文章目錄 不用框架實現web接口 實現簡單的路由 實現分組路由 支持不同的請求方式 支持同一個路徑的不同請求方式 前綴樹 應用前綴樹 完善路由代碼
package mainimport ( "fmt" "log" "net/http"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) http. HandleFunc ( "/hello" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!" ) } ) err := http. ListenAndServe ( "8111" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
http.HandleFunc 注冊一個路由 /hello 并綁定處理函數。當用戶訪問 http://localhost:8111/hello 時,執行匿名函數: w http.ResponseWriter:用于向客戶端發送 HTTP 響應。r *http.Request:包含客戶端發來的請求信息(如 URL、Headers 等)。 fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!"): 向 HTTP 響應寫入 "Hello Go!"(相當于 w.Write([]byte("Hello Go!")))。 默認狀態碼是 200 OK。 http.ListenAndServe(":8111", nil): 啟動 HTTP 服務器,監聽 8111 端口(: 表示監聽所有網絡接口)。 nil 表示使用默認的 DefaultServeMux 路由器(即之前用 http.HandleFunc 注冊的路由)。if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) }:如果服務器啟動失敗(如端口被占用),打印錯誤并終止程序。fmt.Fprintf 是 Go 語言 fmt 包提供的一個格式化輸出函數,用于將格式化后的字符串寫入指定的 io.Writer 接口(如文件、HTTP 響應、標準輸出等)。它的作用類似于 fmt.Printf,但不是輸出到終端,而是寫入到任意實現了 io.Writer 的對象。func Fprintf ( w io. Writer, format string , a ... interface { } ) ( n int , err error )
w io.Writer:目標寫入器(如 http.ResponseWriter、文件、緩沖區等)。format string:格式化字符串(包含占位符,如 %s, %d, %v 等)。a ...interface{}:可變參數,用于填充格式化字符串中的占位符。返回值: n int:成功寫入的字節數。err error:寫入過程中遇到的錯誤(如寫入失敗)。 package zjgoimport ( "log" "net/http"
) type Engine struct {
} func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ }
} func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { err := http. ListenAndServe ( "8111" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
} 經過封裝之后,原來的 main 函數可以簡潔為如下: package mainimport ( "fmt" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) engine. Run ( )
}
注意這里服務啟動后會 404 Not Found,因為我們沒有實現對應的響應函數 Handler。 package zjgoimport ( "log" "net/http"
)
type HandleFunc func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request)
type router struct { handleFuncMap map [ string ] HandleFunc
}
func ( r * router) Add ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { r. handleFuncMap[ name] = handleFunc
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) , } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { for key, value := range e. handleFuncMap { http. HandleFunc ( key, value) } err := http. ListenAndServe ( "8111" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
在 Go 語言中,當你將一個類型(如 router)嵌入到另一個結構體(如 Engine)中時,這被稱為類型嵌入(Embedded Type)。這是一種組合的方式,它允許 Engine 直接訪問 router 的字段和方法,而不需要顯式地通過一個字段名來訪問。 package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) engine. Add ( "/hello" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!" ) } ) engine. Run ( )
}
這樣我們就實現了一個簡單的路由功能,下面進行進一步完善。 大多數情況下我們希望寫的接口歸屬于某一個模塊,這樣便于管理以及維護,代碼也會更為清晰。 例如:/user/getUser 和 /user/createUser 都同屬于 user 模塊。 package zjgoimport ( "log" "net/http"
)
type HandleFunc func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request)
type routerGroup struct { name string handleFuncMap map [ string ] HandleFunc
}
type router struct { routerGroups [ ] * routerGroup
}
func ( r * router) Group ( name string ) * routerGroup { routerGroup := & routerGroup{ name: name, handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) , } r. routerGroups = append ( r. routerGroups, routerGroup) return routerGroup
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Add ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = handleFunc
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { for _ , group := range e. routerGroups { for name, value := range group. handleFuncMap { http. HandleFunc ( "/" + group. name+ name, value) } } err := http. ListenAndServe ( ":3986" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) g1 := engine. Group ( "user" ) g1. Add ( "/hello" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!——user/hello" ) } ) g1. Add ( "/info" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!——user/info" ) } ) g2 := engine. Group ( "order" ) g2. Add ( "/hello" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!——order/hello" ) } ) g2. Add ( "/info" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "Hello Go!——order/info" ) } ) fmt. Println ( "Starting..." ) engine. Run ( ) }
net / http下的路由,只要路徑匹配,就可以進入處理方法。但是在我們實際應用之中,比如我們使用 Restful 風格的接口在同一路徑下,會使用 GET、POST、DELETE、PUT來代替增刪改查,所以我們要對不同的請求方式做相應的支持。 package zjgoimport ( "fmt" "log" "net/http"
)
type HandleFunc func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request)
type routerGroup struct { name string handleFuncMap map [ string ] HandleFunc handlerMethodMap map [ string ] [ ] string
}
type router struct { routerGroups [ ] * routerGroup
}
func ( r * router) Group ( name string ) * routerGroup { routerGroup := & routerGroup{ name: name, handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) , handlerMethodMap: make ( map [ string ] [ ] string ) , } r. routerGroups = append ( r. routerGroups, routerGroup) return routerGroup
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Any ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ "ANY" ] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ "ANY" ] , name)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Post ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ http. MethodPost] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ http. MethodPost] , name)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Get ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ http. MethodGet] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ http. MethodGet] , name)
}
func ( e * Engine) ServeHTTP ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { if r. Method == http. MethodGet { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 GET 請求" ) } else if r. Method == http. MethodPost { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 POST 請求" ) } else { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個其他類型的請求:%s" , r. Method) } for _ , group := range e. routerGroups { for name, methodHandle := range group. handleFuncMap { url := "/" + group. name + nameif r. RequestURI == url { if routers, exist := group. handlerMethodMap[ "ANY" ] ; exist { for _ , routerName := range routers { if routerName == name { methodHandle ( w, r) return } } } if routers, exist := group. handlerMethodMap[ r. Method] ; exist { for _ , routerName := range routers { if routerName == name { methodHandle ( w, r) return } } } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusMethodNotAllowed) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return } } } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusNotFound) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not found!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { http. Handle ( "/" , e) err := http. ListenAndServe ( ":3986" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) g1 := engine. Group ( "user" ) g1. Get ( "/hello" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/hello" ) } ) g1. Post ( "/info" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, http. MethodPost+ " Hello Go!——user/info" ) } ) g1. Any ( "/any" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { fmt. Fprintf ( w, " Hello Go!——user/any" ) } ) fmt. Println ( "Starting..." ) engine. Run ( )
}
但是目前還是存在一些問題的,目前不支持同一個路由進行 GET 和 POST,因為在 map 里面會被覆蓋。 routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc,在 Post 和 Get 方法下都有這段代碼,這就會造成方法的覆蓋。標準庫 net/http 本身只提供了最基礎的路由匹配機制,也就是通過:http.HandleFunc("/path", handler),它的匹配機制非常簡單:只根據請求路徑匹配,不區分請求方法(GET/POST)。 如果在方法中這樣寫,是手動在 handler 里面區分請求方法,net/http 本身并不會替你區分。 http. HandleFunc ( "/info" , func ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { if r. Method == http. MethodPost { } else if r. Method == http. MethodGet { } else { http. Error ( w, "Method not allowed" , http. StatusMethodNotAllowed) }
} )
要限制不同請求方法(GET、POST 分別調用不同的 handler),就得框架(或者你自己)在 ServeHTTP 里手動實現。 像 Gin、Echo、Fiber 等這些 Web 框架,都是在它們內部封裝了: 請求方法和路徑的雙重匹配機制 路由注冊表,支持多種請求方式綁定不同 handler 匹配失敗時返回 405 Method Not Allowed 或 404 Not Found 考慮在每個路由組 routerGroup 的 handleFuncMap 上做文章,原先是 map[name]HandleFunc,現在可以加入 map 中 map,也即 map[name]map[method]HandleFunc。 package zjgoimport "net/http"
type Context struct { W http. ResponseWriterR * http. Request
}
package zjgoimport ( "fmt" "log" "net/http"
) const ANY = "ANY"
type HandleFunc func ( ctx * Context)
type routerGroup struct { name string handleFuncMap map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc handlerMethodMap map [ string ] [ ] string
}
type router struct { routerGroups [ ] * routerGroup
}
func ( r * router) Group ( name string ) * routerGroup { routerGroup := & routerGroup{ name: name, handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc) , handlerMethodMap: make ( map [ string ] [ ] string ) , } r. routerGroups = append ( r. routerGroups, routerGroup) return routerGroup
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) handleRequest ( name string , method string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) } if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] , name) } else { panic ( "Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!" ) }
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Any ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Post ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Get ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
func ( e * Engine) ServeHTTP ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { if r. Method == http. MethodGet { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 GET 請求!!!" ) } else if r. Method == http. MethodPost { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 POST 請求!!!" ) } else { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個其他類型的請求:%s" , r. Method) } for _ , group := range e. routerGroups { for name, methodHandleMap := range group. handleFuncMap { url := "/" + group. name + nameif r. RequestURI == url { ctx := & Context{ W: w, R: r} if handle, exist := methodHandleMap[ ANY] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } if handle, exist := methodHandleMap[ r. Method] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusMethodNotAllowed) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return } } } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusNotFound) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not found!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { http. Handle ( "/" , e) err := http. ListenAndServe ( ":3986" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) g1 := engine. Group ( "user" ) g1. Get ( "/hello" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/hello" ) } ) g1. Post ( "/info" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodPost+ " Hello Go!——user/info——POST" ) } ) g1. Get ( "/info" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/info——GET" ) } ) g1. Any ( "/any" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, " Hello Go!——user/any" ) } ) fmt. Println ( "Starting..." ) engine. Run ( ) }
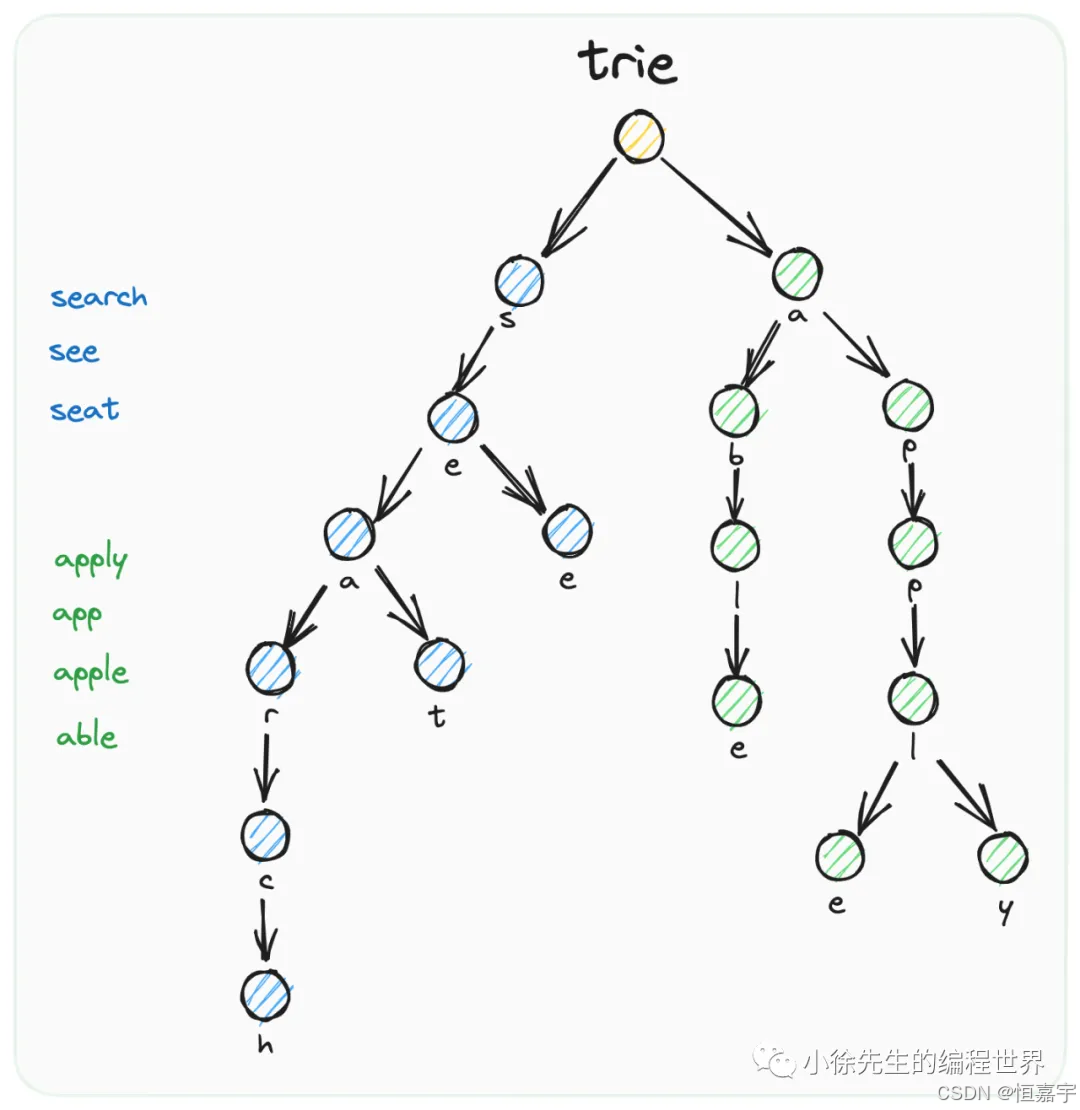
前面的實現,我們只是實現了靜態路由,不能實現更為復雜的需求,比如 /user/get/:id 這種才有參數的。 帶有參數的路由路徑,成為動態路由。 除了帶有參數的,一般情況下我們還希望有更多支持,比如希望支持通配符 **,比如 /static/**,可以匹配 /static/vue.js,/static/css/index.css 這些。 type Trie struct { next [ 26 ] * Trieend bool
} func Constructor ( ) Trie { myTrie := Trie{ } return myTrie
} func ( this * Trie) Insert ( word string ) { if this. Search ( word) { return } node := thisfor _ , ch := range word { if node. next[ ch- 'a' ] == nil { node. next[ ch- 'a' ] = & Trie{ } } node = node. next[ ch- 'a' ] } node. end = true
} func ( this * Trie) Search ( word string ) bool { node := this. search ( word) return node != nil && ( * node) . end
} func ( this * Trie) search ( word string ) * Trie { node := thisfor _ , ch := range word { if node. next[ ch- 'a' ] == nil { return nil } node = node. next[ ch- 'a' ] } return node
} func ( this * Trie) StartsWith ( prefix string ) bool { node := this. search ( prefix) return node != nil
}
package zjgoimport "strings" type TreeNode struct { name string children [ ] * TreeNode
}
func ( t * TreeNode) Put ( path string ) { root := tstrs := strings. Split ( path, "/" ) for index, name := range strs { if index == 0 { continue } isMatch := false for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == name { isMatch = true t = nodebreak } } if ! isMatch { node := & TreeNode{ name: name, children: make ( [ ] * TreeNode, 0 ) , } t. children = append ( t. children, node) t = node} } t = root
}
func ( t * TreeNode) Get ( path string ) * TreeNode { strs := strings. Split ( path, "/" ) for index, name := range strs { if index == 0 { continue } isMatch := false for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == name || node. name == "*" || strings. Contains ( node. name, ":" ) { isMatch = true t = nodeif index == len ( strs) - 1 { return node} break } } if ! isMatch { for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == "**" { return node} } } } return nil
}
package zjgoimport ( "fmt" "testing"
) func TestTreeNode ( t * testing. T) { root := & TreeNode{ name: "/" , children: make ( [ ] * TreeNode, 0 ) } root. Put ( "/user/get/:id" ) root. Put ( "/user/info/hello" ) root. Put ( "/user/create/aaa" ) root. Put ( "/order/get/aaa" ) node := root. Get ( "/user/get/1" ) fmt. Println ( node) node = root. Get ( "/user/info/hello" ) fmt. Println ( node) node = root. Get ( "/user/create/aaa" ) fmt. Println ( node) node = root. Get ( "/order/get/aaa" ) fmt. Println ( node)
} == = RUN TestTreeNode
& { : id [ ] }
& { hello [ ] }
& { aaa [ ] }
& { aaa [ ] }
-- - PASS: TestTreeNode ( 0.00 s)
PASS
ok github. com/ ErizJ/ ZJGo/ zjgo ( cached)
package zjgoimport "strings"
func SubStringLast ( name string , groupName string ) string { if index := strings. Index ( name, groupName) ; index < 0 { return "" } else { return name[ index+ len ( groupName) : ] }
}
package zjgoimport "strings" type TreeNode struct { name string children [ ] * TreeNode routerName string isEnd bool
}
func ( t * TreeNode) Put ( path string ) { strs := strings. Split ( path, "/" ) for index, name := range strs { if index == 0 { continue } isMatch := false for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == name { isMatch = true t = nodebreak } } if ! isMatch { node := & TreeNode{ name: name, children: make ( [ ] * TreeNode, 0 ) , isEnd: index == len ( strs) - 1 , } t. children = append ( t. children, node) t = node} } t. isEnd = true
}
func ( t * TreeNode) Get ( path string ) * TreeNode { strs := strings. Split ( path, "/" ) routerName := "" for index, name := range strs { if index == 0 { continue } isMatch := false for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == name || node. name == "*" || strings. Contains ( node. name, ":" ) { isMatch = true routerName += "/" + node. namenode. routerName = routerNamet = nodeif index == len ( strs) - 1 { return node} break } } if ! isMatch { for _ , node := range t. children { if node. name == "**" { routerName += "/" + node. namenode. routerName = routerNamereturn node} } } } return nil
}
package zjgoimport ( "fmt" "log" "net/http"
) const ANY = "ANY"
type HandleFunc func ( ctx * Context)
type routerGroup struct { name string handleFuncMap map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc handlerMethodMap map [ string ] [ ] string TreeNode * TreeNode
}
type router struct { routerGroups [ ] * routerGroup
}
func ( r * router) Group ( name string ) * routerGroup { routerGroup := & routerGroup{ name: name, handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc) , handlerMethodMap: make ( map [ string ] [ ] string ) , TreeNode: & TreeNode{ name: "/" , children: make ( [ ] * TreeNode, 0 ) } , } r. routerGroups = append ( r. routerGroups, routerGroup) return routerGroup
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) handleRequest ( name string , method string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) } if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] , name) } else { panic ( "Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!" ) } routerGroup. TreeNode. Put ( name)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Any ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Post ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Get ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
func ( e * Engine) ServeHTTP ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { if r. Method == http. MethodGet { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 GET 請求!!! " ) } else if r. Method == http. MethodPost { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 POST 請求!!! " ) } else { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個其他類型的請求:%s!!! " , r. Method) } for _ , group := range e. routerGroups { routerName := SubStringLast ( r. RequestURI, "/" + group. name) if node := group. TreeNode. Get ( routerName) ; node != nil && node. isEnd { ctx := & Context{ W: w, R: r} if handle, exist := group. handleFuncMap[ node. routerName] [ ANY] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } if handle, exist := group. handleFuncMap[ node. routerName] [ r. Method] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusMethodNotAllowed) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return } } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusNotFound) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not found!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { http. Handle ( "/" , e) err := http. ListenAndServe ( ":3986" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
) func main ( ) { fmt. Println ( "Hello World!" ) engine := zjgo. New ( ) g1 := engine. Group ( "user" ) g1. Get ( "/hello" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/hello" ) } ) g1. Post ( "/info" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodPost+ " Hello Go!——user/info——POST" ) } ) g1. Get ( "/info" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/info——GET" ) } ) g1. Get ( "/get/:id" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/get/:id——GET" ) } ) g1. Get ( "/isEnd/get" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, http. MethodGet+ " Hello Go!——user/isEnd/get——GET" ) } ) g1. Any ( "/any" , func ( ctx * zjgo. Context) { fmt. Fprintf ( ctx. W, " Hello Go!——user/any" ) } ) fmt. Println ( "Starting..." ) engine. Run ( ) }
package zjgoimport ( "fmt" "log" "net/http"
) const ANY = "ANY"
type HandleFunc func ( ctx * Context)
type routerGroup struct { name string handleFuncMap map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc handlerMethodMap map [ string ] [ ] string TreeNode * TreeNode
}
type router struct { routerGroups [ ] * routerGroup
}
func ( r * router) Group ( name string ) * routerGroup { routerGroup := & routerGroup{ name: name, handleFuncMap: make ( map [ string ] map [ string ] HandleFunc) , handlerMethodMap: make ( map [ string ] [ ] string ) , TreeNode: & TreeNode{ name: "/" , children: make ( [ ] * TreeNode, 0 ) } , } r. routerGroups = append ( r. routerGroups, routerGroup) return routerGroup
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) handleRequest ( name string , method string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] = make ( map [ string ] HandleFunc) } if _ , exist := routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] ; ! exist { routerGroup. handleFuncMap[ name] [ method] = handleFuncrouterGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] = append ( routerGroup. handlerMethodMap[ method] , name) } else { panic ( "Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!" ) } routerGroup. TreeNode. Put ( name)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Any ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Post ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Get ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Delete ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodDelete, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Put ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodPut, handleFunc)
}
func ( routerGroup * routerGroup) Patch ( name string , handleFunc HandleFunc) { routerGroup. handleRequest ( name, http. MethodPatch, handleFunc)
}
func ( e * Engine) ServeHTTP ( w http. ResponseWriter, r * http. Request) { if r. Method == http. MethodGet { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 GET 請求!!! " ) } else if r. Method == http. MethodPost { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個 POST 請求!!! " ) } else { fmt. Fprintf ( w, "這是一個其他類型的請求:%s!!! " , r. Method) } for _ , group := range e. routerGroups { routerName := SubStringLast ( r. RequestURI, "/" + group. name) if node := group. TreeNode. Get ( routerName) ; node != nil && node. isEnd { ctx := & Context{ W: w, R: r} if handle, exist := group. handleFuncMap[ node. routerName] [ ANY] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } if handle, exist := group. handleFuncMap[ node. routerName] [ r. Method] ; exist { handle ( ctx) return } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusMethodNotAllowed) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return } } w. WriteHeader ( http. StatusNotFound) fmt. Fprintf ( w, "%s %s not found!!!\n" , r. Method, r. RequestURI) return
}
type Engine struct { router
}
func New ( ) * Engine { return & Engine{ router: router{ } , }
}
func ( e * Engine) Run ( ) { http. Handle ( "/" , e) err := http. ListenAndServe ( ":3986" , nil ) if err != nil { log. Fatal ( err) }
}






)





)




試題速瀏、分類及淺析)

