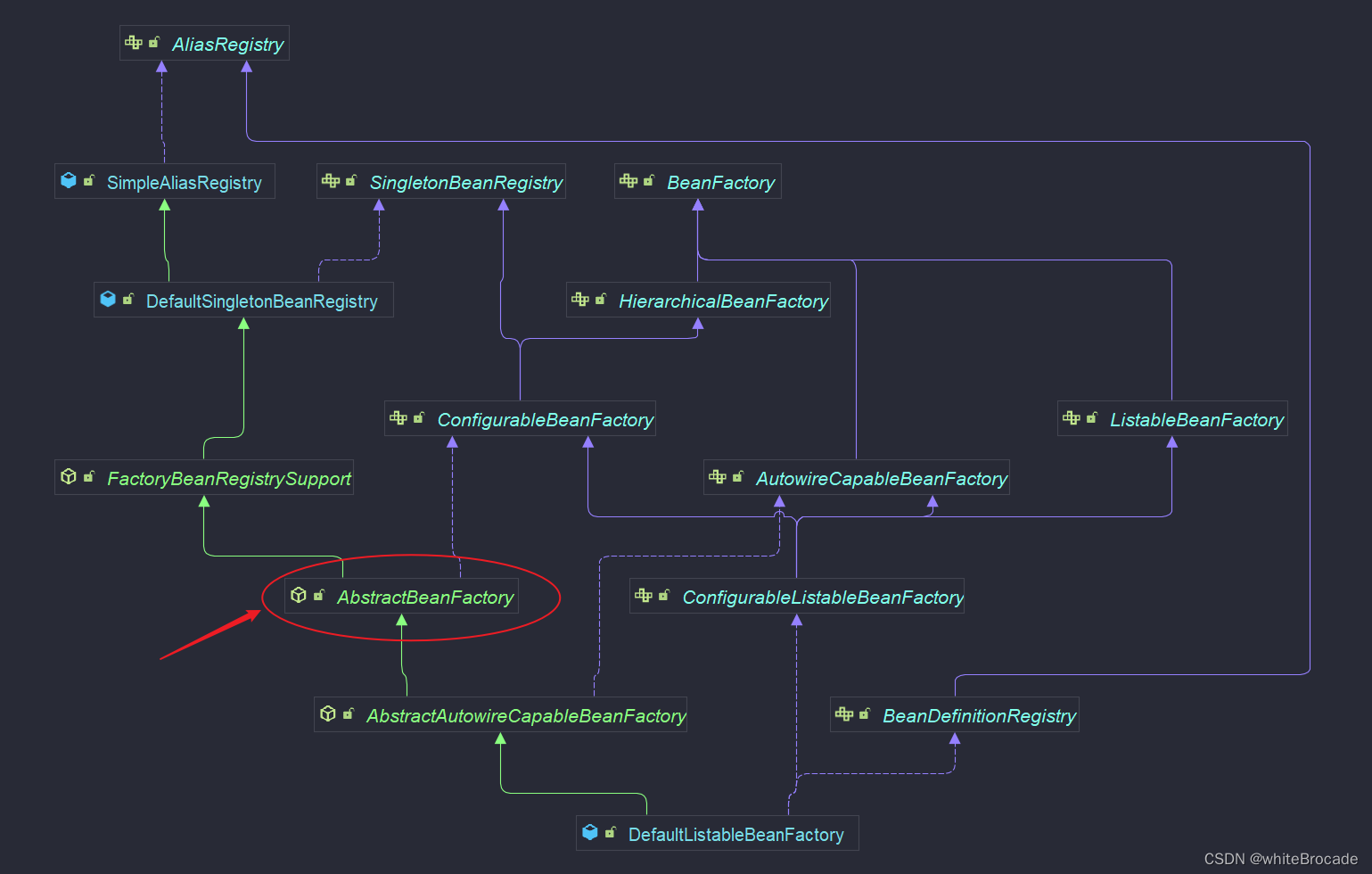
從類名上就知道, 它是 BeanFactory 最基本的抽象實現, 當然作為一個抽象類, 一定是只具備了部分功能
AbstractBeanFactory是最終BeanFactory的基礎實現
Abstract base class for BeanFactory implementations, providing the full capabilities of the ConfigurableBeanFactory SPI. Does not assume a listable bean factory: can therefore also be used as base class for bean factory implementations which obtain bean definitions from some backend resource (where bean definition access is an expensive operation).
翻譯:
它是
BeanFactory接口最基礎的抽象實現類, 提供ConfigurableBeanFactorySPI 的全部功能。我們不假定有一個可迭代的BeanFactory, 因此也可以用作BeanFactory實現的父類, 該實現可以從某些后端資源(其中 bean 定義訪問是一項昂貴的操作)獲取 bean 的定義。
說人話: :AbstractBeanFactory 是作為 BeanFactory 接口下面的第一個抽象的實現類, 它具有最基礎的功能, 并且它可以從配置源(之前看到的 xml 、LDAP 、RDBMS 等)獲取 Bean 的定義信息, 而這個 Bean 的定義信息就是 BeanDefinition。SPI可參考博主的另外一篇博客JDK和Spring的SPI機制原理分析
AbstractBeanFactory對Bean的支持
This class provides a singleton cache (through its base class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry), singleton/prototype determination, FactoryBean handling, aliases, bean definition merging for child bean definitions, and bean destruction (org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean interface, custom destroy methods). Furthermore, it can manage a bean factory hierarchy (delegating to the parent in case of an unknown bean), through implementing the org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory interface.
翻譯:
此類可以提供單實例 Bean 的緩存(通過其父類
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry), 單例/原型 Bean 的決定,FactoryBean處理, Bean 的別名, 用于子 bean 定義的 bean 定義合并以及 bean 銷毀(DisposableBean接口, 自定義destroy方法)。此外, 它可以通過實現HierarchicalBeanFactory接口來管理BeanFactory層次結構(在未知 bean 的情況下委托給父工廠)。
除了在之前 BeanFactory 中介紹的功能和特性之外, 它還擴展了另外一些功能:別名的處理(來源于 AliasRegistry 接口)、Bean 定義的合并、Bean 的銷毀動作支持( DisposableBean )等
AbstractBeanFactory定義了模板方法
The main template methods to be implemented by subclasses are getBeanDefinition and createBean, retrieving a bean definition for a given bean name and creating a bean instance for a given bean definition, respectively. Default implementations of those operations can be found in DefaultListableBeanFactory and AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.
翻譯:
子類要實現的主要模板方法是
getBeanDefinition和createBean, 分別為給定的 bean 名稱檢索 bean 定義信息, 并根據給定的 bean 定義信息創建 bean 的實例。這些操作的默認實現可以在DefaultListableBeanFactory和AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中找到。
結論: SpringFramework 中大量使用模板方法模式(相關介紹最有用的設計模式之一-模板方法)來設計核心組件, 它的思路是:父類提供邏輯規范, 子類提供具體步驟的實現。在文檔注釋中, 說到AbstractBeanFactory 中對 getBeanDefinition 和 createBean 兩個方法進行了規范上的定義, 分別代表獲取 Bean 的定義信息, 以及創建 Bean 的實例。這兩個方法都會在 SpringFramework 的 IOC 容器初始化階段起到至關重要的作用。 而createBean 是 SpringFramework 能管控的所有 Bean 的創建入口(注意了, 這里說的是入口, 不是最終實現Bean創建的地方)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory-掌握
AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接口的落地實現了, 那就意味著, 它可以實現組件的自動裝配
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory提供Bean的創建邏輯實現
Abstract bean factory superclass that implements default bean creation, with the full capabilities specified by the RootBeanDefinition class. Implements the AutowireCapableBeanFactory interface in addition to AbstractBeanFactory’s createBean method.
翻譯:
它是實現了默認 bean 創建邏輯的的抽象的
BeanFactory實現類, 它具有RootBeanDefinition類指定的全部功能。除了AbstractBeanFactory的createBean方法之外, 還實現AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口。
說人話: AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 繼承了 AbstractBeanFactory 抽象類(默認 bean 創建邏輯的的抽象的 BeanFactory指的就是AbstractBeanFactory ), 還額外實現了 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接口, 那么就說明了擁有了自動注入功能, 再者還實現了 AbstractBeanFactory 的 createBean 方法, 那么就說明了它還具有創建Bean的功能
createBean方法也不是最終實現 Bean 的創建, 而是有另外一個叫doCreateBean方法, 它同樣在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中定義, 而且是 protected 方法, 沒有子類重寫它(以后細細分析, 埋個坑)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory實現了屬性賦值和組件注入
Provides bean creation (with constructor resolution), property population, wiring (including autowiring), and initialization. Handles runtime bean references, resolves managed collections, calls initialization methods, etc. Supports autowiring constructors, properties by name, and properties by type.
翻譯:
提供 Bean 的創建(具有構造方法的解析), 屬性填充, 屬性注入(包括自動裝配)和初始化。處理運行時 Bean 的引用, 解析托管集合, 調用初始化方法等。支持自動裝配構造函數, 按名稱的屬性和按類型的屬性。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 中實現的最最核心功能全部列出來了:Bean 的創建、屬性填充和依賴的自動注入、Bean 的初始化。這部分是創建 Bean 最核心的三個步驟(注意了, 這里是脈絡, 后續都以此鋪開)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory保留了模板方法
The main template method to be implemented by subclasses is resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor, String, Set, TypeConverter), used for autowiring by type. In case of a factory which is capable of searching its bean definitions, matching beans will typically be implemented through such a search. For other factory styles, simplified matching algorithms can be implemented.
翻譯:
子類要實現的主要模板方法是
resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor, String, Set, TypeConverter), 用于按類型自動裝配。如果工廠能夠搜索其 bean 定義, 則通常將通過此類搜索來實現匹配的 bean 。對于其他工廠樣式, 可以實現簡化的匹配算法。
跟 AbstractBeanFactory 不太一樣, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 沒有把全部模板方法都實現完, 它保留了文檔注釋中提到的 resolveDependency 方法, 這個方法的作用是解析 Bean 的成員中定義的屬性依賴關系
從這里也可以看出, Spring組件的單一職責切割很好, 組件之間的功能不逾矩
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory不負責BeanDefinition的注冊
Note that this class does not assume or implement bean definition registry capabilities. See DefaultListableBeanFactory for an implementation of the org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory and BeanDefinitionRegistry interfaces, which represent the API and SPI view of such a factory, respectively.
翻譯:
請注意, 此類不承擔或實現 bean 定義注冊的功能。有關
ListableBeanFactory和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的實現, 請參見DefaultListableBeanFactory, 它們分別表示該工廠的 API 和 SPI 視圖。
Spring想表明的是, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 實現了對 Bean 的創建、賦值、注入、初始化的邏輯, 但對于BeanDefinition是如何進入 BeanFactory 的, 它不負責。這里面涉及到兩個流程:Bean 的創建、BeanDefinition的進入(后續BeanDefinition部分會解析)。
DefaultListableBeanFactory-掌握
DefaultListableBeanFactory是唯一一個目前使用的 BeanFactory 的落地實現了
DefaultListableBeanFactory是BeanFactory最終的默認實現
Spring’s default implementation of the ConfigurableListableBeanFactory and BeanDefinitionRegistry interfaces: a full-fledged bean factory based on bean definition metadata, extensible through post-processors.
翻譯:
Spring 的
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的默認實現, 它時基于 Bean 的定義信息的的成熟的BeanFactory實現, 它可通過后置處理器進行擴展。
結論: DefaultListableBeanFactory 已經沒有 abstract 標注了, 說明它可以算作一個成熟的落地實現
DefaultListableBeanFactory會先注冊Bean定義信息再創建Bean
Typical usage is registering all bean definitions first (possibly read from a bean definition file), before accessing beans. Bean lookup by name is therefore an inexpensive operation in a local bean definition table, operating on pre-resolved bean definition metadata objects.
翻譯:
典型的用法是在訪問 bean 之前先注冊所有 bean 定義信息(可能是從有 bean 定義的文件中讀取)。因此, 按名稱查找 Bean 是對本地 Bean 定義表進行的合理操作, 該操作對預先解析的 Bean 定義元數據對象進行操作。
講人話: DefaultListableBeanFactory 在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的基礎上, 完成了注冊 Bean 定義信息的動作, 而這個動作就是通過上面的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 來實現的。所以咱就可以知道一點, 完整的 BeanFactory 對 Bean 的管理, 應該是先注冊 Bean 的定義信息, 再完成 Bean 的創建和初始化動作(注意, 重點句子)
DefaultListableBeanFactory不負責解析Bean定義文件
Note that readers for specific bean definition formats are typically implemented separately rather than as bean factory subclasses: see for example PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader and org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
翻譯:
請注意, 特定 bean 定義信息格式的解析器通常是單獨實現的, 而不是作為
BeanFactory的子類實現的, 有關這部分的內容參見PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader和XmlBeanDefinitionReader。
可以看出SpringFramework 對于組件的單一職責把控的非常好, BeanFactory 作為一個統一管理 Bean 組件的容器, 它的核心工作就是控制 Bean 在創建階段的生命周期, 而對于 Bean 從哪里來, 如何被創建, 都有哪些依賴要被注入, 這些統統與它無關, 而是有專門的組件來處理(就是包括上面提到的 BeanDefinitionReader 在內的一些其它組件)
DefaultListableBeanFactory的替代實現
For an alternative implementation of the org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory interface, have a look at StaticListableBeanFactory, which manages existing bean instances rather than creating new ones based on bean definitions.
翻譯:
對于
ListableBeanFactory接口的替代實現, 請看一下StaticListableBeanFactory, 它管理現有的 bean 實例, 而不是根據 bean 定義創建新的 bean 實例。
StaticListableBeanFactory 實現起來相對簡單且功能也簡單, 因為它只能管理現有的, 且單實例的Bean , 而且沒有跟 Bean 定義等相關的高級概念在里面, 于是 SpringFramewor 默認也不用StaticListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory-了解
在 SpringFramework 3.1 之后, XmlBeanFactory 正式被標注為過時, 代替的方案是使用 DefaultListableBeanFactory + XmlBeanDefinitionReader , 這種設計更符合組件的單一職責原則, 而且還有一點。自打 SpringFramework 3.0 之后出現了注解驅動的 IOC 容器, SpringFramework 就感覺這種 xml 驅動的方式不應該單獨成為一種方案了, 倒不如咱都各退一步, 搞一個通用的容器, 都組合它來用, 這樣就實現了配置源載體分離的目的了
ApplicationContext
推薦使用 ApplicationContext 而不是 BeanFactory , 因為 ApplicationContext 相比較 BeanFactory 擴展的實在是太多了
| Feature | BeanFactory | ApplicationContext |
|---|---|---|
| Bean instantiation/wiring—Bean的實例化和屬性注入 | √ | √ |
| Integrated lifecycle management —— 生命周期管理 | √ | |
Automatic BeanPostProcessor registration —— Bean后置處理器的支持 | √ | |
Automatic BeanFactoryPostProcessor registration —— BeanFactory后置處理器的支持 | √ | |
Convenient MessageSource access (for internalization) —— 消息轉換服務(國際化) | √ | |
Built-in ApplicationEvent publication mechanism —— 事件發布機制(事件驅動) | √ |
類關系圖如下
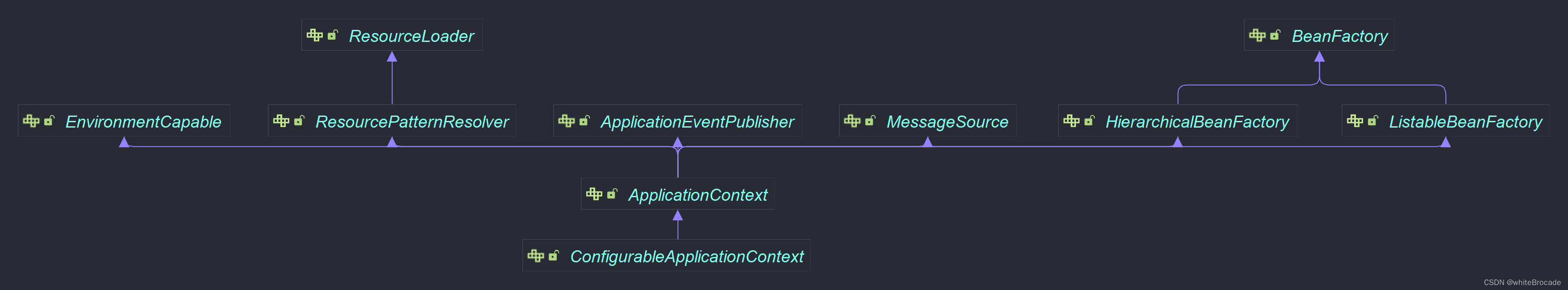
ApplicationContext和它的子接口們
ApplicationContext-掌握
Central interface to provide configuration for an application. This is read-only while the application is running, but may be reloaded if the implementation supports this.
翻譯:
它是為應用程序提供配置的中心接口。在應用程序運行時, 它是只讀的, 但是如果受支持的話, 它可以重新加載。
結論: ApplicationContext 就是中央接口, 它就是 SpringFramework 的最最核心。另外它多提了一個概念:重新加載, 后續介紹
ApplicationContext組合多個功能接口
An ApplicationContext provides:
- Bean factory methods for accessing application components. Inherited from ListableBeanFactory.
- The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion. Inherited from the ResourceLoader interface.
- The ability to publish events to registered listeners. Inherited from the ApplicationEventPublisher interface.
- The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization. Inherited from the MessageSource interface.
- Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet.
翻譯:
ApplicationContext提供:
- 用于訪問應用程序組件的 Bean 工廠方法。繼承自
ListableBeanFactory。- 以通用方式加載文件資源的能力。繼承自
ResourceLoader接口。- 能夠將事件發布給注冊的監聽器。繼承自
ApplicationEventPublisher接口。- 解析消息的能力, 支持國際化。繼承自
MessageSource接口。- 從父context繼承。在子容器中的定義將始終優先。例如, 這意味著整個 Web 應用程序都可以使用單個父context, 而每個 servlet 都有其自己的子context, 該子context獨立于任何其他 servlet 的子context。
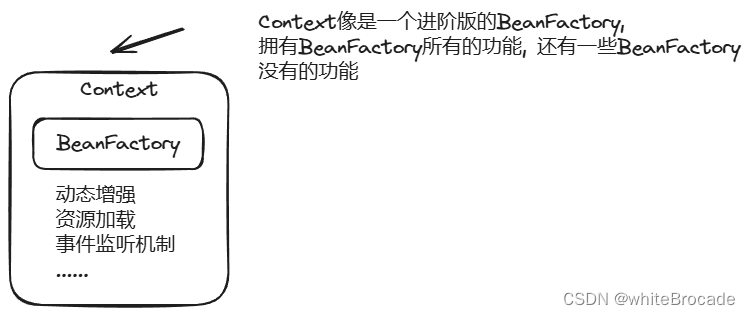
結論: 主要介紹功能和該功能的源自哪個接口。ApplicationContext 也是支持層級結構的, 但這里它的描述是父子context, 這個概念要區分理解。context中包含容器, 但又不僅僅是容器。容器只負責管理Bean(重點中的重點) , 但context中還包括動態增強、資源加載、事件監聽機制等多方面擴展功能(這里也可以體現為什么Application的功能比BeanFactory強大)
Context和Beanfatory之間的關系
ApplicationContext負責部分回調注入
In addition to standard BeanFactory lifecycle capabilities, ApplicationContext implementations detect and invoke ApplicationContextAware beans as well as ResourceLoaderAware , ApplicationEventPublisherAware and MessageSourceAware beans.
翻譯:
除了標準的
BeanFactory生命周期功能外,ApplicationContext實現還檢測并調用ApplicationContextAwarebean 以及ResourceLoaderAwarebean,ApplicationEventPublisherAware和MessageSourceAwarebean。
結論: 也就說除了BeanFactory的生命周期外, ApplicationContext還提供其它的拓展點, 用于執行額外操作。都是以Aware(Aware翻譯過為感知)結尾的接口, *Aware 接口是 Spring 框架中一種回調機制, 允許 Bean 在創建過程中與 Spring 容器進行交互, 從而獲取 Spring 容器提供的資源或服務
ApplicationContextAware讓 Bean 知道它所在的ApplicationContext, 從而可以獲取其他 Bean 或者進行一些 ApplicationContext 特有的操作。ResourceLoaderAware讓 Bean 知道一個ResourceLoader, 可以用來加載資源文件等。ApplicationEventPublisherAware讓 Bean 知道一個ApplicationEventPublisher, 可以用來發布應用程序事件。MessageSourceAware讓 Bean 知道一個MessageSource, 可以用來處理國際化(i18n)相關的消息
當實現了一個 *Aware 接口時, 實際上是在告訴 Spring 框架: “我需要這些資源或服務, 請在創建我的實例時幫我注入它們”, Spring 容器在創建 Bean 實例之后, 會通過調用這些接口的 set* 方法, 將相應的資源或服務注入到 Bean 中。這些資源或服務通常是 Spring 容器本身提供的, 比如 ApplicationContext, ResourceLoader, ApplicationEventPublisher 和 MessageSource。
例如, 在 Spring 中實現 ApplicationContextAware 接口時, 告訴 Spring 在創建你的 Bean 實例之后, 請調用 setApplicationContext 方法, 并將當前的 ApplicationContext 實例注入進去。這樣, 你的Bean就能夠訪問到 Spring 的context環境, 從而能夠做更多的事情(也就是說, 如果你實現*Aware接口, 那么Spring會將該接口對應的資源從容器中取出來供你使用)
ConfigurableApplicationContext-掌握
和ConfigurableBeanFactory有點類似, 為ApplicationContext提供了可寫功能(也就說有相關setter方法), 實現了該接口的實現類可以被客戶端代碼修改內部的某些配置
ConfigurableApplicationContext提供了可配置的可能
SPI interface to be implemented by most if not all application contexts. Provides facilities to configure an application context in addition to the application context client methods in the ApplicationContext interface.
翻譯:
它是一個支持 SPI 的接口, 它會被大多數(如果不是全部)應用程序context的落地實現。除了
ApplicationContext接口中的應用程序context客戶端方法外, 還提供了用于配置應用程序context的功能。
ConfigurableApplicationContext 給 ApplicationContext 添加了用于配置的功能, 而且還擴展了 setParent 、setEnvironment 、addBeanFactoryPostProcessor 、addApplicationListener 等方法, 都是可以改變 ApplicationContext 本身的方法
ConfigurableApplicationContext只希望被調用啟動和關閉
Configuration and lifecycle methods are encapsulated here to avoid making them obvious to ApplicationContext client code. The present methods should only be used by startup and shutdown code.
翻譯:
配置和與生命周期相關的方法都封裝在這里, 以避免暴露給
ApplicationContext的調用者。本接口的方法僅應由啟動和關閉代碼使用。
ConfigurableApplicationContext 本身擴展了一些方法, 但是它一般情況下不希望讓咱開發者調用, 而是只調用**啟動(refresh)和關閉(close)**方法。注意這個一般情況是在程序運行期間的業務代碼中, 但如果是為了定制化 ApplicationContext 或者對其進行擴展, ConfigurableApplicationContext 的擴展則會成為切入的主目標
EnvironmentCapable-熟悉
capable本意為"有能力的", 在這里解釋為**“攜帶/組合”**
在 SpringFramework 中, 以 Capable 結尾的接口, 通常意味著可以通過這個接口的某個特定的方法(通常是 getXXX())拿到特定的組件
也就說 EnvironmentCapable 接口中就應該通過一個 getEnvironment() 方法拿到 Environment
public interface EnvironmentCapable {Environment getEnvironment();
}
ApplicationContext都具有EnvironmentCapable的功能
Interface indicating a component that contains and exposes an Environment reference.
All Spring application contexts are EnvironmentCapable, and the interface is used primarily for performing instanceof checks in framework methods that accept BeanFactory instances that may or may not actually be ApplicationContext instances in order to interact with the environment if indeed it is available.
翻譯:
它是具有獲取并公開
Environment引用的接口。所有 Spring 的
ApplicationContext都具有EnvironmentCapable功能, 并且該接口主要用于在接受BeanFactory實例的框架方法中執行 instanceof 檢查, 以便可以與環境進行交互(如果實際上是ApplicationContext實例)。
ApplicationContext 都實現了這個 EnvironmentCapable 接口, 也就代表著所有的 ApplicationContext 的實現類都可以取到 Environment 抽象(Environment 是 Spring中抽象出來的類似于運行環境的獨立抽象, 它內部存放著應用程序運行的一些配置, Spring將運行時劃分成了兩部分: 應用程序本身, 應用程序運行時的環境)
ConfigurableApplicationContext可以獲取ConfigurableEnvironment
As mentioned, ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, and thus exposes a getEnvironment() method; however, ConfigurableApplicationContext redefines getEnvironment() and narrows the signature to return a ConfigurableEnvironment. The effect is that an Environment object is ‘read-only’ until it is being accessed from a ConfigurableApplicationContext, at which point it too may be configured.
翻譯:
如上面所述,
ApplicationContext擴展了EnvironmentCapable, 因此公開了getEnvironment()方法;但是,ConfigurableApplicationContext重新定義了getEnvironment()并縮小了簽名范圍, 以返回ConfigurableEnvironment。結果是環境對象是 “只讀的” , 直到從ConfigurableApplicationContext訪問它為止, 此時也可以對其進行配置。
指出了可配置的 ApplicationContext , 就可以獲取到可配置的 Environment 抽象
MessageSource-熟悉
國際化, 是針對不同地區、不同國家的訪問, 可以提供對應的符合用戶閱讀習慣(語言)的頁面和數據。
Strategy interface for resolving messages, with support for the parameterization and internationalization of such messages. Spring provides two out-of-the-box implementations for production:
- org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource: built on top of the standard java.util.ResourceBundle, sharing its limitations.
- org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource: highly configurable, in particular with respect to reloading message definitions.
翻譯:
用于解析消息的策略接口, 并支持消息的參數化和國際化。SpringFramework 為生產提供了兩種現有的實現:
ResourceBundleMessageSource:建立在標準java.util.ResourceBundle之上, 共享其局限性。ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource:高度可配置, 尤其是在重新加載消息定義方面。
ApplicationEventPublisher-熟悉
類名可以理解為, 它是事件的發布器。SpringFramework 內部支持很強大的事件監聽機制, 而 ApplicationContext 作為容器的最頂級, 自然也要實現觀察者模式(見觀察者模式, 發布-訂閱模式, 監聽器模式)中廣播器的角色
JavaDoc對它總體概覽如下
Interface that encapsulates event publication functionality. Serves as a super-interface for ApplicationContext.
封裝事件發布功能的接口, 它作為
ApplicationContext的父接口
ResourcePatternResolver-熟悉
類名理解可以解釋為“資源模式解析器”, 實際上它是根據特定的路徑去解析資源文件
ResourcePatternResolver是ResourceLoader的擴展
Strategy interface for resolving a location pattern (for example, an Ant-style path pattern) into Resource objects. This is an extension to the ResourceLoader interface. A passed-in ResourceLoader (for example, an org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext passed in via org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware when running in a context) can be checked whether it implements this extended interface too.
翻譯:
它是一個策略接口, 用于將位置模式(例如, Ant 樣式的路徑模式)解析為
Resource對象。 這是ResourceLoader接口的擴展。可以檢查傳入的ResourceLoader(例如, 在context中運行時通過ResourceLoaderAware傳入的ApplicationContext)是否也實現了此擴展接口。
ResourcePatternResolver本身還是 ResourceLoader 的擴展, ResourceLoader 實現最基本的解析, ResourcePatternResolver 可以支持 Ant 形式的帶星號 ( * ) 的路徑解析
ResourcePatternResolver的實現方式有多種
Can be used with any sort of location pattern (e.g. “/WEB-INF/*-context.xml”): Input patterns have to match the strategy implementation. This interface just specifies the conversion method rather than a specific pattern format.
翻譯:
可以與任何類型的位置模式一起使用(例如
"/WEB-INF/*-context.xml"):輸入模式必須與策略實現相匹配。該接口僅指定轉換方法, 而不是特定的模式格式
Ant 風格的匹配模式有如下寫法:
/WEB-INF/*.xml:匹配/WEB-INF目錄下的任意 xml 文件/WEB-INF/**/beans-*.xml:匹配/WEB-INF下面任意層級目錄的beans-開頭的 xml 文件/**/*.xml:匹配任意 xml 文件
ResourcePatternResolver可以匹配類路徑下的文件
This interface also suggests a new resource prefix “classpath*:” for all matching resources from the class path. Note that the resource location is expected to be a path without placeholders in this case (e.g. “/beans.xml”); JAR files or classes directories can contain multiple files of the same name.
翻譯:
此接口還為類路徑中的所有匹配資源建議一個新的資源前綴
"classpath*: "。請注意, 在這種情況下, 資源位置應該是沒有占位符的路徑(例如"/beans.xml"); jar 文件或類目錄可以包含多個相同名稱的文件。
ResourcePatternResolver 不僅可以匹配 Web 工程中 webapps 的文件, 也可以匹配 classpath 下的文件。匹配類路徑下的資源文件方式如下: 在資源路徑中加一個 classpath*: 的前綴。
ApplicationContext的實現類們
類關系圖如下:
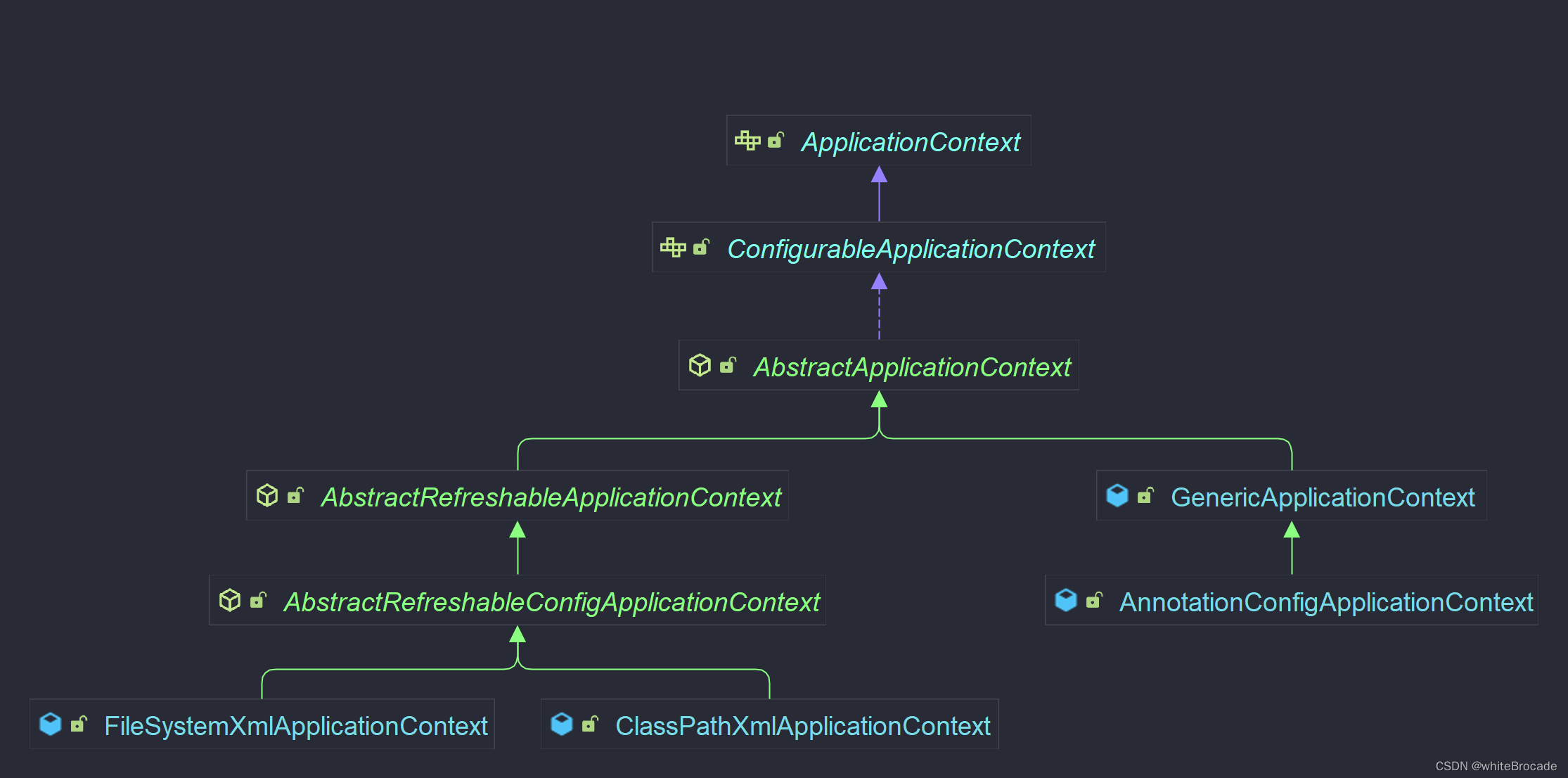
AbstractApplicationContext-掌握
ApplicationContext 是最最最最核心的實現類, 沒有之一。AbstractApplicationContext 中定義和實現了絕大部分ApplicationContext的特性和功能
AbstractApplicationContext只構建功能抽象
Abstract implementation of the ApplicationContext interface. Doesn’t mandate the type of storage used for configuration; simply implements common context functionality. Uses the Template Method design pattern, requiring concrete subclasses to implement abstract methods.
翻譯:
ApplicationContext接口的抽象實現。不強制用于配置的存儲類型;簡單地實現通用context功能。使用模板方法模式, 需要具體的子類來實現抽象方法
和之前的AbstractBeanFactory一樣, 借助模板方法規范功能, 實際邏輯由子類實現
AbstractApplicationContext可以處理特殊類型的Bean
In contrast to a plain BeanFactory, an ApplicationContext is supposed to detect special beans defined in its internal bean factory: Therefore, this class automatically registers BeanFactoryPostProcessors, BeanPostProcessors, and ApplicationListeners which are defined as beans in the context.
翻譯:
與普通的
BeanFactory相比,ApplicationContext應該能夠檢測在其內部 Bean 工廠中定義的特殊 bean :因此, 此類自動注冊在上下文中定義為 bean 的BeanFactoryPostProcessors,BeanPostProcessors和ApplicationListeners。
ApplicationContext 比 BeanFactory 強大的地方是支持更多的機制, 這里面就包括了后置處理器、監聽器等, 而這些器, 說白了也都是一個一個的 Bean , BeanFactory 不會把它們區別對待, 但是 ApplicationContext 就可以區分出來, 并且賦予他們發揮特殊能力的機會
AbstractApplicationContext可以轉換為多種類型
A MessageSource may also be supplied as a bean in the context, with the name “messageSource”; otherwise, message resolution is delegated to the parent context. Furthermore, a multicaster for application events can be supplied as an “applicationEventMulticaster” bean of type ApplicationEventMulticaster in the context; otherwise, a default multicaster of type SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster will be used.
翻譯:
一個
MessageSource也可以在上下文中作為一個普通的 bean 提供, 名稱為"messageSource"。否則, 將消息解析委托給父上下文。此外, 可以在上下文中將用于應用程序事件的廣播器作為類型為ApplicationEventMulticaster的"applicationEventMulticaster"bean 提供。否則, 將使用類型為SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的默認事件廣播器。
ApplicationContext 實現了國際化的接口 MessageSource 、事件廣播器的接口 ApplicationEventMulticaster , 那作為容器, 它也會把自己看成一個 Bean , 以支持不同類型的組件注入需要
AbstractApplicationContext提供默認的加載資源文件策略
Implements resource loading by extending DefaultResourceLoader. Consequently treats non-URL resource paths as class path resources (supporting full class path resource names that include the package path, e.g. “mypackage/myresource.dat”), unless the getResourceByPath method is overridden in a subclass.
翻譯:
通過擴展
DefaultResourceLoader實現資源加載。因此, 除非在子類中覆蓋了getResourceByPath()方法, 否則將非 URL 資源路徑視為類路徑資源(支持包含包路徑的完整類路徑資源名稱, 例如"mypackage/myresource.dat")。
默認情況下, AbstractApplicationContext 加載資源文件的策略是直接繼承了 DefaultResourceLoader 的策略, 從類路徑下加載;但在 Web 項目中, 可能策略就不一樣了, 它可以從 ServletContext 中加載(擴展的子類 ServletContextResourceLoader 等)
AbstractApplicationContext 中定義了一個特別特別重要的方法, 它是控制 ApplicationContext 生命周期的核心方法:refresh, 整體流程如下(細節不扣)
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing.// 1. 初始化前的預處理prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.// 2. 獲取BeanFactory, 加載所有xml配置文件中bean的定義信息(未實例化)ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.// 3. BeanFactory的預處理配置prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.// 4. 準備BeanFactory完成后進行的后置處理postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.// 5. 執行BeanFactory創建后的后置處理器invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.// 6. 注冊Bean的后置處理器registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context.// 7. 初始化MessageSourceinitMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.// 8. 初始化事件派發器initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.// 9. 子類的多態onRefreshonRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.// 10. 注冊監聽器registerListeners();//到此為止, BeanFactory已創建完成// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.// 11. 初始化所有剩下的單例BeanfinishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.// 12. 完成容器的創建工作finishRefresh();} // catch ......finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...// 13. 清除緩存resetCommonCaches();}}
}
GenericApplicationContext-熟悉
GenericApplicationContext 已經是一個普通的類(非抽象類)了, 它里面已經具備了ApplicationContext基本的所有能力
GenericApplicationContext組合了BeanFactory
Generic ApplicationContext implementation that holds a single internal DefaultListableBeanFactory instance and does not assume a specific bean definition format. Implements the BeanDefinitionRegistry interface in order to allow for applying any bean definition readers to it.
翻譯:
通用
ApplicationContext的實現, 該實現擁有一個內部DefaultListableBeanFactory實例, 并且不采用特定的 bean 定義格式。另外它實現BeanDefinitionRegistry接口, 以便允許將任何 bean 定義讀取器應用于該容器中。
重中之重: GenericApplicationContext 中組合了一個 DefaultListableBeanFactory !!!*由此可以得到一個非常非常重要的信息:*ApplicationContext 并不是繼承了 BeanFactory 的容器, 而是組合了 BeanFactory !
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;// 其它代碼
}
GenericApplicationContext借助BeanDefinitionRegistry處理特殊Bean
Typical usage is to register a variety of bean definitions via the BeanDefinitionRegistry interface and then call refresh() to initialize those beans with application context semantics (handling org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware, auto-detecting BeanFactoryPostProcessors, etc).
翻譯:
典型的用法是通過
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口注冊各種 Bean 的定義, 然后調用refresh()以使用應用程序上下文語義來初始化這些 Bean(處理ApplicationContextAware, 自動檢測BeanFactoryPostProcessors等)。
GenericApplicationContext 實現了**BeanDefinitionRegistry(Bean定義注冊器)** , 可以自定義注冊一些 Bean 。然而在 GenericApplicationContext 中, 它實現的定義注冊方法 registerBeanDefinition , 在底層還是調用的 DefaultListableBeanFactory 執行 registerBeanDefinition 方法, 說明它也沒有對此做什么擴展
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;public GenericApplicationContext() {// 內置的beanFactory在GenericApplicationContext創建時就已經初始化好了this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();}@Overridepublic void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);}// 省略其它代碼
}
GenericApplicationContext只能刷新一次
In contrast to other ApplicationContext implementations that create a new internal BeanFactory instance for each refresh, the internal BeanFactory of this context is available right from the start, to be able to register bean definitions on it. refresh() may only be called once.
翻譯:
與為每次刷新創建一個新的內部
BeanFactory實例的其他ApplicationContext實現相反, 此上下文的內部BeanFactory從一開始就可用, 以便能夠在其上注冊 Bean 定義。refresh()只能被調用一次。
由于 GenericApplicationContext 中組合了一個 DefaultListableBeanFactory , 而這個 BeanFactory 是在 GenericApplicationContext 的構造方法中就已經初始化好了, 那么初始化好的 BeanFactory 就不允許在運行期間被重復刷新了, 源碼如下
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;public GenericApplicationContext() {// 內置的beanFactory在GenericApplicationContext創建時就已經初始化好了this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();}@Overrideprotected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {throw new IllegalStateException("GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");}this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());}// 省略其它代碼
}
文檔注釋提到"相反"這個詞, 另外一類 ApplicationContext 它的設計不是這樣的, 而是每次刷新創建一個新的內部 BeanFactory 實例, 如AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext的替代方案是用xml
For the typical case of XML bean definitions, simply use ClassPathXmlApplicationContext or FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, which are easier to set up - but less flexible, since you can just use standard resource locations for XML bean definitions, rather than mixing arbitrary bean definition formats. The equivalent in a web environment is org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext.
翻譯:
對于 XML Bean 定義的典型情況, 只需使用
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext或FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, 因為它們更易于設置(但靈活性較差, 因為只能將從標準的資源配置文件中讀取 XML Bean 定義, 而不能混合使用任意 Bean 定義的格式)。在 Web 環境中, 替代方案是XmlWebApplicationContext。
注解驅動的 IOC 容器可以導入 xml 配置文件, 不過如果大多數都是 xml 配置的話, 官方建議還是直接用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 或者 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 就好 。注解驅動的方式在開發時很靈活, 但如果需要修改配置時, 可能需要重新編譯配置類;xml 驅動的方式在修改配置時直接修改即可, 不需要做任何額外的操作, 但能配置的內容實在是有些有限。所以這也建議咱開發者在實際開發中, 要權衡對比著使用
GenericApplicationContext不支持特殊Bean定義的可刷新讀取
For custom application context implementations that are supposed to read special bean definition formats in a refreshable manner, consider deriving from the AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext base class.
翻譯:
對于應該以可刷新方式讀取特殊bean定義格式的自定義應用程序上下文實現, 請考慮從
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext基類派生。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext-熟悉
類名直譯為 “可刷新的 ApplicationContext ”, 它跟上面 GenericApplicationContext 的最大區別之一就是它可以被重復刷新
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext支持多次刷新
Base class for ApplicationContext implementations which are supposed to support multiple calls to refresh(), creating a new internal bean factory instance every time. Typically (but not necessarily), such a context will be driven by a set of config locations to load bean definitions from.
翻譯:
它是
ApplicationContext接口實現的抽象父類, 應該支持多次調用refresh()方法, 每次都創建一個新的內部BeanFactory實例。通常(但不是必須)這樣的上下文將由一組配置文件驅動, 以從中加載 bean 的定義信息。
每次都會創建一個新的內部的 BeanFactory 實例(也就是 DefaultListableBeanFactory), 而整個 ApplicationContext 的初始化中不創建。通過源碼來看, 它的內部也是組合 DefaultListableBeanFactory , 但構造方法中什么也沒有干
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {@Nullableprivate DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext() {}
}
創建 BeanFactory的方法
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext刷新的核心是加載Bean定義信息
The only method to be implemented by subclasses is loadBeanDefinitions, which gets invoked on each refresh. A concrete implementation is supposed to load bean definitions into the given DefaultListableBeanFactory, typically delegating to one or more specific bean definition readers. Note that there is a similar base class for WebApplicationContexts.
翻譯:
子類唯一需要實現的方法是
loadBeanDefinitions, 它在每次刷新時都會被調用。一個具體的實現應該將 bean 的定義信息加載到給定的DefaultListableBeanFactory中, 通常委托給一個或多個特定的 bean 定義讀取器。 注意,WebApplicationContexts有一個類似的父類。
可刷新的ApplicationContext, 那它里面存放的Bean定義信息應該是可以被覆蓋加載的。由于AbstractApplicationContext就已經實現了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口, 容器本身可以重復刷新, 那么每次刷新時就應該重新加載Bean的定義信息, 以及初始化Bean實例。在Web環境下也有一個類似的父類, 猜都能猜到肯定是名字里多了個Web:AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext, 它的特征與AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext基本一致, 不重復解釋
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext額外擴展了Web環境的功能
org.springframework.web.context.support.AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext provides the same subclassing strategy, but additionally pre-implements all context functionality for web environments. There is also a pre-defined way to receive config locations for a web context.
翻譯:
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext提供了相同的子類化策略,但是還預先實現了 Web 環境的所有上下文功能。還有一種預定義的方式來接收 Web 上下文的配置位置。
與普通的 ApplicationContext 相比,WebApplicationContext 額外擴展的是與Servlet相關的部分( request 、ServletContext 等),AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 內部就組合了一個 ServletContext ,并且支持給Bean注入 ServletContext 、ServletConfig 等 Servlet 中的組件
幾個重要的最終實現類
Concrete standalone subclasses of this base class, reading in a specific bean definition format, are ClassPathXmlApplicationContext and FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, which both derive from the common AbstractXmlApplicationContext base class; org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext supports @Configuration-annotated classes as a source of bean definitions.
翻譯:
以特定的 bean 定義格式讀取的該父類的具體獨立子類是
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,它們均從AbstractXmlApplicationContext基類擴展。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext支持@Configuration注解的類作為BeanDefinition的源。
分別是基于 xml 配置的 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 和 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext ,以及基于注解啟動的 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext-了解
與AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 相比較,只是多了一個 Config ,說明它有擴展跟配置相關的特性。自己定義了 getConfigLocations 方法,意為“獲取配置源路徑”
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext subclass that adds common handling of specified config locations. Serves as base class for XML-based application context implementations such as ClassPathXmlApplicationContext and FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, as well as org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext.
翻譯:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的子類,用于添加對指定配置位置的通用處理。作為基于 XML 的ApplicationContext實現(例如ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext以及XmlWebApplicationContext)的父類。
通篇就抽出來一句話:用于添加對指定配置位置的通用處理。由于它是基于 xml 配置的 ApplicationContext 的父類,所以肯定需要傳入配置源路徑,那這個配置的動作就封裝在這個 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 中了
AbstractXmlApplicationContext-掌握
AbstractXmlApplicationContext是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 和 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 的直接父類
AbstractXmlApplicationContext已具備基本全部功能
Convenient base class for ApplicationContext implementations, drawing configuration from XML documents containing bean definitions understood by an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. Subclasses just have to implement the getConfigResources and/or the getConfigLocations method. Furthermore, they might override the getResourceByPath hook to interpret relative paths in an environment-specific fashion, and/or getResourcePatternResolver for extended pattern resolution.
翻譯:
方便的
ApplicationContext父類,從包含XmlBeanDefinitionReader解析的BeanDefinition的 XML 文檔中提取配置。子類只需要實現
getConfigResources和/或getConfigLocations方法。此外,它們可能會覆蓋getResourceByPath的鉤子回調,以特定于環境的方式解析相對路徑,和/或getResourcePatternResolver來擴展模式解析。
由于 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 已經接近于最終的 xml 驅動 IOC 容器的實現了,所以它應該有基本上所有的功能。又根據子類的兩種不同的配置文件加載方式,說明加載配置文件的策略是不一樣的,所以文檔注釋中有說子類只需要實現 getConfigLocations 這樣的方法就好。AbstractXmlApplicationContext加載到配置文件后如何處理
AbstractXmlApplicationContext中有loadBeanDefinitions的實現
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.// 借助XmlBeanDefinitionReader解析xml配置文件XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's// resource loading environment.beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.// 初始化BeanDefinitionReader,后加載BeanDefinitioninitBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
解析 xml 配置文件不是自己干活,是組合了一個 XmlBeanDefinitionReader ,讓它去解析。而實際解析配置文件的動作
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();if (configResources != null) {reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);}String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();if (configLocations != null) {reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);}
}
這里就是調用上面文檔注釋中提到的 getConfigResources 和 getConfigLocations 方法,取到配置文件的路徑 / 資源類,交給 BeanDefinitionReader 解析
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext-掌握
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext從classpath 下加載 xml 配置文件的 ApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是一個最終落地實現
Standalone XML application context, taking the context definition files from the class path, interpreting plain paths as class path resource names that include the package path (e.g. “mypackage/myresource.txt”). Useful for test harnesses as well as for application contexts embedded within JARs.
翻譯:
獨立的基于 XML 的
ApplicationContext,它從 classpath 中獲取配置文件,將純路徑解釋為包含包路徑的 classpath 資源名稱(例如mypackage / myresource.txt)。對于測試工具以及 jar 包中嵌入的ApplicationContext很有用。
支持的配置文件加載位置都是 classpath 下取,這種方式的一個好處是:如果工程中依賴了一些其他的 jar 包,而工程啟動時需要同時傳入這些 jar 包中的配置文件,那 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 就可以加載它們
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext使用Ant模式聲明配置文件路徑
The config location defaults can be overridden via getConfigLocations, Config locations can either denote concrete files like “/myfiles/context.xml” or Ant-style patterns like “/myfiles/*-context.xml” (see the org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher javadoc for pattern details).
翻譯:
可以通過
getConfigLocations方法覆蓋配置文件位置的默認值,配置位置可以表示具體的文件,例如/myfiles/context.xml,也可以表示Ant樣式的模式,例如/myfiles/*-context.xml(請參見AntPathMatcher的 javadoc 以獲取模式詳細信息)。
上面 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 中就說了,可以重寫 getConfigLocations 方法來調整配置文件的默認讀取位置,它這里又重復了一遍。除此之外它還提到了,加載配置文件的方式可以使用 Ant 模式匹配(比較經典的寫法當屬 web.xml 中聲明的 application-*.xml )
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext解析的配置文件有先后之分
Note: In case of multiple config locations, later bean definitions will override ones defined in earlier loaded files. This can be leveraged to deliberately override certain bean definitions via an extra XML file.
翻譯:
注意:如果有多個配置位置,則較新的
BeanDefinition會覆蓋較早加載的文件中的BeanDefinition,可以利用它來通過一個額外的 XML 文件有意覆蓋某些BeanDefinition。
這一點是配合第一點的多配置文件讀取來的。通常情況下,如果在一個 jar 包的 xml 配置文件中聲明了一個 Bean ,并且又在工程的 resources 目錄下又聲明了同樣的 Bean ,則 jar 包中聲明的 Bean 會被覆蓋,這也就是配置文件加載優先級的設定
ApplicationContext可組合靈活使用
This is a simple, one-stop shop convenience ApplicationContext. Consider using the GenericApplicationContext class in combination with an org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader for more flexible context setup.
翻譯:
這是一個簡單的一站式便利
ApplicationContext。可以考慮將GenericApplicationContext類與XmlBeanDefinitionReader結合使用,以實現更靈活的上下文配置。
最后文檔中并沒有非常強調 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的作用,而是提了另外一個建議:由于 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 繼承了 AbstractXmlApplicationContext ,而 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 實際上是內部組合了一個 XmlBeanDefinitionReader ,所以就可以有一種組合的使用方式:利用 GenericApplicationContext 或者子類 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ,配合 XmlBeanDefinitionReader ,就可以做到注解驅動和 xml 通吃了。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext-掌握
注解驅動的 IOC 容器。它本身繼承了 GenericApplicationContext ,那自然它也只能刷新一次。同樣是最終的落地實現,它自然也應該跟 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 類似的有一些特征
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是一個最終落地實現
Standalone application context, accepting component classes as input — in particular @Configuration-annotated classes, but also plain @Component types and JSR-330 compliant classes using javax.inject annotations.
翻譯:
獨立的注解驅動的
ApplicationContext,接受組件類作為輸入,特別是使用@Configuration注解的類,還可以使用普通的@Component類型和符合 JSR-330 規范(使用javax.inject包的注解)的類。
注解驅動,除了 @Component 及其衍生出來的幾個注解,更重要的是 @Configuration 注解,一個被 @Configuration 標注的類相當于一個 xml 文件。至于下面還提到的關于 JSR-330 的東西,它沒有類似于 @Component 的東西(它只是定義了依賴注入的標準,與組件注冊無關),它只是說如果一個組件 Bean 里面有 JSR-330 的注解,那它能給解析而已。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext解析的配置類也有先后之分
Allows for registering classes one by one using register(Class…) as well as for classpath scanning using scan(String…). In case of multiple @Configuration classes, @Bean methods defined in later classes will override those defined in earlier classes. This can be leveraged to deliberately override certain bean definitions via an extra @Configuration class.
翻譯:
允許使用
register(Class ...)一對一注冊類,以及使用scan(String ...)進行類路徑的包掃描。 如果有多個@Configuration類,則在以后的類中定義的@Bean方法將覆蓋在先前的類中定義的方法。這可以通過一個額外的@Configuration類來故意覆蓋某些BeanDefinition。
和ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 一樣存在配置覆蓋的概念。除此之外,它上面還說了初始化的兩種方式:要么注冊配置類,要么直接進行包掃描。由于注解驅動開發中可能沒有一個主配置類,都是一上來就一堆 @Component ,這個時候完全可以直接聲明根掃描包,進行組件掃描。
參考資料
從 0 開始深入學習 Spring


--手寫實現負載輪詢算法)


的簡介、安裝和使用方法、案例應用之詳細攻略)

)


)

技術架構:springboot + vue-element-plus-admin)

)
![子比主題ACG美化插件[全開源]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/子比主題ACG美化插件[全開源])

、RTKLIB源碼解析 — rnx2rtkp.c)
從零基礎入門到精通)
