目錄
一、list 容器的基本介紹
二、list 容器的成員函數
2.1 - 迭代器
2.2 - 修改操作
三、list 的模擬實現
3.1 - list.h
3.2 - 詳解 list 容器的迭代器
3.2 - test.cpp
?
一、list 容器的基本介紹
list 容器以類模板 list<T>(T 為存儲元素的類型)的形式定義在 <list> 頭文件中,并位于 std 命名空間中。
template < class T, class Alloc = allocator<T> > class list; ? ?list 是序列容器,允許在序列內的任意位置高效地插入和刪除元素(時間復雜度是 O(1) 常數階),其迭代器類型為雙向迭代器(bidirectional iterator)。
list 容器的底層是以雙向鏈表的形式實現的。
list 容器與 forward_list 容器非常相似,最主要的區別在于 forward_list 容器的底層是以單鏈表的形式實現的,其迭代器類型為前向迭代器(forward iterator)。
與其他標準序列容器(array、vector 和 deque)相比,list 容器在序列內已經獲得迭代器的任意位置進行插入、刪除元素時通常表現得更好。
與其他序列容器相比,list 容器和 forward_list 容器的最大缺點是不支持任意位置的隨機訪問,例如:要訪問 list 中的第 6 個元素,必須從已知位置(比如頭部或尾部)迭代到該位置,這需要線性階的時間復雜度的開銷。
二、list 容器的成員函數
2.1 - 迭代器
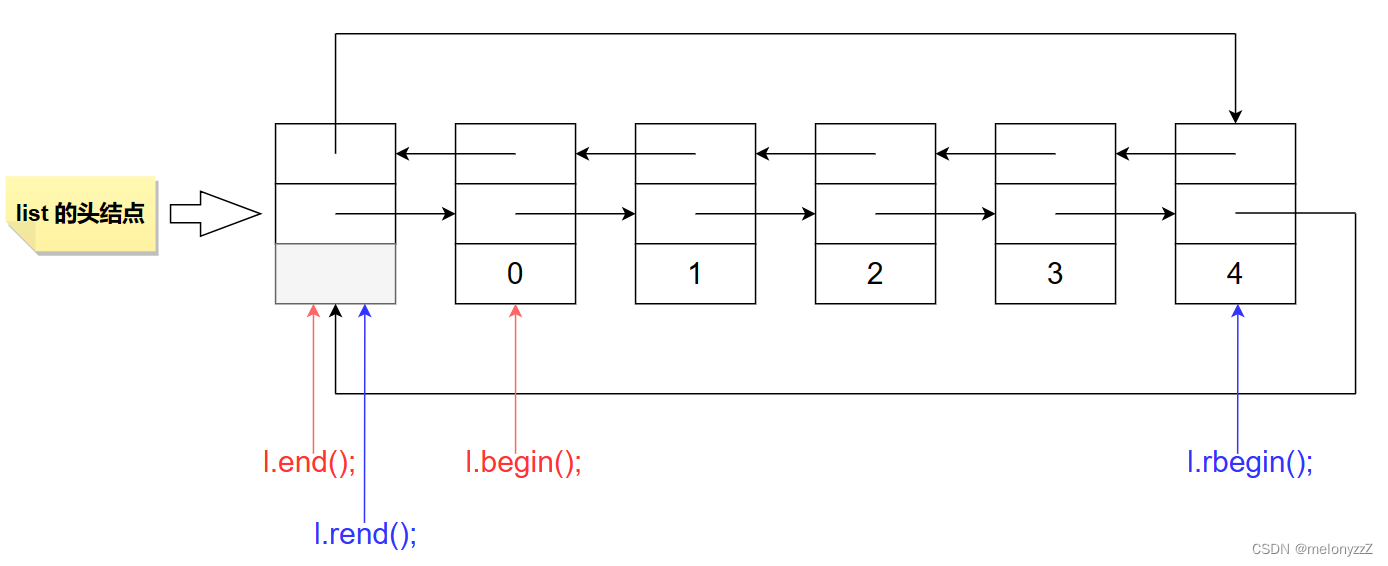
begin:
? ? ?iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;end:
? ? ?iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;rbegin:
? ? ?reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;rend:
? ? ?reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
?
int main()
{list<int> l;l.push_back(0);l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);
?for (list<int>::iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); ++it){cout << *it << " ";}// 0 1 2 3 4cout << endl;
?for (list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = l.rbegin(); rit != l.rend(); ++rit){cout << *rit << " ";}// 4 3 2 1 0cout << endl;return 0;
}
?
2.2 - 修改操作
push_front:
void push_front(const value_type& val);注意:value_type 等價于 T。
pop_front:
void pop_front();push_back:
void push_back(const value_type& val);pop_back:
void pop_back();insert:
// C++ 98
single element (1) iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type& val);fill (2) ? ? void insert(iterator position, size_type n, const value_type& val);range (3) template <class InputIterator>void insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);相較于 vector,執行 list 的 insert 操作不會產生迭代器失效的問題。
示例一:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
?
int main()
{list<int> l;l.push_back(0);l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);
?// 要求:在第三個元素前面插入元素 100// l.insert(l.begin() + 2, 100); // error// 因為 list 對應的迭代器類型為雙向迭代器,所以不支持加法操作,即沒有重載該運算符
?// 解決方案:list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; ++i){++it;}l.insert(it, 100);
?for (auto e : l){cout << e << " ";}// 0 1 100 2 3 4cout << endl;return 0;
}erase:
iterator erase(iterator position);
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);因為節點被刪除后,空間釋放了,所以執行完 list 的 erase 操作,迭代器就失效了,而解決方案依然是通過返回值對迭代器進行重新賦值。
示例二:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
?
int main()
{list<int> l;l.push_back(0);l.push_back(1);l.push_back(2);l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);
?// 刪除 list 中所有值為偶數的元素list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){if (*it % 2 == 0)it = l.erase(it); ?// 直接寫 l.erase(it); 會報錯else++it;}
?for (auto e : l){cout << e << " ";}// 1 3cout << endl;return 0;
}三、list 的模擬實現
3.1 - list.h
#pragma once
?
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
?
namespace yzz
{template<class T>struct __list_node{__list_node<T>* _prev;__list_node<T>* _next;T _data;
?__list_node(const T& val = T()): _prev(0), _next(0), _data(val){ }};
?
?template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;typedef __list_node<T> list_node;list_node* _pnode; ?// 節點指針
?__list_iterator(list_node* p = 0): _pnode(p){ }
?self& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}
?self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_next;return tmp;}
?self& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}
?self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return tmp;}
?Ref operator*() const{return _pnode->_data;}
?Ptr operator->() const{return &_pnode->_data;}
?bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _pnode != it._pnode;}
?bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _pnode == it._pnode;}};
?
?template<class T>class list{private:typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
?void empty_initialize(){_phead = new list_node;_phead->_prev = _phead;_phead->_next = _phead;}
?public:/*-------- 構造函數和析構函數 --------*/list(){empty_initialize();}
?list(const list<T>& l) ?// 實現深拷貝{empty_initialize();for (auto& e : l){push_back(e);}}
?~list(){clear();delete _phead;_phead = 0;}
?/*-------- 賦值運算符重載 --------*/// 利用上面寫好的拷貝構造函數實現深拷貝void swap(list<T>& l){std::swap(_phead, l._phead);}
?list<T>& operator=(list<T> tmp){swap(tmp);return *this;}
?/*-------- 迭代器 --------*/typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _phead->_next;// 等價于:return iterator(_phead);// 返回的過程中發生了隱式類型轉換}
?iterator end(){return _phead;}
?const_iterator begin() const{return _phead->_next;// 等價于:return const_iterator(_phead->_next);}
?const_iterator end() const{return _phead;}
?/*-------- 容量操作 --------*/size_t size() const{size_t sz = 0;list_node* cur = _phead->_next;while (cur != _phead){++sz;cur = cur->_next;}return sz;}
?bool empty() const{return _phead->_next == _phead;}
?/*-------- 修改操作 --------*/iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);newnode->_prev = pos._pnode->_prev;newnode->_next = pos._pnode;
?pos._pnode->_prev->_next = newnode;pos._pnode->_prev = newnode;return newnode;}
?void push_back(const T& val){// 方法一:/*list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);newnode->_prev = _phead->_prev;newnode->_next = _phead;
?_phead->_prev->_next = newnode;_phead->_prev = newnode;*/
?// 方法二(直接復用):insert(end(), val);}
?void push_front(const T& val){// 方法一:/*list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);newnode->_prev = _phead;newnode->_next = _phead->_next;
?_phead->_next->_prev = newnode;_phead->_next = newnode;*/
?// 方法二(直接復用):insert(begin(), val);}
?iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end()); ?// 前提是 list 非空list_node* prev_pnode = pos._pnode->_prev;list_node* next_pnode = pos._pnode->_next;prev_pnode->_next = next_pnode;next_pnode->_prev = prev_pnode;delete pos._pnode;return iterator(next_pnode);}
?void pop_back(){erase(--end());}
?void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
?void clear(){list_node* cur = _phead->_next;while (cur != _phead){list_node* tmp = cur;cur = cur->_next;delete tmp;}_phead->_prev = _phead->_next = _phead;}
?private:list_node* _phead; ?// 頭指針};
}3.2 - 詳解 list 容器的迭代器
我們可以通過循序漸進的方式來了解 list 容器的迭代器:
-
首先,不能使用原生態指針直接作為 list 容器的正向迭代器,即:
typedef list_node* iterator;否則當正向迭代器進行
++/--操作時,無法讓它指向下一個或上一個節點,并且進行解引用*操作時,無法直接獲得節點的值,所以需要對原生態指針進行封裝,然后對這些操作符進行重載,即:typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator; -
其次,不能按以下方式直接定義 list 容器的常量正向迭代器,即:
typedef const __list_iterator<T> const_iterator;否則常量正向迭代器就無法進行
++/--操作,因為 const 類對象只能去調用 const 成員函數,并且 operator* 的返回值類型為 T&,即仍然可以在外部修改 list 容器。可以重新定義一個常量正向迭代器
__list_const_iterator,但需要修改的地方僅僅是 operatr* 的返回值,即將其修改為 const T&,顯然這樣的解決方案會造成代碼的冗余,所以在__list_iterator類模板中增加一個類型參數 Ref,將 operator* 的返回值修改為 Ref,即:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&> const_iterator; -
最后,在重載
->操作符時,對于正向迭代器,返回值類型應該是 T*,對于常量正向迭代器,返回值類型應該是 const T*,所以再增加一個類型參數 Ptr,將 operator-> 的返回值類型修改為 Ptr,即:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
3.2 - test.cpp
#include "list.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
?
void Print1(const yzz::list<int>& l)
{yzz::list<int>::const_iterator cit = l.begin();while (cit != l.end()){cout << *cit << " ";++cit;}cout << endl;
}
?
void test_list1()
{yzz::list<int> l1;l1.push_back(1);l1.push_back(2);l1.push_back(3);l1.push_back(4);cout << l1.size() << endl; ?// 4yzz::list<int> l2(l1);for (yzz::list<int>::iterator it = l2.begin(); it != l2.end(); ++it){cout << *it << " ";}// 1 2 3 4cout << endl;
?l1.push_front(10);l1.push_front(20);l1.push_front(30);l1.push_front(40);cout << l1.size() << endl; ?// 8yzz::list<int> l3;l3 = l1;for (auto& e : l3){cout << e << " ";}// 40 30 20 10 1 2 3 4cout << endl;
?l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_front();l1.pop_front();cout << l1.size() << endl; ?// 4Print1(l1);// 20 10 1 2
?l1.clear();cout << l1.size() << endl; ?// 0cout << l1.empty() << endl; ?// 1
}
?
struct Point
{int _x;int _y;
?Point(int x = 0, int y = 0): _x(x), _y(y){ }
};
?
void Print2(const yzz::list<Point>& l)
{yzz::list<Point>::const_iterator cit = l.begin();while (cit != l.end()){// 方法一:// cout << "(" << (*cit)._x << ", " << (*cit)._y << ")" << " ";// 方法二:cout << "(" << cit->_x << ", " << cit->_y << ")" << " ";// 注意:operator-> 是單參數,所以本應該是 cit->->_i 和 cit->->_j,// 但為了可讀性,編譯器做了優化,即省去一個 ->++cit;}cout << endl;
}
?
void test_list2()
{yzz::list<Point> l;l.push_back(Point(1, 1));l.push_back(Point(2, 2));l.push_back(Point(3, 3));l.push_back(Point(4, 4));Print2(l);// (1, 1) (2, 2) (3, 3) (4, 4)
}
?
int main()
{// test_list1();test_list2();return 0;
}








)








)
