《C++ list 完全指南:從基礎到高效使用》
文章目錄
- 《C++ list 完全指南:從基礎到高效使用》
- 一、forward_list和list比較
- 二、list的接口介紹
- 1.list的構造
- 2.list iterator的使用
- 3.list的容量操作
- 4.list的訪問操作
- 5.list的其他操作接口
- 三、list的迭代器失效
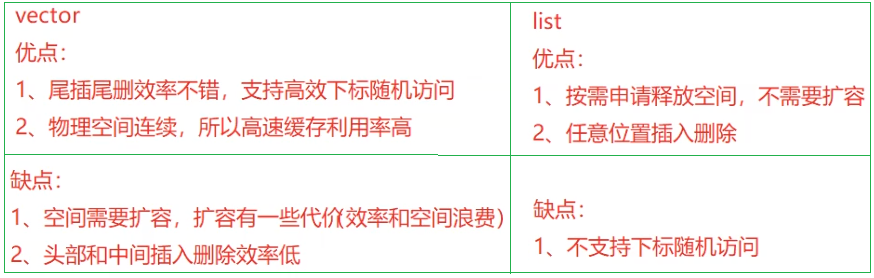
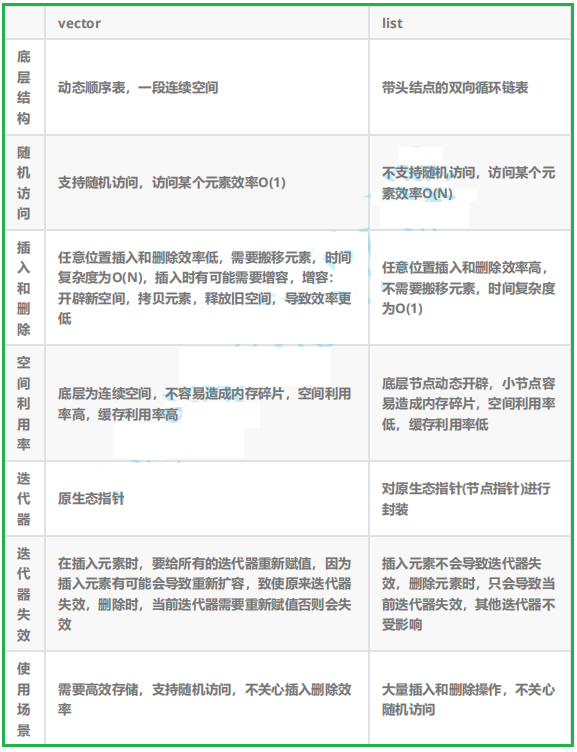
- 四、list與vector的對比
- 五、源代碼總結
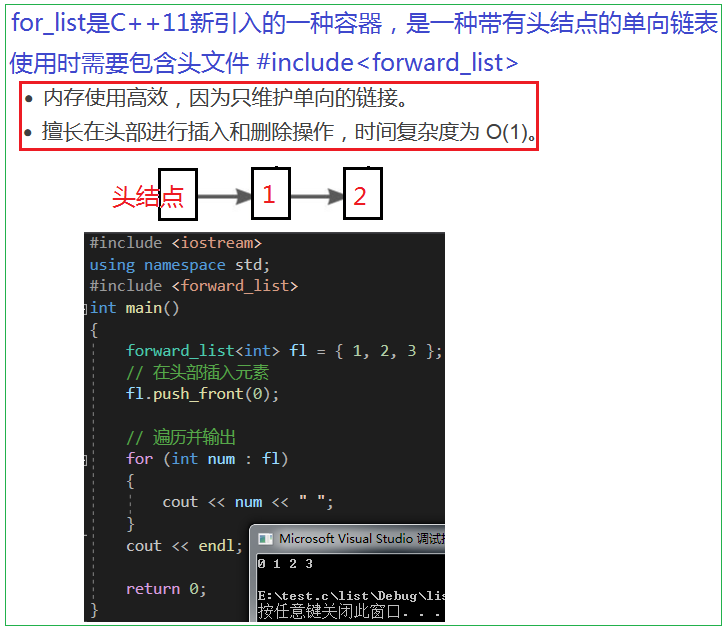
一、forward_list和list比較
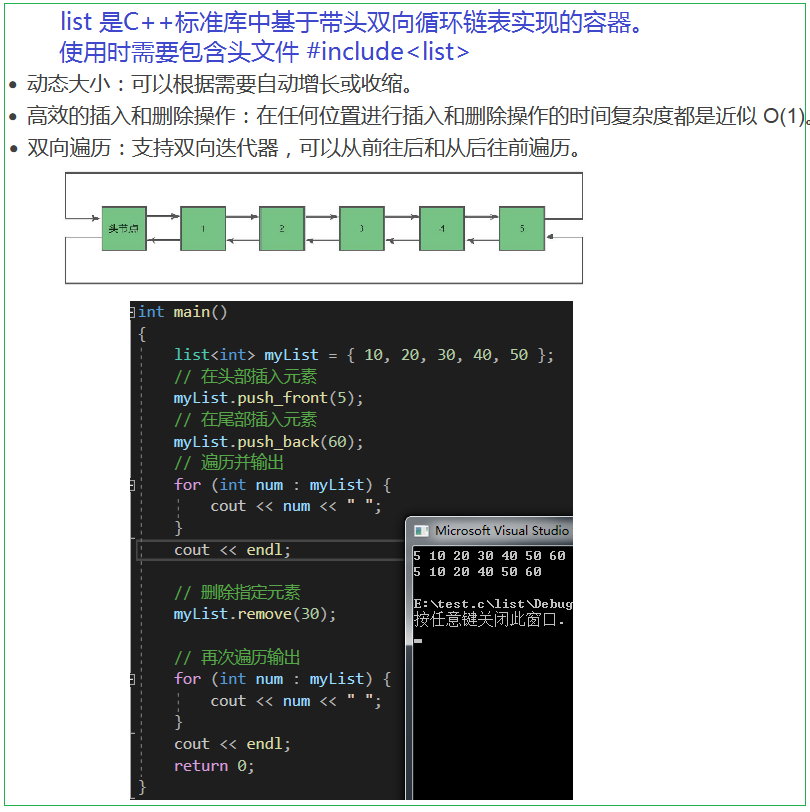

二、list的接口介紹
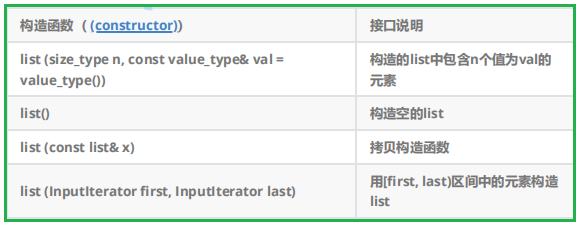
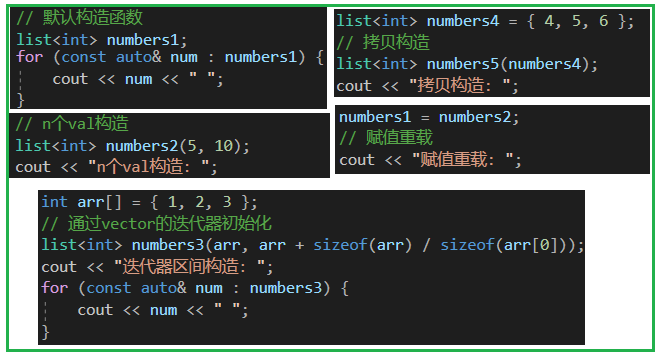
1.list的構造
2.list iterator的使用
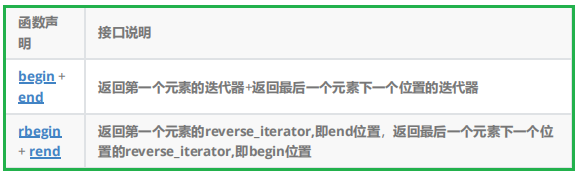
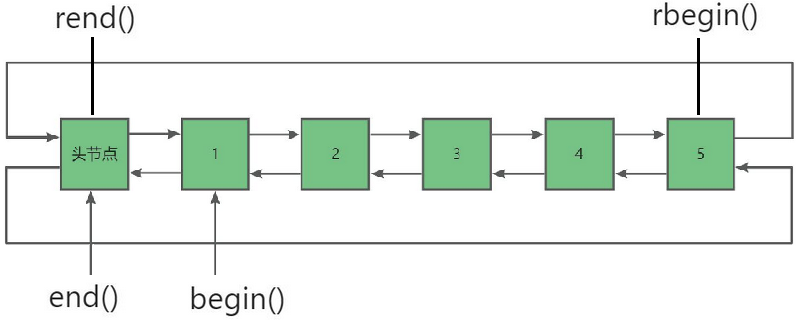
迭代器可以理解成一個指針,該指針指向list中的某個節點!

3.list的容量操作
這里指介紹重要的接口,一些不重要的接口可以參考string和vector

resize的用法和string、vector幾乎相同,這里不再過多贅述
4.list的訪問操作
迭代器失效問題一會就會進行講解!
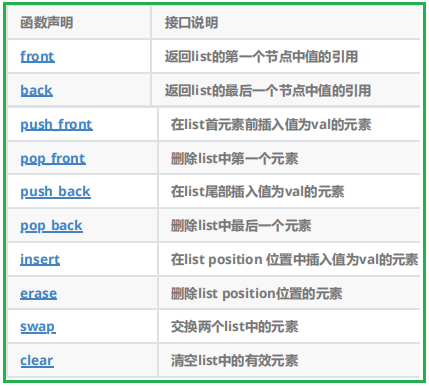
5.list的其他操作接口
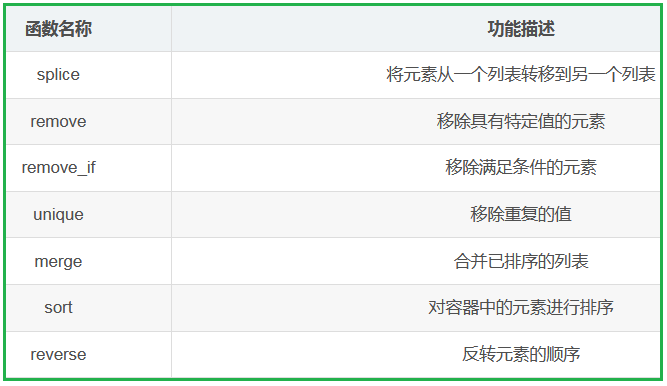
splice()函數主要用于在列表中進行元素的轉移操作。
它可以將一個列表中的部分或全部元素轉移到另一個列表中。
可以指定要轉移的元素范圍以及目標插入位置等,實現了高效靈活的元素移動和重組
remove函數相當于一直遍歷列表,然后erase刪除指定元素
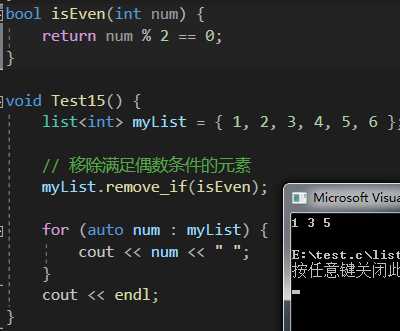
remove_if 函數 相當于 remove 的補充,它支持傳參函數或者仿函數
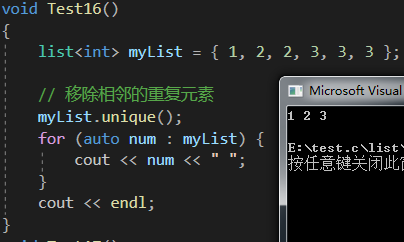
unique函數主要用于移除列表中相鄰的重復元素。
他使得容器中只保留不重復的元素序列,
但需要注意:他并不保證取出所有重復元素,知識處理相鄰的重復項,通常也需要結合其他操作
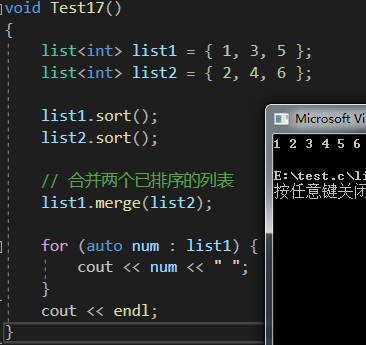
merge( )函數主要用于將兩個已排序的序列合并成一個新的已排序序列
他會按照排序順序將一個序列中的元素與另一個序列中的元素合理地組合在一起,形成一個合并后的有序序列
需要注意的是,在合并之前,兩個源序列本身需要時已經排序好的
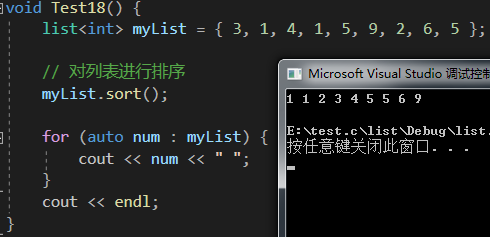
list中的sort( )函數用于對列表進行排序。他會按照指定的排序規則(默認是升序)對列表中的元素進行重新排列,使得元素按有序多的方式呈現!
reverse( )函數,用于實現list的逆置
三、list的迭代器失效

四、list與vector的對比
五、源代碼總結
代碼如下(示例):
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//#include <forward_list>
//int main()
//{
// forward_list<int> fl = { 1, 2, 3 };
// // 在頭部插入元素
// fl.push_front(0);
//
// // 遍歷并輸出
// for (int num : fl)
// {
// cout << num << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// list<int> myList = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// // 在頭部插入元素
// myList.push_front(5);
// // 在尾部插入元素
// myList.push_back(60);
// // 遍歷并輸出
// for (int num : myList) {
// cout << num << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// // 刪除指定元素
// myList.remove(30);
//
// // 再次遍歷輸出
// for (int num : myList) {
// cout << num << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}void Test1()
{// 默認構造函數list<int> numbers1;cout << "默認構造: ";for (const auto& num : numbers1) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;// n個val構造list<int> numbers2(5, 10);cout << "n個val構造: ";for (const auto& num : numbers2) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };// 通過vector的迭代器初始化list<int> numbers3(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));cout << "迭代器區間構造: ";for (const auto& num : numbers3) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;list<int> numbers4 = { 4, 5, 6 };// 拷貝構造list<int> numbers5(numbers4);cout << "拷貝構造: ";for (const auto& num : numbers5) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;numbers1 = numbers2;// 賦值重載cout << "賦值重載: ";for (const auto& num : numbers1) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
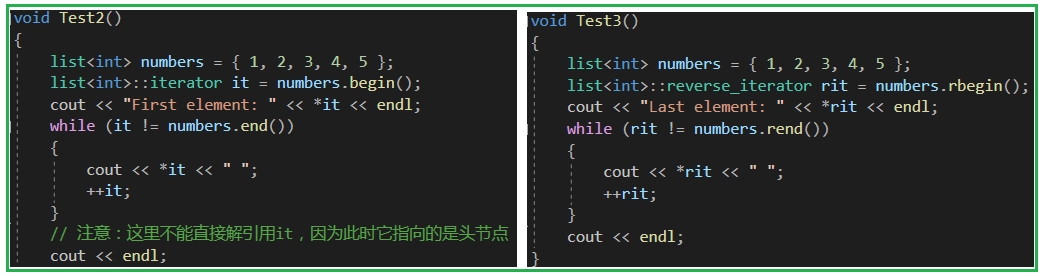
void Test2()
{list<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };list<int>::iterator it = numbers.begin();cout << "First element: " << *it << endl;while (it != numbers.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}// 注意:這里不能直接解引用it,因為此時它指向的是頭節點cout << endl;
}
void Test3()
{list<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = numbers.rbegin();cout << "Last element: " << *rit << endl;while (rit != numbers.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;
}
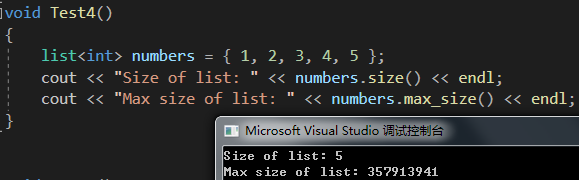
void Test4()
{list<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };cout << "Size of list: " << numbers.size() << endl;cout << "Max size of list: " << numbers.max_size() << endl;
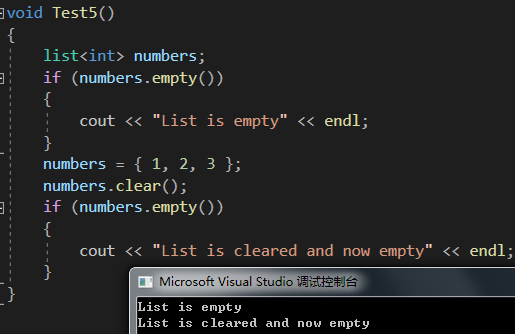
}void Test5()
{list<int> numbers;if (numbers.empty()){cout << "List is empty" << endl;}numbers = { 1, 2, 3 };numbers.clear();if (numbers.empty()){cout << "List is cleared and now empty" << endl;}
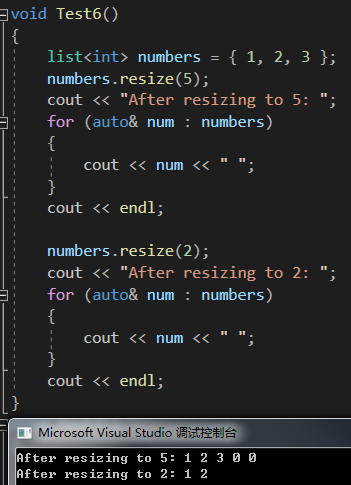
}void Test6()
{list<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3 };numbers.resize(5);cout << "After resizing to 5: ";for (auto& num : numbers){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;numbers.resize(2);cout << "After resizing to 2: ";for (auto& num : numbers){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
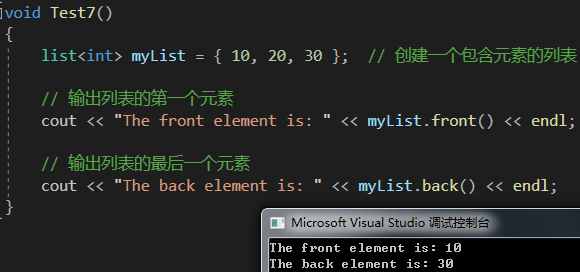
void Test7()
{list<int> myList = { 10, 20, 30 }; // 創建一個包含元素的列表// 輸出列表的第一個元素cout << "The front element is: " << myList.front() << endl;// 輸出列表的最后一個元素cout << "The back element is: " << myList.back() << endl;
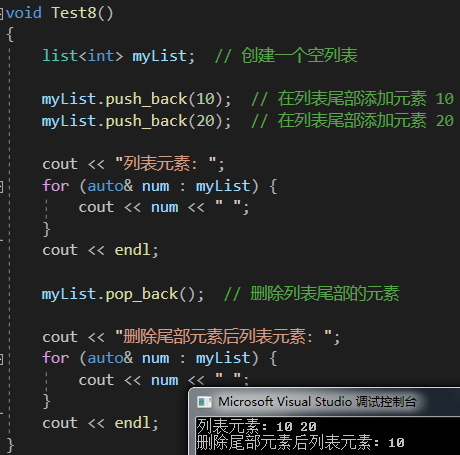
}void Test8()
{list<int> myList; // 創建一個空列表myList.push_back(10); // 在列表尾部添加元素 10myList.push_back(20); // 在列表尾部添加元素 20cout << "列表元素: ";for (auto& num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;myList.pop_back(); // 刪除列表尾部的元素cout << "刪除尾部元素后列表元素: ";for (auto& num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
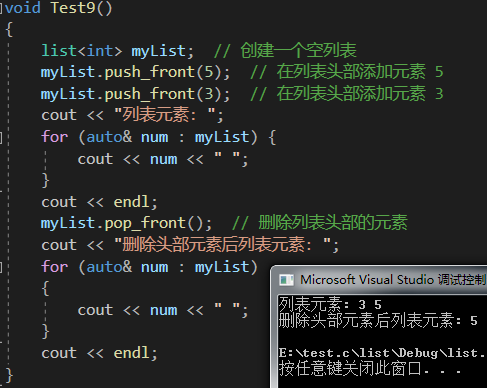
void Test9()
{list<int> myList; // 創建一個空列表myList.push_front(5); // 在列表頭部添加元素 5myList.push_front(3); // 在列表頭部添加元素 3cout << "列表元素: ";for (auto& num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;myList.pop_front(); // 刪除列表頭部的元素cout << "刪除頭部元素后列表元素: ";for (auto& num : myList){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
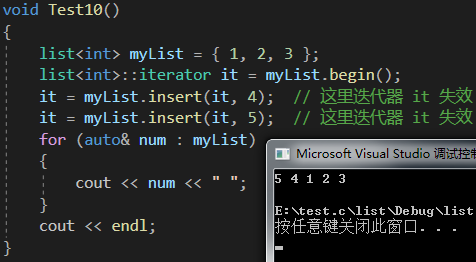
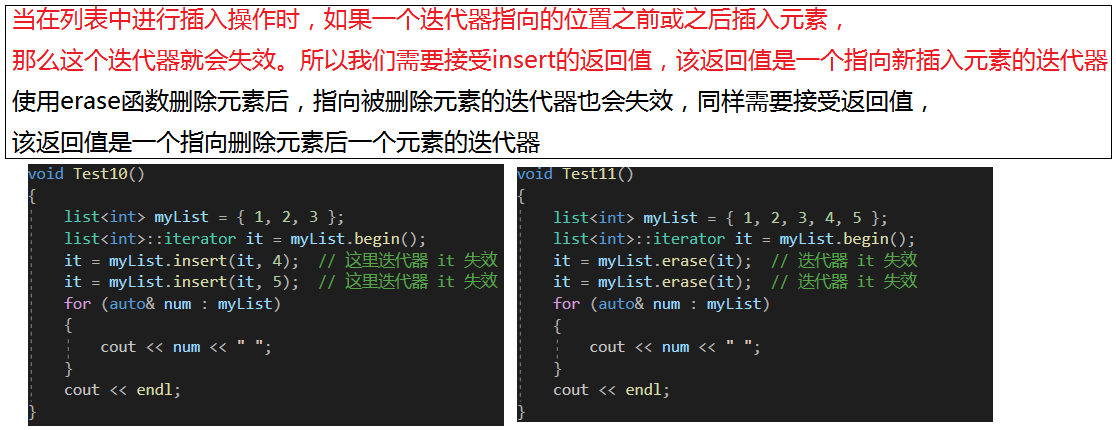
void Test10()
{list<int> myList = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int>::iterator it = myList.begin();it = myList.insert(it, 4); // 這里迭代器 it 失效it = myList.insert(it, 5); // 這里迭代器 it 失效for (auto& num : myList){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
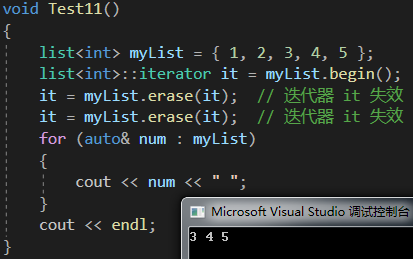
void Test11()
{list<int> myList = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };list<int>::iterator it = myList.begin();it = myList.erase(it); // 迭代器 it 失效it = myList.erase(it); // 迭代器 it 失效for (auto& num : myList){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
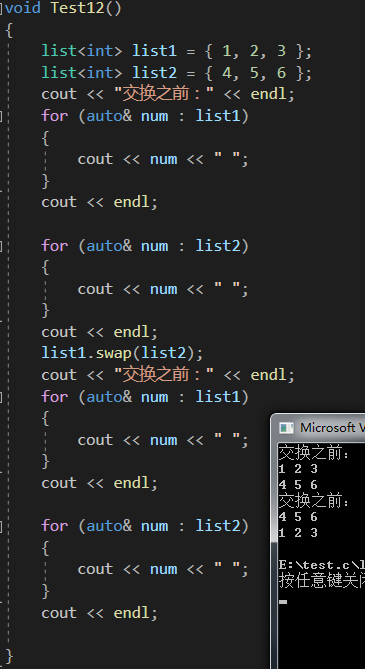
void Test12()
{list<int> list1 = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int> list2 = { 4, 5, 6 };cout << "交換之前:" << endl;for (auto& num : list1){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto& num : list2){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;list1.swap(list2);cout << "交換之前:" << endl;for (auto& num : list1){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto& num : list2){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;}
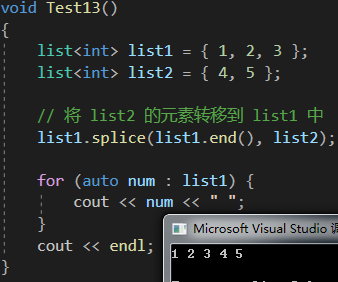
void Test13()
{list<int> list1 = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int> list2 = { 4, 5 };// 將 list2 的元素轉移到 list1 中list1.splice(list1.end(), list2);for (auto num : list1) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
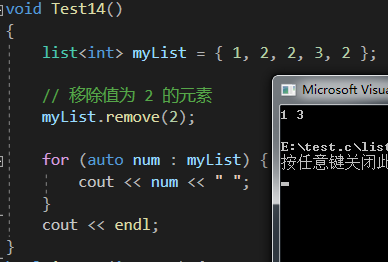
void Test14()
{list<int> myList = { 1, 2, 2, 3, 2 };// 移除值為 2 的元素myList.remove(2);for (auto num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
bool isEven(int num) {return num % 2 == 0;
}void Test15() {list<int> myList = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };// 移除滿足偶數條件的元素myList.remove_if(isEven);for (auto num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
void Test16()
{list<int> myList = { 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3 };// 移除相鄰的重復元素myList.unique();for (auto num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
void Test17()
{list<int> list1 = { 1, 3, 5 };list<int> list2 = { 2, 4, 6 };list1.sort();list2.sort();// 合并兩個已排序的列表list1.merge(list2);for (auto num : list1) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
void Test18() {list<int> myList = { 3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5 };// 對列表進行排序myList.sort();for (auto num : myList) {cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;
}
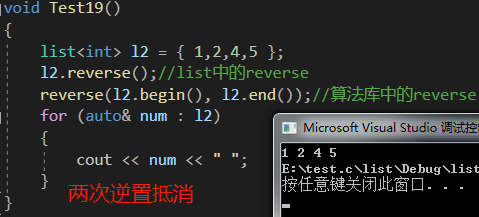
void Test19()
{list<int> l2 = { 1,2,4,5 };l2.reverse();//list中的reversereverse(l2.begin(), l2.end());//算法庫中的reversefor (auto& num : l2){cout << num << " ";}
}
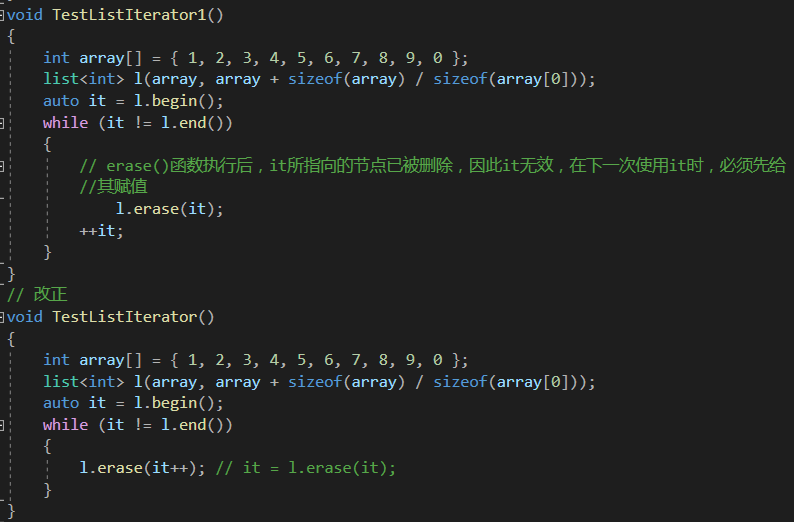
void TestListIterator1()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));auto it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){// erase()函數執行后,it所指向的節點已被刪除,因此it無效,在下一次使用it時,必須先給//其賦值l.erase(it);++it;}
}
// 改正
void TestListIterator()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));auto it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){l.erase(it++); // it = l.erase(it);}
}int main()
{//Test1();//Test2();//Test4();//Test5();//Test6();//Test7();//Test8();//Test9();//Test10();//Test11();//Test12();//Test13();//Test14();//Test15();//Test16();//Test17();//Test18();Test19();
}



















