1,前言
本文期望描述如何使用Shiro構建基本的安全登錄和權限驗證。本文實戰場景有如下特殊需求:1,在集群和分布式環境實現session共享;2,前端只使用HTML/CSS/JS。因此無法直接使用Shiro提供的SessionManager,以及Shiro針對web應用提供的Filter攔截方式。當然,除非是一定要通過共享緩存的方式共享session,否則還是使用Shiro默認的session管理,畢竟增加獨立緩存就意味著維護成本的提高和可用性的下降。
2, Shiro架構
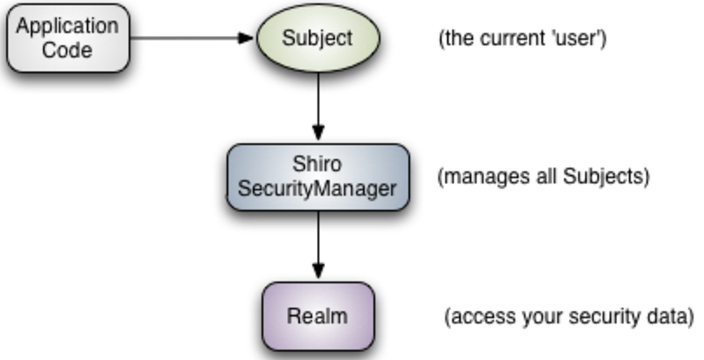
首先一睹官方給出的Shiro架構圖,如圖1所示。刨除最右側的加密工具類,主要圍繞SercurityManager來闡述。SercurityManager是Shiro安全框架里的頂層安全管理中心,所有安全控制相關邏輯都是在SercurityManager里面通過delegate的方式,調用到真正的動作執行者。從圖1可以清楚看到主要管理的組件:authentication管理,authorization管理,session管理,session緩存管理,cache管理,realms管理。(本文不想重復已有的文字,想要更好的了解Shiro,詳見官方推薦的Shiro full intro: https://www.infoq.com/articles/apache-shiro)
1)Shiro提供的CacheManager比較單薄,提供實現是MemoryConstrainedCacheManager,主要是依賴SoftHashMap來做基于內存條件的緩存,也即是當內存吃緊,沒有新的內存空間來存放new出來的對象時,會去釋放SoftHashMap中存放的對象,在本文中的應用場景是面向集群和分布式應用環境,使用了Redi緩存登錄用戶的相關信息,所以需要自定義cache處理。
2)Shiro對于session的緩存管理,定義了SessionDAO抽象,并提供了兩個存放于本地JVM內存的EnterpriseCacheSessionDAO和MemorySessionDAO,兩者主要區別是EnterpriseCacheSessionDAO的session存放在SoftHashMap中,原則上可以自己實現SessionDAO 接口,實際存儲使用Redis來做到完整的session共享,但是缺陷是:a,不安全,因為把所有數據都共享出去了;b,當每次需要獲取session數據時,都需要通過網絡來把整個session反序列化回來,而考慮很多情況下,只是間斷的需要幾個key的數據,這樣在session數據量大一些的時候,就會產生大量消耗。因此在共享session時,不去替換默認SessionDao的實現,而是通過@overwrite AbstractNativeSessionManager getter/setter attribute方法,實現有選擇的共享session的基本初始化和指定attribute key的數據。
3)Shiro的authentication和authorization過程主要是依據用戶定義的 AuthorizingRealm中提供的AuthenticationInfo和AuthorizationInfo。特別地,authentication 還提供類似驗證鏈的authentication策略,允許用戶提供多個Realm。第3部分會具體的示例Shiro集成Spring的使用范例,并詳細解釋AuthorizingRealm 。

圖 1 Shiro官方架構圖
3, Shiro使用范例
官方提供了集成Spring Web應用的使用例子,但是就如前文提到的,這里前端只能使用JS的Http和后端通信,因此無法直接使用ShiroFilterFactoryBean來做Request的Filter。本文鑒于簡單和初期的原則,可以選擇定義一個RequestInterceptor類繼承HandlerInterceptorAdapter并overwrite preHandle 方法。Interceptor的applicationContext和源碼定義如下:
applicationContext.xml
1 <mvc:interceptors> 2 <mvc:interceptor> 3 <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> 4 <!--攔截的url --> 5 <mvc:mapping path="/admin/**"/> 6 <!-- 不攔截的url start --> 7 <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/login"/> 8 <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/code"/> 9 <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/logout"/> 10 <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/msgErrorInfo"/> 11 <!--不攔截的url end --> 12 <bean class="authorizing.RequestInterceptor"> 13 <property name="unauthenticatedUrl" value="/admin/msgErrorInfo" /> 14 </bean> 15 </mvc:interceptor> 16 </mvc:interceptors>
RequestInterceptor.java
1 public class RequestInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { 2 3 private String unauthenticatedUrl; 4 5 public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, 6 Object handler) throws Exception { 7 if(PermissionUtils.isLogin(request)){ 8 return true; 9 } 10 //token已失效,返回提示信息 11 request.getRequestDispatcher(unauthenticatedUrl).forward(request, response); 12 return false; 13 } 14 15 public void setUnauthenticatedUrl(String unauthenticatedUrl) { 16 this.unauthenticatedUrl = unauthenticatedUrl; 17 } 18 }
?
RequestInterceptor.java定義非常簡單,主要是在preHandler方法中驗證了一下請求是否是登錄用戶發出的,否則響應給前端一個重定向。然后看一下PermissionUtils.isLogin(request)是怎樣做登錄驗證的。
PermissionUtils.java
1 public class PermissionUtils { 2 private static ThreadLocal<String> sessionToken = new ThreadLocal<String>(); 3 4 public static boolean isLogin(HttpServletRequest request){ 5 String token = sessionToken(request); 6 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) 7 return false; 8 /** 9 * 使用token檢查是否存在登錄session 10 */ 11 //Session session = SecurityUtils.getSecurityManager().getSession(new WebSessionKey(token, request, response)); 12 Session session = SecurityUtils.getSecurityManager().getSession(new DefaultSessionKey(token)); 13 if(session != null){ 14 session.touch(); 15 sessionToken.set(token); 16 return true; 17 } 18 return false; 19 } 20 21 private static String sessionToken(HttpServletRequest request){ 22 return request.getHeader("token"); 23 } 24 }
?
從PermissionUtils.java可以判斷,保存前后端session的方式是通過token的形式。也即是每次request中的header部分都攜帶了登錄成功后獲取的token,以token為標識獲取登錄用戶的session。特別地,對于Shiro而言,session并非特定于Web應用,Shiro有自己的session定義,可以獨立于應用環境而存在。因此為了追求簡單(既已棄用了Shiro針對web.xml應用提供的Filter),直接使用Shiro創建的默認session(實際是SimpleSession)。此外,需要說明的一個細節是通過Shiro的SecurityManager 返回的session實際都是一個代理(DelegatingSession的實例)。因此,通過 SecurityManager獲取的session,然后對session執行的動作實際都是通過 SecurityManager的SessionManager來完成的(因為共享session,每一次session的touch動作都應該反映到共享session中,后文,可以看到overwrite SessionManager#touch(SessionKey key)和start session)。Shiro提供的默認SessionManager都繼承了AbstractValidatingSessionManager$sessionValidationSchedulerEnabled屬性,該屬性控制了是否執行一個后臺守護線程(Thread#setDaemon(true))在給定的一個固定時間間隔(默認1個小時)內周期性的檢查session是否過期,并且在每一次獲取到session之后都會去檢查session是否過期(對于共享session的集群,共享緩存基本都已具備超時管理功能,所以可以重新實現后文提到的 AbstractNativeSessionManager#getSession(SessionKey))。PermissionUtils.java中定義了一個ThreadLocal類型的sessionToken變量,該變量是用于暫存當前request authentication成功之后的session標識,避免每次獲取token都要從request中拿(后文中使用到的每一個url的authorization都需要首先執行一次checkPermission方法,通過token來驗證是否有訪問權限)。
接下來描述Authentication和Authorization,具體地說明如何基于Shiro實現login和check permission。下面先給出applicationContext配置。
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager"><property name="realm" ref="authorizingRealm" /><property name="sessionManager"><bean class="service.authorizing.shiro.RedisSessionManager" ><property name="globalSessionTimeout" value="${session.timeout}" /></bean></property> </bean> <bean id="realmCache" class="service.authorizing.shiro.cache.RedisShiroCache" /> <bean id="authorizingRealm" class="service.authorizing.shiro.DefaultAuthorizingRealm"><property name="authorizationCachingEnabled" value="true"/><property name="authorizationCache" ref="realmCache" /> </bean> <bean id="lifecycleBeanPostProcessor" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor"/><bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingFactoryBean"><property name="staticMethod" value="org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager"/><property name="arguments" ref="securityManager"/> </bean>
?
applicationContext.xml中配置的DefaultSecurityManager,RedisSessionManager,DefaultAuthorizingRealm和RedisShiroCache,分別代表Shiro的默認SecurityManager,自定義基于Redis的session manager,繼承自Shiro的AuthorizingRealm的默認實現,以及自定義基于Redis的用戶權限相關的Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo>實現。注意到,本文的應用場景雖然是web.xml應用,但是并沒有使用Shiro提供的 DefaultWebSecurityManager和DefaultWebSessionManager這兩個針對web應用的拓展。使用針對web應用的拓展實現自然也沒問題,但是個人認為對于純粹的前后端分離權限認證的應用場景中,前端和后端應當是完全獨立的,它們之間唯一的耦合是通過Http request交互的token。因此就目前簡單和初期的原則,不需要DefaultWebSecurityManager和DefaultWebSessionManager。
?
圖2 Shiro組件交互過程
在講解程序具體怎樣執行login和check permission之前,先看圖2所示的Shiro各組件的交互過程,可以看到Real是安全驗證的依據。所以有必要先理解Shiro提供的abstract類AuthorizingRealm,該類定義了兩個抽象方法doGetAuthorizationInfo和doGetAuthenticationInfo,分別用于check permission和login驗證。具體如下DefaultAuthorizingRealm.java的定義:
DefaultAuthorizingRealm.java
1 public class DefaultAuthorizingRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { 2 3 @Autowired 4 private AuthorizingService authorizingService; 5 6 /** 7 * 獲取登錄用戶角色和功能權限信息, 8 * 使用{@link org.apache.shiro.cache.CacheManager}和{@link org.apache.shiro.cache.Cache}獲取數據. 9 * @param principals 登錄用戶ID 10 * @return 11 */ 12 protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { 13 Object username =principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); 14 Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> infoCache = getAuthorizationCache(); 15 AuthorizationInfo info = infoCache.get(username); 16 return info; 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * 根據登錄用戶token,獲取用戶信息。 21 * 對于session timeout時間較短的場景可以考慮使用AuthenticationCache 22 * 若驗證失敗,會拋出異常 {@link AuthenticationException} 23 * @param token 24 * @return 25 * @throws AuthenticationException 26 */ 27 protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { 28 Object username = token.getPrincipal(); 29 //對于session timeout時間較短的場景,可緩存用戶authentication信息 30 //Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> infoCache = getAuthenticationCache(); 31 //return infoCache.get(username); 32 return authorizingService.authentication(username); 33 } 34 }
DefaultAuthorizingRealm.java的實現,可以看到用戶只需要通過 doGetAuthorizationInfo和doGetAuthenticationInfo兩個方法給Shiro的SecurityManager提供Authorization和Authentication信息,SecurityManager就會在執行check permission和login操作時自動調用這兩個函數來驗證操作。下面我們再看執行login和check permission操作時具體做了什么。
- Authentication
下面在LoginController.java定義了login請求操作。
LoginController.java
1 @Controller 2 @RequestMapping("/admin") 3 public class LoginController { 4 Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginController.class); 5 6 @Autowired 7 private AuthorizingService authorizingService; 8 9 @RequestMapping("/login") 10 @ResponseBody 11 public LoginToken login(User user, HttpServletRequest request){ 12 Subject subject = new Subject.Builder().buildSubject(); 13 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName, UtilTool.md5Tool(password)); 14 token.setRememberMe(true); 15 LoginToken loginToken = new LoginToken(); 16 try{ 17 subject.login(token); 18 Session session = subject.getSession(); 19 user.setToken((String) session.getId()); 20 loginToken.setResultCode(WebConstants.RESULT_SUCCESS_CODE); 21 } catch (AuthenticationException e) { 22 loginToken.setResultCode(WebConstants.RESULT_FAIL_CODE); 23 loginToken.setMessage("用戶名或密碼錯誤!"); 24 } 25 return loginToken; 26 } 27 }
?
上述login代碼只做了非常簡單用戶名和密碼的驗證示例。可以看出login如果沒有拋出AuthenticationExeception,則說明登錄成功。
- Authorization
訪問權限控制需要在所有的訪問controller的函數中配置,因此使用工具類最合適(在工具類的基礎上做成spring annotation也可以很方便),既是PermissionUtils.java。
PermissionUtils.java
1 private static AuthorizingService authorizingService; 2 3 private static ThreadLocal<String> sessionToken = new ThreadLocal<String>(); 4 5 /** 6 * 7 * @param url eg: /admin/review 8 * @param argv eg: WAIT_BIZ_MANAGER 9 */ 10 public static void checkPermission(String url, @Nullable String argv){ 11 Subject subject = getSubject(); 12 String permissionCode = authorizingService.uriMappingCode(url, argv); 13 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(permissionCode)) 14 throw new IllegalArgumentException("不明操作"); 15 subject.checkPermission(permissionCode); 16 } 17 18 public static Subject getSubject(){ 19 String token = sessionToken.get(); 20 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) 21 throw new AuthenticationException("未經認證"); 22 return new Subject.Builder() 23 .sessionId(sessionToken.get()) 24 .buildSubject(); 25 } 26 27 public static void setAuthorizingService(AuthorizingService authorizingService) { 28 PermissionUtils.authorizingService = authorizingService; 29 }
?
從上述代碼來看,每一個request的checkPermission操作,都需要依賴前文RequestInterceptor.java中提到的,從request中獲取的token,并依賴該token找到緩存的session 。在權限控制的設計時,不同的業務場景可能需要不同粒度的權限控制,在這里做到了request參數級別的權限控制(在workflow應用中,一個流程涉及多個角色的參與,但很可能只抽象一個接口,如下文的/review操作)。在實現的時,靈活的方式是可以維護一張uri和permission_code之間的關系表(簡單可以propertites文件)。對于前端用戶而言,為了提升用戶體驗,擁有不同權限的用戶得到的界面會有相應的隱藏和顯示,因此會給前端的登錄用戶提供一張可訪問權限表。在這里一個細節的設計,個人覺得有意義的是,在返回給前端的權限表的Key值不應當是permission_code,而是uri。因為permission_code對于前端而言毫無意義,而uri正是前后端溝通的橋梁。因此,check Permission操作可以如下:
ReviewApiController.java
1 @RestController 2 @RequestMapping(value = "/review") 3 public class ReviewApiController { 4 5 @Autowired 6 private ReviewService reviewService; 7 8 @ResponseBody 9 @RequestMapping(value = "/review", method = POST) 10 public WebResult review(@RequestBody NewReviewVo reviewVo){ 11 //檢查訪問權限 12 PermissionUtils.checkPermission("/review/review", reviewVo.getFeatureCode()); 13 WebResult result = WebResult.successResult(); 14 try { 15 Review review = ReviewAssembler.voToReview(reviewVo); 16 reviewService.review(review); 17 }catch (Exception e){ 18 result = WebResult.failureResult(e.getMessage()); 19 } 20 return result; 21 } 22 }
?
- SessionManager
由于要實現有選擇的共享session數據,因此session管理成了最棘手的問題,因為你不是粗暴地將整個session序列化到緩存并仍以local session的方式管理,其間需要額外得小心處理共享的session數據和本地的session數據。下面給出RedisSessionManager.java的實現:
RedisSessionManager.java


1 /** 2 * 根據 attributeKey,有選擇的緩存session信息; 3 * 設置 {@parm enabledSharedSessionData}來有選擇的啟用共享session功能。 4 */ 5 public class RedisSessionManager extends DefaultSessionManager { 6 7 private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisSessionManager.class); 8 9 private boolean enabledSharedSessionData; 10 11 private Set<String> sharedSessionDataKeys; 12 13 public RedisSessionManager() { 14 enabledSharedSessionData = true; 15 sharedSessionDataKeys = new HashSet<String>(); 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public Collection<Object> getAttributeKeys(SessionKey key) { 20 21 Collection<Object> keys = super.getAttributeKeys(key); 22 if(enabledSharedSessionData) { 23 /** 24 * 從redis獲取 {@param key} 對應session的所有attribute key 25 */ 26 Set sharedKeys = RedisClient.extractAttributeKey((String) key.getSessionId()); 27 keys.addAll(sharedKeys); 28 } 29 return keys; 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public Object getAttribute(SessionKey sessionKey, Object attributeKey) 34 throws InvalidSessionException { 35 if(checkSharedStrategy(attributeKey)){ 36 Object object = RedisClient.getValue((String) attributeKey, (String) sessionKey.getSessionId()); 37 return object; 38 } 39 return super.getAttribute(sessionKey, attributeKey); 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 public void setAttribute(SessionKey sessionKey, Object attributeKey, Object value) 44 throws InvalidSessionException { 45 if(checkSharedStrategy(attributeKey)) { 46 if(value instanceof Serializable) 47 RedisClient.setValue((String) attributeKey, (String) sessionKey.getSessionId(), 48 (Serializable) value, getGlobalSessionTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 49 else 50 throw new IllegalArgumentException("不可共享非序列化value"); 51 return; 52 } 53 super.setAttribute(sessionKey, attributeKey, value); 54 } 55 56 private boolean checkSharedStrategy(Object attributeKey){ 57 return enabledSharedSessionData && sharedSessionDataKeys.contains(attributeKey); 58 } 59 60 /** 61 * 如果是集群, session只在一臺機器上創建,因此必須共享 SessionId。 62 * 當request發過來,獲取request中攜帶的 SessionId,使用 SessionId 在本地獲取session, 63 * 如果為null,則用 SessionId 去redis檢查是否存在,如果存在則在本地構建session返回 64 * (實際就是{@link SimpleSession}的代理{@link DelegatingSession},{@see RedisSessionManager#restoreSession}), 65 * 否則返回空, 請求重新登錄。 66 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractNativeSessionManager#getSession(SessionKey)} 67 * @param key 68 * @return 69 * @throws SessionException 70 */ 71 @Override 72 public Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException { 73 Session session = null; 74 try { 75 session = getLocalSession(key); 76 } catch (UnknownSessionException use){ 77 //ignored 78 session = null; 79 } 80 if(!enabledSharedSessionData || session != null) 81 return session; 82 /** 83 * 檢查redis,判斷session是否已創建, 84 * 若已創建,則使用SessionFactory在本地構建SimpleSession 85 */ 86 Serializable sid = RedisClient.getValue((String) key.getSessionId()); 87 if(sid != null){ 88 session = restoreSession(key); 89 } 90 91 return session; 92 } 93 94 /** 95 * 每一次通過 96 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager#doGetSession(SessionKey)}} 97 * 獲取session 98 * 或是通過{@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler} 99 * 定時檢查,都會去調用 100 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager#doValidate(Session)} 101 * 驗證session是否過期。 102 * 共享session過期的標準是該redis中sessionId過期, 由于redis已經幫助完成了session過期檢查, 103 * 所以這里只需要定期清理本地內存中的過期session。 104 * 然而{@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager#doGetSession(SessionKey)}} 105 * 是一個final方法,無法被overwrite,所以只能copy Shiro原來的代碼實現來定義getLocalSession(SessionKey key) 106 * @param key 107 * @return 108 */ 109 private Session getLocalSession(SessionKey key){ 110 Session session = lookupSession(key); 111 return session != null ? createExposedSession(session, key) : null; 112 } 113 private Session lookupSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException { 114 if (key == null) { 115 throw new NullPointerException("SessionKey argument cannot be null."); 116 } 117 //enableSessionValidationIfNecessary 118 SessionValidationScheduler scheduler = getSessionValidationScheduler(); 119 if (enabledSharedSessionData || 120 (isSessionValidationSchedulerEnabled() && (scheduler == null || !scheduler.isEnabled())) 121 ) { 122 enableSessionValidation(); 123 } 124 Session s = retrieveSession(key); 125 if (!enabledSharedSessionData && s != null) { 126 validate(s, key); 127 } 128 return s; 129 } 130 131 /** 132 * 根據{@link SessionKey}以及繼承自{@link DefaultSessionManager}的默認創建方法, 133 * 重新在本地構建session。 134 * @param key 135 * @return 136 */ 137 private Session restoreSession(SessionKey key){ 138 SimpleSession restoreSession = (SimpleSession) getSessionFactory().createSession(null); 139 restoreSession.setId(key.getSessionId()); 140 restoreSession.setTimeout(getGlobalSessionTimeout()); 141 create(restoreSession); 142 return createExposedSession(restoreSession, key); 143 } 144 145 /** 146 * 開啟一個新的session, 并且在新的session開啟之后做一系列的session共享工作。 147 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractNativeSessionManager#start(SessionContext)} 148 * @param context 149 * @return 150 */ 151 @Override 152 public Session start(SessionContext context) { 153 Session session = super.start(context); 154 if(enabledSharedSessionData){ 155 shareSessionData(session); 156 } 157 return session; 158 } 159 /** 160 * 完成session基本數據共享 161 */ 162 private void shareSessionData(Session session){ 163 refreshTTL(session.getId()); 164 } 165 /** 166 * 刷新session存活時間 167 */ 168 private void refreshTTL(Serializable sessionId){ 169 RedisClient.setValue((String) sessionId, new Date(), 170 getGlobalSessionTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 171 } 172 173 /** 174 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractNativeSessionManager#touch(SessionKey)} 175 * @param key 176 * @throws InvalidSessionException 177 */ 178 @Override 179 public void touch(SessionKey key) throws InvalidSessionException { 180 if(enabledSharedSessionData){ 181 //刷新session存活時間 182 refreshTTL(key.getSessionId()); 183 } 184 super.touch(key); 185 } 186 187 /** 188 * 當主動調用{@link Subject#logout()}時,相應會調用該方法來停止session。 189 * 因此,如果共享了session,也需要即時清除共享session。 190 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractNativeSessionManager#stop(SessionKey)} 191 * @param key 192 * @throws InvalidSessionException 193 */ 194 @Override 195 public void stop(SessionKey key) throws InvalidSessionException { 196 super.stop(key); 197 if(enabledSharedSessionData) 198 RedisClient.delete((String) key.getSessionId()); 199 } 200 201 /** 202 * {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractNativeSessionManager#getLastAccessTime(SessionKey)} 203 * @param key 204 * @return 205 */ 206 @Override 207 public Date getLastAccessTime(SessionKey key) { 208 Serializable lastAccessTime = enabledSharedSessionData ? 209 RedisUtils.getValue((String) key.getSessionId()) : 210 super.getLastAccessTime(key); 211 if(lastAccessTime == null) 212 throw new SessionTimeoutException(); 213 return (Date) lastAccessTime; 214 } 215 216 /** 217 * 通知session manager那些attribute key對應的數據需要共享。 218 * @param key 219 */ 220 public void registerSharedAttributeKey(String key){ 221 if(!enabledSharedSessionData) 222 throw new IllegalArgumentException("不允許共享session數據"); 223 if(sharedSessionDataKeys == null) 224 sharedSessionDataKeys = new HashSet<String>(); 225 sharedSessionDataKeys.add(key); 226 } 227 }
由于Redis本身就是單線程模型,所以作為客戶端基本不需要考慮線程安全問題。下面就各個問題來詳細說明?RedisSessionManager。既然需求是想要實現在集群和分布式環境下,有選擇的共享session數據,這意味著有一下問題需要處理:1,怎樣做到有選擇的共享session數據?2,本地session過期了怎樣清理,以及怎樣避免Shiro每次獲取本地session都會進行過期驗證和Redis的過期驗證之間的重復? 3,怎樣管理session存活時間?4,session只在一臺機器上創建,既然不是共享了整個session,那么其它機器如何重建session?
對于第1個問題,RedisSessionManager.java定義了enabledSharedSessionData和sharedSessionDataKeys兩個變量來控制session數據共享,如果要求共享session數據,則需要通過registerSharedAttributeKey(String key)來告知session manager那些attribute key需要被共享,并定義checkSharedStrategy(Object attributeKey) 方法來檢查attribute key是否共享。余下就是overwrite getter/setter attribute方法就可以了。這里再提一下,對于設置enabledSharedSessionData=true,除非是一定要通過共享緩存的方式共享session,否則還是使用Shiro默認的session管理,畢竟增加獨立緩存就意味著維護成本的提高和可用性的下降。
對于第2個問題,Shiro提供的session manager已經完成了local session的管理動作,因此我們只需要把local session的管理操作直接交給Shiro提供的默認session manager就可以了,而對于共享的session數據,Redis已經提供了數據過期管理功能(或者其它緩存工具基本都提供了)。因為Shiro提供的session manager清理session的原則是session已經過期或已經stop,那么session manager是怎樣自動讓session進入過期狀態的呢?從AbstractNativeSessionManager#getSession(SessionKey)方法就可以追溯到,每一次通過該方法獲取session不為空,都會調用SimpleSesion#validate()方法來驗證session是否過期。此外,Shiro也提供了ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler類來開啟一個后臺的固定周期執行的守護線程來執行session驗證。既然Redis已經可以做到session有效性管理,那就沒必要在每次獲取session的時候都去主動的驗證一次session。然而,getSession操作實際,Shiro提供的實現實際是調用了一個final類型AbstractValidatingSessionManager#doGetSession(SessionKey)方法,這意味著無法通過overwrite的方式來避免主動調用SimpleSesion#validate()。因此,在自定義sesssion manager中定義了getLocalSession(SessionKey key)方法,該方法本質實際是參照Shiro提供的實現,并在基礎之上加上場景約束。
對于第3個問題,在解釋第2問題時已提到,Redis已自帶超時管理功能,因此session存活時間只需要由Redis管理即可,而Shiro只需要開啟一個固定周期的后臺任務來清理本地無效session即可。
對于第4個問題,在前后端完全分離的應用場景下,用戶authentication通過之后由Shiro自動創建的session,里面包含的大部分數據都是可選共享的,而Shiro提供的最核心的Session實現,實際就是允許空參構造函數的SimpleSession。所以,實際我們只需共享出全局唯一的sessionId(shareSessionData(Session session) 方法實現),即可使用session manager提供的getSessionFactory()方法獲取默認session factory,然后通過該factory即可創建SimpleSession并設置相應的共享數據,即restoreSession(SessionKey key)方法定義的過程。在Shiro提供的默認session manager中可以看到,所有的session創建都是通過AbstractNativeSessionManager#start(SessionContext)完成的,所以只需要overwrite這個方法并共享新創建session的必要數據即可。最后,結合問題2中提到的getLocalSession(SessionKey key)方法,獲取session的方法getSession(SessionKey key)的實現分為兩步:第一步是通過 getLocalSession(SessionKey key) 獲取;如果第一步返回null且Redis中session未過期,則第二步通過restoreSession(SessionKey key)在本地重建session 。特別地,從refreshTTL(Serializable sessionId)方法的定義,可以看到共享sessionId的同時,對應的存放了該session的LastAccessTime。
4,Authentication和Authorization執行時序
在第3部分,已經給出了一個基本的基于Shiro的前后端分離的共享session實戰范例,因此在這一部分將基于第3部分,通過時序圖來表述Authentication和Authorization的執行流程。
- 簡要的合并時序
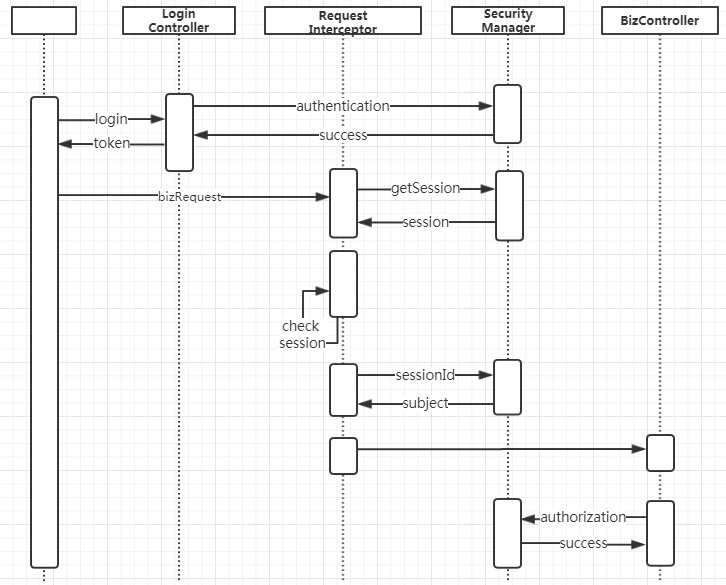
?
圖3 合并時序
- Authentication時序
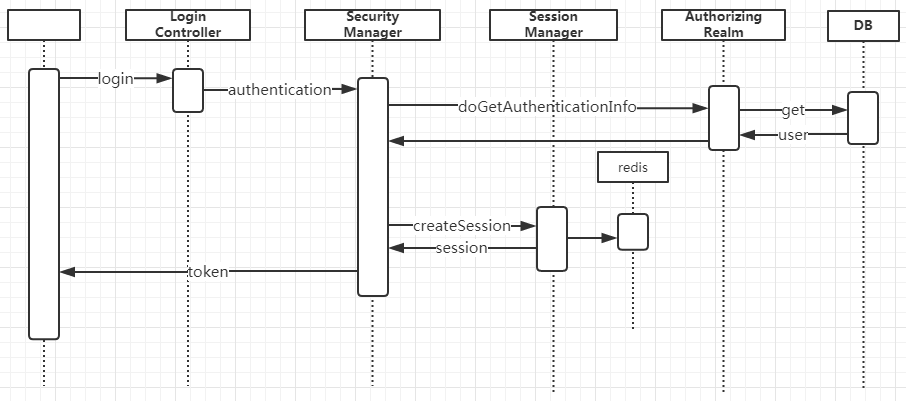
圖4 Authentication時序
- Authorization時序
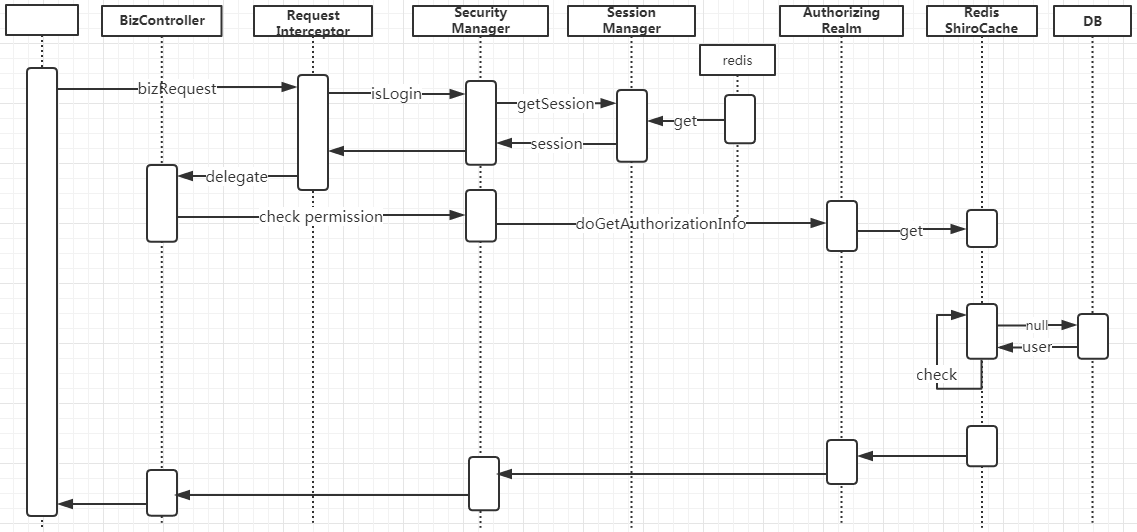
圖4 Authorization時序
5,總結
在使用Shiro框架進行Authentication和Authorization實踐時,雖然根據不同的業務場景需要做不同的修改或調整,但是基本也是最佳的實踐方式是時刻圍繞Shiro的設計原則和已有可借鑒的實現方案來操作,盡可能少或者不修改,從而避免一些預想不到的Bug。最后,重提前言部分說到的,除非是一定要通過共享緩存的方式共享session,否則還是使用Shiro默認的session管理。
)











![BZOJ 1662: [Usaco2006 Nov]Round Numbers 圓環數(數位DP+惡心細節)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BZOJ 1662: [Usaco2006 Nov]Round Numbers 圓環數(數位DP+惡心細節))






![JAVA命令符找不到符號_[轉]Java命令行編譯文件時出現的錯誤,找不到符號或軟件包不存在等...](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/JAVA命令符找不到符號_[轉]Java命令行編譯文件時出現的錯誤,找不到符號或軟件包不存在等...)