目錄
1.預備知識
2.初步代碼
3.對紅黑樹實現的代碼進行改造
4.對map和set的改造
5.對RBTree::insert的改造
6.對RBTree::Find函數的改造
7.實現iterator(最重要)
8.實現const_iterator
9.完成set和map的key不能修改
10.實現map的operator[]
11.代碼匯總
12.總結

1.預備知識
我們要了解一下map和set這兩個容器,可以到C++官網中搜索map和set進行了解,以下是C++官網鏈接:
Reference - C++ Reference
如果想了解更多,可以去看我寫的兩篇關于map和set的博客:
C++進階-set-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀608次,點贊23次,收藏17次。本文系統介紹了C++ STL中的set容器的特性與使用方法。set作為關聯式容器,基于紅黑樹實現,具有自動去重和排序功能,增刪查效率為O(logN)。文章詳細講解了set的構造函數、常用成員函數(如emplace_hint、key_comp等)以及邊界查找函數(lower_bound、upper_bound等),并通過代碼示例演示了其具體用法。同時對比了set與multiset的差異,指出后者允許重復元素。最后通過兩個力扣編程題(查找數組交集和環形鏈表入口)展示了set的實際應用場景,體現了其在數據去重和快https://blog.csdn.net/2401_86446710/article/details/149322360?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_linkC++進階-map-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀835次,點贊26次,收藏14次。本文介紹了C++ STL中的map容器。map是基于二叉搜索樹實現的鍵值對容器,具有自動排序特性。文章詳細講解了map的聲明方式、構造函數、operator[]操作符(可查找/插入元素)、at方法(安全訪問)、emplace_hint高效插入等核心功能。特別強調了map與set的區別在于存儲鍵值對,以及operator[]的獨特行為(找不到鍵時會自動插入)。還介紹了輔助類pair的用法,以及key_comp/value_comp比較函數的使用。通過多個代碼示例演示了map的基本操作,包括元素訪問、修改和異常
https://blog.csdn.net/2401_86446710/article/details/149344636?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_link非常建議去了解一下C++的紅黑樹的內容,以方便我們實現map和set:
C++進階-紅黑樹(難度較高)-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀1.7k次,點贊52次,收藏56次。本文詳細講解了紅黑樹的實現原理和代碼實現。主要內容包括: 紅黑樹的基本概念和五大規則,確保最長路徑不超過最短路徑的兩倍; 紅黑樹的插入操作,重點分析了不同情況下的變色和旋轉處理(單旋、雙旋); 完整代碼實現,包括結點定義、旋轉操作、插入邏輯和驗證方法; 紅黑樹查找的實現和測試用例; 簡要介紹了刪除操作的思路。 紅黑樹通過顏色約束和旋轉操作保持近似平衡,效率與AVL樹相當但旋轉次數更少。本文強調理解旋轉邏輯的重要性,建議通過畫圖輔助理解。代碼經過測試驗證,為后續用紅黑樹實現map和set打下基礎。https://blog.csdn.net/2401_86446710/article/details/149436642?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_link
map和set的iterator和list差不多,建議各位參考一下list的模擬實現,可以見以下博客:
C++初階-list的模擬實現(難度較高)-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀916次,點贊27次,收藏24次。這篇文章詳細講解了C++中list容器的模擬實現過程。主要內容包括:1) list基本結構的定義,使用雙向鏈表實現;2) 無參構造函數和節點構造函數的實現;3) push_back等基本操作的實現;4) 迭代器類的設計與實現,包括普通迭代器和const迭代器;5) list類迭代器相關函數的實現;6) 增刪查改等操作的實現;7) 拷貝控制成員函數和特殊成員函數的實現;8) 測試用例的編寫。文章通過代碼示例詳細展示了list容器的底層實現原理,包括哨兵位的使用、迭代器封裝等技術細節,并提供了完整的測試代碼驗證https://blog.csdn.net/2401_86446710/article/details/148548215?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_link
2.初步代碼
該代碼是實現紅黑樹的實現時,去掉注釋后的代碼:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{Red,Black
};
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv):_kv(kv),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){ }
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:void RotateR(Node* parent){assert(parent != nullptr);Node* subL = parent->_left;assert(subL != nullptr);Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;subL->_right = parent;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){subL->_parent = nullptr;_root = subL;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){assert(parent != nullptr);Node* subR = parent->_right;assert(subR != nullptr);Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){subR->_parent = nullptr;_root = subR;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = Black;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_parent = parent;if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_col = Red;while (parent && parent->_col == Red){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = Red;cur->_col = Black;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black;return true;}Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum){if (root == nullptr){if (refNum != blackNum){cout << "存在??結點的數量不相等的路徑" << endl;return false;}return true;}if (root->_col == Red && root->_parent->_col == Red){cout << root->_kv.first << "存在連續的紅?結點" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == Black){blackNum++;}return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);}bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == Red)return false;int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == Black){++refNum;}cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, 0, refNum);}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};以上代碼將會放到RBTree.h文件中。
3.對紅黑樹實現的代碼進行改造
改造紅黑樹代碼是為了實現我們的set和map兩個容器。
由于set是只存放了一個值,故我們要把紅黑樹的結點結構改成key結構:
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;//存放數據,可以傳遞T為pair類型RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};我們還需要把RBTree.h中改一部分:
template<class K,class T>
class RBTree
{
public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;bool Insert(const T& kv){//……}
//……
};Insert函數里面結構我們先不要改,之后再進行集中改變。
4.對map和set的改造
首先我們需要把map和set的基本結構寫出來,這里map的模擬實現放到mymap.h中,set的模擬實現放到myset.h中:
//myset.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K>
class myset
{
public://以后代碼增加的地方bool insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}
private:RBTree<K, K> _t;
};為了不破壞太多的RBTree結構,我們這里的set就構造成key-key結構,保持和set的源碼的方式一樣(源碼各位可以自行搜索,如果想改造成一個參數的結構就把RBTree第二個模板參數置為缺省參數,缺省值為K)。
//mymap.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{
public://以后代碼增加的地方bool insert(const pair<K,V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}
private:RBTree<K, pair<K,V>> _t;
};這樣寫的原因是:我們的RBTree的第二個模板參數是T,相當于我們的鍵值對,這樣寫主要是為了適應RBTree的insert函數。
5.對RBTree::insert的改造
改造該函數之前的代碼:
bool Insert(const T& kv)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = Black;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_parent = parent;if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_col = Red;while (parent && parent->_col == Red){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = Red;cur->_col = Black;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black;return true;
}由于參數改變,我們需要把_kv.first直接變成_data,所以有:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = Black;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_data > data){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_data < data){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(data);cur->_parent = parent;if (parent->_data > data){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_col = Red;while (parent && parent->_col == Red){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = Red;cur->_col = Black;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black;return true;
}這里主要是要注意一下:如果我們是插入一個鍵值對即pair類型時,如果我們直接用parent->_data<data能不能比較出正確的結果,實際上,我們在C++官網中也很容易得到結論:
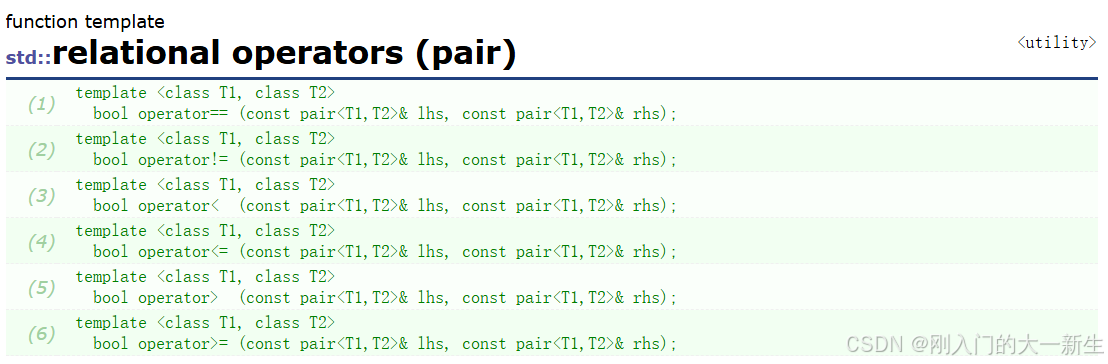

但是我們就想要只用first進行比較,所以我們不能直接這樣寫。
如果我們使用仿函數來進行比較邏輯,那么在這個時候也是不行的,因為如果用仿函數的話,我們要Find,而Find是用key來比較的,如果用仿函數,我們如何取得map的key值從而使比較邏輯正確?
實際上,我們可以用仿函數進行,但是這個仿函數不能單單用來比較大小,還要取得key,這個時候,我們可以這樣寫:
//RBTree.h
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{};通過給RBTree增加一個模板參數來接收仿函數進行比較的邏輯,同時要改:
//myset.h
template<class K>
class myset
{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};
private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};//mymap.h
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};同時,我們還需要把比較邏輯改成二者key的比較,所以可以這樣寫:
bool Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = Black;return true;}KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(data);cur->_parent = parent;if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data)){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}
//……
}6.對RBTree::Find函數的改造
和insert函數類似,我們也可以對Find函數進行改造:
//RBTree.h
bool Find(const K& key)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return true;}}return false;
}7.實現iterator(最重要)
實現iterator的思路:
(1)iterator實現的?框架跟list的iterator思路是?致的,??個類型封裝結點的指針,再通過重載運算符實現,迭代器像指針?樣訪問的?為。
這里我先把iterator基本結構寫出來:
//RBTree.h
template<class T>
struct _TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;_TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){ }T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node!=s._node;}
};我們這里主要要理解一下如何實現operator++和operator--。
首先map和set走的是中序遍歷,所以返回的第一個結點的iterator是begin()。
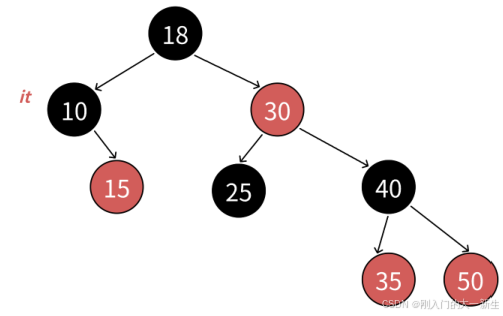
第一個結點就是10這個結點,也就是說我們需要從根結點開始走起,一直往左子樹遍歷,直到左子樹為空時。
(2)迭代器++的核?邏輯就是不看全局,只看局部,只考慮當前中序局部要訪問的下?個結點。
我們不用管其他結點,就看這個子樹,如果這棵子樹遍歷到左孩子,就看根;如果遍歷到根,就看右孩子。
(3)迭代器++時,如果it指向的結點的右?樹不為空,代表當前結點已經訪問完了,要訪問下?個結點是右?樹的中序第?個,?棵樹中序第?個是最左結點,所以直接找右?樹的最左結點即可。
(4)迭代器++時,如果it指向的結點的右?樹空,代表當前結點已經訪問完了且當前結點所在的?樹也訪問完了,要訪問的下?個結點在當前結點的祖先??,所以要沿著當前結點到根的祖先路徑向上找。
(5)如果當前結點是?親的左,根據中序左?樹->根結點->右?樹,那么下?個訪問的結點就是當前結點的?親;
(6)如果當前結點是?親的右,根據中序左?樹->根結點->右?樹,當前結點所在的?樹訪問完了,當前結點所在?親的?樹也訪問完了,那么下?個訪問的需要繼續往根的祖先中去找,直到找到孩?是?親左的那個祖先就是中序要訪問的下?個結點。
這上面都是有些難以理解的,我這里就直接用畫圖的方式加以講解:
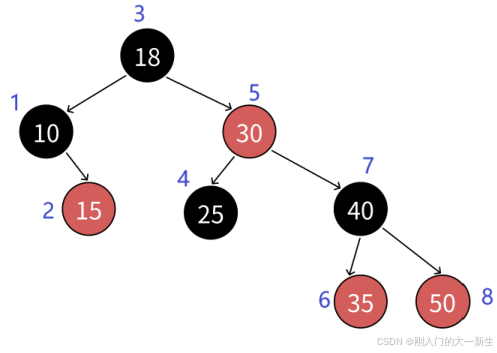
我按照中序遍歷的順序進行講解。
首先從根結點開始往左子樹遍歷,發現18的左孩子不為空,則10作為左子樹的根結點繼續遍歷,然后發現10沒有左孩子,這個時候就遍歷到10這個結點。
遍歷到10結點后,++,我們發現10為根結點,所以要繼續遍歷右子樹,遍歷到15結點,發現15結點沒有左孩子,所以直接返回到15這個結點。
遍歷到15結點后,++,我們發現15結點沒有右子樹,所以往上遞歸,然后發現10為18的左孩子,所以是一定遍歷過的,所以就繼續往上;發現18是根結點,這個時候就返回18這個結點了。
遍歷到18結點后,++,發現30為右孩子,而且30還有左孩子,所以遍歷到25,發現25沒有左孩子,所以返回25。
遍歷到25結點后,++,發現25沒有右孩子,所以返回到25的父親,到30結點,返回30。
遍歷到30結點后,………………
直到到達50結點(已經被訪問過),如果++,發現沒有右孩子,然后往上,發現父親都為爺爺的右孩子,證明該子樹遍歷完,所以繼續往上訪問,直到沒有父親或者該孩子為父親的左結點為止。這個時候我們發現父親為空,則這個時候返回nullptr,所以這個時候直接就是用nullptr構造一個結點進行返回。
//_TreeIterator
Self& operator++()
{//中序遍歷,這個時候就需要訪問右孩子if (_node->_right){//找右子樹的最左結點_node = _node->_right;while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{//右子樹為空//對應15結點或者50結點Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;//當parent不為空,且cur為parent的右孩子是繼續往上//因為這代表該子樹已經遍歷完了while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//要么cur是parent的左孩子,這個時候就可以直接用_node=parent//這兩種情況都可以這樣寫_node = parent;}return *this;
}以上邏輯需要結合畫圖理解,最重要的是我們要理解為什么當右孩子沒有時要往上遞歸,因為這個時候該子樹都遍歷完了(如:15結點,為10的右孩子,根據左根右的遍歷方式,右孩子都被遍歷完了,那么也就代表根也被遍歷完了,所以我們需要往上,此外,如果cur(當前結點)是父親的左孩子,代表父親(根)還沒有被遍歷,所以直接用父親作為結點返回)。
相似的邏輯我們還可以寫出--,其邏輯和++完全相反,不過還有特殊處理一下當_node==nullptr的情況,這個時候就是end(),我們需要得到root以遍歷子樹:
//_TreeIterator
Node* _root;
_TreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root):_node(node),_root(root)
{ }
Self& operator--()
{if (_node == nullptr) // end(){// --end(),特殊處理,?到中序最后?個結點,整棵樹的最右結點Node* rightMost = _root;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}else if (_node->_left){//代表該子樹還沒遍歷完//找左子樹的最右結點_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{//該子樹被遍歷完//向上查找,直到查找到根或者該孩子為父親的右孩子Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}我們的目的是為了得到Bgein和End,所以在RBTree中加:
//RBTree
public:
typedef _TreeIterator<T> Iterator;
Iterator Begin()
{Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}//調用_TreeIterator//相當于_TreeIterator(minleft)return Iterator(minleft, _root);
}
Iterator End()
{return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}同樣,我們還需要在mymap和myset中進行修改:
//myset
public:
typedef RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{return _t.End();
}//mymap
public:
typedef RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{return _t.End();
}這個時候要注意:我們現在在測試文件中隨便寫一個主函數都會報錯:
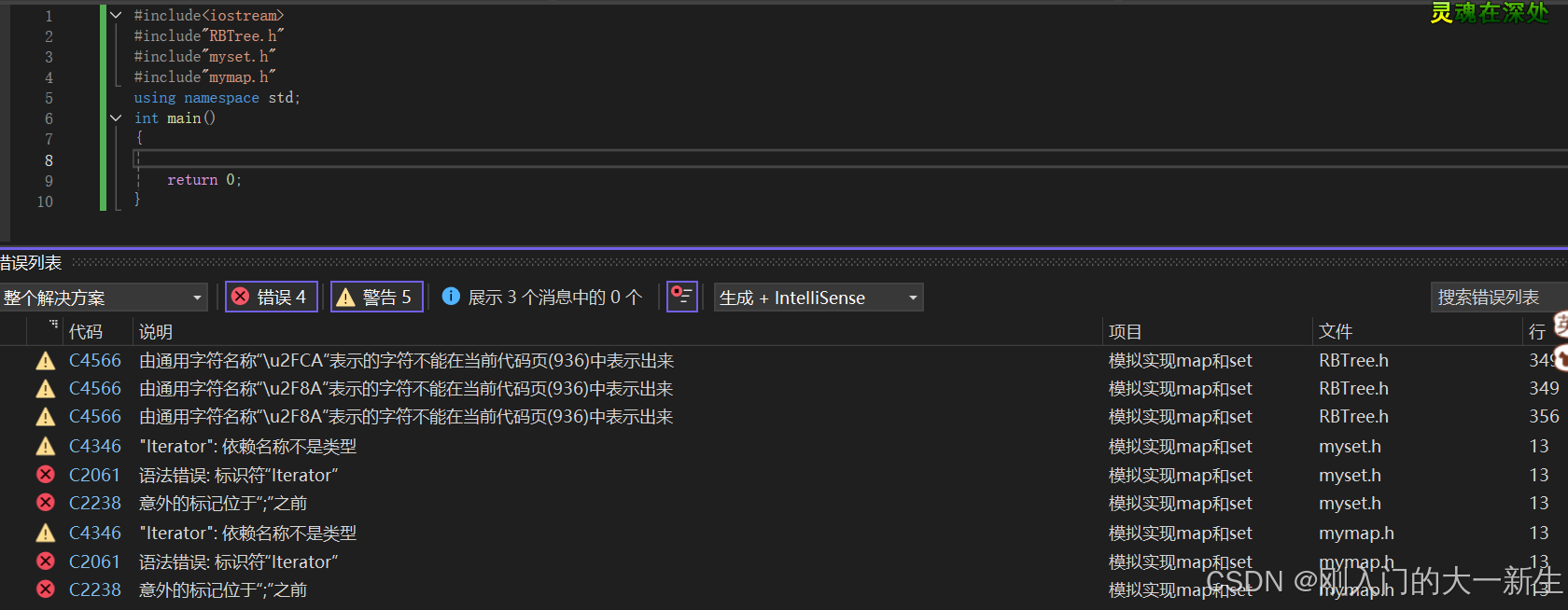
這主要是因為:如果我們要取模板里面的類型(含內嵌類型、內部類)都要加typename,因為取模板里的東西,現在的模板可能還沒有實例化,此時取的模板里面的類型編譯器分不清楚它是靜態成員變量還是內嵌類型,而我們這樣寫:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;那個typename就是告訴編譯器這是一個類型,是合乎語法的,而確定這個類型要等到類模板被實例化后就可以了,這樣就沒問題了。
不過我們也可以改造成這樣也是沒問題的:
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;這種寫法更好一些,以后見到這種寫法也不要奇怪。
以上是iterator基本的實現,不過如果你覺得可以再進行完善功能的話也可以,以下代碼可以選擇性加到_TreeIterator中:
//_TreeIterator
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{return _node == s._node;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{Self tmp = *this; // 保存當前狀態++(*this); // 調用前置++實現return tmp; // 返回舊值
}
//后置--
Self operator--(int)
{Self tmp = *this; // 保存當前狀態--(*this); // 調用前置--實現return tmp; // 返回舊值
}8.實現const_iterator
和list一樣,我們最好還是不要增加一個一樣的類來實現const_iterator,可以在_TreeIterator模板參數后加兩個模板參數,以下是_TreeIterator的改造:
//_TreeIterator
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator
{
typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//Ref:引用,Ptr:指針
Ref operator*()
{return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{return &_node->_data;
}
};以下是對RBTree的改造:
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef _TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
ConstIterator Begin() const
{Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return ConstIterator(minleft, _root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);
}
};同理,我們還需要在mymap和myset中進行改造:
//myset
public:
//下面兩種隨意選:
//typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{return _t.End();
}//mymap
//下面兩種隨便選一種
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{return _t.End();
}9.完成set和map的key不能修改
這個是改造代碼比較少的部分,但是還是需要注意,我們不支持key修改不是代表value不支持修改,所以需要改造成這樣:
//myset
public:
//下面兩種隨意選
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面兩種隨意選
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;需要注意的是RBTree的第二個參數才是所存儲的東西,所以是第二個參數加const,第一個參數代表的是類型,第二個參數代表的是所存儲的值。
類似,我們還可以對mymap進行改造:
//mymap
public:
//下面兩種隨便選一種
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面兩種隨便選一種
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;10.實現map的operator[]
首先,實際上,map的Insert函數返回值是pair<Iterator,bool>類型,map的operator[]會根據insert的返回值的bool來判斷是否需要插入,當insert成功時,第一個參數是為新插入位置的結點地址,當insert失敗時,第一個參數是為原結點的地址。
而這個時候operator[]就返回了該結點對應的值(value)。
所以關鍵是對Insert的改造,我們可以改造成這樣:
//RBTree
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = Black;return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };//隱式類型轉換}KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return { Iterator(cur,_root),true };}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_parent = parent;if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data)){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_col = Red;while (parent && parent->_col == Red){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = Red;cur->_col = Black;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black;return { Iterator(newnode,_root),true };
}再對myset和mymap進行改造:
//myset
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{return _t.Insert(key);
}如果對于mymap則不僅需要改造insert函數,還需要完成operator[]的實現這個時候我們需要返回值的類型是V&,我們需要接收一下insert的返回值,如:pair<iterator,bool> ret=_t.Insert({key,V()});我們這樣寫的目的是mymap對RBTree的模板參數T實例化為pair<const K,V>了,所以需要構造一個pair對象進行傳入,然后我們需要返回這個返回值的iterator里的值,因為iterator實際上存儲的還是一個pair對象,所以要返回的是值,為second,所以寫成了如下奇怪的形式:
ret.first->second;
再解釋一遍是Insert返回的是插入的值的迭代器作為鍵,是否插入成功的結果作為值,我們想得到的是鍵,所以用對象.first訪問到,而iterator本質上是存儲了一個鍵值對的,而訪問只能通過迭代器->second或者->first進行,(也可以*(對象).first和*(對象).second進行),但是為了方便理解,這里就用->形式了。
總之我們用operator[]的結果就是為了得到鍵對應的值,而我們調用Insert的目的是避免重復插入并且返回最終該值對應的迭代器,而該迭代器是存儲了一個鍵值對的,我們要得到傳入的鍵所對應的值,所以要這樣寫,所以在mymap中:
//mymap
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });//調用V對應的類型的構造函數初始化該鍵對應的值return ret.first->second;
}11.代碼匯總
在map和set中重要的函數已經實現了,像什么:
剩余的函數感興趣的可以自行實現一下,掌握到這個地步已經可以了。
以下是三個文件的代碼:
//myset.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K>
class myset
{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};
public://typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;//using iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;//下面兩種隨意選//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;using iterator = typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;//下面兩種隨意選://typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;//using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;//下面兩種隨意選//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}
private://RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};//mymap.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public://typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;//using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;//下面兩種隨便選一種//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;//下面兩種隨便選一種//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;//using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;//下面兩種隨便選一種//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });//調用V對應的類型的構造函數初始化該鍵對應的值return ret.first->second;}iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}
private://RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};//RBTree.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{Red,Black
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;//存放數據,可以傳遞T為pair類型RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//Ref:引用,Ptr:指針Node* _node;Node* _root;_TreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root):_node(node),_root(root){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}//后置++Self operator++(int){Self tmp = *this; // 保存當前狀態++(*this); // 調用前置++實現return tmp; // 返回舊值}//后置--Self operator--(int){Self tmp = *this; // 保存當前狀態--(*this); // 調用前置--實現return tmp; // 返回舊值}//前置++Self& operator++(){//中序遍歷,這個時候就需要訪問右孩子if (_node->_right){//找右子樹的最左結點_node = _node->_right;while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{//右子樹為空//對應15結點或者50結點Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;//當parent不為空,且cur為parent的右孩子是繼續往上//因為這代表該子樹已經遍歷完了while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//要么cur是parent的左孩子,這個時候就可以直接用_node=parent//這兩種情況都可以這樣寫_node = parent;}return *this;}//前置--Self& operator--(){if (_node == nullptr) // end(){// --end(),特殊處理,?到中序最后?個結點,整棵樹的最右結點Node* rightMost = _root;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}else if (_node->_left){//代表該子樹還沒遍歷完//找左子樹的最右結點_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{//該子樹被遍歷完//向上查找,直到查找到根或者該孩子為父親的右孩子Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}
};
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef _TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;void RotateR(Node* parent){assert(parent != nullptr);Node* subL = parent->_left;assert(subL != nullptr);Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;subL->_right = parent;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){subL->_parent = nullptr;_root = subL;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){assert(parent != nullptr);Node* subR = parent->_right;assert(subR != nullptr);Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){subR->_parent = nullptr;_root = subR;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = Black;return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };//隱式類型轉換}KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return { Iterator(cur,_root),true };}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_parent = parent;if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data)){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_col = Red;while (parent && parent->_col == Red){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = Red;cur->_col = Black;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black;return { Iterator(newnode,_root),true };}Iterator Begin(){Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}//調用_TreeIterator//相當于_TreeIterator(minleft)return Iterator(minleft, _root);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr, _root);}ConstIterator Begin() const{Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return ConstIterator(minleft, _root);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);}bool Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return true;}}return false;}bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum){if (root == nullptr){if (refNum != blackNum){cout << "存在??結點的數量不相等的路徑" << endl;return false;}return true;}if (root->_col == Red && root->_parent->_col == Red){cout << root->_kv.first << "存在連續的紅?結點" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == Black){blackNum++;}return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);}bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == Red)return false;int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == Black){++refNum;}cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, 0, refNum);}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};12.總結
map和set和紅黑樹在C++進階中都算比較重要的知識,如果能學會這些就比較厲害了,封裝紅黑樹實現map和set的邏輯性比較強,建議各位加以理解。
好了,該講內容就到這里,下講將講解C++進階-哈希(非常重要),哈希理解起來不是很難,但是實現的時候可能難度比較高,所以各位做好心理準備哦。
喜歡的可以一鍵三連哦,下講再見!








![洛谷P1036 [NOIP 2002 普及組] 選數](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/洛谷P1036 [NOIP 2002 普及組] 選數)
文件共享)



詳細教程(2025.3最新可用鏡像,全網最詳細))



)
-卷積神經網絡架構)

