小紅的直角三角形

思路:
當作向量來求,向量乘為0;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
int n;
vector<pll> u;
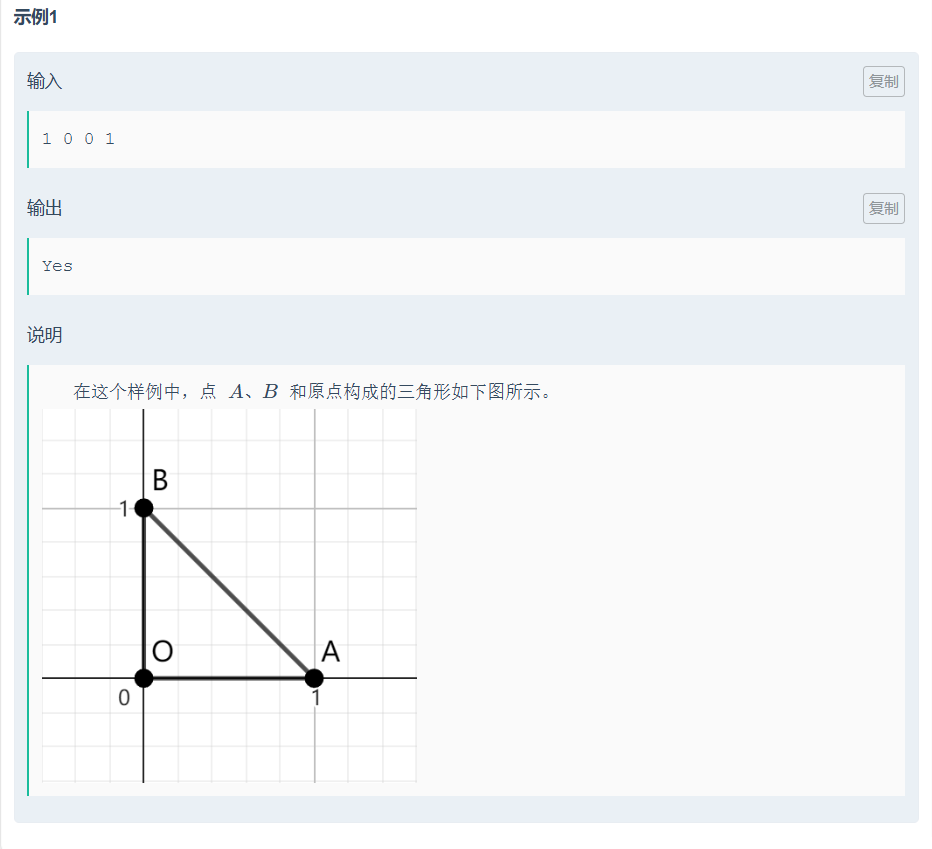
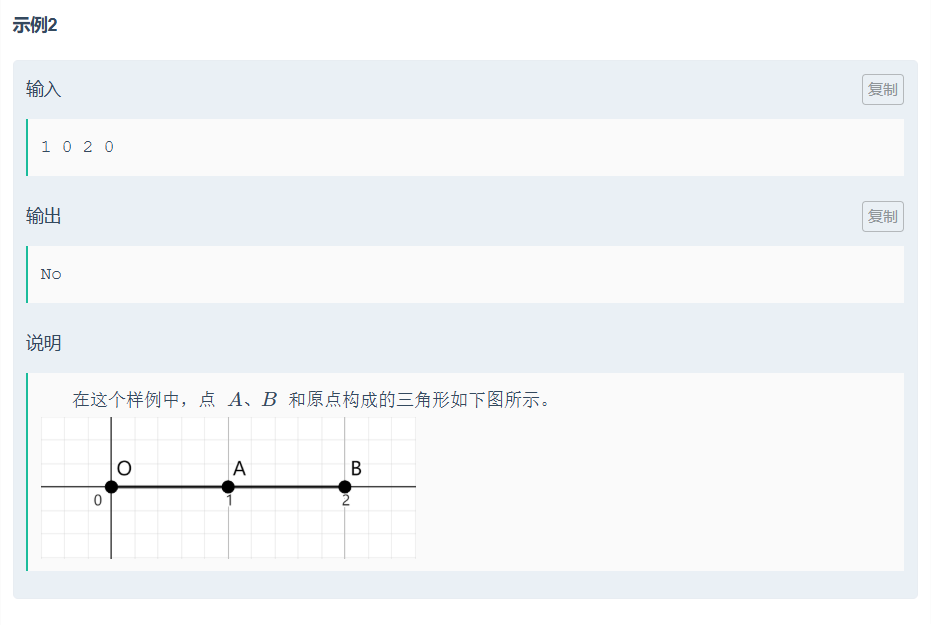
void solve() {int x, y, l, r;cin >> x >> y >> l >> r;if (x * l + y * r == 0 || -x * (l - x) + (-y) * (r - y) == 0 || -l * (x - l) + (-r) * (y - r) == 0) {cout << "Yes" << endl;}else {cout << "No" << endl;}return;
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin與cout綁定int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--) {solve();}return 0;
}小紅的好點對
思路:
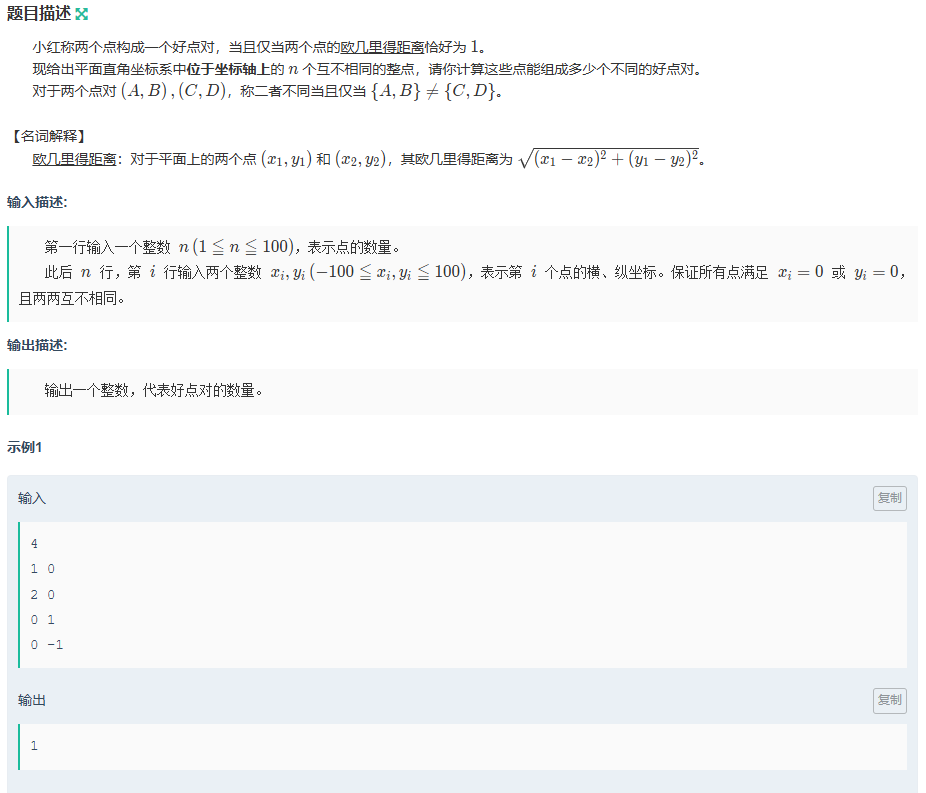
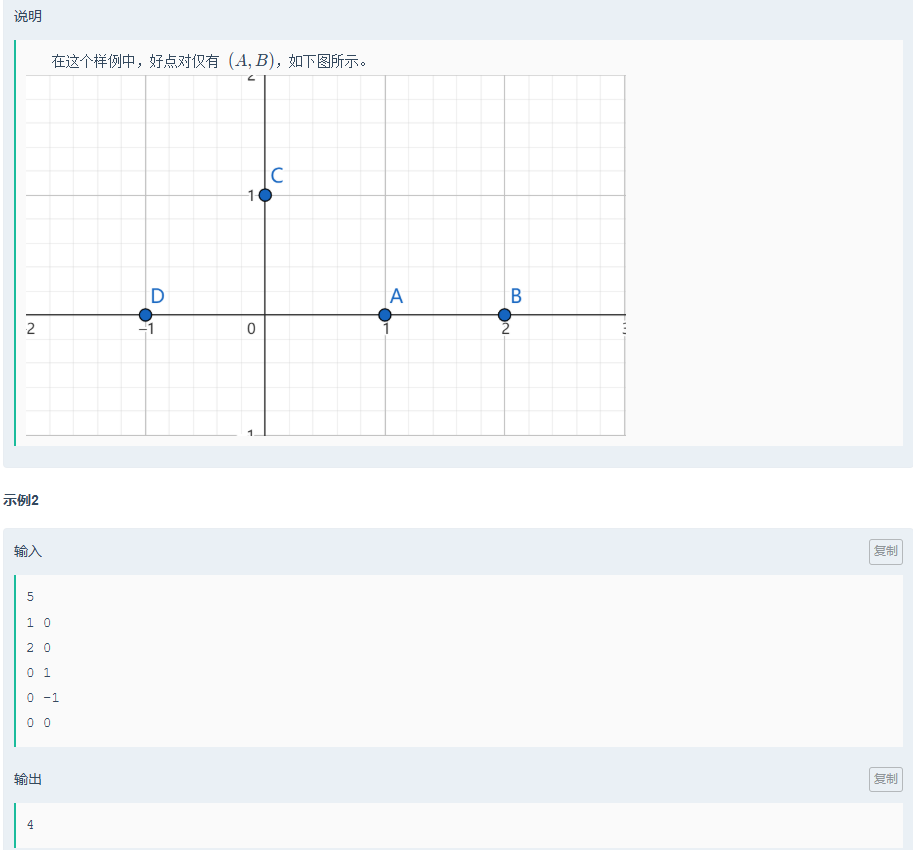
因為在坐標軸上,所以只有同x軸/y軸相差為1才成立,(0,0)單獨討論與(1,0)(0,-1)(-1,0)(0,1)的情況;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n;
void solve() {int n;cin >> n;vector<int>a, b;bool pan = false;int x, y;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> x >> y;if (x == 0 && y == 0) {pan = true;}else if(x==0) {a.push_back(y);}else {b.push_back(x);}}sort(a.begin(), a.end());sort(b.begin(), b.end());int ans = 0;if (!a.empty() && (a[0] == -1 || a[0] == 1)&&pan) {ans++;}for (int i = 1; i < a.size(); i++) {if (a[i] == 1 || a[i] == -1) {if (pan)ans++;}if (a[i] - a[i - 1] == 1) {ans++;}}if (!b.empty() && (b[0] == -1 || b[0] == 1) && pan) {ans++;}for (int i = 1; i < b.size(); i++) {if (b[i] == 1 || b[i] == -1) {if (pan)ans++;}if (b[i] - b[i - 1] == 1) {ans++;}}cout << ans << endl;return;
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin與cout綁定int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--) {solve();}return 0;
}小紅的整數三角形
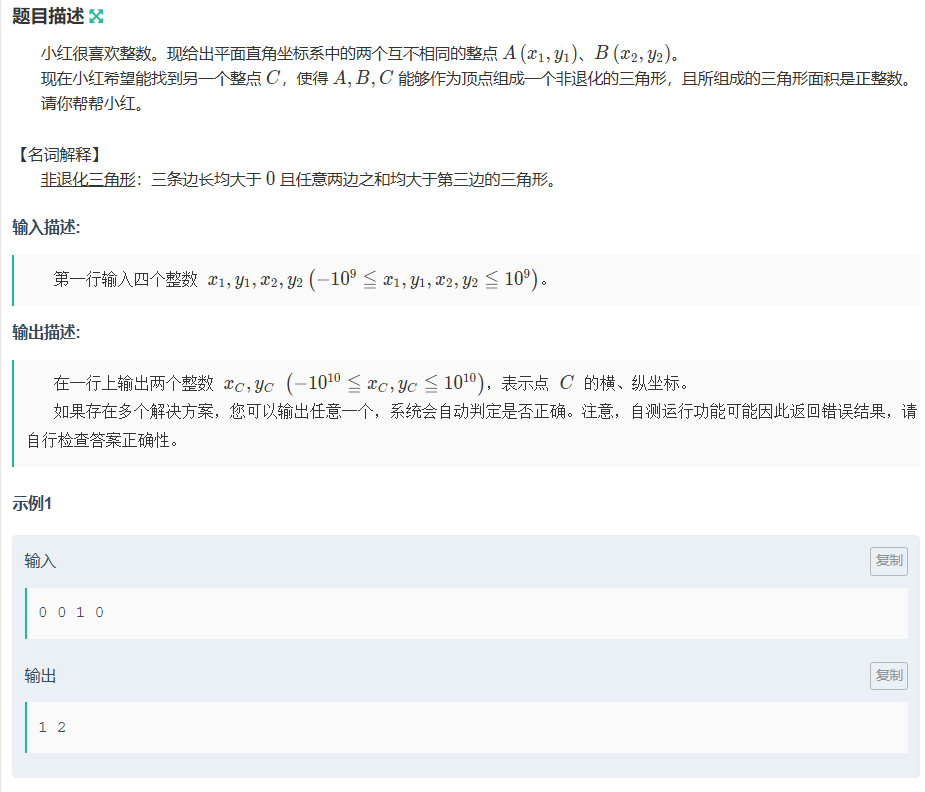
思路:
兩種情況,若y1!=y2,C點位(x1+(-)2,y1)或(x2+(-)2,y2)? S=2*|y1-y2|/2;
若y1=y1,C點位(x1,y+(-)21)或(x2,y2+(-)2)? ?S=2*|x1-x2|/2;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n;
void solve() {ll x, y, l, r;cin >> x >> y >> l >> r;ll q = y - r;if (q != 0) {cout << l + 2 << " " << r << endl;}else {cout << l << " " << r+2 << endl;}return;
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin與cout綁定int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--) {solve();}return 0;
}小紅的馬

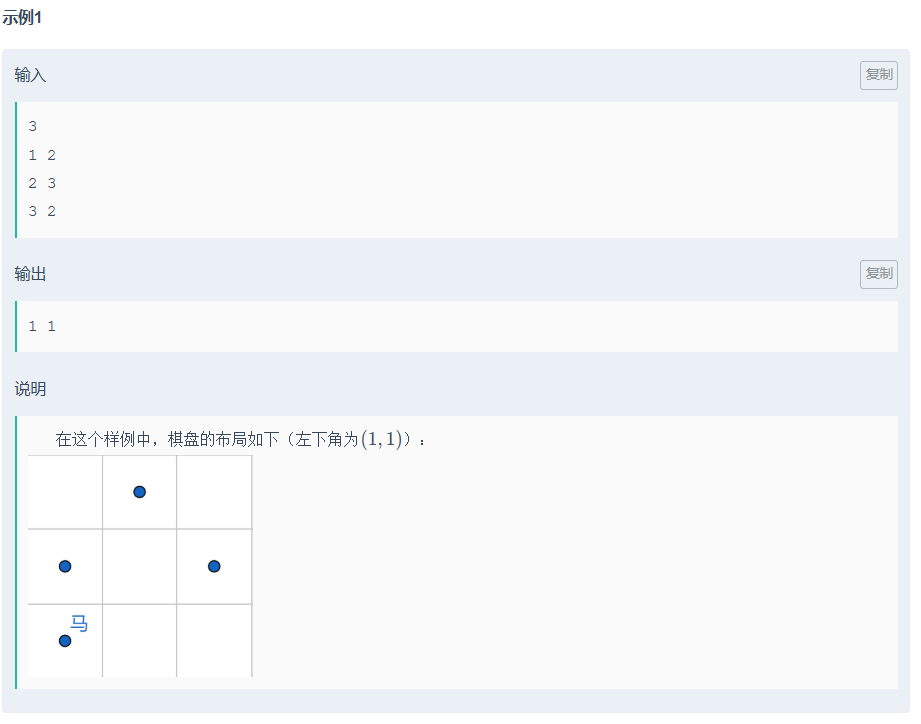
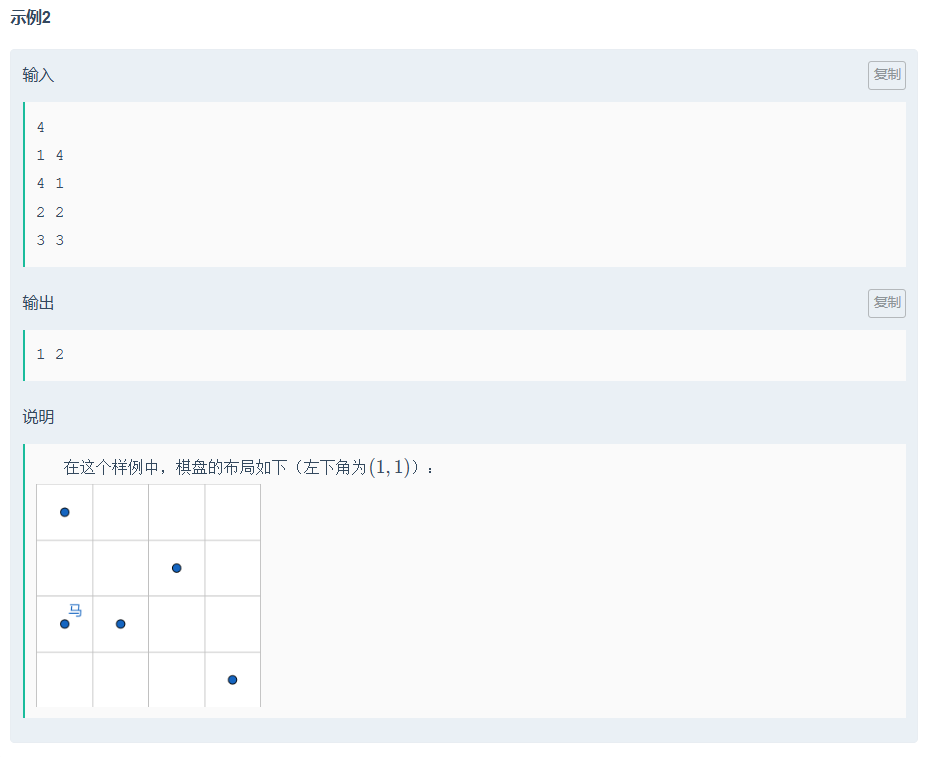
思路:
兩個map,一個存可以吃到兵的所以點位+該點位可以吃幾個兵,第二個map存,兵的點位
最后遍歷第一個map,并舍去第二個map存在的點后,取最大值。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
pii b[8] = { {-1,2},{-1,-2},{1,2},{1,-2},{-2,1},{-2,-1},{2,1},{2,-1} };
void solve() {int n;cin >> n;pii a;map<pii, int> f, pan;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> a.first >> a.second;pan.insert({ a, 0 });for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {auto it = f.find({ a.first + b[j].first,a.second + b[j].second });if (it == f.end()) {f.insert({ { a.first + b[j].first,a.second + b[j].second },1 });}else {(*it).second++;}}}int max_f = 0;pii g = { n,n };for (auto& it : f) {if (it.first.first < 1 || it.first.second < 1) {continue;}auto yy = pan.find(it.first);if (yy == pan.end()) {if (max_f < it.second) {g = it.first;max_f = it.second;}}}cout << g.first<<" "<<g.second << endl;return;
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin與cout綁定int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--) {solve();}return 0;
}小紅的好矩形

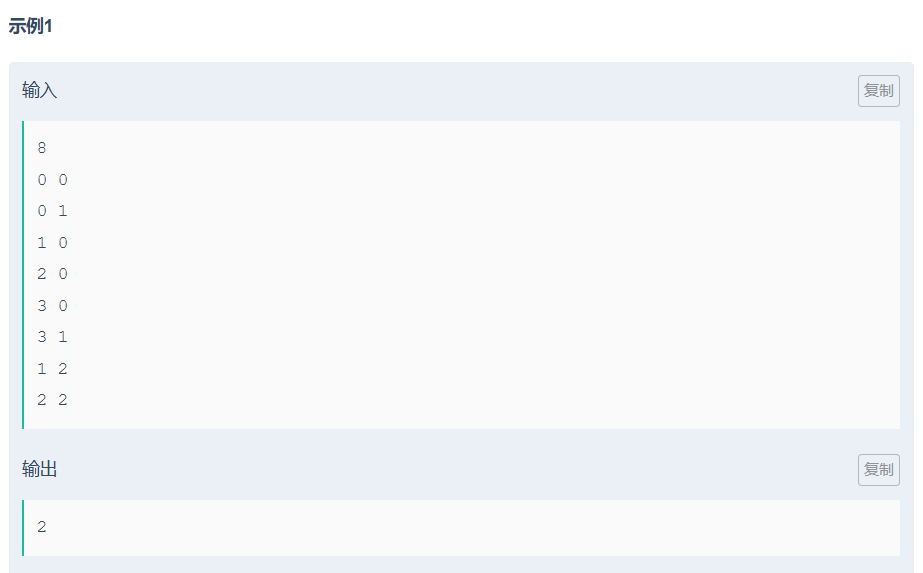
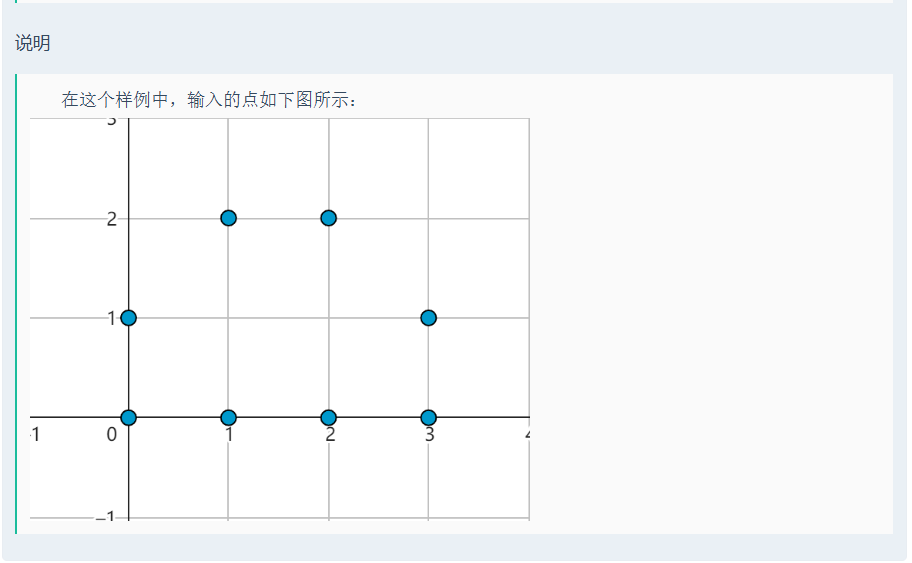
思路:
- 預處理:將點按?
x?坐標和?y?坐標分別排序,方便后續處理。 - 查找滿足條件的點:對于每個點,檢查是否存在?
(x+1, y)?或?(x, y+1)。 - 統計點對:
- 對于相同?
x?坐標的點,統計滿足?(x+1, y)?存在的點數目,計算組合數。 - 對于相同?
y?坐標的點,統計滿足?(x, y+1)?存在的點數目,計算組合數。
- 對于相同?
- 去重處理:如果存在點同時滿足?
(x+1, y)?和?(x, y+1),需要減去重復計數的情況。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n;
vector<pii> u;
bool find(pii q) {q.first++;int l = 0, r = n - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = (l + r) / 2;if (u[mid] > q) {r = mid - 1;}else if(u[mid]<q) {l = mid + 1;}else {return true;}}if (u[l] == q) {return true;}else {return false;}
}
void solve() {cin >> n;vector<pii> a(n), b(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;b[i].second = a[i].first, b[i].first = a[i].second;}sort(a.begin(), a.end());sort(b.begin(), b.end());ll ans = 0;int i = 0;u = a;while (i < n) {while (i<n&&!find(a[i])) {i++;}if (i >= n) {break;}pii w = a[i];i++;if (i >= n) {break;}ll sum = 1;for (; i < n&&w.first==a[i].first; i++) {if (find(a[i])) {sum++;}}ans += (sum - 1) * sum / 2;}i = 0;u = b;while (i < n) {while (i < n && !find(b[i])) {i++;}if (i >= n) {break;}pii w = b[i];i++;if (i >= n) {break;}ll sum = 1;for (; i < n && w.first == b[i].first; i++) {if (find(b[i])) {sum++;}}ans += (sum - 1) * sum / 2;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (i + 1 < n && b[i].first == b[i + 1].first &&b[i+1].second-b[i].second==1&& find(b[i]) && find(b[i + 1])) {ans--;}}cout << ans << endl;return;
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin與cout綁定int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--) {solve();}return 0;
}


)






![[Dify] 實現“多知識庫切換”功能的最佳實踐](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Dify] 實現“多知識庫切換”功能的最佳實踐)
)
)


)

BGP路由 選路規則)
:梯度下降)
