反射(reflect)是在計算機程序運行時,訪問,檢查,修改它自身的一種能力,是元編程的一種形式。在Java等語言中都很好地支持了反射。Golang也實現了反射,主要核心位于reflect包,官方文檔為:
https://golang.org/pkg/reflect/?golang.org本文將主要介紹Golang中的反射原理和支持的反射操作。
1. reflect原理:結構體與關系
Golang是強類型語言,每一個對象都有具體的靜態類型。為什么說是靜態類型呢?舉個例子,如下代碼:
type MyInt intvar a int
var b MyInt
a和b在Go中會被認為是不同的類型,即不會被隱式轉換。另外,在Golang中的對象其實是同時記錄了兩個信息:變量的真實值,與該變量的類型描述。具體地,interface {}在內部是通過emptyInterface結構體表示的,結構體的定義如下:
type emptyInterface struct {typ *rtypeword unsafe.Pointer
}
其中, typ為類型信息,word為指針。
另外interface{}是一個沒有函數定義的接口定義,Golang中的繼承實現是通過比較函數判斷的。也就是說,所有的結構體都實現了默認接口interface{},這也是為什么所有值都能夠隱式賦值給interface{}的原因。
以上的結構體便是Golang中反射的核心,也就是通過操作該結構來進行反射運算,包括獲取對象的類型信息(rtype)和具體值(word指針),rtype的定義如下:
// rtype is the common implementation of most values.
// It is embedded in other struct types.
//
// rtype must be kept in sync with ../runtime/type.go:/^type._type.
type rtype struct {size uintptrptrdata uintptr // number of bytes in the type that can contain pointershash uint32 // hash of type; avoids computation in hash tablestflag tflag // extra type information flagsalign uint8 // alignment of variable with this typefieldAlign uint8 // alignment of struct field with this typekind uint8 // enumeration for C// function for comparing objects of this type// (ptr to object A, ptr to object B) -> ==?equal func(unsafe.Pointer, unsafe.Pointer) boolgcdata *byte // garbage collection datastr nameOff // string formptrToThis typeOff // type for pointer to this type, may be zero
}
定義了類型需要的數據。
1.1 reflect中的結構體
在Golang的反射中,另外兩個核心結構體是Type和Value。
Type是描述類型信息的接口,包括:結構體的對齊方式、方法、字段、包路徑、與其他結構體的關系等,具體定義可以參考源碼:
https://golang.org/src/reflect/type.go?s=1310:7552#L27?golang.orgValue是保存了對象的類型、指針和其他元數據,具體定義如下:
type Value struct {// typ holds the type of the value represented by a Value.typ *rtype// Pointer-valued data or, if flagIndir is set, pointer to data.// Valid when either flagIndir is set or typ.pointers() is true.ptr unsafe.Pointer// flag holds metadata about the value.// The lowest bits are flag bits:// - flagStickyRO: obtained via unexported not embedded field, so read-only// - flagEmbedRO: obtained via unexported embedded field, so read-only// - flagIndir: val holds a pointer to the data// - flagAddr: v.CanAddr is true (implies flagIndir)// - flagMethod: v is a method value.// The next five bits give the Kind of the value.// This repeats typ.Kind() except for method values.// The remaining 23+ bits give a method number for method values.// If flag.kind() != Func, code can assume that flagMethod is unset.// If ifaceIndir(typ), code can assume that flagIndir is set.flag// A method value represents a curried method invocation// like r.Read for some receiver r. The typ+val+flag bits describe// the receiver r, but the flag's Kind bits say Func (methods are// functions), and the top bits of the flag give the method number// in r's type's method table.
}
1.2 reflect對象的關系
reflect中的對象關系如下圖所示,Type和Value稱為反射對象,interface{}和Special Type是應用程序中的對象,其中,Special Type指應用程序中的具體類型。具體關系如下:
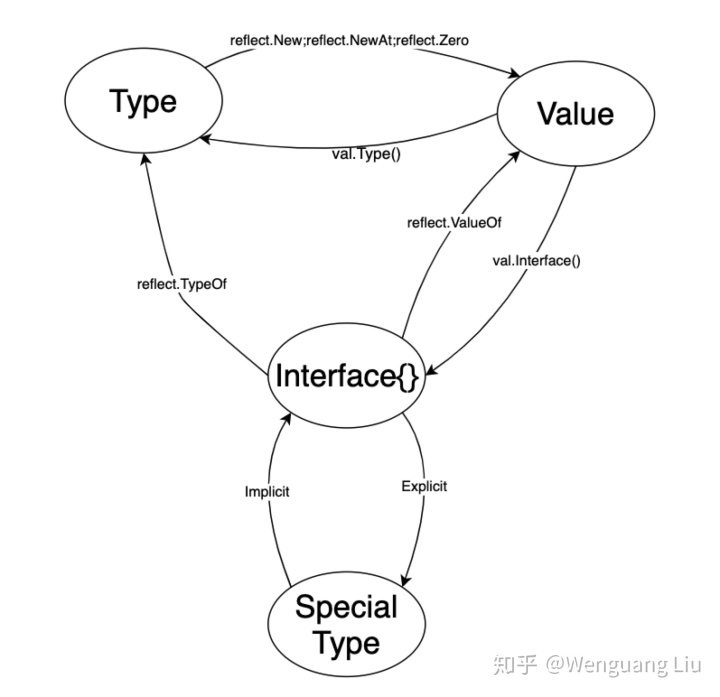
1) 從接口值到反射對象
interface{} -> Type: 通過reflect.TypeOf(interface{})獲得interface的類型信息對象;
interface{} -> Value:通過reflect.ValueOf(interface{})獲得interface的Value反射類型對象;
2) 從反射對象到接口值
Value->interface{}:通過Value.Interface()方法可以獲得值對象Value對應的接口;注意,這里不能夠直接獲得具體類型,如果要獲得具體類型,還需要顯式地進行轉換。例如,
var f float64 = 3.1415
v := reflect.ValueOf(f) // f 隱式地被轉成了interface{}
y := v.Interface().(float64) // y的類型是float64
其中1)和2)兩條關系也是Golang反射中三條大規則中的前兩條。另外第三條是:
3) 想要修改一個反射對象,那么該值必須是可以被設置的
這個可以一個例子進行說明。如下:
var f float64 = 3.1415
v := reflect.ValueOf(f) // f 隱式地被轉成了interface{}
v.SetFloat(2.873) // Error: 發生Panic
以上在最后一行代碼將會拋出異常:
panic: reflect.Value.SetFloat using unaddressable value也就是說,Value v指向的不是一個可尋址的值,簡單地說就是不是一個地址塊。但是如果改成如下代碼:
var f float64 = 3.1415
v := reflect.ValueOf(&f) // 傳了f的指針,&f 隱式地被轉成了interface{}
v.SetFloat(2.873) // 成功修改
綜上,也就是說當Value中管理的值是一個可被尋址的值那么改置便是一個可被修改的Value。
或者換一個方式去理解,在Golang中方法調用是值傳遞,然后,假如我們想要該一個方法中修改某一個對象的值,那么我們應該將指向該值的指針傳入,而不是直接將值傳入。
4) Type/Value轉換
Value->Type:可以通過Value.Type()方法獲得;而Type->Value是指創建一個Type的實例對象,則可以通過reflect.New(typ)等方法創建。
2. reflect中的結構體與方法
這里分五個維度進行介紹reflect中的結構和方法,便于理解反射的使用方法。這些操作最終都會落到前面定義的結構體emptyInterface,除在外層封裝中變能夠確定的方法外。
2.1 結構體
reflect中的結構體主要包括:Type,Value,ChanDir,Kind,MapIter,Method,SelectCase,SelectDir,SliceHeader,StringHeader,StructField,StructTag,ValueError等。其中,Type和Value之前已經介紹過了。
- ChanDir:管道的方向,有三個值:RecvDir/SendDir/BothDir,分別為接受,發送,雙向;
- Kind:Type中的類型信息,包括:Invalid, Bool, Int, Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64, Uint, Uint8, Uint16, Uint32, Uint64, Uintptr, Float32, Float64, Complex64, Complex128, Array, Chan, Func, Interface, Map, Ptr, Slice, String, Struct, UnsafePointer,
- MapIter:Map的迭代器,包括三個方法:Key、Value、Next
- Method:描述方法的信息,包括:方法名,包路徑,類型,函數,所處的下表;
- SelectCase:描述select 操作的信息,case的方向SelectDir,使用的Channel,發送的值Send;
- SelectDir:描述SelectCase中的方向,有三個值:SelectSend/SelectRecv/SelectDefault
- SliceHeader:描述切片Slice的信息,包括指針,長度,容量;
- StringHeader:描述字符串string的信息,包括指針,長度;
- StructField:描述結構體中的域field中的信息,包括:域名,包路徑,類型,標簽Tag,在結構體中的偏移量offset,Type.FieldByIndex中的下標index,是否是匿名;
- StructTag:描述標簽信息,有兩個方法:Get、Lookup
- ValueError:在調用一個Value不支持的方法時會報錯,并記錄到ValueError中。
2.2 reflect靜態方法
reflect的靜態方法主要用于反射對象的的操作,包括如下:
- reflect.Copy(dst, src Value) int:將src對象(Slice或Array)復制給dst對象,返回復制的個數;
- func DeepEqual(x, y interface{}) bool:比較兩個對象是否是“深度相等”。具體如何比較可以參考:https://golang.org/pkg/reflect/#DeepEqual
- func Swapper(slice interface{}) func(i, j int):生成一個Swapper交換方法,必須為slice;
2.3 域Type相關的方法
該類方法主要定義在https://golang.org/src/reflect/type.go?s=78900:78939#L2811中,包括,返回值都是Type:
- reflect.ArrayOf:創建一個指定Type和個數的數組;
- reflect.ChanOf:創建一個類型和方向的管道類型;
- reflect.FuncOf:創建一個指定輸入/輸出/是否可變(variadic)的函數定義;
- reflect.MapOf:創建一個指定key/value類型的Map類型;
- reflect.PtrTo:創建一個類型的指針;
- reflect.SliceOf:創建一個類型的Slice類型;
- reflect.StructOf:創建一個指定StructField 列表的結構體定義類型;
- reflect.TypeOf:獲得interface的類型;
2.4 值Value相關靜態方法
該類方法主要定義在https://golang.org/src/reflect/value.go?s=60334:60372#L2014中,包括:
- reflect.Append:將值append到一個Slice中,并且返回結果;
- reflect.AppendSlice:將一個slice append到slice中;
- reflect.Indirect:返回該Value的指向對象,如果是nil,返回零值,如果非指針,返回該值;
- reflect.MakeChan:創建一個執行類型和大小的channel;
- reflect.MakeFunc:在指定類型上創建一個指定定義的函數;
- reflect.MakeMap:創建一個指定類型的map;
- reflect.MakeMapWithSize:同上,指定大小;
- reflect.MakeSlice:創建Slice;
- reflect.New:創建一個指定類型的實例對象;
- reflect.NewAt:指定了指針類型?
- reflect.Select:創建一個select操作,需指定SelectCase;
- reflect.ValueOf:獲得接口interface{}的Value;
- reflect.Zero:創建一個指定類型的零值;
2.5 Value的實例方法
這里將不一一介紹Value的實例方法,大致可以分成三類:
- 判斷性方法:判斷是否具有某些特性/能力;
- 訪問性方法:訪問值的一些屬性;
- 修改性方法:修改Value中特性/值的方法;
這里介紹一個函數Elem(),該函數返回的是interface{}中包含的值或指針指向的值,如果value的類型不是reflect.Ptr,那么將返回零值。
具體如下:
func (v Value) Addr() Value
func (v Value) Bool() bool
func (v Value) Bytes() []byte
func (v Value) Call(in []Value) []Value// 最后會進入匯編代碼進行方法調用
func (v Value) CallSlice(in []Value) []Value
func (v Value) CanAddr() bool
func (v Value) CanInterface() bool
func (v Value) CanSet() bool
func (v Value) Cap() int
func (v Value) Close()
func (v Value) Complex() complex128
func (v Value) Convert(t Type) Value
func (v Value) Elem() Value
func (v Value) Field(i int) Value
func (v Value) FieldByIndex(index []int) Value
func (v Value) FieldByName(name string) Value
func (v Value) FieldByNameFunc(match func(string) bool) Value
func (v Value) Float() float64
func (v Value) Index(i int) Value
func (v Value) Int() int64
func (v Value) Interface() (i interface{})
func (v Value) InterfaceData() [2]uintptr
func (v Value) IsNil() bool
func (v Value) IsValid() bool
func (v Value) IsZero() bool
func (v Value) Kind() Kind
func (v Value) Len() int
func (v Value) MapIndex(key Value) Value
func (v Value) MapKeys() []Value
func (v Value) MapRange() *MapIter
func (v Value) Method(i int) Value
func (v Value) MethodByName(name string) Value
func (v Value) NumField() int
func (v Value) NumMethod() int
func (v Value) OverflowComplex(x complex128) bool
func (v Value) OverflowFloat(x float64) bool
func (v Value) OverflowInt(x int64) bool
func (v Value) OverflowUint(x uint64) bool
func (v Value) Pointer() uintptr
func (v Value) Recv() (x Value, ok bool)
func (v Value) Send(x Value)
func (v Value) Set(x Value)
func (v Value) SetBool(x bool)
func (v Value) SetBytes(x []byte)
func (v Value) SetCap(n int)
func (v Value) SetComplex(x complex128)
func (v Value) SetFloat(x float64)
func (v Value) SetInt(x int64)
func (v Value) SetLen(n int)
func (v Value) SetMapIndex(key, elem Value)
func (v Value) SetPointer(x unsafe.Pointer)
func (v Value) SetString(x string)
func (v Value) SetUint(x uint64)
func (v Value) Slice(i, j int) Value
func (v Value) Slice3(i, j, k int) Value
func (v Value) String() string
func (v Value) TryRecv() (x Value, ok bool)
func (v Value) TrySend(x Value) bool
func (v Value) Type() Type
func (v Value) Uint() uint64
func (v Value) UnsafeAddr() uintptr
3. 總結
最后簡單總結一下,本文首先介紹了Golang中反射的原理,包括其中的核心結構體和關系;然后介紹了Golang中reflect包下包含的結構體,靜態函數,Type靜態函數,Value靜態函數和Value的實例函數。
參考
https://golang.org/pkg/reflect/https://draveness.me/golang/docs/part2-foundation/ch04-basic/golang-reflect/
Wenguang Liu:Golang中Routine閉包中的一個坑?zhuanlan.zhihu.com)


)


)





)



傳感器)


