邊際概率條件概率
Probability plays a very important role in Data Science, as Data Scientist regularly attempt to draw statistical inferences that could be used to predict data or analyse data better.
P robability起著數據科學非常重要的作用,為數據科學家經常試圖繪制可以用來更好地預測數據或分析數據的統計推斷。
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to deduce properties of an underlying distribution of probability (Source: Wikipedia), hence understanding random variables and their probability distributions is a required skill to work on many Data Science problems.
統計推斷是使用數據分析來推斷潛在概率分布的屬性的過程( 來源 :Wikipedia),因此了解隨機變量及其概率分布是解決許多數據科學問題的必備技能。
I am going to start this discussion by providing a scenario as we are going to be learning about probability distributions from this scenario.
我將通過提供一個場景開始此討論,因為我們將從該場景中學習概率分布。
情境 (Scenario)
A survey was carried out with 500 strangers in London’s West End to determine people’s favorite sports. The options were Football, Rugby and the rest was grouped together in Other; The results of the test are displayed in Figure 1.
在倫敦西區,對500個陌生人進行了一項調查,以確定人們最喜歡的運動。 選項包括“足球”,“橄欖球”,其余分組在“其他”中。 測試結果如圖1所示。

Figure 1 is not quite a probability distribution, but if we want to get the probability distribution we can simply divide each number in Figure 1 by 500 (number of observations) and the result will be the image in Figure 2.
圖1并不是一個概率分布,但是如果我們想要獲得概率分布,我們可以簡單地將圖1中的每個數字除以500(觀察值的數量),結果將是圖2中的圖像。
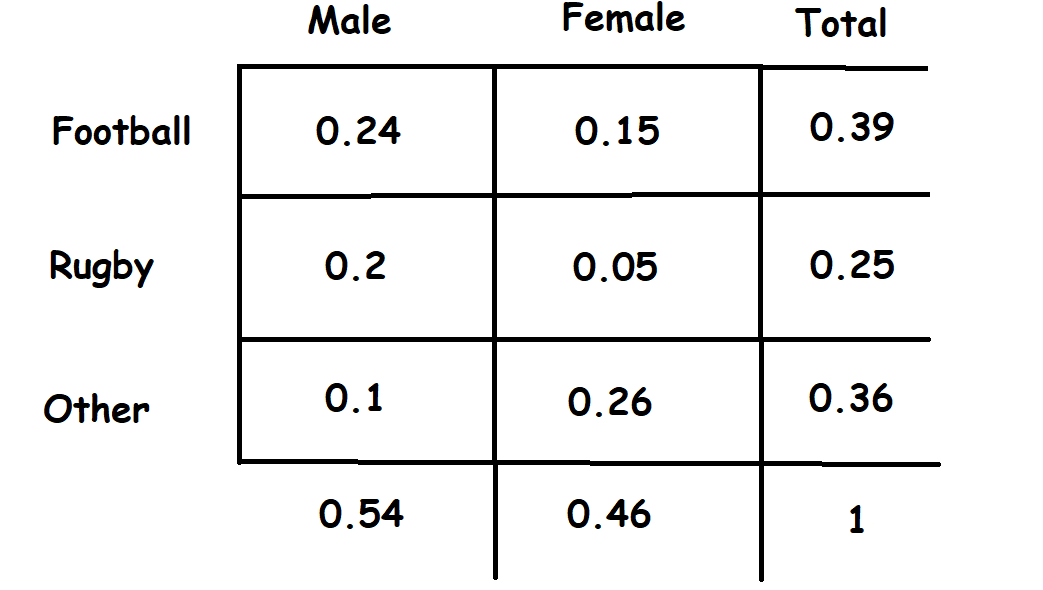
聯合概率 (Joint Probability)
The Joint probability is a statistical measure that is used to calculate the probability of two events occurring together at the same time — P(A and B) or P(A,B). For example, using Figure 2 we can see that the joint probability of someone being a male and liking football is 0.24.
聯合概率是一種統計量度,用于計算兩個事件同時發生的概率-P(A和B)或P(A,B)。 例如,使用圖2可以看到某人是男性并且喜歡足球的聯合概率為0.24。
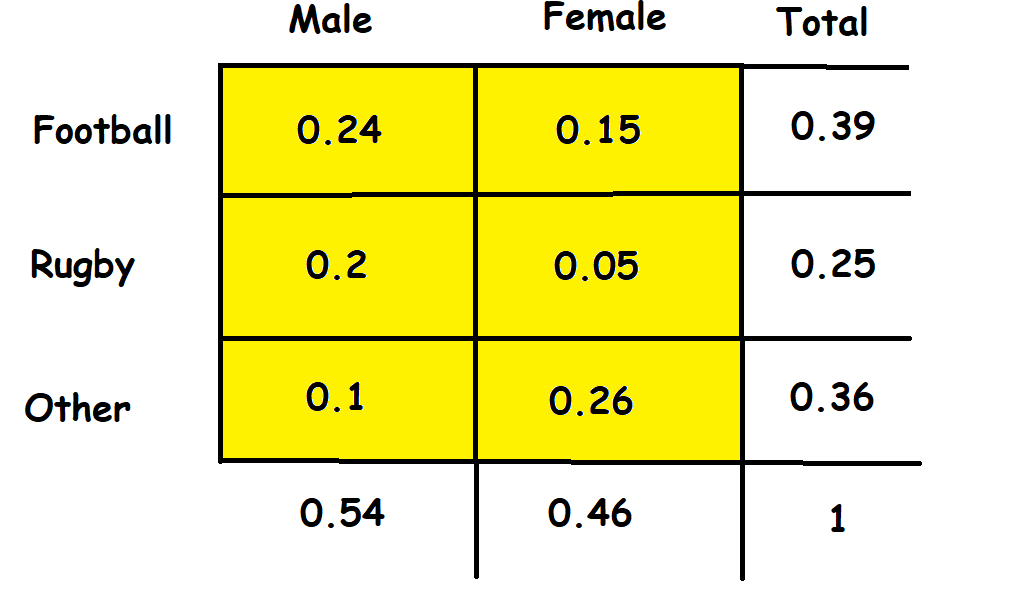
Note: The cells highlighted in Figure 3 (the Joint Probability Distribution) must sum to 1 because everyone in the distribution must be in one of the cells.
注意 :圖3中的單元格(聯合概率分布)必須加1,因為分布中的每個人都必須位于其中一個單元格中。
The Joint probability is symmetrical meaning that P(Male and Football) = P(Football and Male) and we can also use it to find other types of distributions, the marginal distribution and the conditional distribution.
聯合概率是對稱的,意味著P(男和足球)= P(足球和男),我們也可以用它來找到其他類型的分布,即邊際分布和條件分布。
邊際分布 (Marginal Distribution)
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. It gives the probabilities of various values of the variables in the subset without reference to the values of the other variables (Source: Wikipedia) — If that was too much jargon, to put it simply, the marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable — P(A) or P(B).
在概率論和統計學中,隨機變量集合的子集的邊際分布是子集中包含的變量的概率分布。 它給出了子集中變量的各種值的概率,而沒有參考其他變量的值( 來源 : Wikipedia )—如果說的話太多了,簡單來說,邊際概率就是事件的概率另一個變量-P(A)或P(B)的結果。
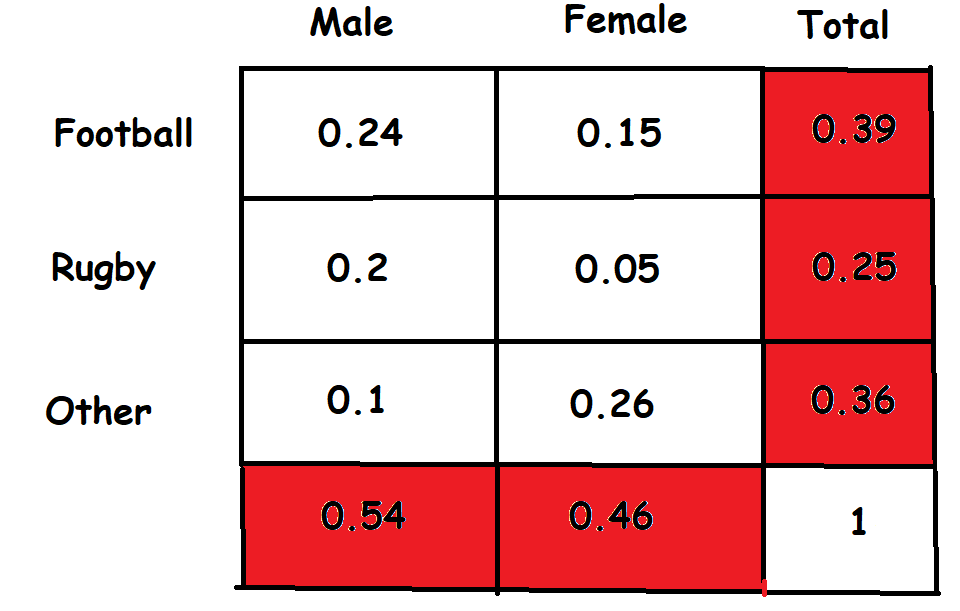
Note: Whether we ignore the gender or the sport our Marginal Distributions must sum to 1.
注意 :無論我們忽略性別還是運動,我們的邊際分布總和必須為1。
A fun fact of marginal probability is that all the marginal probabilities appear in the margins — how cool is that. Hence the P(Female) = 0.46 which completely ignores the sport the Female prefers, and the P(Rugby) = 0.25 completely ignores the gender.
邊際概率的一個有趣的事實是,所有邊際概率都出現在邊際中-這多么酷。 因此,P(女性)= 0.46完全忽略了女性偏愛的運動,而P(Rugby)= 0.25則完全忽略了性別。
條件概率 (Conditional Probability)
The conditional probability concept is one of the most fundamental in probability theory and in my opinion is a trickier type of probability. It defines the probability of one event occurring given that another event has occurred (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence).
條件概率概念是概率論中最基本的概念之一,在我看來是一種棘手的概率類型。 它定義了假設已發生另一事件(通過假設,推定,主張或證據)而發生一個事件的概率。

To make sense of this let’s again use Figure 2; If we want to calculate the probability that a person would like Rugby given that they are a female, we must take the joint probability that the person is female and likes rugby (P(Female and Rugby)) and divide it by the probability of the condition. In this case, the probability is that the person is a female (P(Female)) which we can work out from the margin to be 0.46 hence we get 0.11 (2 decimal places).
為了理解這一點,讓我們再次使用圖2 ; 如果要計算某人喜歡橄欖球的概率(假設某人是女性),則必須考慮該人是女性并且喜歡橄欖球的聯合概率( P(Female and Rugby) ),然后將其除以概率健康)狀況。 在這種情況下,概率是該人是一個女性( P(Female) ),我們可以從裕度算出其為0.46,因此得到0.11(小數點后兩位)。
Let's write that up neater:
讓我們寫得更整潔一些:
P(Female, Rugby) = 0.05
P(女,橄欖球)= 0.05
P(Female) = 0.46
P(女)= 0.46
P(Rugby | Female) = 0.05 / 0.46 = 0.11 (to 2 decimal places).
P(橄欖球|母)= 0.05 / 0.46 = 0.11(小數點后2位)。
If we continued to fill in the probability of preferring a sport given the observant is a female then we would have a Conditional Probability Distribution.
如果在觀察者是女性的情況下,如果我們繼續填寫喜歡某項運動的可能性,那么我們將獲得條件概率分布。
結語 (Wrap Up)
This is guide is a very simple introduction to joint, marginal and conditional probability. Being a Data Scientist and knowing about these distributions may still get you death stares from the envious Statisticians, but at least this time it’s because they are just angry people rather than you being wrong — I am joking!
本指南是對聯合概率,邊際概率和條件概率的非常簡單的介紹。 作為數據科學家并了解這些分布可能仍然會讓您羨慕嫉妒的統計學家,但至少這次是因為他們只是在生氣,而不是您在做錯- 我在開玩笑!
Let’s continue the conversation on LinkedIn…
讓我們繼續在LinkedIn上進行對話…
翻譯自: https://towardsdatascience.com/marginal-joint-and-conditional-probabilities-explained-by-data-scientist-4225b28907a4
邊際概率條件概率
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。 如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/389660.shtml 繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/389660.shtml 英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/389660.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!



![[JS 分析] 天_眼_查 字體文件](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[JS 分析] 天_眼_查 字體文件)
:哨兵)








 譯文五、六、七)




