書接上文
java一個腳手架搭建_redission java腳手架-CSDN博客
以微服務為基礎搭建一套腳手架開始前的介紹-CSDN博客
腳手架開發-準備配置-進行數據初始化-配置文件的準備-CSDN博客
腳手架開發-準備配置-配置文件的準備項目的一些中間件-CSDN博客
腳手架開發-Nacos集成-CSDN博客
腳手架開發-網關集成-CSDN博客
Common包
????????在項?開發過程中,常常會進?諸如操作JSON、操作字符串、操作時間等?具類。在不同的項? ?,這些操作往往是相同的。因此,在這個項?中,我們可以將這部分操作封裝為基礎通?的部 分。
- 了解封裝基礎?具類;
- 公共模塊及基礎通?包創建;
- 基礎通??具類封裝完成;
- 基礎通??具類功能驗證測試通過。
公共模塊及基礎通用包創建
? ? ? ? 相信有的朋友已經注意到了,在這個腳手架開發中是有一個公共模塊的,它獨立出來就是未來存放所有其他模塊公共使用的類,而common包下有一個具體的層次common-core就是專門用來存放我們的基礎通用工具類。
common和common-core都是用module創建出來的,到了后面的包則是package
? ? ? ? 廢話不多說,如圖
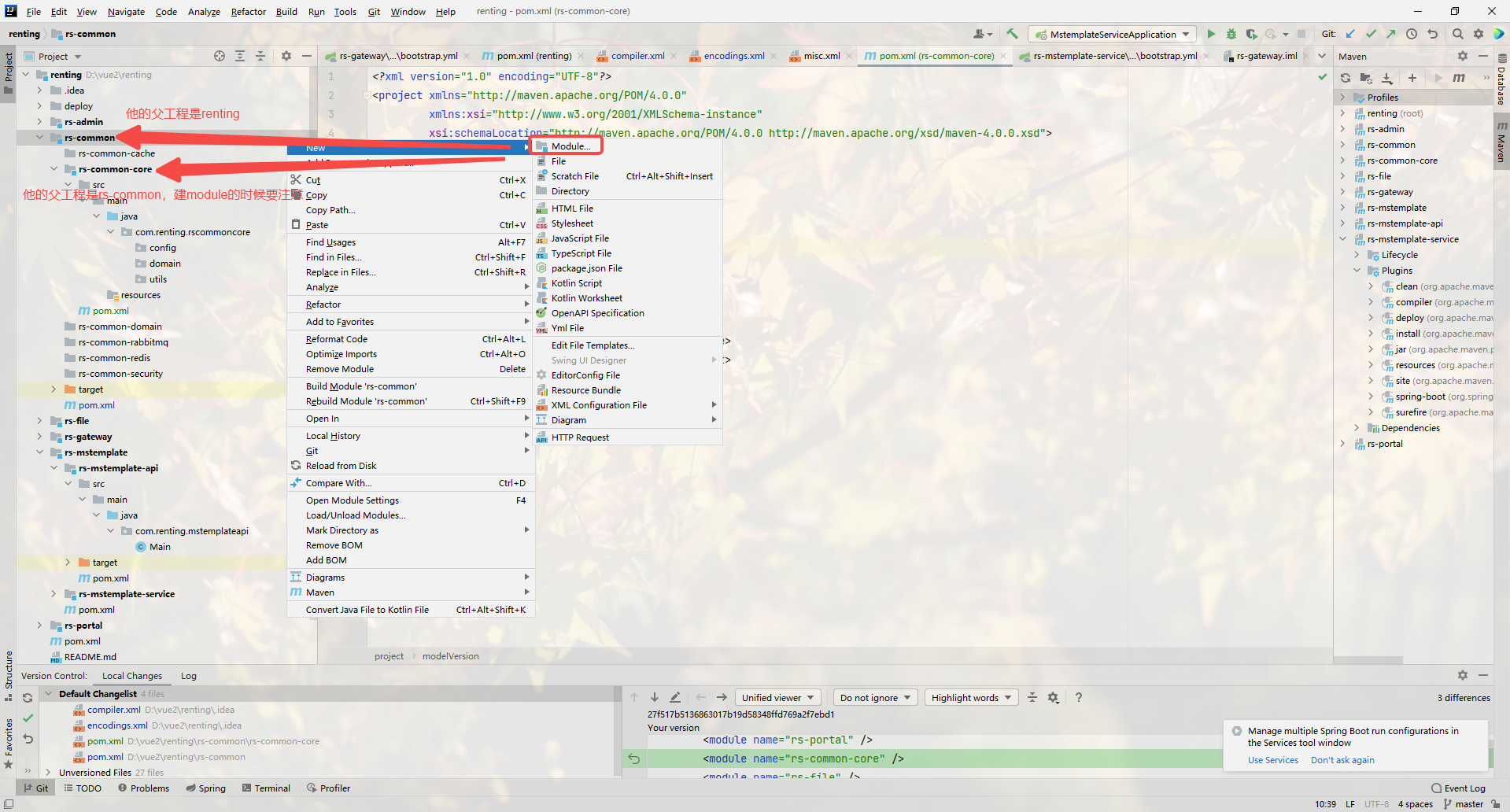
- 1. 創建公共模塊 rs-common
- 2.創建公共模塊的??程基礎通?包( rs-common-core)
- 3. 在 rs-common-core ?程中創建 com.renting.rscommoncore 包。
- 4. 在 com.renting.rscommoncore 包下創建 utils 包?于存放基礎通??具類。
封裝JSON基礎?具類
????????JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是?種輕量級的數據交換格式。數據交換指的是客?端和服務 器之間業務數據的傳輸格式。 JSON 是?種完全獨?于語?的?本格式,開發者很容易閱讀和編寫, 機器很容易解析和?成,能有效地提升?絡傳輸效率。這些優點也使 JSON 成為?種理想的獨?語??本格式。
????????需要所有?具類的理由都是?樣的,就是項?開發中使?的頻率?。
????????在?絡傳輸場景中,JSON?格式的數據量相對較?。與其他格式(如 XML)相?,JSON 沒有過多的標簽和冗余信息,這使得它在帶寬有限的?絡環境下能夠更?效地傳輸數據。所以在?絡傳輸中我們? 般選擇JSON作為數據傳輸格式。
????????在項?開發中我們經常會涉及到要將對象數據進?存儲。?如說要將對象存儲到Redis等存儲機制中。 描述同樣的消息,json相?xml占?更少的空間。
????????我們可以看一個直觀的例子。
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<user><id>1</id><name>張三</name><age>30</age>
</user>
Json
{"id": 1,"name": "張三","age": 30}那么我們應該做的,是什么?
- 提供對象轉json(對象序列化)
- 提供對象轉json格式化
- 提供json轉對象(對象反序列化)
怎么封裝?
1.創建JsonUtil類
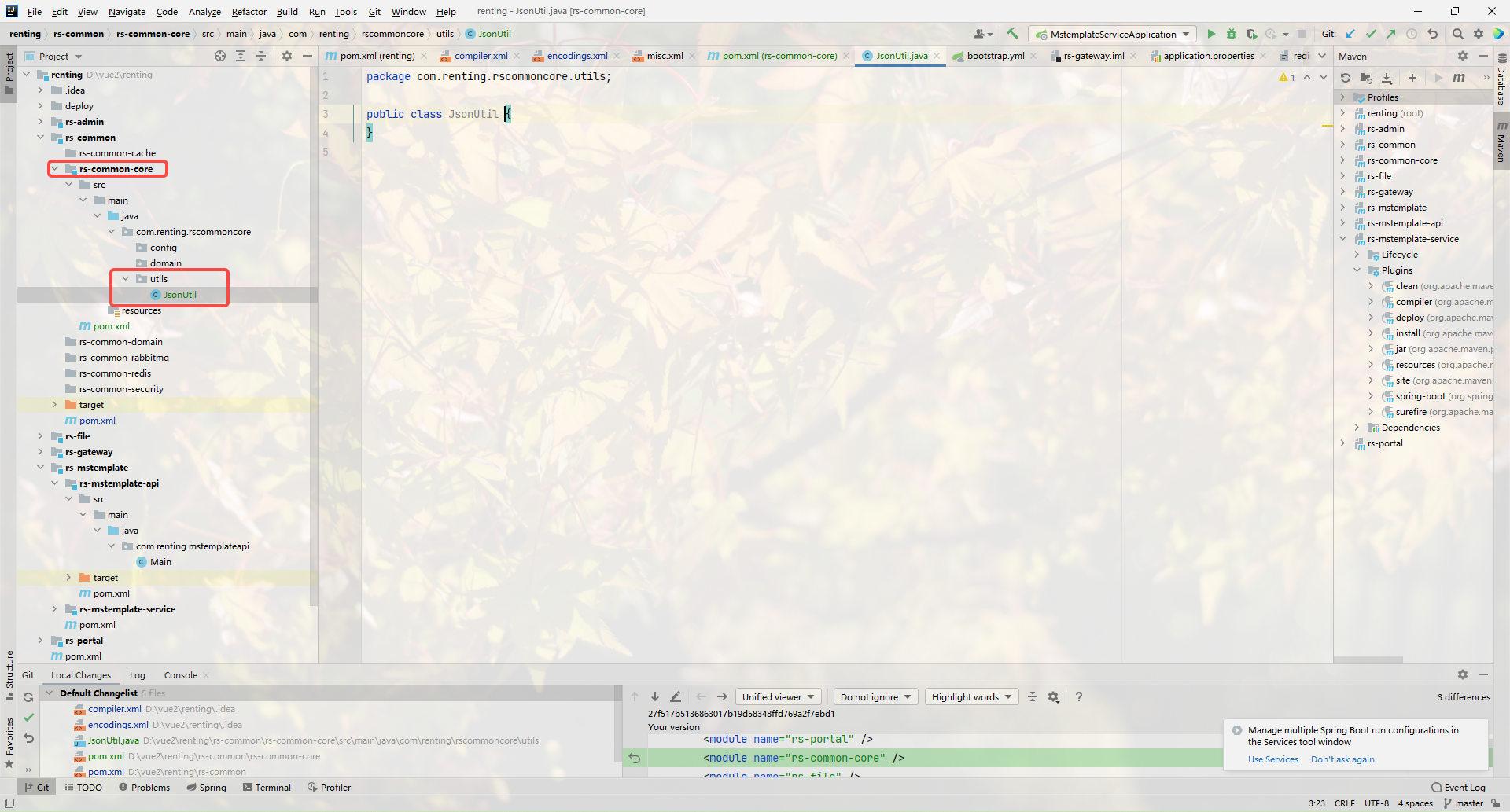
2.引入依賴
rs-common中的pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><parent><artifactId>renting</artifactId><groupId>org.example</groupId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version></parent><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><artifactId>rs-common</artifactId><packaging>pom</packaging><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><configuration><source>16</source><target>16</target></configuration></plugin></plugins></build><modules><module>rs-common-core</module></modules><properties><maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies>
</project>
3.JsonUtil中的代碼
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.json.JsonMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;/*** JSON?具類*/@Slf4jpublic class JsonUtil {/*** 對象轉換器*/private static ObjectMapper OBJECT_MAPPER;static {OBJECT_MAPPER =JsonMapper.builder().configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false).configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false).configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false).configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false).configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false).configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false).addModule(new JavaTimeModule()).defaultDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat(CommonConstants.S)).serializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL).build();}/*** 禁?構造*/private JsonUtil() {}/*** 對象轉Json格式字符串* @param obj 對象* @return Json格式字符串* @param <T> 對象類型*/public static <T> String obj2String(T obj) {if (obj == null) {return null;}try {return obj instanceof String ? (String) obj :OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsString(obj);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse Object to String error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 對象轉Json格式字符串(格式化的Json字符串)* @param obj 對象* @return 美化的Json格式字符串* @param <T> 對象類型*/public static <T> String obj2StringPretty(T obj) {if (obj == null) {return null;}try {return obj instanceof String ? (String) obj :OBJECT_MAPPER.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(obj);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse Object to String error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串轉換為?定義對象* @param str 要轉換的字符串* @param clazz ?定義對象的class對象* @return ?定義對象* @param <T> 對象類型*/public static <T> T string2Obj(String str, Class<T> clazz) {if (str == null || str.isEmpty()|| clazz == null) {return null;}try {return clazz.equals(String.class) ? (T) str :OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, clazz);} catch (Exception e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串轉換為?定義對象,?持復雜的泛型嵌套* @param str json字符串* @param valueTypeRef 對象模板信息* @return 對象類對應的對象* @param <T> 對象類*/public static <T> T string2Obj(String str, TypeReference<T> valueTypeRef){if (str == null || str.isEmpty() || valueTypeRef == null) {return null;}try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str,valueTypeRef);} catch (Exception e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串轉換為?定義字段轉為list,?持List嵌套簡單對象* @param str json字符串* @param clazz 對象類* @return 對象列表* @param <T> 對象類型*/public static <T> List<T> string2List(String str, Class<T> clazz) {if (str == null || str.isEmpty()|| clazz == null) {return null;}JavaType javaType =OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, clazz);try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, javaType);} catch (IOException e) {log.error("Parse String to Object error : {}" + e.getMessage());return null;}}/*** 字符串轉換為?定義字段轉為map,?持Map嵌套簡單對象* @param str str 字符串信息* @param valueClass valueClass value的類別* @return map對象* @param <T> value 的類型*/public static <T> Map<String, T> string2Map(String str, Class<T>valueClass){if (str == null || str.isEmpty() || valueClass == null) {return null;}JavaType javaType =OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructMapType(LinkedHashMap.class,String.class, valueClass);try {return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, javaType);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.warn("Parse String to Object error : {}", e.getMessage());return null;}}
}
解釋:
1.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false)
在反序列化時,當遇到JSON數據中存在Java對象對應類中沒有定義的屬性時,默認情況下?Jackson會拋出異常。通過將這個配置項設置為false,表?允許在反序列化時忽略那些未知的屬性,不會因為出現額外的屬性?導致反序列化失敗,增強了對不同來源JSON數據的兼容性。
2. .configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS,?false)在序列化時,如果Java對象中包含?期類型默認情況下Jackson可能會將?期轉換為時間戳(?個表?從某個特定時間點開始到當前時間的毫秒數等形式的數值來表?。將此配置設置為false,意味著不采?時間戳的?式來表??期,?是會按照后續配置的其他?期相關格式進?序列 化,以便?成更具可讀性的?期格式表?在JSON數據中。
3. .configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS,false)在序列化時,Java對象中沒有任何屬性值(為空),默認情況下Jackson可能會拋出異常。設置 此項為false后,允許對這樣的空對象進?序列化,即便對象沒有實質內容也能?成對應的JSON?表?(通常可能是?個空的JSON對象{}),避免了因對象為空導致序列化失敗的情況。
4. .configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false)在反序列化時,如果JSON數據中指定的類型信息與期望的Java類型層次結構不匹配(例如類型 標識錯誤等情況),默認會拋出異常。將這個配置設為false,可以放寬這種限制,使得在遇到類 型不太準確但仍有可能處理的情況下,嘗試繼續進?反序列化?不是直接失敗,提?對可能存在錯誤類型標識的JSON數據的容錯性。
5. .configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)在序列化時,如果Java對象中有以?期類型作為鍵(?如在Map中,鍵是Date類型等情況的結構,如果設置為true會將?期鍵轉換為時間戳形式。設置為false則按照其他?期相關配置來處 理,保證?期鍵也以期望的格式進?序列化,使得整個JSON結構中?期相關內容都能保持統?的 格式呈現。(默認值為false)
6. .configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false)?Jackson?持通過在Java類的屬性或?法上添加各種注解來定制序列化和反序列化?為。將此配 置設為false,表?不依賴這些注解來進?相關操作,?是更多地依據全局配置(如上述其他配置 項)來控制序列化和反序列化過程,適?于希望統?管理JSON處理規則,減少因注解使?不當或 過多導致的復雜性的場景。
7. addModule(newJavaTimeModule())?這是序列化LocalDateTIme和LocalDate的必要配置,由Jackson-data-JSR310實現。
8. .defaultDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat(CommonConstants.STANDARD_FORMAT))?所有的?期格式都統?為以下的樣式,即yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
4.泛型擦除<理解>
我們給出這樣一段代碼
@Test2
public void string2ListObjTest(){
// TestRegion testRegion = new TestRegion();
// testRegion.setId(1L);
// testRegion.setName("北京");
// testRegion.setFullName("北京市");
// testRegion.setCode("110000");
// List<TestRegion> regionList = new ArrayList<>();
// regionList.add(testRegion);
// System.out.println(JsonUtil.obj2String(regionList));
// [{"id":1,"name":"北京","fullName":"北京市","code":"110000"}]
List list = JsonUtil.string2Obj("[{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"北京\",\"fullName\":\"北京市\",\"code\":\"110000\"}]", List.class);System.out.println(list);我們單步調試可以看到list和我們定義的類型不?致
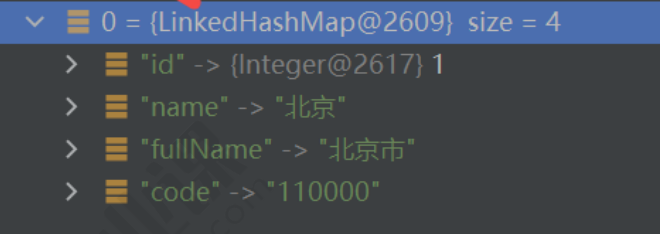
????????這是因為java的泛型擦除導致的,如果后?代碼我們基于List繼續定義,那么會報類型不匹配。
什么是泛型擦除?
????????Java中的泛型擦除(Type Erasure)是指Java編譯器在編譯泛型代碼時,會移除泛型類型參數的相關信息,使得?成的字節碼中不包含泛型類型信息。這使得Java泛型在運?時(Runtime)表現為原始類型(Raw Type)。
為什么出現泛型擦除:
? ? ? ? 向后兼容:新舊代碼兼容,在編譯時泛型信息就擦除了,所以舊版本jvm可以運載新代碼
? ? ? ? 類型安全:盡管泛型信息在編譯時被擦除,但在編譯時會進?類型檢查,確保泛型的使用是安全的。這意味著你可以在編譯時發現類型錯誤,而不是在運行時
? ? ? ? 避免性能開銷:所有的類型信息在編譯時就已經確定,泛型擦除避免了如果JVM需要在運?時維護泛型類型信息引入的額外開銷。
解決方法:
????????常見的Collection如 List、Map 中包含泛型,需要先反序列化Collection類型為泛型的CollectionType。
????????如果是ArrayList那么使?ObjectMapper的 getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(collectionClass,YourBean.class)。
????????HashMap那么 ObjectMapper 的 getTypeFactory().constructMapType(HashMap.class,String.class, YourBean.class)。
封裝Bean拷貝基礎工具類
????????Bean拷?(BeanCopy)是指在?向對象編程中,將?個Java對象(通常稱為源Bean)的屬性值復制到另?個Java對象(目標Bean)中的操作。
示例:
@Testpublic void beanCopyTest() {//源bean : TestUser {"name" : "張三","sex" : "男","age" : 29}//?標bean: TestUserVO TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();userVO.setName(testUser.getName());userVO.setAge(testUser.getAge());
}
????????Web項目中有控制器(Controller)層、業務邏輯(service)層、數據訪問 (DAO)層。不同層之間通常會使用不同的數據模型,這就意味著項目中往往不止一種數據模型,經常需要將數據從一種數據模型轉換成另外一種 數據模型,正因如此,才需要Bean拷貝。
具體來說分為這
幾種常見的數據模型:
DO(Data Object)是?個與數據庫表結構對應的對象,也叫持久化對象。DO通常?來在DAO層 (數據訪問層)和數據庫進?交互。
BO(Business Object)是?個封裝業務邏輯的對象,主要存在于業務邏輯層。它封裝了業務邏輯 相關的數據和操作。BO不僅僅是簡單的數據容器,還包含了業務規則和業務流程相關的?法。?
DTO(Data Transfer Object)是?個?來傳輸數據的對象。DTO?來在不同層或不同系統之間傳 遞數據,?如從Service層傳遞到Controller層或者Controller層傳遞到service層等。DTO可以避免 在層與層之間傳遞過多的不必要的數據,同時也可以隱藏內部的數據結構和實現細節。
VO(View Object)是?個?來展?數據的對象(返回給前端的數據)。它是根據具體的視圖(如?Web??、桌?應?的界?等)的要求,將數據以?種合適的形式進?組織和封裝,以便于在視圖中進進行展示。
POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object)是?個普通的Java對象,它沒有任何特殊的要求或約束,可 以?來表?任何類型的數據。
拷貝
????????手動拷貝
private String QQ;...............public TestUserVO convertToVO() {TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();userVO.setName(this.name);userVO.setAge(this.age);............return userVO ;
? ? ? ? 拷貝工具
BeanUtils.copyProperties() 是 Spring 框架提供的?個?具?法,它可以簡化對象屬性的拷貝操作
TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(user, userVO);? ? ? ? 但如果源bean和?標bean之間的屬性名稱不?致,或者源bean向?標bean拷?時需要對源bean 中的屬性值進?處理后再進?拷?。此時使??具類就?法準確的完成拷??作了
????????拷貝工具類+手動拷貝
使?spring提供的?具類,針對具體的對象提供專?的bean拷??法,就是拷貝工具類+手動拷貝
例如
@Getter
@Setter
@ToStringpublic class TestUserVO {private String nickName;private int age;private String school;private String contactInfo;
}
public class TestUser {private String name;private int age;private String sex;private String school;private String weChat;private String QQ;...............public TestUserVO convertToVO() {TestUserVO userVO = new TestUserVO();BeanUtils.copyProperties(user, userVO);userVO.setNickName(this.name);userVO.setContactInfo(this.weChat + "--" + this.QQ);return userVO ;}
}
????????內置拷??具類+拷??具類+?動拷?
單個對象普通拷?:直接使?spring提供的?具類。
列表對象普通拷?:由于拷?spring框架提供的bean拷??具類?法?持對列表對象的拷??作,所 以我們需要??封裝內置Bean拷??具類提供對列表對象的拷??法。
特殊拷?(包括列表對象和單個對象):需要?動拷?。針對具體的對象提供專?的bean拷??法。
Bean拷貝工具類
1.創建BeanCopyUtil工具類
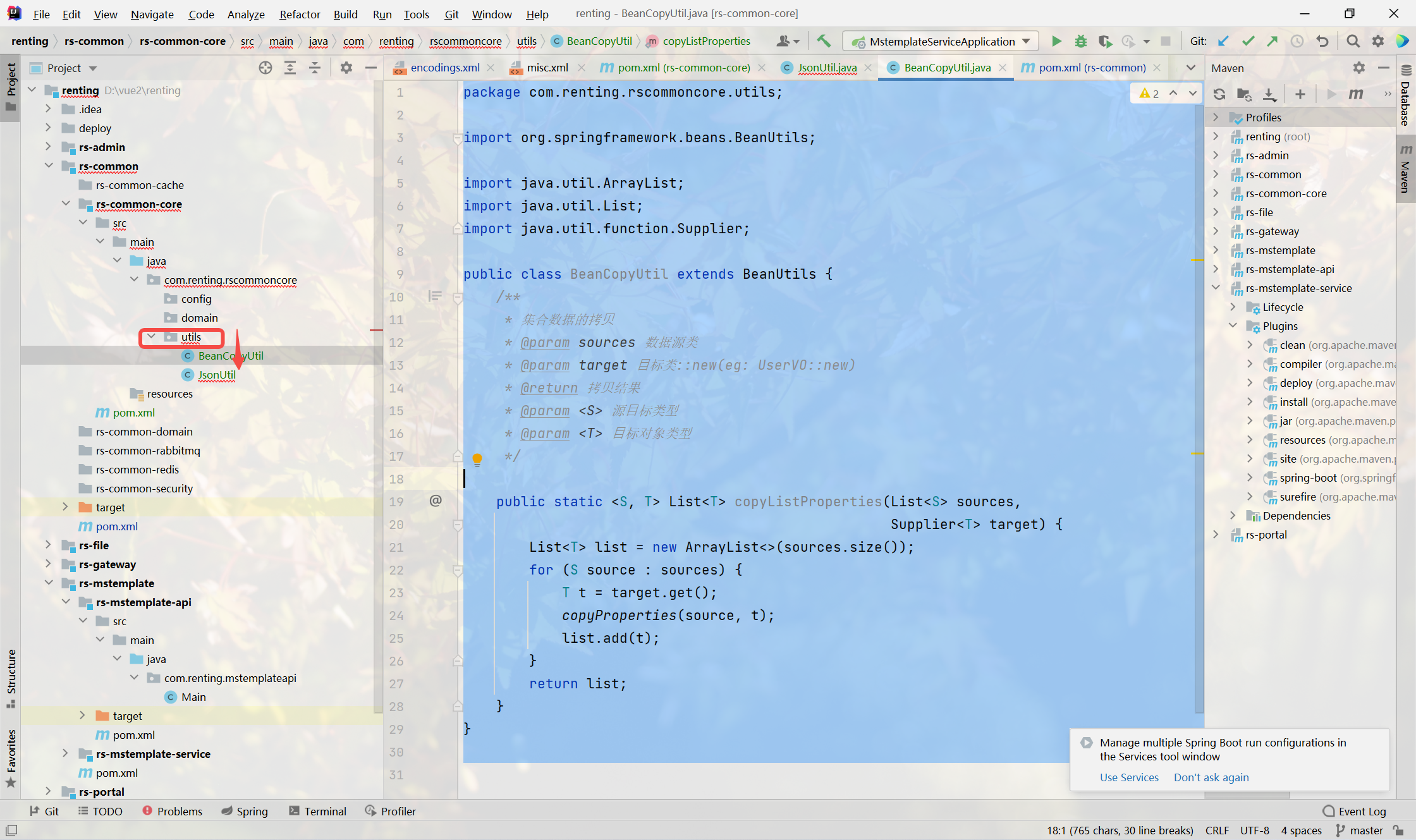
BeanUtils.copyProperties 不?持列表拷?,默認只?持java bean,我們擴展下該?法?持 列表拷?
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Supplier;public class BeanCopyUtil extends BeanUtils {/*** 集合數據的拷?* @param sources 數據源類* @param target ?標類::new(eg: UserVO::new)* @return 拷?結果* @param <S> 源?標類型* @param <T> ?標對象類型*/public static <S, T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<S> sources,Supplier<T> target) {List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(sources.size());for (S source : sources) {T t = target.get();copyProperties(source, t);list.add(t);}return list;}
}2.Spring框架提供的Bean拷??具類問題
?屬性類型不?致導致拷?失敗
實際開發中,很可能會出現同?字段在不同的類中定義的類型不?致,例如ID,可能在A類中 定義的類型為Long,在B類中定義的類型為String,此時如果使?BeanUtils.copyProperties進?拷?,就會出現拷?失敗的現象,導致對應的字段為null
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructorclass SourcePoJo{private String username;private Long id;
}@Data class TargetPoJo{private String username;private String id;
}@Testvoid copyfail1() {SourcePoJo sourcePoJo = new SourcePoJo("bite", (long) 1000000);TargetPoJo targetPoJo = new TargetPoJo();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePoJo,targetPoJo);System.out.println(targetPoJo);
}輸出結果會變成
BeanUtilsTests.TargetPoJo(username=bite, id=null)在實際開發中,很可能會出現同?字段在不同的類中定義的類型不?致,例如ID,可能在A類中 定義的類型為Long,在B類中定義的類型為long,此時如果使BeanUtils.copyProperties進?拷?,就會出現拷?失敗的現象,會拋出FatalBeanException。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructorclass SourcePoJo{private String username;private Long id;
}@Dataclass TargetPoJo2{private String username;private long id;
}@Testvoid copyfail2() {SourcePoJo sourcePoJo = new SourcePoJo();sourcePoJo.setUsername("bite");TargetPoJo2 targetPoJo2 = new TargetPoJo2();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePoJo,targetPoJo2);System.out.println(targetPoJo2);
}輸出結果:
org.springframework.beans.FatalBeanException: Could not copy property 'id'
from source to targetat
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties(BeanUtils.java...(報錯信息)
底層實現為反射拷?效率低
BeanUtils.copyProperties底層是通過反射獲取到對象的set和get?法,然后通過get、set完成數據的 拷?,整體拷?效率較低。
????????使?BeanUtils.copyProperties拷?數據和直接set的?式賦值效率對?,為了便于直觀的看出 效果,這?以拷?1萬次為例:
@Testvoid copyslow(){long copyStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();SourcePoJo source = new SourcePoJo("bite",1000000L);TargetPoJo2 target = new TargetPoJo2();for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);}System.out.println("copy?式:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-
copyStartTime));long setStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {target.setUsername(source.getUsername());target.setId(source.getId());}System.out.println("set?式:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-setStartTime));
}結果:
copy?式:127
set?式:0BeanUtils.copyProperties是淺拷?
? ? ? ? 淺拷貝是說在創建?個新對象(?標對象),?標對象的屬性值與原始對象相同,但對于引?類型的屬性,仍然共享相同的引?。也就是說在淺拷?下,當源對象的引?屬性的值發?變化時,?標對象的引?屬性值也會隨之發?變化。
我們可以舉一個簡單的例子
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructorclass Card {private String num;
}@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Dataclass Person {private String name;private Card card;
}@Testvoid copylight(){Person sourcePerson = new Person("bite",new Card("123456"));Person targetPerson = new Person();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson, targetPerson);System.out.println(targetPerson);sourcePerson.getCard().setNum("654321");System.out.println(targetPerson);//修改后代碼:
Person sourcePerson = new Person("bite",new Card("123456"));Person targetPerson = new Person();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson, targetPerson);Card targetCard = new Card();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson.getCard(), targetCard);targetPerson.setCard(targetCard);System.out.println(targetPerson);sourcePerson.getCard().setNum("654321");System.out.println(targetPerson);
}結果如下:
BeanCopyUtilTests.Person(name=bite, card=BeanCopyUtilTests.Card(num=123456))
BeanCopyUtilTests.Person(name=bite, card=BeanCopyUtilTests.Card(num=654321))內部類數據無法成功拷貝
Spring 的?BeanUtils.copyProperties?在處理內部類屬性時會遇到拷貝失敗的問題,這是由其設計機制決定的。
-
訪問權限限制:
-
內部類的字段默認是?
private?訪問級別 -
BeanUtils?使用反射訪問字段時,無法突破 Java 的訪問控制規則 -
示例:內部類?
Inner?的字段?innerValue?無法被外部訪問
-
-
Getter/Setter 缺失:
-
內部類的字段通常沒有公共的 getter/setter 方法
-
BeanUtils?依賴標準的 JavaBean 規范(通過 getter/setter 訪問屬性) -
當缺少這些方法時,屬性拷貝會靜默失敗
-
其它的一些公共工具類
時間戳工具類
- 獲取當前時間戳
- 獲取未來x秒的時間戳
- 獲取未來x天的時間戳
- 獲取未來x?的時間戳
- 獲取未來x年的時間戳
- 計算兩個時間戳之間的差異
- 所有?法均提供返回秒級時間和毫秒級時間兩種實現
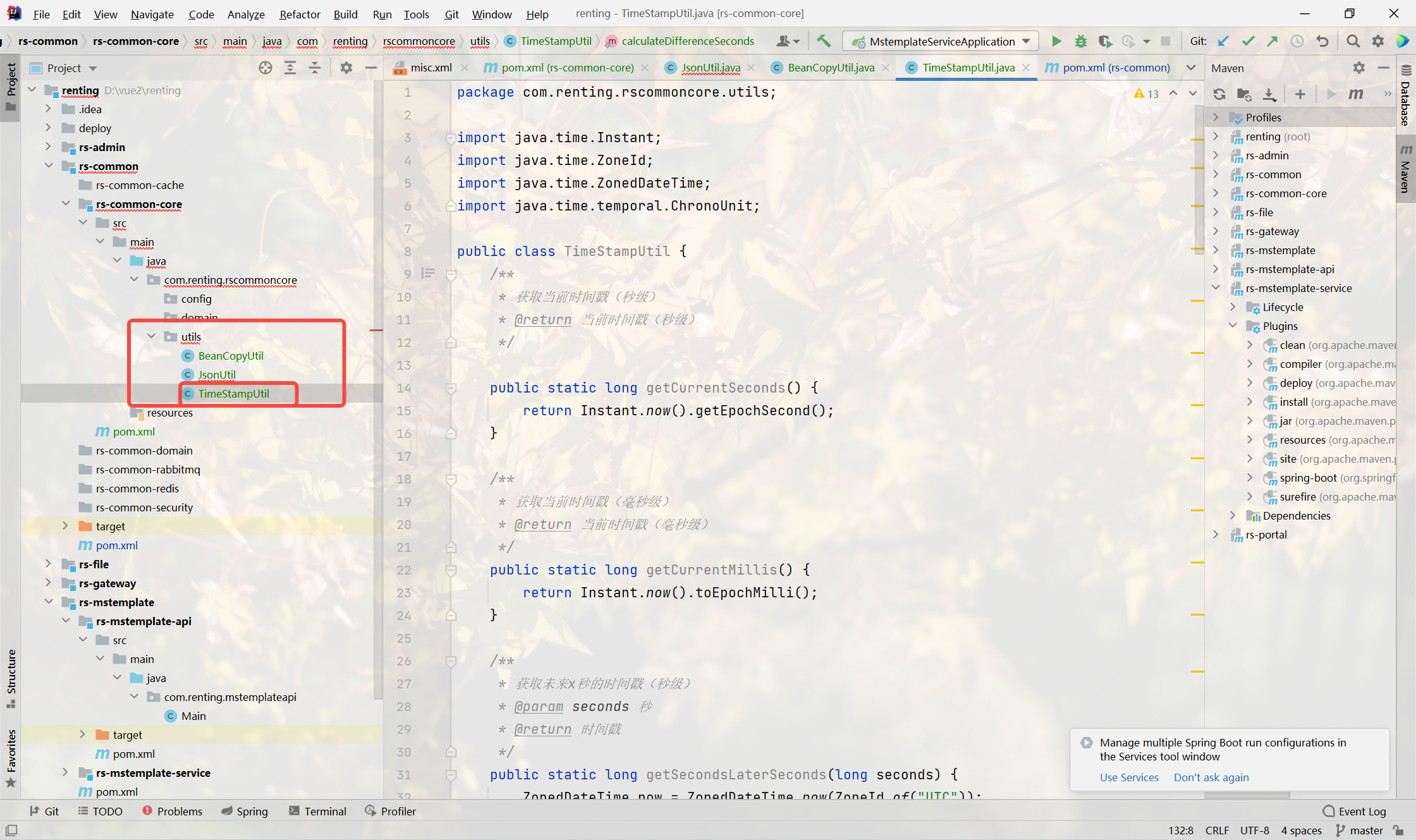
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;public class TimeStampUtil {/*** 獲取當前時間戳(秒級)* @return 當前時間戳(秒級)*/public static long getCurrentSeconds() {return Instant.now().getEpochSecond();}/*** 獲取當前時間戳(毫秒級)* @return 當前時間戳(毫秒級)*/public static long getCurrentMillis() {return Instant.now().toEpochMilli();}/*** 獲取未來x秒的時間戳(秒級)* @param seconds 秒* @return 時間戳*/public static long getSecondsLaterSeconds(long seconds) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 獲取未來x秒的時間戳(毫秒級)* @param seconds 秒* @return 時間戳*/public static long getSecondsLaterMillis(long seconds) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);return secondsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 獲取未來x天的時間戳(秒級)* @param days 天* @return 時間戳*/public static long getDaysLaterSeconds(long days) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusDays(days);return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 獲取未來x天的時間戳(毫秒級)* @param days 天* @return 時間戳*/public static long getDaysLaterMillis(long days) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusDays(days);return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 獲取未來x?的時間戳(秒級)* @param months ?* @return 時間戳*/public static long getMonthsLaterSeconds(long months) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);return monthsLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 獲取未來x?的時間戳(毫秒級)* @param months ?* @return 時間戳*/public static long getMonthsLaterMillis(long months) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 獲取未來x年的時間戳(秒級)* @param years 年* @return 時間戳*/public static long getYearLaterSeconds(long years) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);return yearLater.toEpochSecond();}/*** 獲取未來x年的時間戳(毫秒級)* @param years 年* @return 時間戳*/public static long getYearLaterMillis(long years) {ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);return yearLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();}/*** 計算兩個時間戳之間的差異(毫秒)* @param timestamp1 時間戳1* @param timestamp2 時間戳2* @return 時間戳差異(毫秒)*/public static long calculateDifferenceMillis(long timestamp1, longtimestamp2) {return ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp1),Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp2));}/*** 計算兩個時間戳之間的差異(秒)* @param timestamp1 時間戳1* @param timestamp2 時間戳2* @return 時間戳差異(秒)*/public static long calculateDifferenceSeconds(long timestamp1, longtimestamp2) {return ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp1),Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp2));}
}String?具類
- 提供字符串常?操作
- 判斷url是否與規則匹配(url:特殊的字符串)
- 判斷指定字符串(url)是否與指定匹配規則鏈表中的任意?個匹配規則匹配
引入依賴
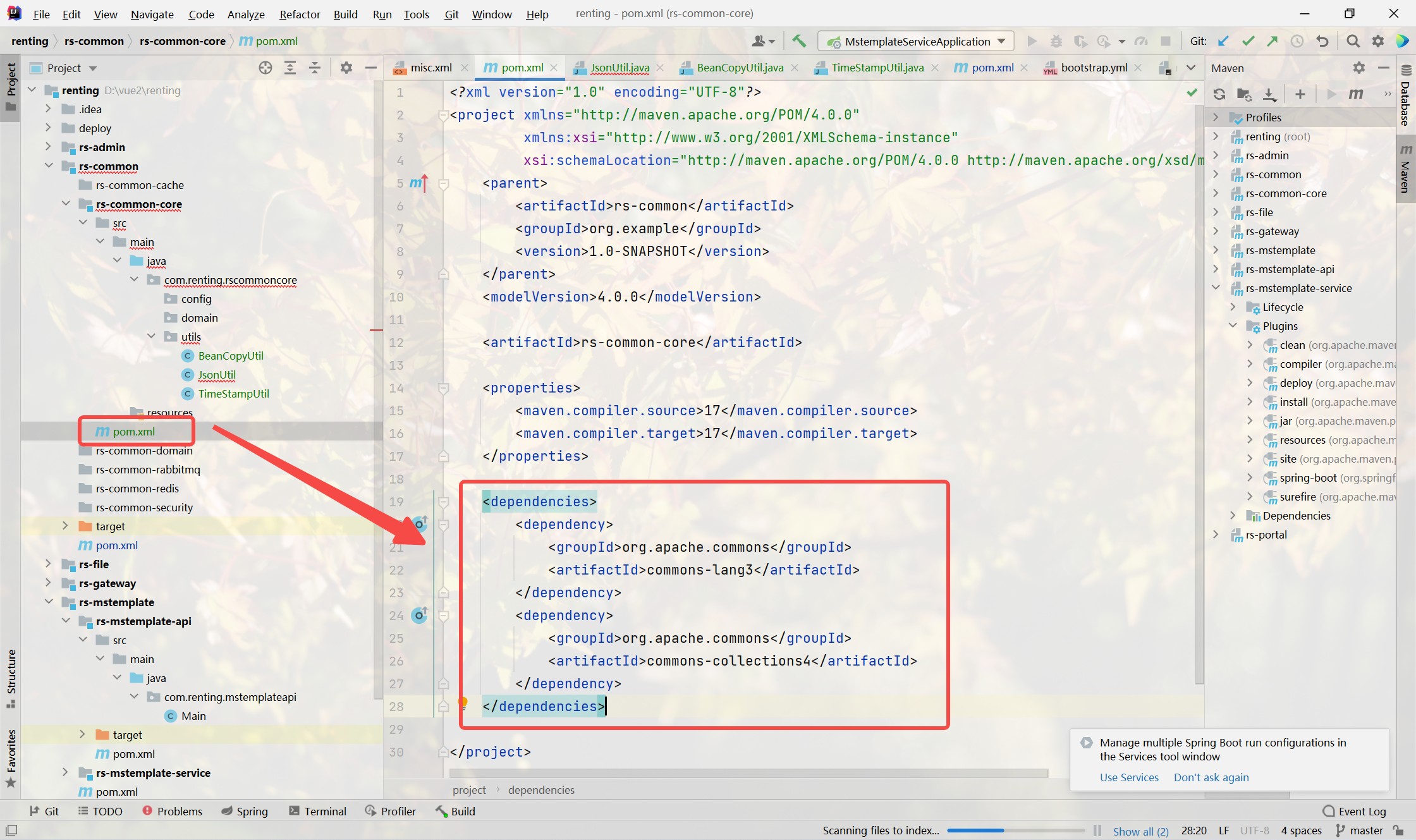
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId></dependency>
</dependencies>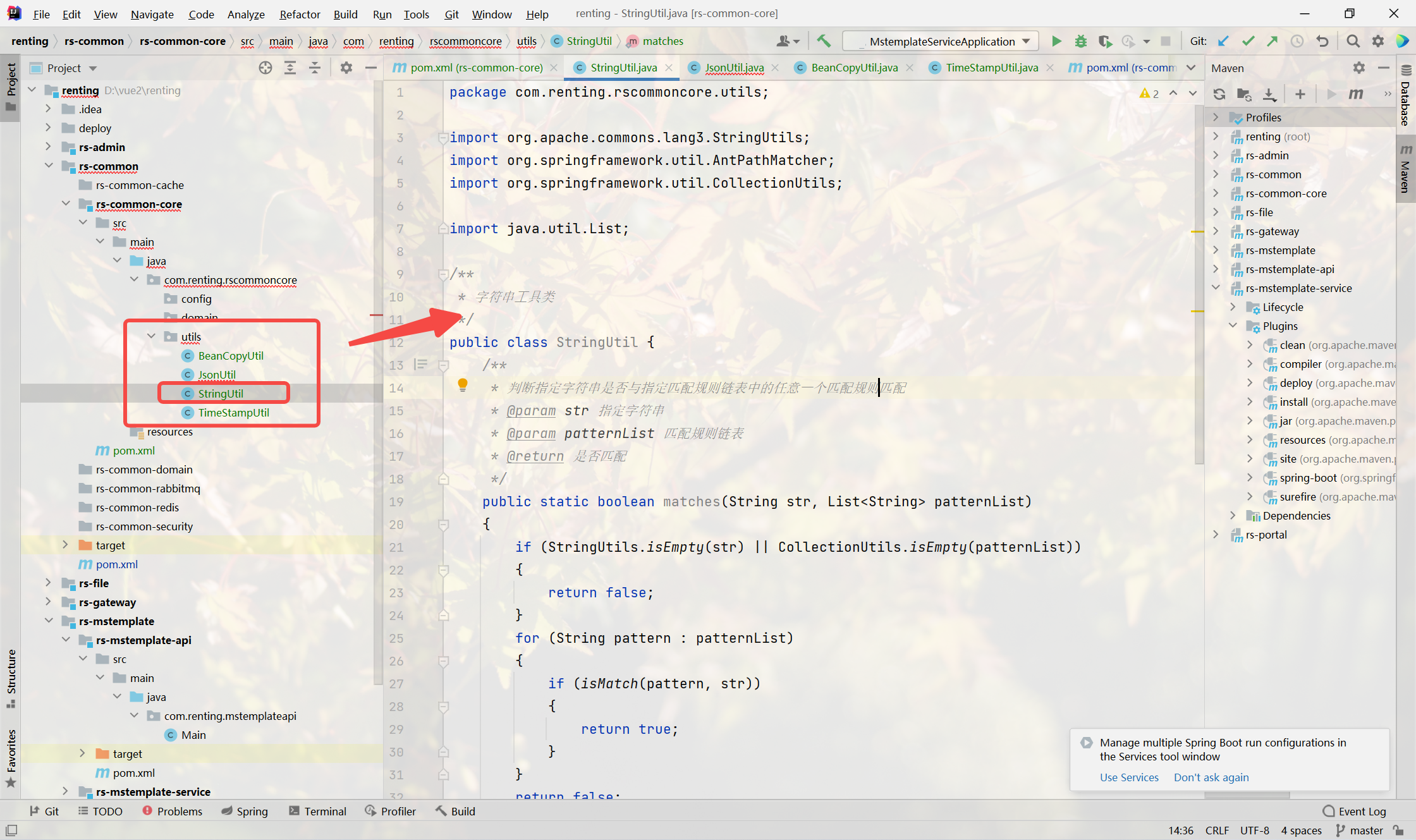
package com.renting.rscommoncore.utils;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;import java.util.List;/*** 字符串?具類*/
public class StringUtil {/*** 判斷指定字符串是否與指定匹配規則鏈表中的任意?個匹配規則匹配* @param str 指定字符串* @param patternList 匹配規則鏈表* @return 是否匹配*/public static boolean matches(String str, List<String> patternList){if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(patternList)){return false;}for (String pattern : patternList){if (isMatch(pattern, str)){return true;}}return false;}/*** 判斷url是否與規則匹配* 匹配規則:* 精確匹配* 匹配規則中包含 ? 表?任意單個字符;* 匹配規則中包含 * 表??層路徑內的任意字符串,不可跨層級;* 匹配規則中包含 ** 表?任意層路徑的任意字符,可跨層級* @param pattern 匹配規則* @param url 需要匹配的url* @return 是否匹配*/public static boolean isMatch(String pattern, String url){if (StringUtils.isEmpty(url) || StringUtils.isEmpty(pattern)) {return false;}AntPathMatcher matcher = new AntPathMatcher();return matcher.match(pattern, url);}
}
如果說還有需要添加的,不論是說你需要的還是后面加上來的,滿足下面三個原則即可
?具類封裝原則
- 先從成熟的?商所提供的?具類當中尋找,推薦:spring和apache,具體不做限制,但是要確定安 全可靠,明確?具類的特點。
- 如果成熟?商所提供的?具類當中沒有們想要使?的?法,再封裝內置?具類提供。
- 公司如果對此有明確要求,以公司要求為準。(常?要求:對于?種?具類的使?盡可能統?)





)
)



詳解和完整示例)




變量的梯度)



摘自Openloong社區)