題目:
有一種特殊的加密算法,明文為一段數字串,經過密碼本查找轉換,生成另一段密文數字串。?
規則如下
1?明文為一段數字串由0-9組成
2.密碼本為數字0-9組成的二維數組
3?需要按明文串的數字順序在密碼本里找到同樣的數字串,密碼本里的數字串是由相鄰的單元?
格數字組成,上下和左右是相鄰的,注意:對角線不相鄰,同一個單元格的數字不能重復使?
用。
4??每一位明文對應密文即為密碼本中找到的單元格所在的行和列序號(序號從0開始)組成的兩個?
數字。如明文第位Data[i]對應密碼本單元格為Book[x][y],則明文第i位對應的密文為XY, X和?
Y之間用空格隔開
如果有多條密文,返回字符序最小的密文。如果密碼本無法匹配,返回"error"
請你設計這個加密程序
示例1:
密碼本
[0 0 2]
[1 3 4]
[6 6 4]
明文:3,密文."1 1”
示例2:
示例2:
密碼本:
0 0 2
1 3 4
6 6?4
明文:"0 3”密文:0 1 1 1”
輸入描述
第一行輸入1個正整數N,代表明文的長度(1 <= N <= 200)
第二行輸入N個明文數字組成的序列Data[i](整數:0<= Data[i] <= 9)
第三行1個正整數M,代表密文的長度接下來M行,每行M個數,代表密文矩陣
輸出描述
輸出字典序最小密文?如果無法匹配,輸出"error
示例1:
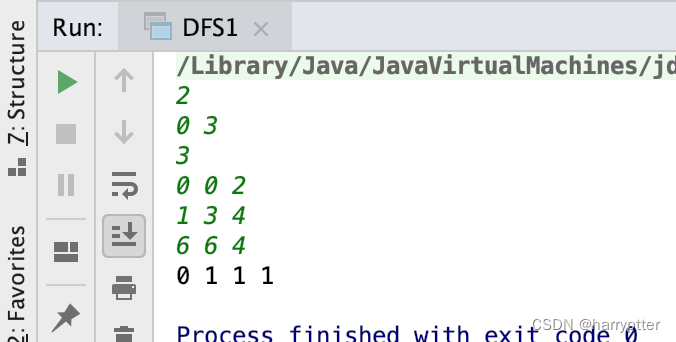
輸入:
2
0 3
3
0 0 2
1 3 4
6 6 4
輸出:
0 1 1 1
示例2:
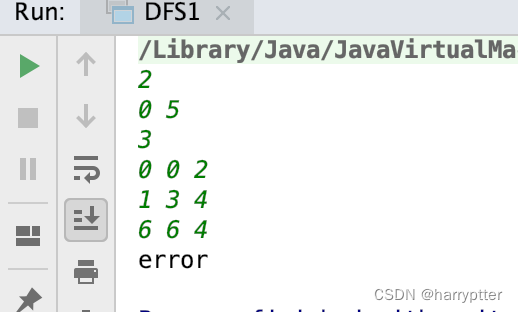
輸入:
2
0 5
3
0 0 2
1 3 4
6 6 4
輸出:
error
題解:
要在矩陣中找到連續的坐標位置,那么這種搜索就直接使用DFS搜索算法。這個題要注意有多條密文時候返回字符序最小的密文。所有搜索的時候順序應該是左->上->下->右(因為排列是先x坐標后y坐標),這樣找到第一個符合條件的數據就是最小的密文。
如果不按這個順序的話,那么就需要將多條密文序列進行排序,找出最小結果了(這個邏輯比較好理解)
這個題只有100分,但感覺還是有點難度的
代碼
import java.util.*;public class DFS1 {private static String result = "";// private static String sumResult = "";public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int num = Integer.valueOf(sc.nextLine());String nums[] =sc.nextLine().split(" ");int value[] = new int[num];for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){value[i] = Integer.valueOf(nums[i]);}int m = Integer.valueOf(sc.nextLine());int arr[][] = new int[m][m];for(int i=0;i<m;i++){String arrs[] = sc.nextLine().split(" ");for(int j =0;j<m;j++){arr[i][j] = Integer.valueOf(arrs[j]);}}int directions[][] = {{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,0}}; // 搜索順序 很重要,這樣第一個結果就是最小值了boolean hasdata = false;// Map<String,List<String>> resultMap = new HashMap<>();// List<String> resultValues = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<m;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(arr[i][j] == value[0]){result = i+" "+j;// sumResult = String.valueOf(i)+String.valueOf(j);// System.out.println("first is i"+i+"j "+j);if(dfs(directions,arr,i,j,value,1,m)){hasdata = true;// List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();// stringList.add(result);// resultMap.put(sumResult,stringList);// resultValues.add(sumResult);break;}}}if(hasdata){break;}}if(hasdata){
// Collections.sort(resultValues);
// System.out.println(resultMap.get(resultValues.get(0)).get(0));System.out.println(result);}else {System.out.println("error");}}public static boolean dfs(int[][] directions, int[][] arrs, int x, int y, int[] value, int index, int m) {int presentValue = value[index];int i = 0;while (i < 4) {if(i>=4){break;}int newX = x + directions[i][0];int newY = y + directions[i][1];
// if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < m) {
// System.out.println("newX " + newX + " newY " + newY + " arrs[newX][newY " + arrs[newX][newY] + "presentValue " + presentValue);
// }if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < m && arrs[newX][newY] == presentValue) {result += " " + newX + " " + newY;// sumResult = sumResult + String.valueOf(newX) + String.valueOf(newY);if (index == value.length - 1) {return true;}index++;return dfs(directions, arrs, newX, newY, value, index, m);}if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= m || arrs[newX][newY] != presentValue) {i++;continue;}}return false;}}
方法2:不考慮搜索順序,按照結果集排序,找出最小的
import java.util.*;public class DFS1 {private static String result = "";private static String sumResult = "";public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int num = Integer.valueOf(sc.nextLine());String nums[] =sc.nextLine().split(" ");int value[] = new int[num];for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){value[i] = Integer.valueOf(nums[i]);}int m = Integer.valueOf(sc.nextLine());int arr[][] = new int[m][m];for(int i=0;i<m;i++){String arrs[] = sc.nextLine().split(" ");for(int j =0;j<m;j++){arr[i][j] = Integer.valueOf(arrs[j]);}}// int directions[][] = {{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,0}}; // 搜索順序 很重要,這樣第一個結果就是最小值了int directions[][] = {{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}}; // 搜索順序 很重要,這樣第一個結果就是最小值了boolean hasdata = false;Map<String,List<String>> resultMap = new HashMap<>();List<String> resultValues = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<m;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(arr[i][j] == value[0]){result = i+" "+j;sumResult = String.valueOf(i)+String.valueOf(j);// System.out.println("first is i"+i+"j "+j);if(dfs(directions,arr,i,j,value,1,m)){hasdata = true;List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();stringList.add(result);resultMap.put(sumResult,stringList);resultValues.add(sumResult);break;}}}
// if(hasdata){
// break;
// }}if(hasdata){Collections.sort(resultValues);System.out.println(resultMap.get(resultValues.get(0)).get(0));// System.out.println(result);}else {System.out.println("error");}}public static boolean dfs(int[][] directions, int[][] arrs, int x, int y, int[] value, int index, int m) {int presentValue = value[index];int i = 0;while (i < 4) {if(i>=4){break;}int newX = x + directions[i][0];int newY = y + directions[i][1];
// if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < m) {
// System.out.println("newX " + newX + " newY " + newY + " arrs[newX][newY " + arrs[newX][newY] + "presentValue " + presentValue);
// }if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < m && arrs[newX][newY] == presentValue) {result += " " + newX + " " + newY;sumResult = sumResult + String.valueOf(newX) + String.valueOf(newY);if (index == value.length - 1) {return true;}index++;return dfs(directions, arrs, newX, newY, value, index, m);}if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= m || arrs[newX][newY] != presentValue) {i++;continue;}}return false;}}
驗證結果:










 v3.2.5安裝教程)







excel導出)

