Handler生產者-消費者模型
在android開發中,經常會在子線程中進行一些耗時操作,當操作完畢后會通過handler發送一些數據給主線程,通知主線程做相應的操作。 其中:子線程、handler、主線程,其實構成了線程模型中經典的生產者-消費者模型。
生產者-消費者模型:生產者和消費者在同一時間段內共用同一個存儲空間,生產者往存儲空間中添加數據,消費者從存儲空間中取走數據。?

這么設計有什么好處呢?
保證數據生產消費的順序(通過MessageQueue,先進先出) - 不管是生產者(子線程)還是消費者(主線程)都只依賴緩沖區(handler),生產者消費者之間不會相互持有,使他們之間沒有任何耦合?。
Handler是Android消息管理機制,屏幕觸摸事件、生命周期事件等都是封裝成message,發送到handler進行處理。通過源碼,我們進一步分析Handler的機制。
Handler機制
Hanlder:發送和接收消息;
Looper:用于輪詢消息隊列,一個線程只能有一個Looper;
Message: 消息實體;
MessageQueue: 消息隊列用于存儲消息和管理消息?。
創建Looper
public static void main(String[] args) {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");//其他代碼省略...Looper.prepareMainLooper(); //初始化Looper以及MessageQueueActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();thread.attach(false);if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();}if (false) {Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(newLogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));}// End of event ActivityThreadMain.Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);Looper.loop(); //開始輪循操作throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
Looper.prepareMainLooper();?
public static void prepareMainLooper() {prepare(false);//消息隊列不可以quitsynchronized (Looper.class) {if (sMainLooper != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already beenprepared.");}sMainLooper = myLooper();}
}prepare有兩個重載的方法,主要看 prepare(boolean quitAllowed) quitAllowed的作用是在創建MessageQueue時標識消息隊列是否可以銷毀, 主線程不可被銷毀 下面有介紹。
public static void prepare() {prepare(true);//消息隊列可以quit
}
//quitAllowed 主要
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {//不為空表示當前線程已經創建了Looperthrow new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");//每個線程只能創建一個Looper}sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));//創建Looper并設置給sThreadLocal,這樣get的時候就不會為null了
}創建MessageQueue以及Looper與當前線程的綁定
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);//創建了MessageQueuemThread = Thread.currentThread(); //當前線程的綁定
}MessageQueue的構造方法
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) {//mQuitAllowed決定隊列是否可以銷毀 主線程的隊列不可以被銷毀需要傳入false, 在MessageQueue的quit()方法就不貼源碼了mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed;mPtr = nativeInit();
}Looper.loop()
同時是在main方法中 Looper.prepareMainLooper() 后Looper.loop(); 開始輪詢
public static void loop() {final Looper me = myLooper();//里面調用了sThreadLocal.get()獲得剛才創建的Looper對象if (me == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on thisthread.");}//如果Looper為空則會拋出異常final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.Binder.clearCallingIdentity();final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();for (;;) {//這是一個死循環,從消息隊列不斷的取消息Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {//由于剛創建MessageQueue就開始輪詢,隊列里是沒有消息的,等到Handler sendMessageenqueueMessage后//隊列里才有消息// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the loggerPrinter logging = me.mLogging;if (logging != null) {logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);}msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);//msg.target就是綁定的Handler,詳見后面Message的部分,Handler開始//后面代碼省略.....msg.recycleUnchecked();}
}Handler handler=new Handler(){@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);}
};public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {//前面省略mLooper = Looper.myLooper();//獲取Looper,**注意不是創建Looper**!if (mLooper == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");}mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;//創建消息隊列MessageQueuemCallback = callback; //初始化了回調接口mAsynchronous = async;
}創建Handler
Handler handler=new Handler(){@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);}
};public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {//前面省略mLooper = Looper.myLooper();//獲取Looper,**注意不是創建Looper**!if (mLooper == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");}mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;//創建消息隊列MessageQueuemCallback = callback; //初始化了回調接口mAsynchronous = async;
}//這是Handler中定義的ThreadLocal ThreadLocal主要解多線程并發的問題
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {return sThreadLocal.get();
}創建Message
public static Message obtain(Handler h) {Message m = obtain();//調用重載的obtain方法m.target = h;//并綁定的創建Message對象的handlerreturn m;
}public static Message obtain() {synchronized (sPoolSync) {//sPoolSync是一個Object對象,用來同步保證線程安全if (sPool != null) {//sPool是就是handler dispatchMessage 后 通過recycleUnchecked回收用以復用的MessageMessage m = sPool;sPool = m.next;m.next = null;m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flagsPoolSize--;return m;}}return new Message();
}Message和Handler的綁定
創建Message的時候可以通過 Message.obtain(Handler h) 這個構造方法綁定。當然可以在 在Handler 中的enqueueMessage()也綁定了,所有發送Message的方法都會調用此方法入隊,所以在創建Message的時候是可以不綁定的。
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {msg.target = this; //綁定if (mAsynchronous) {msg.setAsynchronous(true);}return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}Handler發送消息
Handler發送消息的重載方法很多,但是主要只有2種。 sendMessage(Message) sendMessage方法通過一系列重載方法的調用,sendMessage調用sendMessageDelayed,繼續調用sendMessageAtTime,繼續調用enqueueMessage,繼續調用messageQueue的enqueueMessage方法,將消息保存在了消息隊列中,而最終由Looper取出,交給Handler的dispatchMessage進行處理;
我們可以看到在dispatchMessage方法中,message中callback是一個Runnable對象,如果callback不為空,則直接調用callback的run方法,否則判斷mCallback是否為空,mCallback在Handler構造方法中初始化,在主線程通直接通過無參的構造方法new出來的為null,所以會直接執行后面的handleMessage()方法。
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {if (msg.callback != null) {//callback在message的構造方法中初始化或者使用handler.post(Runnable)時候才不為空handleCallback(msg);} else {if (mCallback != null) {//mCallback是一個Callback對象,通過無參的構造方法創建出來的handler,該屬性為null,此段不執行if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {return;}}handleMessage(msg);//最終執行handleMessage方法}
}private static void handleCallback(Message message) {message.callback.run();
}Handler處理消息
在handleMessage(Message)方法中,我們可以拿到message對象,根據不同的需求進行處理,整個Handler機制的流程就結束了。?
總結:
handler.sendMessage 發送消息到消息隊列MessageQueue,然后looper調用自己的loop()函數帶動MessageQueue從而輪詢messageQueue里面的每個Message,當Message達到了可以執行的時間的時候開始執行,執行后就會調用message綁定的Handler來處理消息。
大致的過程如下圖所示:

handler機制就是一個傳送帶的運轉機制。
1)MessageQueue就像履帶。
2)Thread就像背后的動力,就是我們通信都是基于線程而來的。
3)傳送帶的滾動需要一個開關給電機通電,那么就相當于我們的loop函數,而這個loop里面的for循環就會帶著不斷的滾動,去輪詢messageQueue。
4)Message就是我們的貨物了。?
Handler線程同步問題
Handler是用于線程間通信的,但是它產生的根本并不只是用于UI處理,而更多的是handler是整個app通信的框架,大家可以在ActivityThread里面感受到,整個App都是用它來進行線程間的協調。Handler既然這么重要,那么它的線程安全就至關重要了,那么它是如何保證自己的線程安全呢?
Handler機制里面最主要的類MessageQueue,這個類就是所有消息的存儲倉庫,在這個倉庫中,我們如何的管理好消息,這個就是一個關鍵點了。消息管理就2點:1)消息入庫(enqueueMessage),2)消息出庫(next),所以這兩個接口是確保線程安全的主要檔口。
enqueueMessage 源碼:
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {if (msg.target == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");}if (msg.isInUse()) {throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");}// 鎖開始的地方synchronized (this) {if (mQuitting) {IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);msg.recycle();return false;}msg.markInUse();msg.when = when;Message p = mMessages;boolean needWake;if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.msg.next = p;mMessages = msg;needWake = mBlocked;} else {// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();Message prev;for (;;) {prev = p;p = p.next;if (p == null || when < p.when) {break;}if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {needWake = false;}}msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.nextprev.next = msg;}// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.if (needWake) {nativeWake(mPtr);}}
//鎖結束的地方synchronized鎖是一個內置鎖,也就是由系統控制鎖的lock unlock時機的。這個鎖,說明的是對所有調用同一個MessageQueue對象的線程來說,他們都是互斥的,然而,在我們的Handler里面,一個線程是對應著一個唯一的Looper對象,而Looper中又只有一個唯一的MessageQueue(這個在上文中也有介紹)。所以,我們主線程就只有一個MessageQueue對象,也就是說,所有的子線程向主線程發送消息的時候,主線程一次都只會處理一個消息,其他的都需要等待,那么這個時候消息隊列就不會出現混亂。
next函數 源碼:
Message next() {....for (;;) {....nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found....return msg;}} else {// No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}...}//synchronized 結束之處// Run the idle handlers.// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handlerboolean keep = false;try {keep = idler.queueIdle();} catch (Throwable t) {Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);}if (!keep) {synchronized (this) {mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);}}}// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;}
}next函數很多同學會有疑問:我從線程里面取消息,而且每次都是隊列的頭部取,那么它加鎖是不是沒有意義呢?
答案是否定的,我們必須要在next里面加鎖,因為,這樣由于synchronized(this)作用范圍是所有 this正在訪問的代碼塊都會有保護作用,也就是它可以保證 next函數和 enqueueMessage函數能夠實現互斥。這樣才能真正的保證多線程訪問的時候messagequeue的有序進行。
Handler消息機制--同步屏障
同步屏障,view繪制中使用,同步屏障的概念,在Android開發中非常容易被人忽略,因為這個概念在我們普通的開發中太少見了,很容易被忽略。
大家經過上面的學習應該知道,線程的消息都是放到同一個MessageQueue里面,取消息的時候是互斥取消息,而且只能從頭部取消息,而添加消息是按照消息的執行的先后順序進行的排序,那么問題來了,同一個時間范圍內的消息,如果它是需要立刻執行的,那我們怎么辦,按照常規的辦法,我們需要等到隊列輪詢到我自己的時候才能執行哦,那豈不是黃花菜都涼了。所以,我們需要給緊急需要執行的消息一個綠色通道,這個綠色通道就是同步屏障的概念。
同步屏障是什么?
屏障的意思即為阻礙,顧名思義,同步屏障就是阻礙同步消息,只讓異步消息通過。如何開啟同步屏障呢?使用:MessageQueue#postSyncBarrier()
public int postSyncBarrier() {return postSyncBarrier(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
}private int postSyncBarrier(long when) {// Enqueue a new sync barrier tokensynchronized (this) {final int token = mNextBarrierToken++;//從消息池中獲取Messagefinal Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.markInUse();//就是這里!!!初始化Message對象的時候,并沒有給target賦值,因此 target==nullmsg.when = when;msg.arg1 = token;Message prev = null;Message p = mMessages;if (when != 0) {while (p != null && p.when <= when) {//如果開啟同步屏障的時間(假設記為T)T不為0,且當前的同步消息里有時間小于T,則prev也不為nullprev = p;p = p.next;}}//根據prev是不是為null,將 msg 按照時間順序插入到 消息隊列(鏈表)的合適位置if (prev != null) { // invariant: p == prev.nextmsg.next = p;prev.next = msg;} else {msg.next = p;mMessages = msg;}return token;}
}可以看到,Message 對象初始化的時候并沒有給 target 賦值,因此, target == null 的 來源就找到了。上面消息的插入也做了相應的注釋。這樣,一條 target == null 的消息就進入了消息隊列。
同步屏障總結:
1)messageQueue.postSyncBarrier(),發送一個message.target = null消息,開啟同步屏障;
2)隨后發送一個異步消息(massage.setAsynchronous(true))到messageQueue;
3)messageQueue會優先處理異步消息;
4)異步消息處理完,調用MessageQueue.removeSyncBarrier移除屏障消息。
那么,開啟同步屏障后,所謂的異步消息又是如何被處理的呢?
如果對消息機制有所了解的話,應該知道消息的最終處理是在消息輪詢器 Looper#loop() 中,而 loop() 循環中會調用 MessageQueue#next() 從消息隊列中進行取消息。
.....//省略一些代碼int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration// 1.如果nextPollTimeoutMillis=-1,一直阻塞不會超時。// 2.如果nextPollTimeoutMillis=0,不會阻塞,立即返回。// 3.如果nextPollTimeoutMillis>0,最長阻塞nextPollTimeoutMillis毫秒(超時)// 如果期間有程序喚醒會立即返回。int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;//next()也是一個無限循環for (;;) {if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {Binder.flushPendingCommands();}nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {//獲取系統開機到現在的時間final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();Message prevMsg = null;Message msg = mMessages; //當前鏈表的頭結點//關鍵!!!//如果target==null,那么它就是屏障,需要循環遍歷,一直往后找到第一個異步的消息if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.do {prevMsg = msg;msg = msg.next;} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}if (msg != null) {//如果有消息需要處理,先判斷時間有沒有到,如果沒到的話設置一下阻塞時間,//場景如常用的postDelayif (now < msg.when) {//計算出離執行時間還有多久賦值給nextPollTimeoutMillis,//表示nativePollOnce方法要等待nextPollTimeoutMillis時長后返回nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now,Integer.MAX_VALUE);} else {// 獲取到消息mBlocked = false;//鏈表操作,獲取msg并且刪除該節點if (prevMsg != null)prevMsg.next = msg.next;} else {mMessages = msg.next;}msg.next = null;msg.markInUse();//返回拿到的消息return msg;}} else {//沒有消息,nextPollTimeoutMillis復位nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}.....//省略
}從上面可以看出,當消息隊列開啟同步屏障的時候(即標識為 msg.target == null ),消息機制在處理消息的時候,優先處理異步消息。這樣,同步屏障就起到了一種過濾和優先級的作用。
下面用示意圖簡單說明:
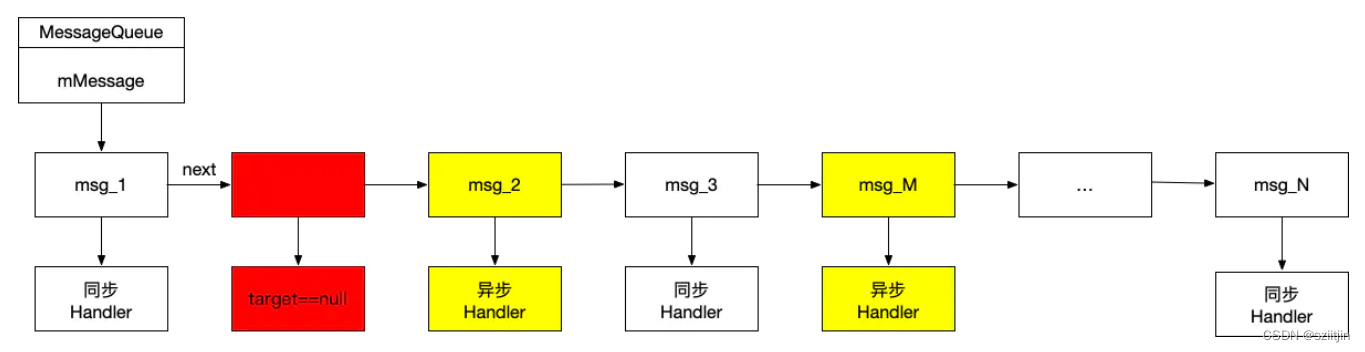
如上圖所示,在消息隊列中有同步消息和異步消息(黃色部分)以及一道墻----同步屏障(紅色部分)。有了同步屏障的存在,msg_2 和 msg_M 這兩個異步消息可以被優先處理,而后面的 msg_3 等同步消息則不會被處理。那么這些同步消息什么時候可以被處理呢?那就需要先移除這個同步屏障,即調用 removeSyncBarrier() 。
同步消息的應用場景
似乎在日常的應用開發中,很少會用到同步屏障。那么,同步屏障在系統源碼中有哪些使用場景呢?Android 系統中的 UI 更新相關的消息即為異步消息,需要優先處理。
比如,在 View 更新時,draw、requestLayout、invalidate 等很多地方都調用了ViewRootImpl#scheduleTraversals() ,如下:
void scheduleTraversals() {if (!mTraversalScheduled) {mTraversalScheduled = true;//開啟同步屏障mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();//發送異步消息mChoreographer.postCallback(Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();}notifyRendererOfFramePending();pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();}
}postCallback() 最終走到了 ChoreographerpostCallbackDelayedInternal() :
private void postCallbackDelayedInternal(int callbackType,Object action, Object token, long delayMillis) {if (DEBUG_FRAMES) {Log.d(TAG, "PostCallback: type=" + callbackType- ", action=" + action + ",token=" + token =" + delayMillis);}synchronized (mLock) {final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();final long dueTime = now + delayMillis;mCallbackQueues[callbackType].addCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token);if (dueTime <= now) {scheduleFrameLocked(now);} else {Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DO_SCHEDULE_CALLBACK, action);msg.arg1 = callbackType;msg.setAsynchronous(true); //異步消息mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, dueTime);}}
}這里就開啟了同步屏障,并發送異步消息,由于 UI 更新相關的消息是優先級最高的,這樣系統就會優先處理這些異步消息。最后,當要移除同步屏障的時候需要調用 ViewRootImpl#unscheduleTraversals() 。
void unscheduleTraversals() {if (mTraversalScheduled) {mTraversalScheduled = false;//移除同步屏障mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);mChoreographer.removeCallbacks(Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);}
}小結:
同步屏障的設置可以方便地處理那些優先級較高的異步消息。當我們調用
Handler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier() 并設置消息的 setAsynchronous(true) 時,target 即為 null ,也就開啟了同步屏障。當在消息輪詢器 Looper 在 loop() 中循環處理消息時,如若開啟了同步屏障,會優先處理其中的異步消息,而阻礙同步消息。




)








)



--某得科技登錄)


)