CSharpGL(49)試水OpenGL軟實現
CSharpGL迎來了第49篇。本篇內容是用C#編寫一個OpenGL的軟實現。暫且將其命名為SoftGL。
目前已經實現了由Vertex Shader和Fragment Shader組成的Pipeline,其效果與顯卡支持的OpenGL實現幾乎相同。下圖左是常規OpenGL渲染的結果,右是SoftGL渲染的結果。
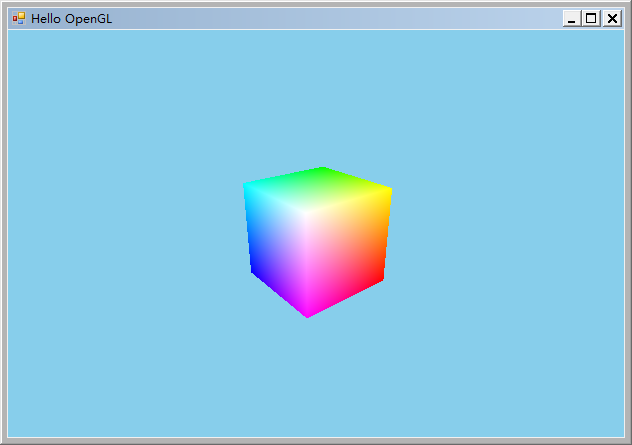
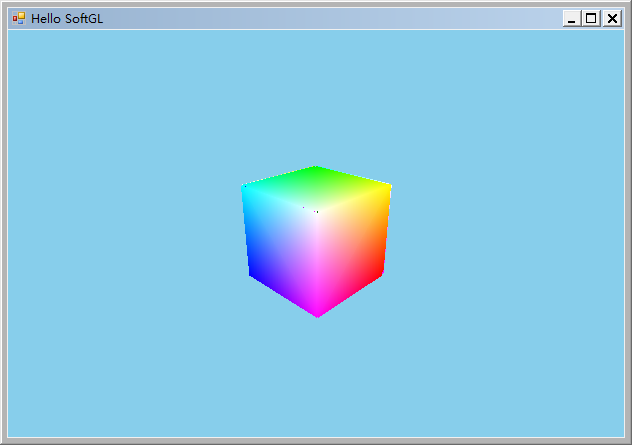
下載
CSharpGL已在GitHub開源,歡迎對OpenGL有興趣的同學加入(https://github.com/bitzhuwei/CSharpGL)
SoftGL也已在GitHub開源,歡迎對OpenGL有興趣的同學加入(https://github.com/bitzhuwei/SoftGL)
從使用者的角度開始
OpenGL的使用者就是OpenGL應用程序開發者(Dev)。
下面按其被執行的先后順序陳列OpenGL相關的命令(只陳列最基本的命令):
創建Device Context
用一個System.Windows.Forms.Control類型的對象即可。
最后會發現,這個Device Context的作用之一是為創建Render Context提供參數。目前在SoftGL中不需要這個參數。
創建Render Context
Render Context包含OpenGL的所有狀態字段。例如,當Dev調用glLineWidth(float width);時,Render Context會記下這一width值,從而使之長期有效(直到下次調用glLineWidth(float width);來修改它)。
可能同時存在多個Render Context,每個都保存自己的lineWidth等字段。當使用靜態的OpenGL函數static void glLineWidth(float width);時,它會首先找到當前的Render Context對象(詳見后面的MakeCurrent(..)),然后讓此對象執行真正的glLineWidth(float width);函數。
可見Render Context就是一個典型的class,其偽代碼如下:
1 partial class SoftGLRenderContext: 2 { 3 private float lineWidth; 4 // .. other fields. 5 6 public static void glLineWidth(float width) 7 { 8 SoftGLRenderContext obj = SoftGLRenderContext .GetCurrentContext(); 9 if (obj != null) { obj.LineWidth(width); } 10 } 11 12 private void LineWidth(float width) 13 { 14 this.lineWidth = width; 15 } 16 17 // .. other OpenGL functions. 18 }
MakeCurrent(IntPtr dc, IntPtr rc);
函數static void MakeCurrent(IntPtr dc, IntPtr rc);不是OpenGL函數。它的作用是指定當前線程(Thread)與哪個Render Context對應,即在Dictionary<Thread, RenderContext>這一字典類型中記錄下Thread與Render Context的對應關系。
當然,如果rc為IntPtr.Zero,就是要解除當前Thread與其Render Context的對應關系。
偽代碼如下:
1 partial class SoftGLRenderContext 2 { 3 // Thread -> Binding Render Context Object. 4 static Dictionary<Thread, SoftGLRenderContext> threadContextDict = new Dictionary<Thread, SoftGLRenderContext>(); 5 6 // Make specified renderContext the current one of current thread. 7 public static void MakeCurrent(IntPtr deviceContext, IntPtr renderContext) 8 { 9 var threadContextDict = SoftGLRenderContext.threadContextDict; 10 if (renderContext == IntPtr.Zero) // cancel current render context to current thread. 11 { 12 SoftGLRenderContext context = null; 13 14 Thread thread = System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread; 15 if (threadContextDict.TryGetValue(thread, out context)) 16 { 17 threadContextDict.Remove(thread); 18 } 19 } 20 else // change current render context to current thread. 21 { 22 SoftGLRenderContext context = GetContextObj(renderContext); 23 if (context != null) 24 { 25 SoftGLRenderContext oldContext = GetCurrentContextObj(); 26 if (oldContext != context) 27 { 28 Thread thread = Thread.CurrentThread; 29 if (oldContext != null) { threadContextDict.Remove(thread); } 30 threadContextDict.Add(thread, context); 31 context.DeviceContextHandle = deviceContext; 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }
獲取OpenGL函數指針
在CSharpGL.Windows項目中,我們可以通過Win32 API找到在opengl32.dll中的OpenGL函數指針,并將其轉換為C#中的函數委托(Delegate),從而可以像使用普通函數一樣使用OpenGL函數。其偽代碼如下:
1 public partial class WinGL : CSharpGL.GL 2 { 3 public override Delegate GetDelegateFor(string functionName, Type functionDeclaration) 4 { 5 Delegate del = null; 6 if (!extensionFunctions.TryGetValue(functionName, out del)) 7 { 8 IntPtr proc = Win32.wglGetProcAddress(name); 9 if (proc != IntPtr.Zero) 10 { 11 // Get the delegate for the function pointer. 12 del = Marshal.GetDelegateForFunctionPointer(proc, functionDeclaration); 13 14 // Add to the dictionary. 15 extensionFunctions.Add(functionName, del); 16 } 17 } 18 19 return del; 20 } 21 22 // Gets a proc address. 23 [DllImport("opengl32.dll", SetLastError = true)] 24 internal static extern IntPtr wglGetProcAddress(string name); 25 26 // The set of extension functions. 27 static Dictionary<string, Delegate> extensionFunctions = new Dictionary<string, Delegate>(); 28 }
此時我們想使用SoftGL,那么要相應地為其編寫一個SoftGL.Windows項目。這個項目通過在類似opengl32.dll的SoftOpengl32項目(或者SoftOpengl32.dll)中查找函數的方式來找到我們自己實現的OpenGL函數。其偽代碼如下:
1 partial class WinSoftGL : CSharpGL.GL 2 { 3 private static readonly Type thisType = typeof(SoftOpengl32.StaticCalls); 4 public override Delegate GetDelegateFor(string functionName, Type functionDeclaration) 5 { 6 Delegate result = null; 7 if (!extensionFunctions.TryGetValue(functionName, out result)) 8 { 9 MethodInfo methodInfo = thisType.GetMethod(functionName, BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.Public); 10 if (methodInfo != null) 11 { 12 result = System.Delegate.CreateDelegate(functionDeclaration, methodInfo); 13 } 14 15 if (result != null) 16 { 17 // Add to the dictionary. 18 extensionFunctions.Add(functionName, result); 19 } 20 } 21 22 return result; 23 } 24 25 // The set of extension functions. 26 static Dictionary<string, Delegate> extensionFunctions = new Dictionary<string, Delegate>(); 27 }
可見只需通過C#和.NET提供的反射機制即可實現。在找到System.Delegate.CreateDelegate(..)這個方法時,我感覺到一種“完美”。
此時,我們應當注意到另一個涉及大局的問題,就是整個SoftGL的框架結構。
SoftGL項目本身的作用與顯卡驅動中的OpenGL實現相同。操作系統(例如Windows)提供了一個opengl32.dll之類的方式來讓Dev找到OpenGL函數指針,從而使用OpenGL。CSharpGL項目是對OpenGL的封裝,具體地講,是對OpenGL的函數聲明的封裝,它不包含對OpenGL的實現、初始化等功能。這些功能是在CSharpGL.Windows中實現的。Dev通過引用CSharpGL項目和CSharpGL.Windows項目就可以直接使用OpenGL了。
如果不使用顯卡中的OpenGL實現,而是換做SoftGL,那么這一切就要相應地變化。SoftOpengl32項目代替操作系統的opengl32.dll。CSharpGL保持不變。SoftGL.Windows代替CSharpGL.Windows。Dev通過引用CSharpGL項目和SoftGL.Windows項目就可以直接使用軟實現的OpenGL了。
最重要的是,這樣保證了應用程序的代碼不需任何改變,應用程序只需將對CSharpGL.Windows的引用修改為對SoftGL.Windows的引用即可。真的。
創建ShaderProgram和Shader
根據OpenGL命令,可以推測一種可能的創建和刪除ShaderProgram對象的方式,偽代碼如下:
1 partial class SoftGLRenderContext 2 { 3 private uint nextShaderProgramName = 1; 4 5 // name -> ShaderProgram object 6 Dictionary<uint, ShaderProgram> nameShaderProgramDict = new Dictionary<uint, ShaderProgram>(); 7 8 private ShaderProgram currentShaderProgram = null; 9 10 public static uint glCreateProgram() // OpenGL functions. 11 { 12 uint id = 0; 13 SoftGLRenderContext context = ContextManager.GetCurrentContextObj(); 14 if (context != null) 15 { 16 id = context.CreateProgram(); 17 } 18 19 return id; 20 } 21 22 private uint CreateProgram() 23 { 24 uint name = nextShaderProgramName; 25 var program = new ShaderProgram(name); //create object. 26 this.nameShaderProgramDict.Add(name, program); // bind name and object. 27 nextShaderProgramName++; // prepare for next name. 28 29 return name; 30 } 31 32 public static void glDeleteProgram(uint program) 33 { 34 SoftGLRenderContext context = ContextManager.GetCurrentContextObj(); 35 if (context != null) 36 { 37 context.DeleteProgram(program); 38 } 39 } 40 41 private void DeleteProgram(uint program) 42 { 43 Dictionary<uint, ShaderProgram> dict = this.nameShaderProgramDict; 44 if (!dict.ContainsKey(program)) { SetLastError(ErrorCode.InvalidValue); return; } 45 46 dict.Remove(program); 47 } 48 }
創建ShaderProgram對象的邏輯很簡單,首先找到當前的Render Context對象,然后讓它創建一個ShaderProgram對象,并使之與一個name綁定(記錄到一個Dictionary<uint, ShaderProgram>字典類型的字段中)。刪除ShaderProgram對象的邏輯也很簡單,首先判斷參數是否合法,然后將字典中的ShaderProgram對象刪除即可。
OpenGL中的很多對象都遵循這樣的創建模式,例如Shader、Buffer、VertexArrayObject、Framebuffer、Renderbuffer、Texture等。
ShaderProgram是一個大塊頭的類型,它要處理很多和GLSL Shader相關的東西。到時候再具體說。
創建VertexBuffer、IndexBuffer和VertexArrayObject
參見創建ShaderProgram對象的方式。要注意的是,這些類型的創建分2步。第一步是調用glGen*(int count, uint[] names);,此時只為其分配了name,沒有創建對象。第二步是首次調用glBind*(uint target, uint name);,此時才會真正創建對象。我猜這是早期的函數接口,所以用了這么啰嗦的方式。
對頂點屬性進行設置
一個頂點緩存對象(GLBuffer)實際上是一個字節數組(byte[])。它里面保存的,可能是頂點的位置屬性(vec3[]),可能是頂點的紋理坐標屬性(vec2[]),可能是頂點的密度屬性(float[]),可能是頂點的法線屬性(vec3[]),還可能是這些屬性的某種組合(如一個位置屬性+一個紋理坐標屬性這樣的輪流出現)。OpenGL函數glVertexAttribPointer(uint index, int size, uint type, bool normalized, int stride, IntPtr pointer)的作用就是描述頂點緩存對象保存的是什么,是如何保存的。
glClear(uint mask)
每次渲染場景前,都應清空畫布,即用glClear(uint mask);清空指定的緩存。
OpenGL函數glClearColor(float r, float g, float b, float a);用于指定將畫布清空為什么顏色。這是十分簡單的,只需設置Render Context中的一個字段即可。
需要清空顏色緩存(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)時,實際上是將當前Framebuffer對象上的顏色緩存設置為指定的顏色。需要清空深度緩存(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)或模板緩存(GL_STENCIL_BUFFER_BIT)時,實際上也是將當前Framebuffer對象上的深度緩存或模板緩存設置為指定的值。
所以,為了實現glClear(uint mask)函數,必須將Framebuffer和各類緩存都準備好。
Framebuffer中的各種緩存都可以簡單的用一個Renderbuffer對象充當。一個Renderbuffer對象實際上也是一個字節數組(byte[]),只不過它還用額外的字段記錄了自己的數據格式(GL_RGBA等)等信息。紋理(Texture)對象里的各個Image也可以充當Framebuffer中的各種緩存。所以Image是和Renderbuffer類似的東西,或者說,它們支持同一個接口IAttachable。
1 interface IAttachable 2 { 3 uint Format { get; } // buffer’s format 4 int Width { get; } // buffer’s width. 5 int Height { get; } // buffer’s height. 6 byte[] DataStore { get; } // buffer data. 7 }
這里就涉及到對與byte[]這樣的數組與各種其他類型的數組(例如描述位置的vec3[])相互賦值的問題。一般,可以用下面的方式解決:
1 byte[] bytes = ... 2 this.pin = GCHandle.Alloc(bytes, GCHandleType.Pinned); 3 IntPtr pointer = this.pin.AddrOfPinnedObject(); 4 var array = (vec3*)pointer.ToPointer(); 5 for (in i = 0; i< ...; i++) { 6 array[i] = ... 7 }
只要能將數組轉換為?void*?類型,就沒有什么做不到的了。
?
glGetIntegerv(uint target, int[] values)
這個十分簡單。一個大大的switch語句。
?
設置Viewport
設置viewport本身是十分簡單的,與設置lineWidth類似。但是,在一個Render Context對象被首次MakeCurrent()到一個線程時,要將Device Context的Width和Height賦值給viewport。這個有點麻煩。
更新uniform變量的值
?
glDrawElements(..)
?
總結
?


合同怎么寫?)











 python_python的apply應用:一般性的“拆分-應用-合并”,附加詳細講解)
Slave DNS及高級特性)



