線程
Threading用于提供線程相關的操作,線程是應用程序中工作的最小單元。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import threading,time 7 8 def show(arg): 9 time.sleep(2) 10 print('線程: ' + str(arg)) 11 12 for i in range(5): 13 t = threading.Thread(target=show,args=(i,)) 14 t.start()
如上述代碼創建了5個線程,target指向函數,arges參數傳遞數值。
- 其它方法:
- start 線程準備就緒,等待CPU調度
- setName 為線程設置名稱
- getName 獲取線程名稱
- setDaemon 設置為后臺線程或前臺線程(默認)。如果是后臺線程,主線程執行過程中,后臺線程也在進行,主線程執行完畢后,后臺線程不論成功與否,均停止;如果是前臺線程,主線程執行過程中,前臺線程也在進行,主線程執行完畢后,等待前臺線程也執行完成后,程序停止
- join 逐個執行每個線程,執行完畢后繼續往下執行,該方法使得多線程變得無意義
- run 線程被cpu調度后自動執行線程對象的run方法
- setName\getName使用方法
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import threading,time 7 8 def test(i): 9 print("線程:%s" %str(i)) 10 time.sleep(2) 11 12 for i in range(2): 13 t = threading.Thread(target=test,args=(i,)) 14 t.start() 15 t.setName("我的線程: {0}".format(str(i))) 16 print(t.getName()) 17 18 運行結果: 19 線程:0 20 我的線程: 0 21 線程:1 22 我的線程: 1


1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import threading,time 7 8 class MyThread(threading.Thread): 9 def __init__(self,num): 10 threading.Thread.__init__(self) 11 self.num = num 12 13 def run(self): 14 print("running thread:%s" % self.num) 15 time.sleep(2) 16 17 if __name__ == '__main__': 18 for i in range(2): 19 t1 = MyThread(i) 20 t1.start() 21 t1.setName("我的線程: {0}".format(str(i))) 22 print(t1.getName()) 23 24 運行結果: 25 running thread:0 26 我的線程: 0 27 running thread:1 28 我的線程: 1
- ?setDaemon方法使用
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import threading,time 7 8 def run(num): 9 print("running thread %s" % str(num)) 10 time.sleep(2) 11 print("OK! %s" % str(num)) 12 13 for i in range(2): 14 t = threading.Thread(target=run,args=(i,)) 15 #未使用setDaemon時默認是前臺線程 16 #t.setDaemon(True) 17 t.start() 18 t.setName("MyThread_{0}".format(str(i))) 19 print(t.getName()) 20 21 運行結果: 22 running thread 0 23 MyThread_0 24 running thread 1 25 MyThread_1 26 OK! 1 27 OK! 0
后臺線程:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import threading,time 7 8 def run(num): 9 print("running thread %s" % str(num)) 10 time.sleep(2)
#主線程執行結束后,不會執行以下語句 11 print("OK! %s" % str(num)) 12 13 for i in range(2): 14 t = threading.Thread(target=run,args=(i,)) 15 #使用setDaemon時是后臺線程 16 t.setDaemon(True) 17 t.start() 18 t.setName("MyThread_{0}".format(str(i))) 19 print(t.getName()) 20 21 22 運行結果: 23 running thread 0 24 MyThread_0 25 running thread 1 26 MyThread_1
- ?join用法理解
當未使用join方法時候,先執行完主線程再根據超時決定等待子線程執行完才能程序結束;如果使用join方法,先執行子線程執行完后,才開始執行下一步主線程,此方法沒有達到并行效果。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 def do_thread(num): 8 time.sleep(3) 9 print("this is thread %s" % str(num)) 10 11 for i in range(2): 12 t = threading.Thread(target=do_thread, args=(i,)) 13 t.start() 14 t.setName("Mythread_{0}".format(str(i))) 15 print("print in main thread: thread name:", t.getName()) 16 17 運行效果:【#先同時執行兩個主線程,等待3秒后再執行兩個子線程】 18 print in main thread: thread name: Mythread_0 #主線程 19 print in main thread: thread name: Mythread_1 #主線程 20 this is thread 0 #子線程 21 this is thread 1 #子線程
使用join效果如下:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ ='yinjia' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 def do_thread(num): 8 time.sleep(3) 9 print("this is thread %s" % str(num)) 10 11 for i in range(2): 12 t = threading.Thread(target=do_thread, args=(i,)) 13 t.start() 14 t.join() #增加join 15 t.setName("Mythread_{0}".format(str(i))) 16 print("print in main thread: thread name:", t.getName()) 17 18 19 運行結果:【先執行子線程,然后再執行主線程,單一逐步執行】 20 this is thread 0 21 print in main thread: thread name: Mythread_0 22 this is thread 1 23 print in main thread: thread name: Mythread_1
- 線程鎖(Lock、RLock)
線程是共享內存,當多個線程對一個公共變量修改數據,會導致線程爭搶問題,為了解決此問題,采用線程鎖。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 gl_num = 0 8 lock = threading.RLock() 9 10 def Func(): 11 global gl_num 12 #加鎖 13 lock.acquire() 14 gl_num += 1 15 time.sleep(1) 16 print(gl_num) 17 #解鎖 18 lock.release() 19 20 for i in range(10): 21 t = threading.Thread(target=Func) 22 t.start()
- 信號量(Semaphore)
信號量同時允許一定數量的線程更改數據 ,比如廁所有3個坑,那最多只允許3個人上廁所,后面的人只能等里面有人出來了才能再進去。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 def run(n): 8 semaphore.acquire() 9 time.sleep(1) 10 print("run the thread: %s" % n) 11 semaphore.release() 12 13 if __name__ == '__main__': 14 num = 0 15 semaphore = threading.BoundedSemaphore(5) # 最多允許5個線程同時運行 16 for i in range(20): 17 t = threading.Thread(target=run, args=(i,)) 18 t.start()
- 事件(event)
事件用于主線程控制其他線程的執行,事件主要提供了三個方法?set、wait、clear。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 def run(event): 8 print("start") 9 event.wait() 10 print('END.....') 11 12 event_obj = threading.Event() 13 for i in range(2): 14 t = threading.Thread(target=run,args=(event_obj,)) 15 t.start() 16 17 event_obj.clear() 18 inp = input("input: ") 19 if inp == 'true': 20 event_obj.set() 21 22 #運行結果: 23 start 24 start 25 input: true 26 END..... 27 END.....
- 條件(Condition)
滿足條件,才能釋放N個線程。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import time,threading 6 7 def condition_func(): 8 ret = False 9 inp = input('>>>') 10 if inp == '1': 11 ret = True 12 return ret 13 14 def run(n): 15 con.acquire() 16 con.wait_for(condition_func) 17 print("run the thread: %s" %n) 18 con.release() 19 20 if __name__ == '__main__': 21 22 con = threading.Condition() 23 for i in range(10): 24 t = threading.Thread(target=run, args=(i,)) 25 t.start() 26 27 #運行結果: 28 >>>1 29 run the thread: 0 30 >>>1 31 run the thread: 1 32 >>>1 33 run the thread: 2
- 定時器
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 from threading import Timer 6 7 def hello(): 8 print("hello, world") 9 10 t = Timer(1, hello) 11 t.start()
?進程
- ?進程數據共享
?方法一:Array
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 from multiprocessing import Process, Array, RLock 7 8 def Foo(lock,temp,i): 9 """ 10 將第0個數加100 11 """ 12 lock.acquire() 13 temp[0] = 100+i 14 for item in temp: 15 print(i,'----->',item) 16 lock.release() 17 18 lock = RLock() 19 temp = Array('i', [11, 22, 33, 44]) 20 21 for i in range(20): 22 p = Process(target=Foo,args=(lock,temp,i,)) 23 p.start()
方法二:manage.dict()共享數據
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 from multiprocessing import Process, Manager 6 7 manage = Manager() 8 dic = manage.dict() 9 10 11 def Foo(i): 12 dic[i] = 100 + i 13 print(dic) 14 print(dic.values()) 15 16 17 for i in range(2): 18 p = Process(target=Foo, args=(i,)) 19 p.start() 20 p.join()
?
- 進程池
?進程池方法:?
apply(func[, args[, kwds]]): 阻塞的執行,比如創建一個有3個線程的線程池,當執行時是創建完一個 執行完函數再創建另一個,變成一個線性的執行?
apply_async(func[, args[, kwds[, callback]]]) : 它是非阻塞執行,同時創建3個線程的線程池,同時執行,只要有一個執行完立刻放回池子待下一個執行,并行的執行?
close(): 關閉pool,使其不在接受新的任務。?
terminate() : 結束工作進程,不在處理未完成的任務。?
join() 主進程阻塞,等待子進程的退出, join方法要在close或terminate之后使用。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 from multiprocessing import Pool 6 import time 7 8 def myFun(i): 9 time.sleep(2) 10 return i+100 11 12 def end_call(arg): 13 print("end_call",arg) 14 15 p = Pool(5) 16 #print(p.apply(myFun,(1,))) 17 #print(p.apply_async(func =myFun, args=(1,)).get()) 18 19 print(p.map(myFun,range(10))) 20 21 for i in range(10): 22 p.apply_async(func=myFun,args=(i,),callback=end_call) 23 24 print("end") 25 p.close() 26 p.join()
?
- 生產者&消費型
產生數據的模塊,就形象地稱為生產者;而處理數據的模塊,就稱為消費者。在生產者與消費者之間在加個緩沖區,我們形象的稱之為倉庫,生產者負責往倉庫了進商 品,而消費者負責從倉庫里拿商品,這就構成了生產者消費者模型。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding=utf-8 3 __author__ = 'yinjia' 4 5 6 import queue 7 import threading,time 8 9 10 message = queue.Queue(10) 11 12 13 def producer(): 14 name = threading.current_thread().getName() 15 print(name + "線程啟動....") 16 for i in range(10): 17 time.sleep(1) 18 print('\033[45m<%s> 生產了 [%s]個餃子\033[0m' % (name, i)) 19 message.put(name) 20 21 22 def consumer(): 23 name = threading.current_thread().getName() 24 print(name + "線程啟動.....") 25 for i in range(10): 26 message.get() 27 print('\033[43m<%s> 吃了 [%s]個餃子\033[0m' % (name, i)) 28 29 30 if __name__ == '__main__': 31 32 p = threading.Thread(target=producer, name='東北餃子店') 33 c = threading.Thread(target=consumer, name='消費者') 34 p.start() 35 c.start()
?運行結果:
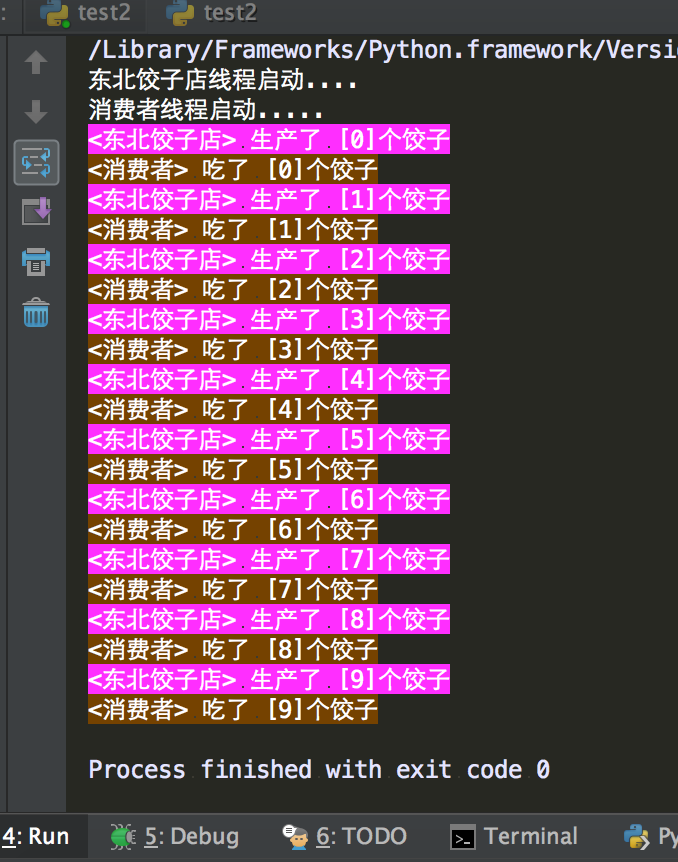
?
協程
協程存在的意義:對于多線程應用,CPU通過切片的方式來切換線程間的執行,線程切換時需要耗時(保存狀態,下次繼續)。協程,則只使用一個線程,在一個線程中規定某個代碼塊執行順序。
協程的適用場景:當程序中存在大量不需要CPU的操作時(IO),適用于協程;
- gevent
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import gevent 6 7 def foo(): 8 print('Running in foo') 9 gevent.sleep(0) 10 print('Explicit context switch to foo again') 11 12 def bar(): 13 print('Explicit context to bar') 14 gevent.sleep(0) 15 print('Implicit context switch back to bar') 16 17 gevent.joinall([ 18 gevent.spawn(foo), 19 gevent.spawn(bar), 20 ]) 21 22 #運行結果: 23 Running in foo 24 Explicit context to bar 25 Explicit context switch to foo again 26 Implicit context switch back to bar
- 遇到IO操作自動切換
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 4 from gevent import monkey; monkey.patch_all() 5 import gevent 6 import urllib.request 7 8 def f(url): 9 print('GET: %s' % url) 10 resp = urllib.request.urlopen(url) 11 data = resp.read() 12 print('%d bytes received from %s.' % (len(data), url)) 13 14 gevent.joinall([ 15 gevent.spawn(f, 'https://www.python.org/'), 16 gevent.spawn(f, 'https://www.baidu.com/'), 17 gevent.spawn(f, 'https://github.com/'), 18 ]) 19 20 #運行結果: 21 GET: https://www.python.org/ 22 GET: https://www.baidu.com/ 23 GET: https://github.com/ 24 227 bytes received from https://www.baidu.com/. 25 49273 bytes received from https://www.python.org/. 26 53756 bytes received from https://github.com/.
?上下文管理
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import contextlib 6 7 @contextlib.contextmanager 8 def tag(name): 9 print("<%s>" % name) 10 yield 11 print("</%s>" % name) 12 13 with tag("h1"): 14 print("foo") 15 16 #運行結果: 17 <h1> 18 foo 19 </h1>
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 __author__ = 'Administrator' 4 5 import contextlib 6 7 @contextlib.contextmanager 8 def myopen(file_path,mode): 9 f = open(file_path,mode,encoding='utf-8') 10 try: 11 yield f 12 finally: 13 f.close() 14 with myopen('index.html','r') as file_obj: 15 for i in file_obj: 16 print(i)
更多方法參見:https://docs.python.org/3.6/library/contextlib.html









![[IoC容器Unity]第三回:依賴注入](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[IoC容器Unity]第三回:依賴注入)




)




