注:本文同步發布于稀土掘金。
7 多路查找樹
??多路查找樹(multi-way search tree),其每個結點的孩子可以多于兩個,且每一個結點處可以存儲多個元素。由于它是查找樹,所有元素之間存在某種特定的排序關系。
7.1 2-3樹
7.1.1 生成2-3樹
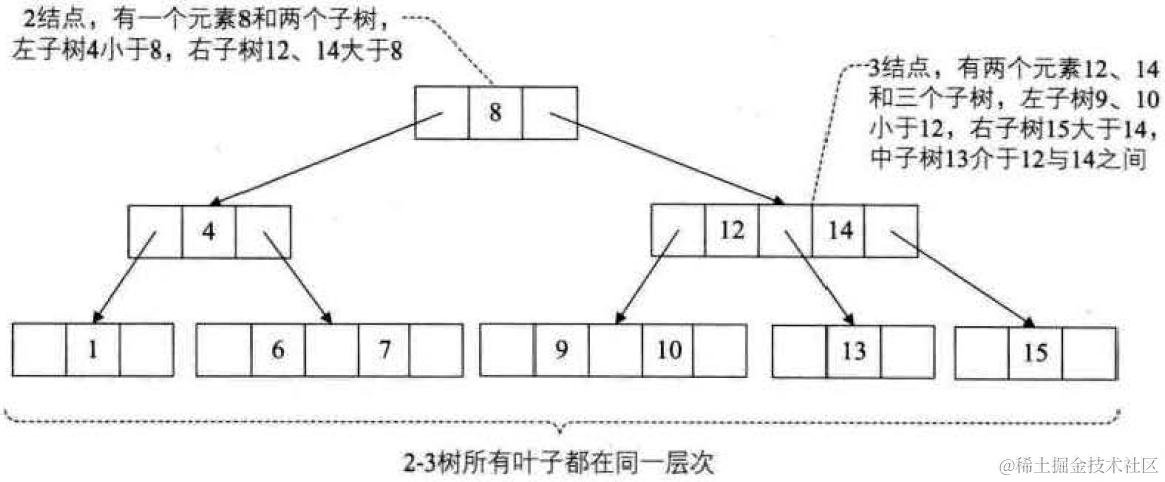
??2-3樹是這樣的一棵多路查找樹:其中的每一個結點都有兩個孩子(我們稱它為2結點)或三個孩子(我們稱它為3結點)。
??一個2結點包含一個元素和兩個孩子(或沒有孩子),且與二叉排序樹類似,左子樹包含的元素小于該元素,右子樹包含的元素大于該元素。不過,與二叉排序樹不同,這個2結點要么沒有孩子,要么就有兩個,不能只有一個孩子。
??一個3結點包含一小一大兩個元素和三個孩子(或沒有孩子),一個3結點要么沒有孩子,要有就有3個孩子,如果某個3結點有孩子的話,左子樹包含小于較小元素的元素,右子樹包含大于較大元素的元素,中間子樹包含介于兩元素之間的元素。
??總之,2-3樹有以下特性:
??(1) 對于每一個結點有1或者2個元素;
??(2) 當節點有1個元素時,節點有0個子樹或2個子樹;
??(3) 當節點有2個元素時,節點有0個子樹或3個子樹。
??(4) 所有葉子點都在樹的同一層;
??如下是一棵有效的2-3樹:
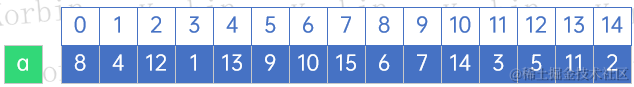
??來看2-3樹的生成,假設我們要根據以下數組生成一棵2-3樹:
??由于2-3樹的每個結點可以放置1至2個元素,因此我們使用如下結構來表示一個結點,其中x和y分別表示元素值:

??然后我們來按序插入元素,由于一個結點可以存放2個元素,因此前兩個元素,直接生成一個根結點:

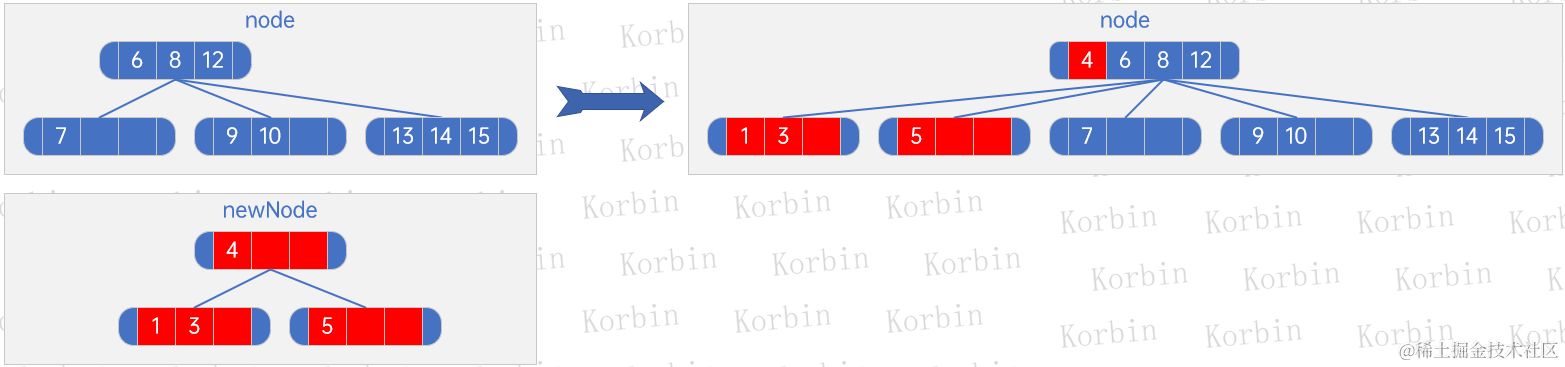
??對于第三個元素12,因為當前2-3樹只有一個結點,因此只需要將元素12插入該結點即可,而由于該結點已有二個元素,因此不能直接插入,而是需要將其中一個元素頂上去作為父結點,我們把被插入的結點設為node,待插入的元素則構建一個只有一個元素的結點,如下所示:
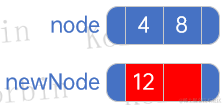
??然后 將 n e w N o d e 中的元素先插入到 n o d e 中,如果 n e w N o d e 有孩子結點,也將之作為 n o d e 的孩子 \color{red}{將newNode中的元素先插入到node中,如果newNode有孩子結點,也將之作為node的孩子} 將newNode中的元素先插入到node中,如果newNode有孩子結點,也將之作為node的孩子:

??這時,根據node元素數量進行不同處理——如果node結點數量小于3個,則不進行任何處理,否則將所有元素按最大結點數量分成多段,然后從第一段開始,將每段的最后一個元素往上提,作為父結點:

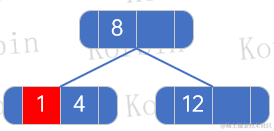
??然后插入元素1,直接插入即可:
??接下來插入元素13:
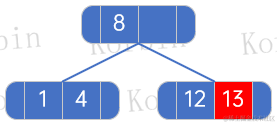
??然后是元素9,先將它插入到12、13所在的結點,然后構建子樹,然后將被頂上去的元素12,插入到結點8:
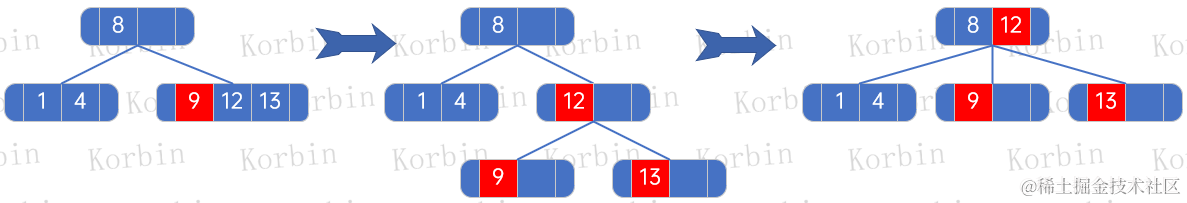
??為方便后續描述,我們把要插入的結點設置為newNode,被插入的結點設置為node。
??然后插入元素10:
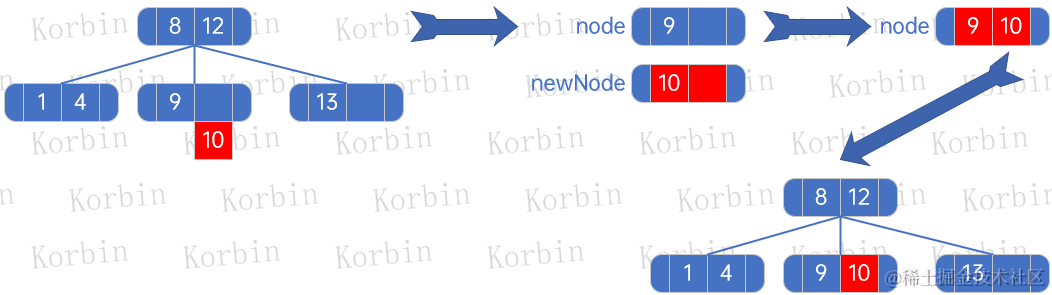
??然后插入元素15:

??然后插入元素6,首先插入到1、4所在的結點,并生成子樹:

??然后把新生成的子樹當成新的newNode,把原來1、4所在的結點的父結點,當成新的node,進行處理:

??這時,發現根結點有三個元素,按照規則“如果node結點數量小于3個,則不進行任何處理,否則將所有元素按最大結點數量分成多段,然后從第一段開始,將每段的最后一個元素往上提,作為父結點”進行處理,并加入新的規則“然后將所有孩子結點按每個被拆分的元素個數+1,分配到新生成的子結點上”:
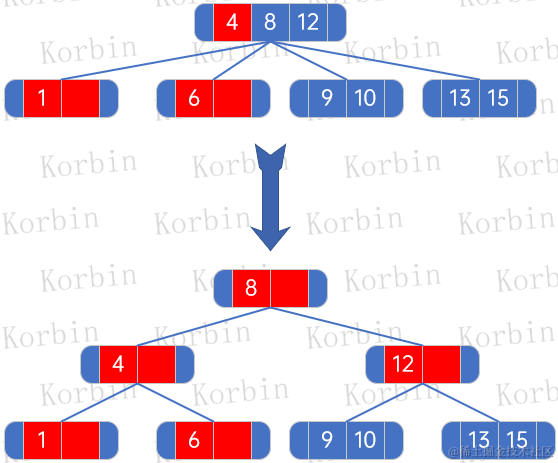
??如上圖所示,孩子結點有四個,由于第一個新的子結點只有一個元素,因此分配兩個孩子給它,另一個新子結點也只有一個元素,因此也分配兩個孩子給它。
??然后插入元素7:
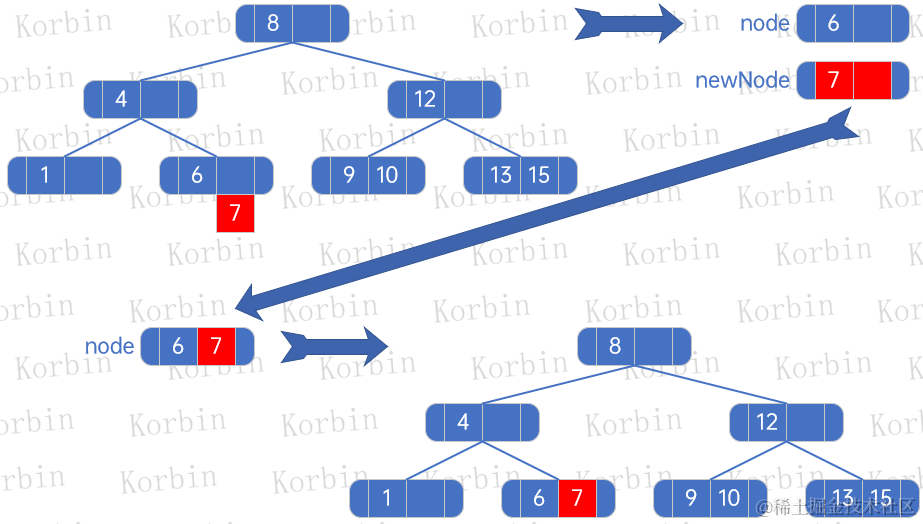
??然后插入元素14:
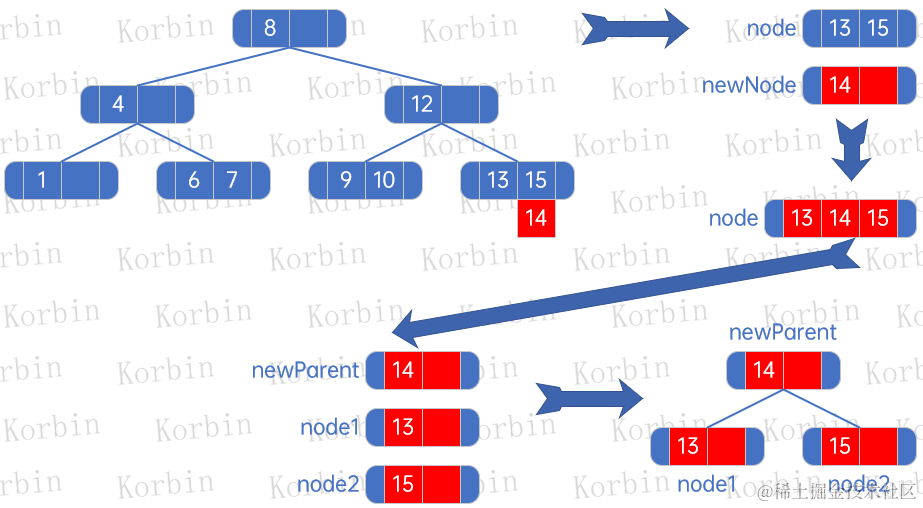
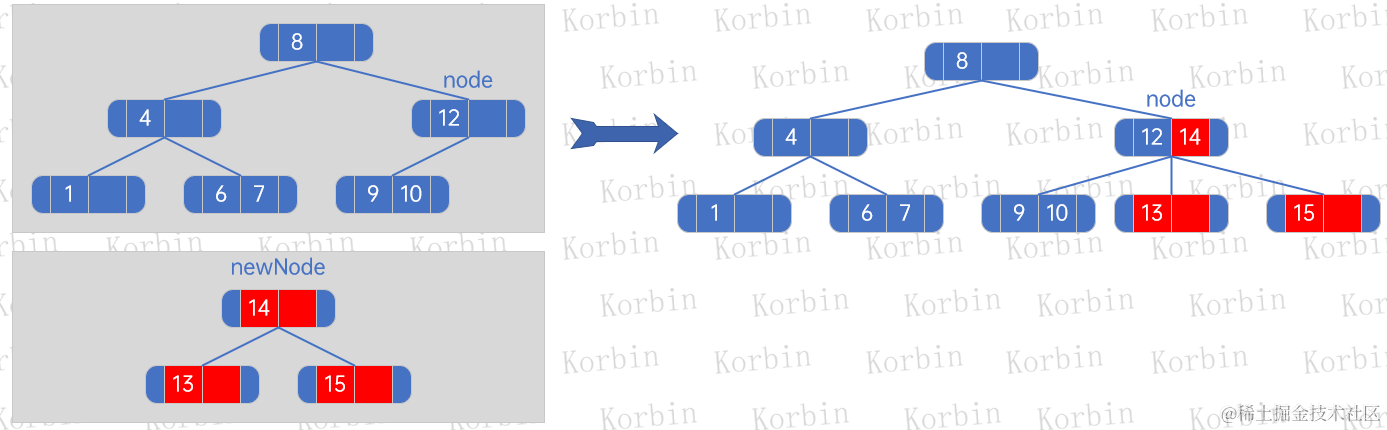
??然后插入元素3:
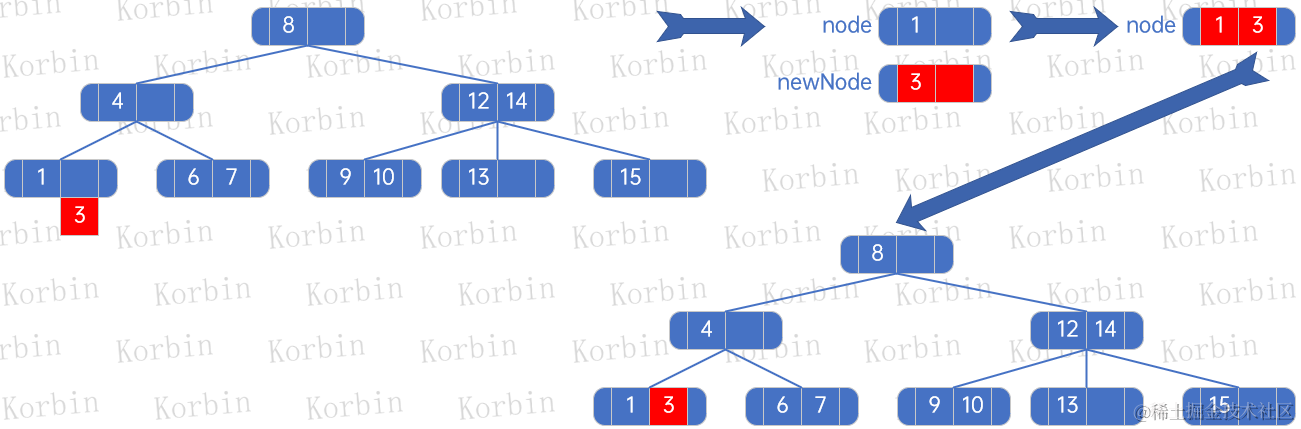
??然后插入元素5:
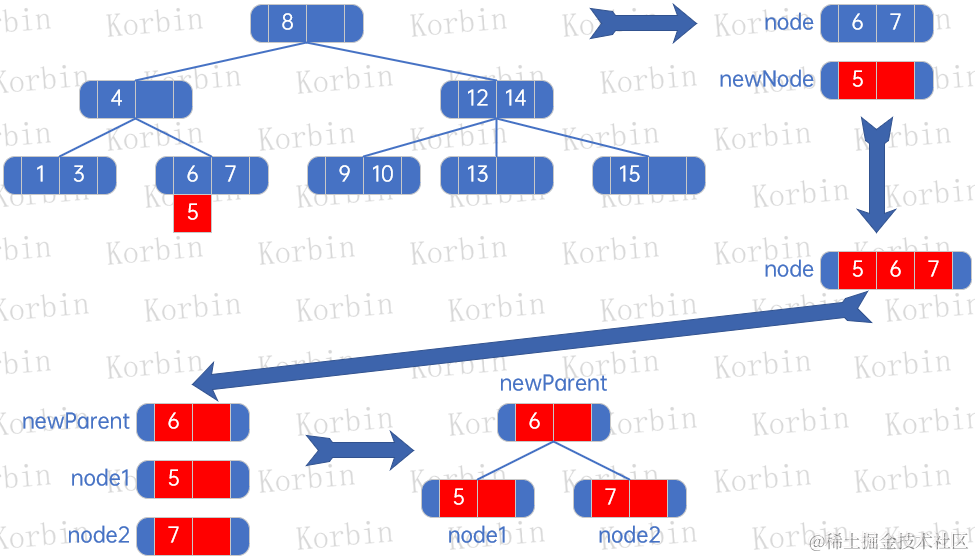
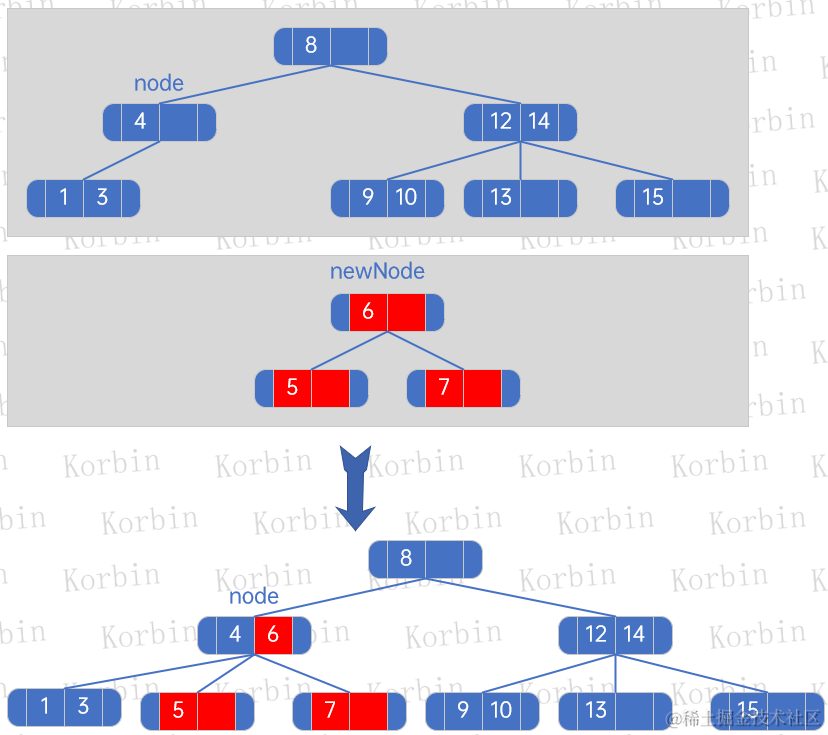
??然后插入元素11,參考上述規則,得到如下結果:
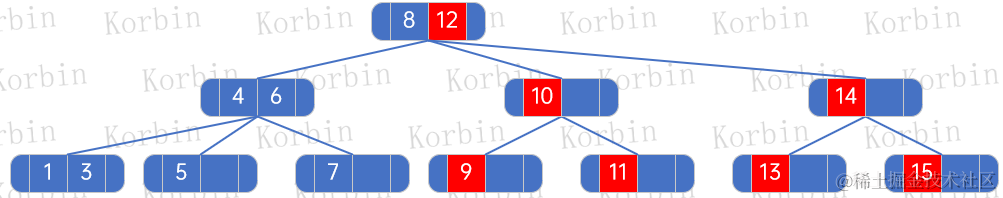
??然后插入元素2,參考上述規則,得到如下結果:
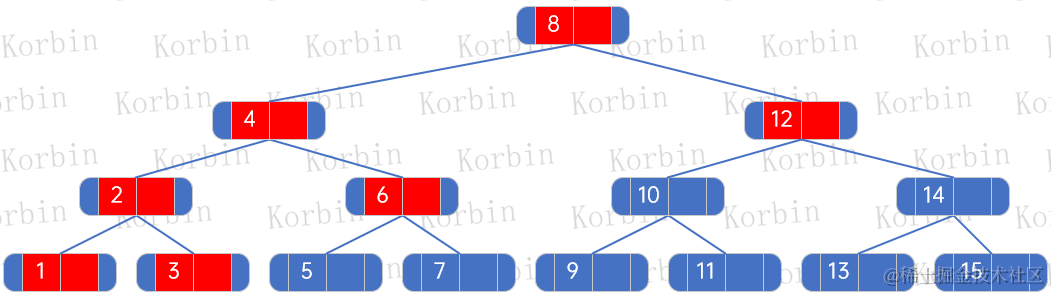
??此時2-3樹創建完成。
7.1.2 刪除2-3樹上的結點
??為保證2-3樹的特性,在2-3樹上刪除元素,有以下規則:
??(1) 若刪除的是葉子結點上的元素,且葉子結點的元素個數大于1,則直接將該元素刪除;
??(2) 若刪除的是葉子結點上的元素,且葉子結點的元素個數等于1,則先將此結點刪除,然后從parent開始按規則”將parent的所有子結點的元素添加到parent中,將parent的所有子結點的孩子也添加到parent中,然后根據parent重新構建子樹“向上迭代,直到parent的元素個數大于最大孩子數量,或者parent為null時,停止迭代;
??(3) 若刪除的是非葉子結點上的元素,則找到該元素的下標,然后找到該下標對應的孩子樹上的最大值,將孩子樹上的最大值與要刪除的這個元素替換,然后根據(1)、(2)相同的規則,刪除新的這個葉子結點上的元素;
??我們通過示例來看,假設有以下2-3樹:
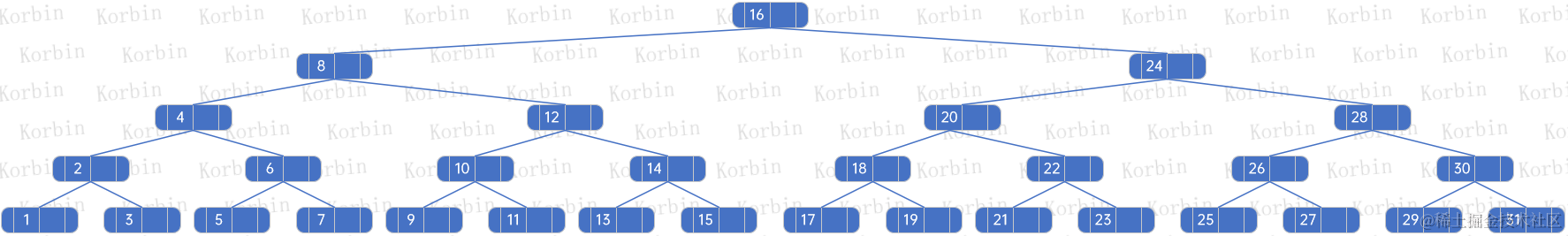
??假設我們要刪除元素1,由于要刪除的是葉子結點上的元素,且該結點只有一個元素,按照上述規則,我們先刪除元素1所在的結點:
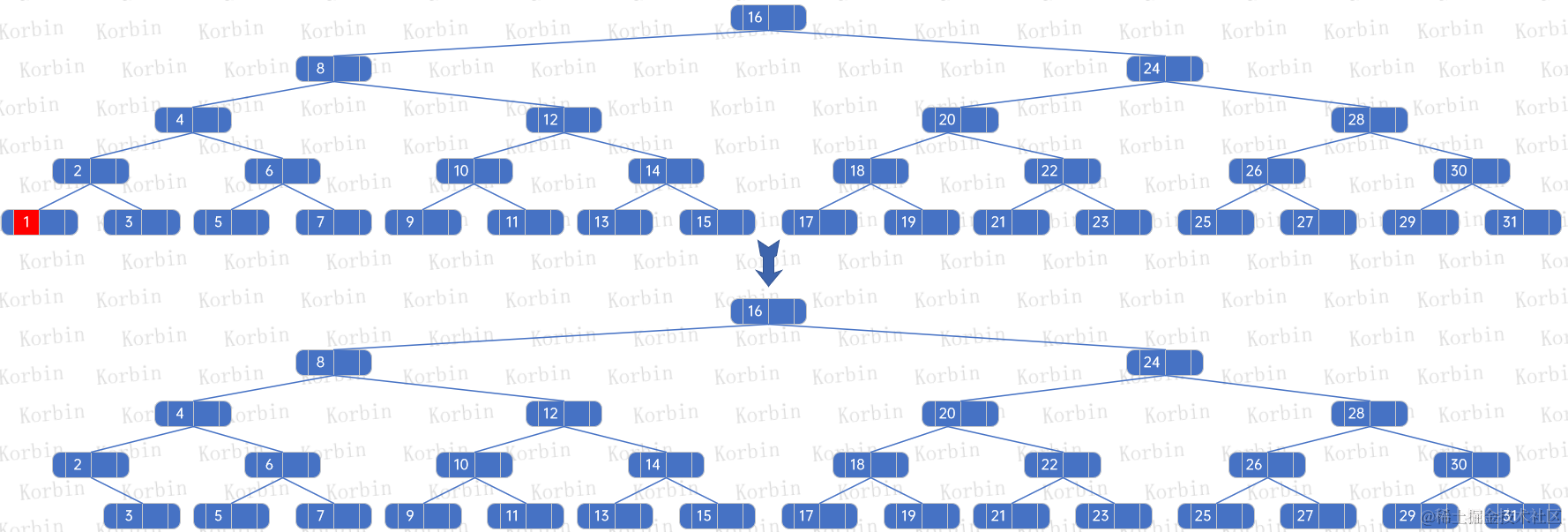
??然后找到parent結點,即元素為2的結點,將其所有孩子的元素和孩子的所有孩子加到parent結點上,并刪除原來的孩子結點:
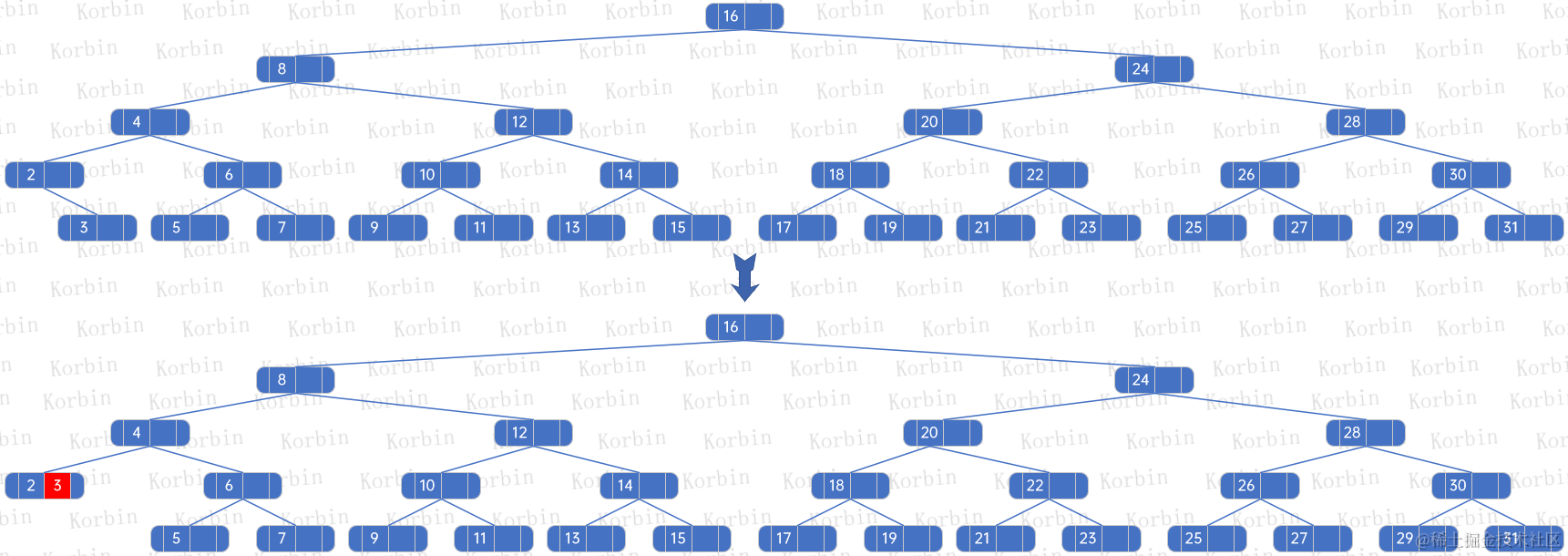
??發現parent的元素個數仍小于最大孩子數量(2-3樹的最大孩子數量是3個),因此找到parent的parent,繼續按規則處理:
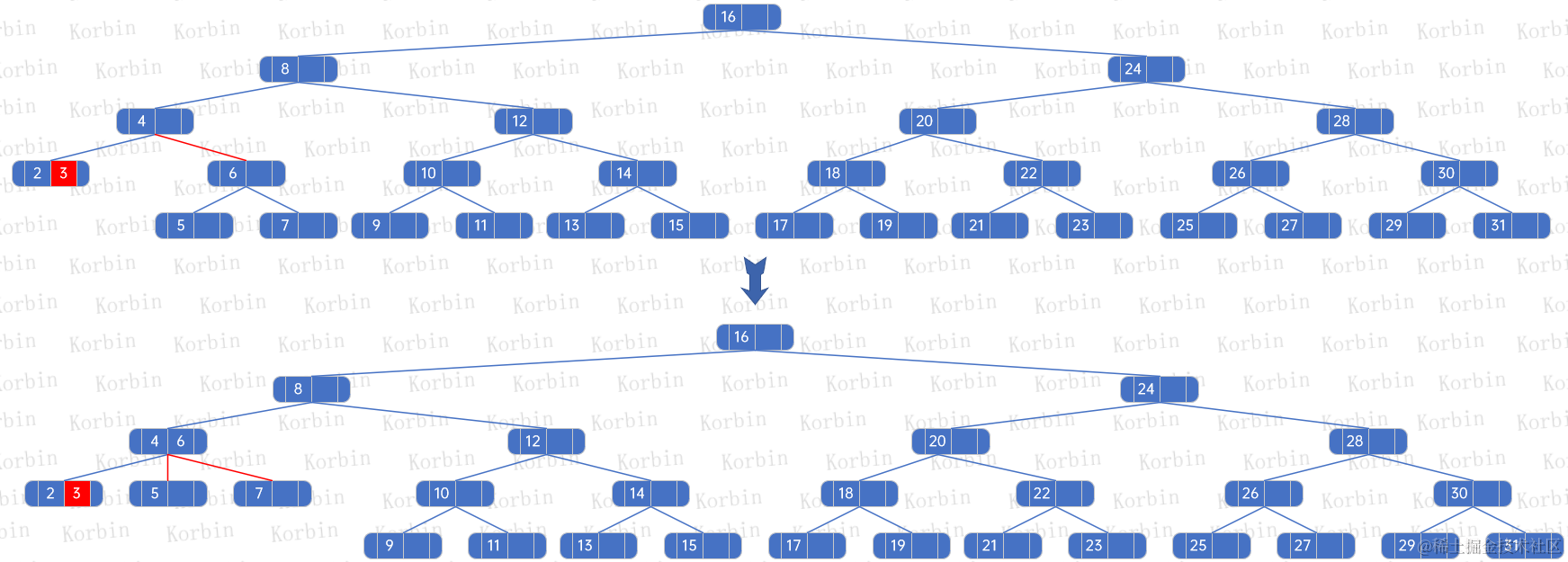
??新結點的元素數量仍小于3,于是繼續往上迭代,直到迭代到根結點,元素的數量也不超過3,這時停止迭代,樹已經變成一棵正常的2-3樹,操作結束:

??接下來我們來刪除元素20,首先,找到20所在的結點,發現它只有一個元素,因此找到此結點的第一棵樹上的最大元素,將之與20替換:
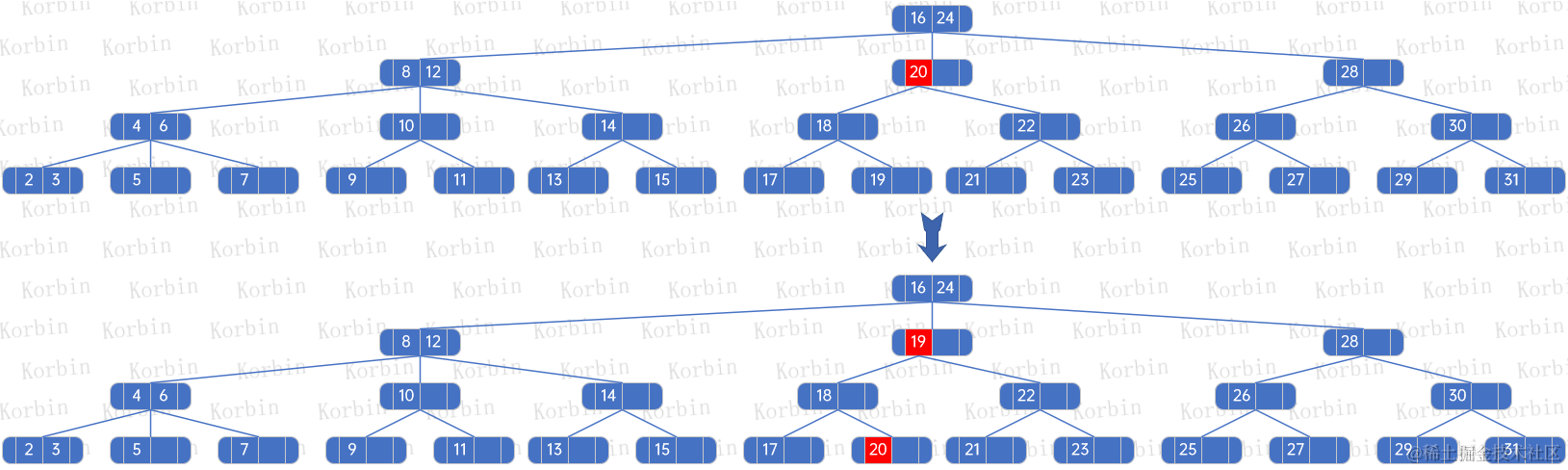
??然后刪除替換后的結點上的元素,由于替換后的結點也只有一個元素,因此按照規則,一層層往上迭代:

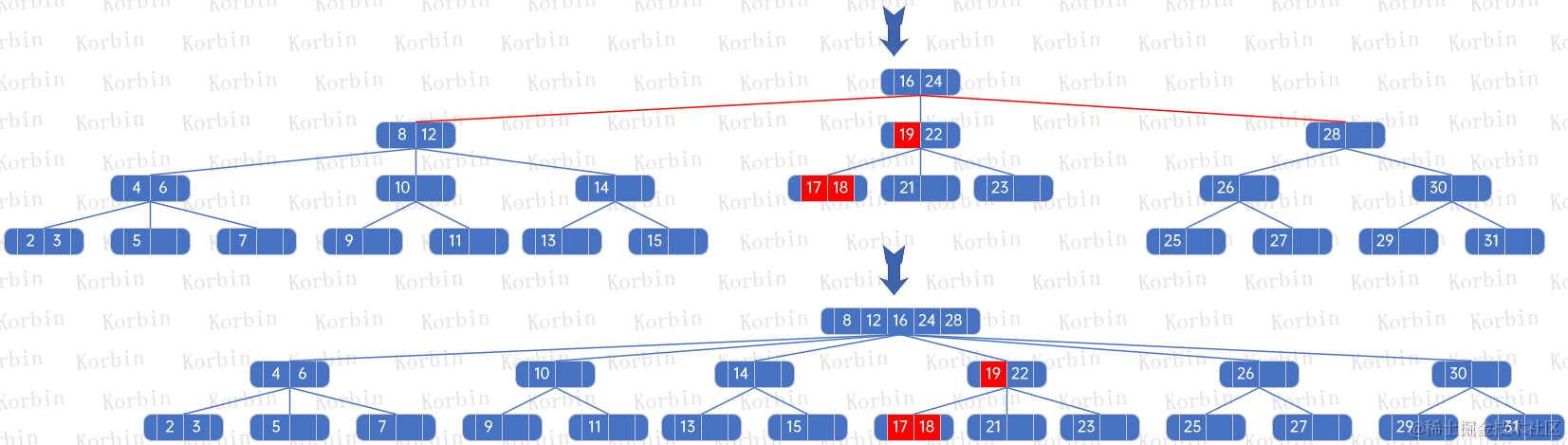
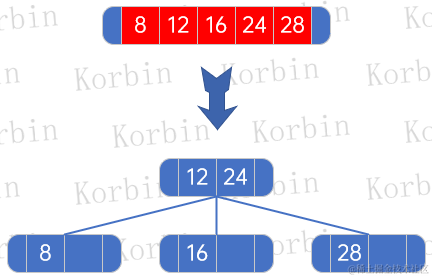
??迭代到根結點時,發現根結點的元素數量超過了3,于是重新生成樹,規則與插入時重新生成樹的方法一致——將所有結點合到一起,然后按最大結點數分成多段,然后把每一段的最大元素往上提作為父結點的元素,最后把所有孩子按新生成的結點的元素數量進行分配。
??以本例為例,parent有5個元素,而每個結點最大的元素數量是2,因此將它們分成“8、12”、“16、24”和“28”三段,然后將前面兩段的最大值往上提作為父結點,即得到如下結構:
??然后將6個孩子結點,根據新孩子的元素數量進行分配:
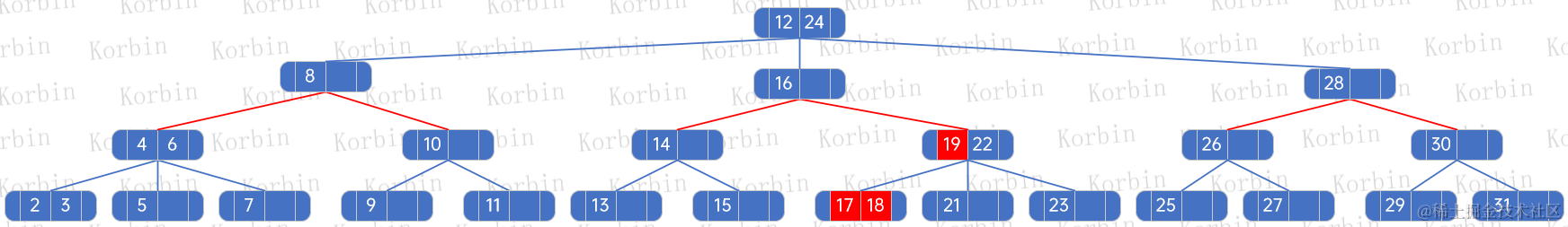
??而如果要刪除元素18,由于它是葉子結點上的元素,且該結點有兩個元素,因此直接刪除即可:
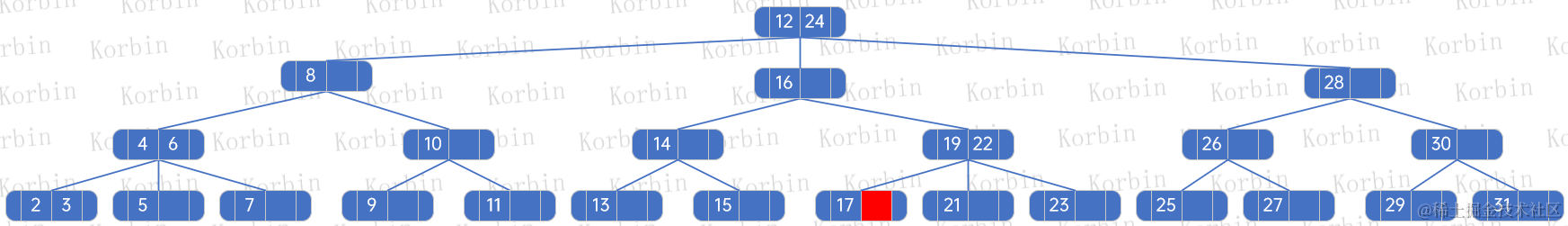
??我們來刪除元素12,發現它不是葉子結點上的元素,且其在該結點上的索引為0,因此我們找到children[0]子樹上的最大元素,即11,并將這兩個元素替換:
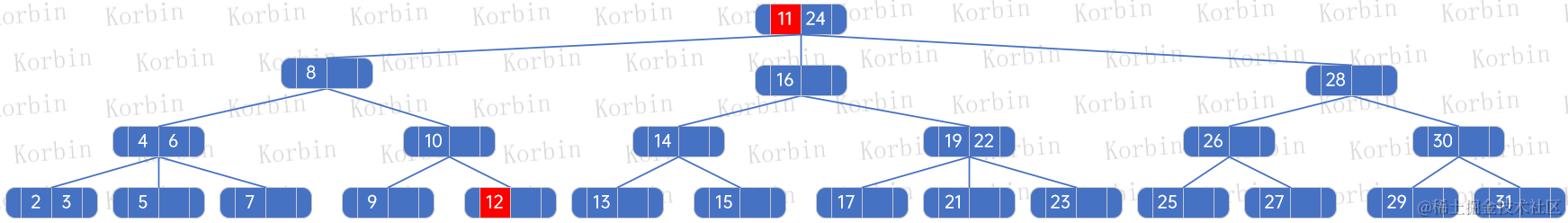
??然后刪除當前元素12所在的結點,并按照規則向上迭代:

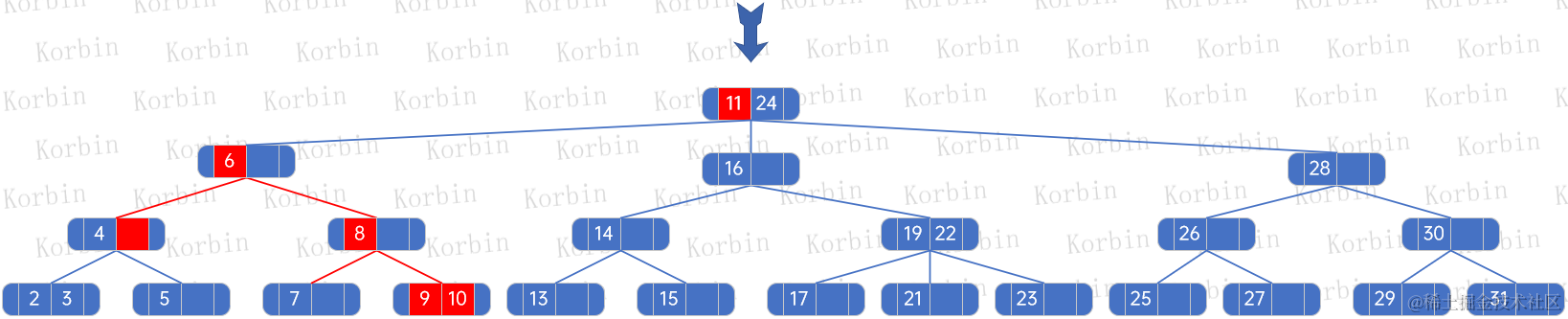
??其他元素的刪除,則不再演示,按規則處理即可。
7.2 2-3-4樹
7.2.1 生成2-3-4樹
??2-3-4樹是2-3樹的擴展,因此2-3-4樹有以下特性:
??(1) 對于每一個結點有1或者2或者3個元素;
??(2) 當節點有1個元素時,節點有0個子樹或2個子樹;
??(3) 當節點有2個元素時,節點有0個子樹或3個子樹。
??(4) 當節點有3個元素時,節點有0個子樹或4個子樹。
??(4) 所有葉子點都在樹的同一層;
??我們同樣用以下數組來構建2-3-4樹:
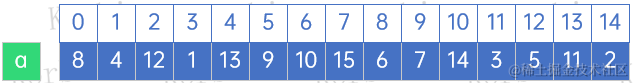
??對于前三個元素,因為一個結點最多可以放置三個元素,因此直接將它們依序放置到一個結點即可:
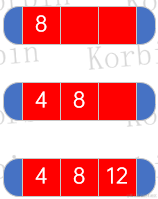
??對于第四個元素1,因為當前2-3-4樹只有一個結點,因此只需要將元素1插入該結點即可,而由于該結點已有三個元素,因此不能直接插入,而是需要將其中一個元素頂上去作為父結點,我們把被插入的結點設為node,待插入的元素則構建一個只有一個元素的結點,如下所示:
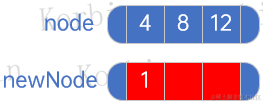
??然后 將 n e w N o d e 中的元素先插入到 n o d e 中,如果 n e w N o d e 有孩子結點,也將之作為 n o d e 的孩子 \color{red}{將newNode中的元素先插入到node中,如果newNode有孩子結點,也將之作為node的孩子} 將newNode中的元素先插入到node中,如果newNode有孩子結點,也將之作為node的孩子:

??這時,根據node元素數量進行不同處理——如果node結點數量小于4個,則不進行任何處理,否則將所有元素按每組3個,分成多組,處理方式與2-3樹的插入一致:

??插入元素13,根據上述規則,直接插入到12所在的結點即可:

??接下來插入元素9:
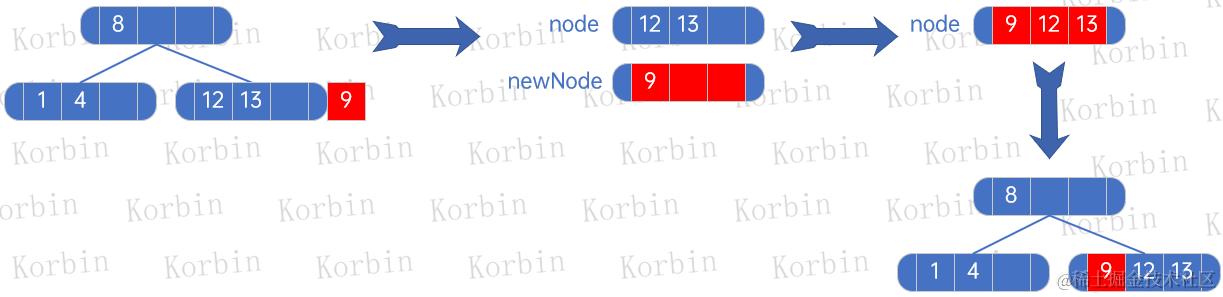
??接下來插入元素10,首先將元素10與元素9、12、13所在的結點,生成一棵新的子樹:
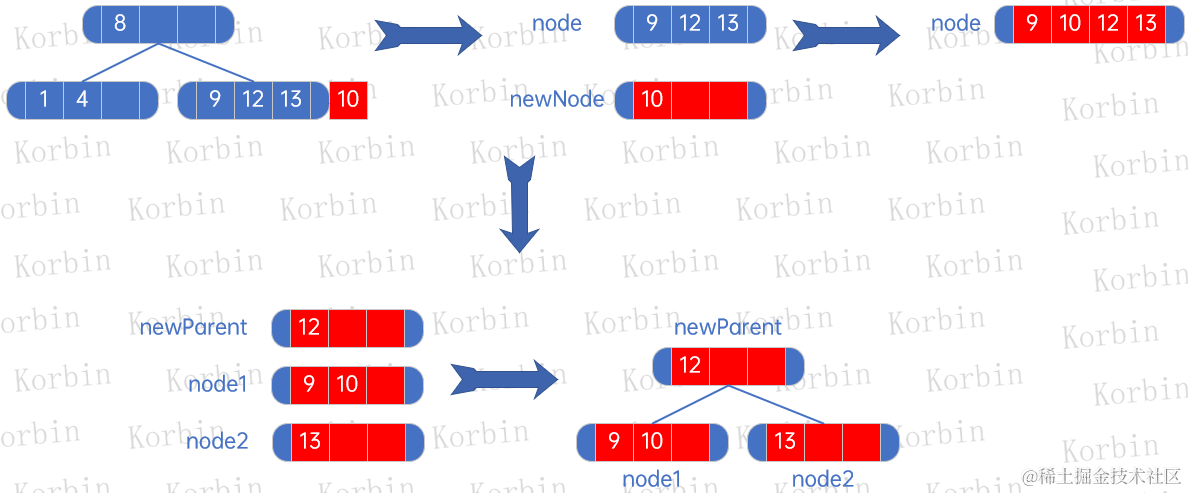
??接下來處理新的子樹的原子樹,即以下兩棵子樹:

??我們先將原子樹上,9、12、13元素所在的結點從樹上去除:
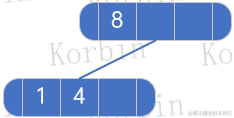
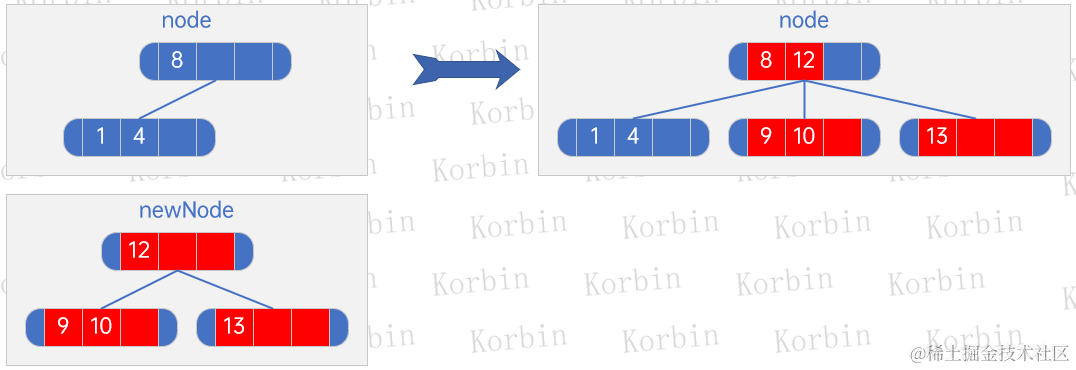
??然后仍按上述規則,設置node和newNode,然后把newNode的元素加入node,并把newNode的所有孩子都加入node的孩子,因新的根結點8、12的元素數量小于3,因此插入結束:
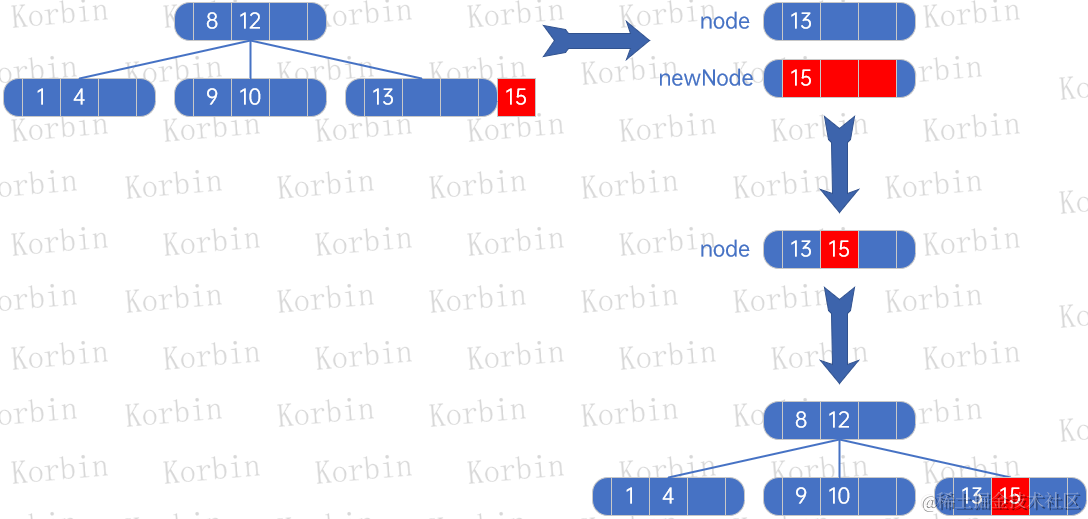
??接下來插入元素15,直接插入即可:
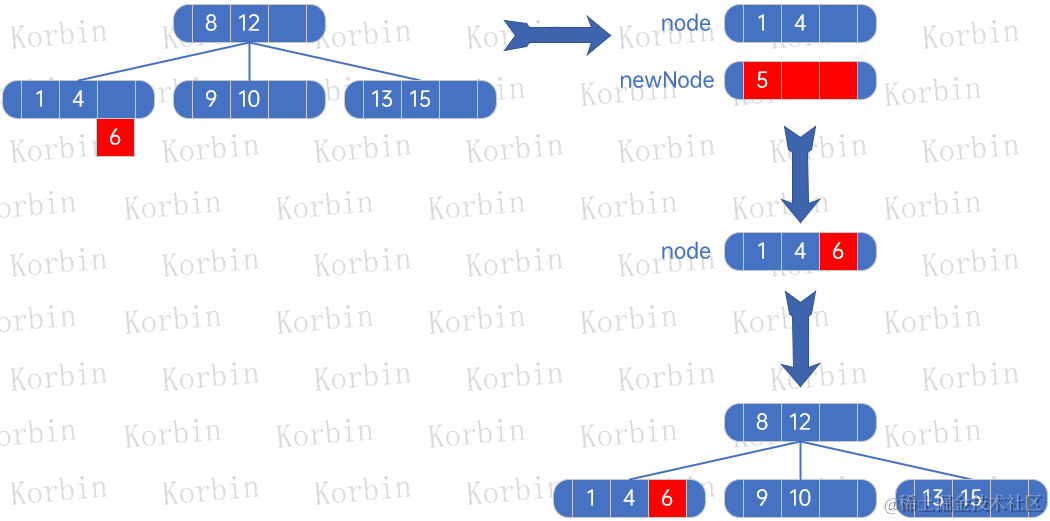
??接下來插入元素6,仍是直接插入:
??接下來插入元素7,先處理元素7和元素1、4、6所在的結點,生成一棵新子樹:
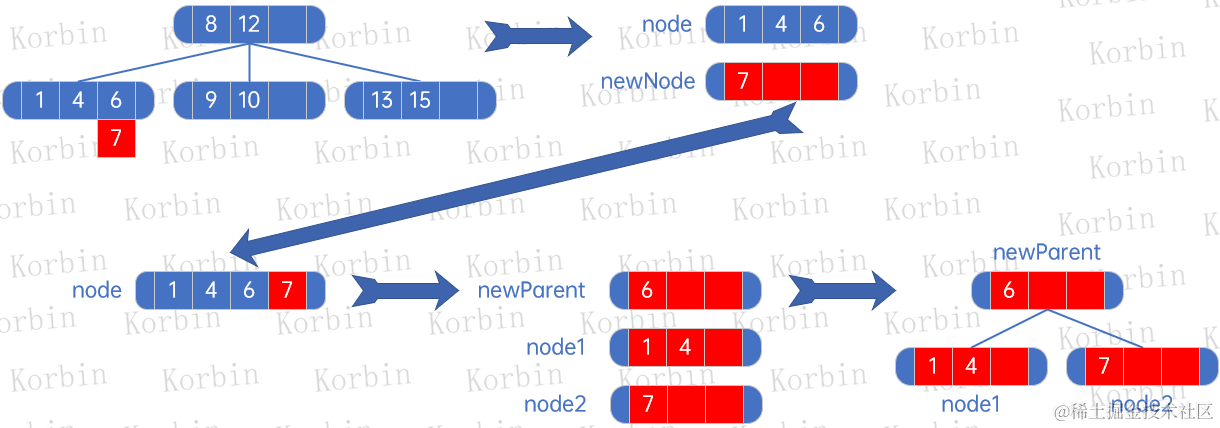
??然后將原樹中的1、4、6所在的結點刪除,生成新子樹,并將兩棵子樹合并處理:
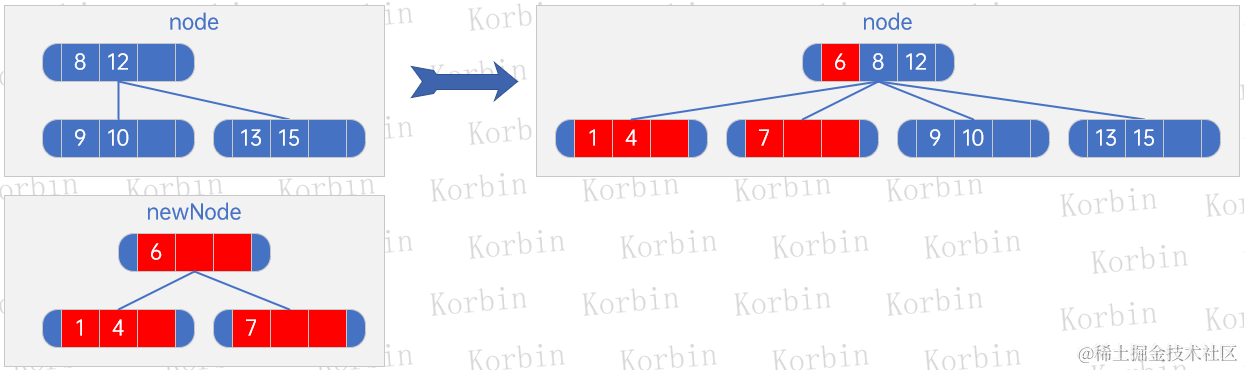
??接下來插入元素14,直接插入即可:

??接下來插入元素3,直接插入即可:
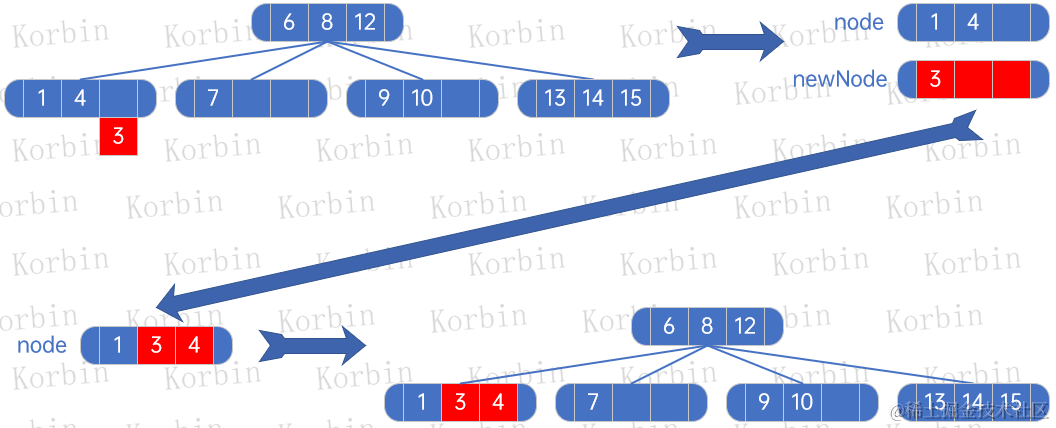
??接下來插入元素5,先處理元素5和元素1、3、4所在的結點,生成一棵子樹:
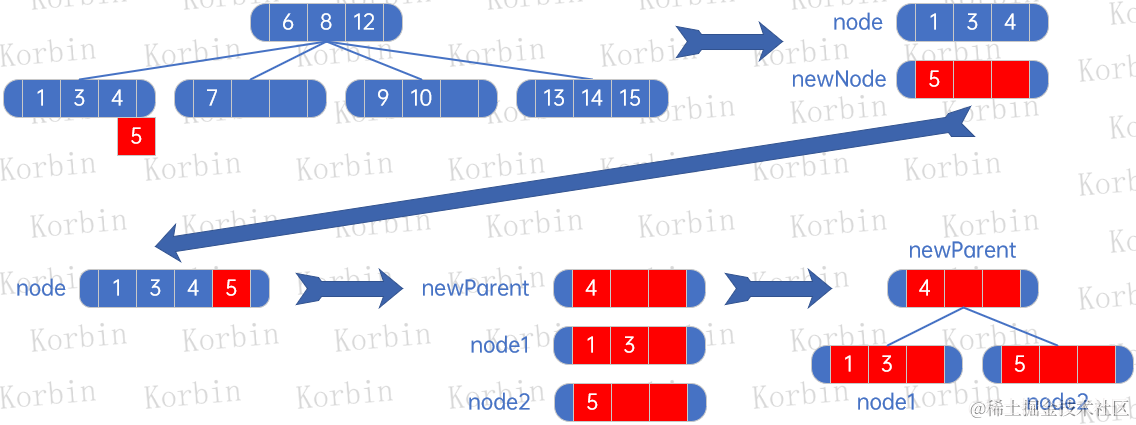
??然后將原樹中的1、3、4所在的結點去除,生成新子樹,將上一步生成的子樹與此子樹合并:
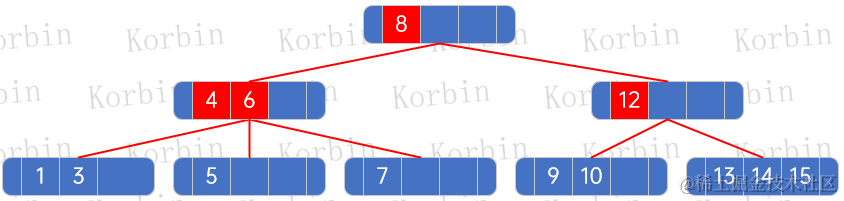
??發現根結點的元素數量超過3個,于是按規則處理,即——將所有元素按每組3個分組,然后將除最后一組外的其他組的最后一個元素,提升為父結點,然后將所有孩子(現在是孫子)按新子結點元素個數進行分配,即“4、6、8”一組,“12”一組,然后將8往上提,再將五個孩子分配——“4、6”結點有兩個元素,因此分配3個孩子,“12”只有一個孩子,因此分配兩個:
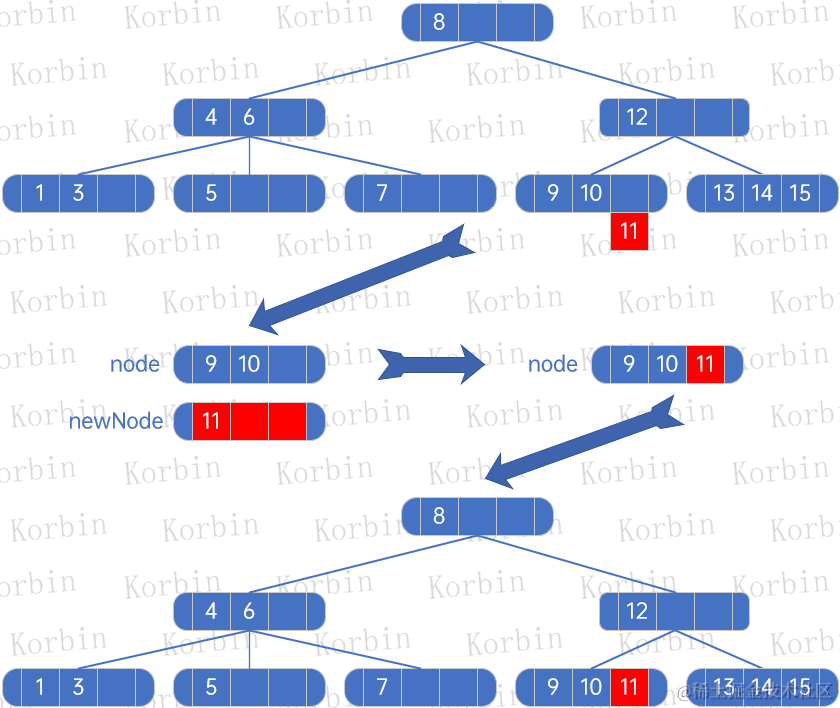
??然后插入元素11,直接插入即可:
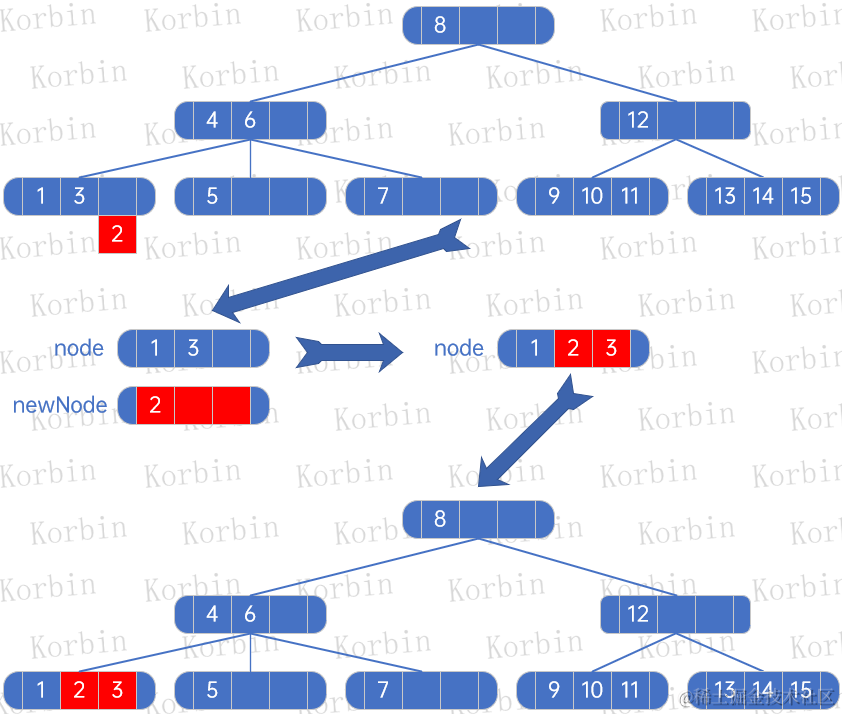
??然后插入元素2,直接插入即可:
??2-3-4樹創建的代碼與2-3樹創建代碼一致。
7.2.2 刪除2-3-4樹上的元素
??刪除邏輯與2-3樹一致,不再贅述。
7.3 B樹
??B樹(B tree)是一種平衡的多路查找樹,2-3樹和2-3-4樹都是B樹的特例,結點最大的孩子數目稱為B樹的階(order),因此,2-3樹是3階的B樹,2-3-4樹是4階的B樹。
??一個m階的B樹具有如下屬性:
??(1) 每個結點要么是葉子結點,要么擁有2~n個孩子,孩子數量是結點中元素數量+1,即2元素的結點擁有3個孩子,5元素的結點擁有6個孩子;
??(2) 所有葉子結點都在同一層次;
??(3) 若結點有孩子,則結點中的每個元素,都會有對應的一個小于該結點的孩子,和一個大于該結點的孩子;
??B樹的元素插入和刪除,與2-3樹、2-3-4樹一致。
7.4 B+樹
??B+樹是應文件系統所需而出的一種B樹的變形樹,在B樹中,每一個元素在該樹中只出現一次,有可能在葉子結點上,也有可能在分支結點上,而在B+樹中,出現在分支結點中的元素會被當作它們在該分支結點位置的中序后繼者(葉子結點)中再次列出,另外,每一個葉子結點都會保存一個指向后一葉子結點的指針。
??這樣一來,一棵B+樹就被分成了兩部分,主要部分是葉子結點,保存了所有數據信息和指針,而除葉子結點外的其他結點,均為索引。
??如下是一棵B樹和其對應的B+樹:
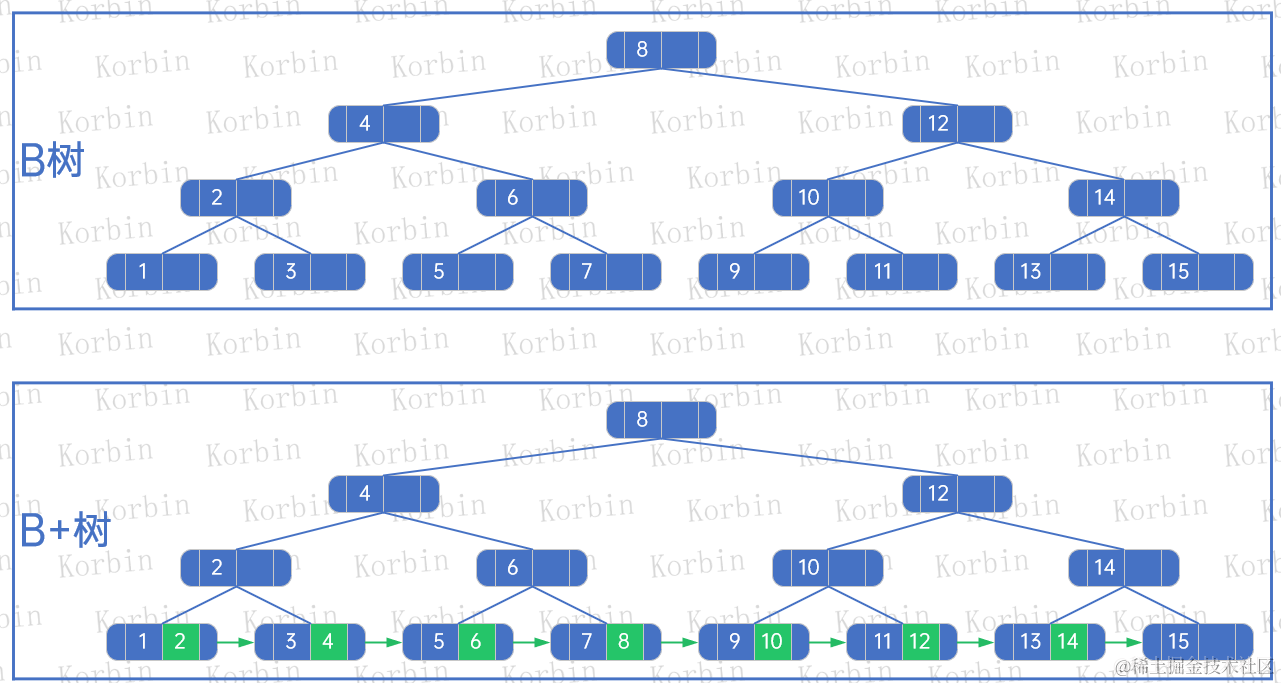
??可以看到,B+樹有很明確的特征:
??(1) 非葉子結點與B樹相同;
??(2) 葉子結點除了存儲元素外,還存放著中遍歷的下一個結點索引,例如結點1,如果進行中序遍歷的話,接下來的元素是2,因此將2的索引放在結點1上;
??(3) 葉子結點除了存儲元素外,還存放著后一葉子結點的指針,即其右兄弟或堂兄弟的指針;
7.4.1 B+樹的插入
??我們仍然按下述數組來生成B+樹:

??首先是第1、2個元素,直接插入:

??然后是第3個元素,按照2-3樹的插入方法,按如下插入:
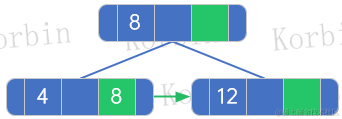
??注意看,與普通的2-3樹相比,結點4上多了一個指針,指向元素8,8是如何來的呢?是其parent上,比4大的第一個元素。
??另外,結點4不僅多了一個索引8,還有一個指針,指向了其兄弟結點,這個索引怎么來的呢?規則是——如果不需要重新生成樹,則一般直接插入即可,若需要生成樹,則:
??(1) 在重新生成樹前,記住被插入結點的leftBrother(記為originalLeftBrother)、rightBrother(記為originalRightBrother)和nextElement(記為originalNextElement);
??(2) 重新生成樹后,再重新迭代新的孩子,若originalLeftBrother不為null,則令originalLeftBrother的rightBrother為第一個新孩子;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,若最后一個新孩子沒有孩子,則令其nextElement和rightBrother為前面記住的originalNextElement和originalRightBrother,若最后一個新孩子有孩子,則nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
??(4) 然后迭代新孩子,若這些新孩子都沒有孩子結點,則除最后一個新孩子外,每一個新孩子的nextElement為新的parent的elements的同索引元素,每一個新孩子的rightBrother為下一個新孩子;若這些新孩子有孩子結點,則nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
??(5) 最后設置新生成樹的根結點的rightBrother和nextElement為null。
??在本例中,由于原結點沒有孩子,因此:
??(1) 被插入的結點是4和8所在的結點,originalLeftBrother=null,originalRightBrother=null,originalNextElement=null;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子是4所在的結點,因originalLeftBrother為null,因此不用處理;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子是12,因originalRightBrother和originalNextElement為null,直接設置結點12的nextElement為null,rightBrother為null;
??(4) 除最后一個孩子12外,只有一個新孩子,即結點4,它在所有孩子中索引是0,因此設置其nextElement為parent.elements[0],設置其rightBrother為下一個孩子,即結點12這個孩子;
??(5) 新生成的樹的根結點是結點[8],令其nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
??接下來插入元素1和元素13,直接插入,結點1、4對應的索引和指針不需要變更:
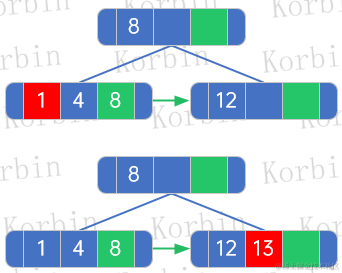
??接下來插入元素9,按照2-3樹的插入規則,首先把9插入元素12、13所在的結點,進行變換后,加上nextElement索引和rightBrother索引,按以下步驟執行:
??(1) 被插入的結點是12、13所在的結點,originalLeftBrother=[1,4]結點,originalRightBrother=null,originalNextElement=null;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子是9所在的結點,因此令originalLeftBrother,即[1,4]結點的rightBrother為結點9;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子是13,因originalRightBrother和originalNextElement為null,直接設置結點13的nextElement為null,rightBrother為null;
??(4) 除最后一個孩子13外,只有一個新孩子,即結點9,它在所有孩子中索引是0,因此設置其nextElement為parent.elements[0],即12,設置其rightBrother為下一個孩子,即結點13這個孩子;
??(5) 新生成的樹的根結點是結點[12],令其nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
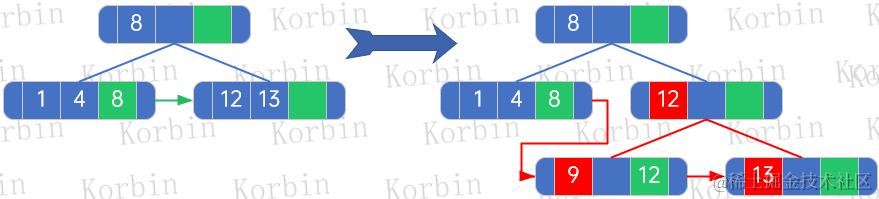
??然后進行二次變形,把元素12插入結點8,同樣的規則:
??(1) 被插入的結點是8所在的結點,originalLeftBrother=null,originalRightBrother=null,originalNextElement=null;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子是[1,4]結點,因originalLeftBrother為null,因此不需要處理;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子是13,因originalRightBrother和originalNextElement為null,直接設置結點13的nextElement為null,rightBrother為null;
??(4) 除最后一個孩子13外,有兩個孩子[1,4]和[9],在孩子數組中索引分別是0和1,因此child[1,4].nextElement=parent.elements[0]=8,child[1,4].rightBrother=parent.children[0+1]=child[9],child[9].nextElement=parent.elements[1]=12,child[9].rightBrother=parent.children[1+1]=child[13];
??(5) 新生成的樹的根結點是結點[8,12],令其nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
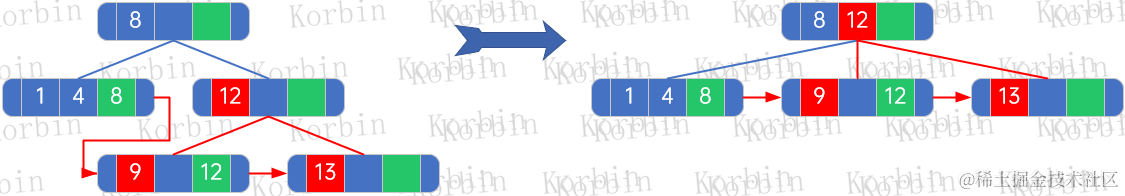
??元素10和15是直接插入,無需進行任何變更:
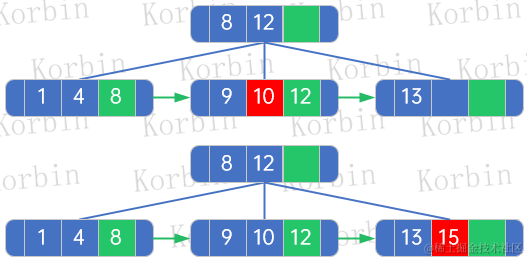
??來看元素6的插入,首先按插入規則進行處理:
??(1) 被插入的結點是[1,4]結點,originalLeftBrother=null,originalRightBrother=[9,10]結點,originalNextElement=8;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子是[1]結點,因originalLeftBrother為null,因此不需要處理;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子是[6]結點,令其nextElement=originalNextElement=8,令其rightBrother=originalRightBrother=[9,10]結點;
??(4) 除最后一個孩子6外,只有一個孩子[1],在孩子數組中索引是0,因此child[1].nextElement=parent.elements[0]=4,child[1].rightBrother=parent.children[0+1]=child[6];
??(5) 新生成的樹的根結點是結點[4],令其nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
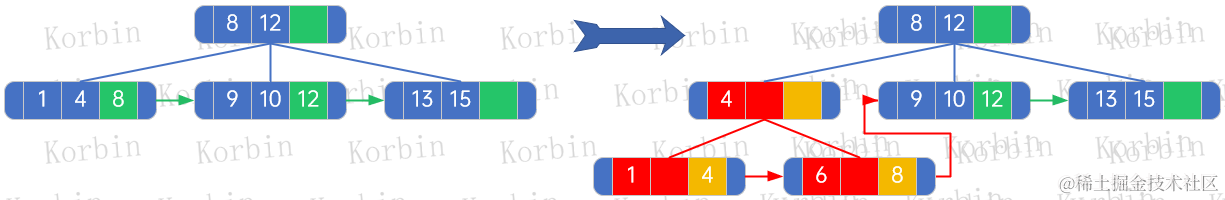
??然后繼續插入,被插入的結點為[8,12]:
??(1) 被插入的結點是[8,12]結點,originalLeftBrother=null,originalRightBrother=null,originalNextElement=null;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子是[4]結點,因originalLeftBrother為null,因此不需要處理;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子是[12]結點,令其nextElement=originalNextElement=null,令其rightBrother=originalRightBrother=null;
??(4) 除最后一個孩子[12]外,只有一個孩子[4],由于其有孩子結點,因此設置nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
??(5) 新生成的樹的根結點是結點[8],令其nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
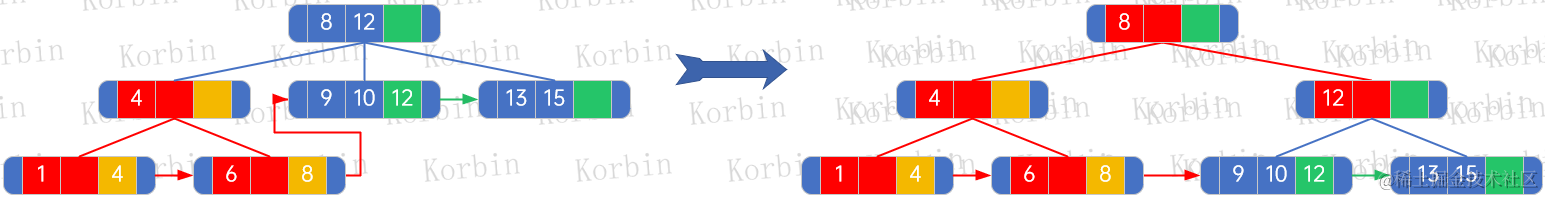
??其他元素的插入則按規則進行,不再贅述。
7.4.1 B+樹的元素刪除
??B+樹的刪除邏輯與2-3樹或2-3-4樹的刪除邏輯一致,但需要加上leftBrother、rightBrother和nextElement的處理,我們以以下B+樹為例進行處理:
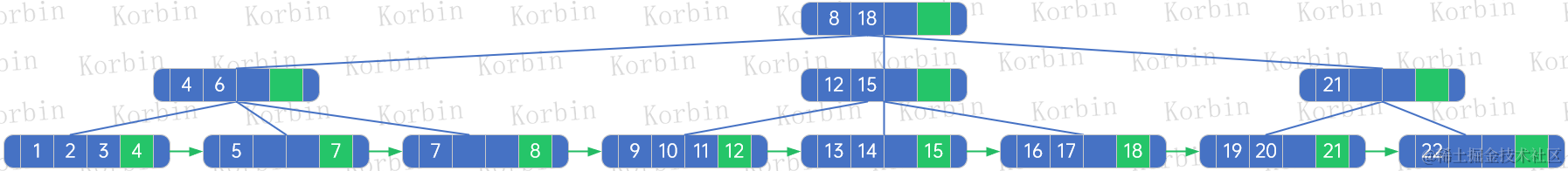
??首先來刪除元素7,由于該結點只有一個元素,相關結點的nextElement和rightElement需要進行調整,規則與新增時類似,如果不需要重新生成樹,則一般直接刪除元素即可,如果需要重新生成樹,則
??(1) 在重新生成樹前,記住被刪除結點父結點的第一個孩子的leftBrother(記為originalLeftBrother),和最后一個孩子的rightBrother(記為originalRightBrother)和nextElement(記為originalNextElement);
??(2) 重新生成樹后,若重新生成的樹有孩子,則迭代新的孩子,若originalLeftBrother不為null,則令originalLeftBrother的rightBrother為第一個新孩子;而若重新生成的樹沒有孩子,且originalLeftBrother不為null,則令originalLeftBrother的rightBrother為重新生成的樹的根結點;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,若重新生成的樹有孩子,且最后一個新孩子沒有孩子,則令其nextElement和rightBrother為前面記住的originalNextElement和originalRightBrother,若最后一個新孩子有孩子,則nextElement和rightBrother都為null;若重新生成的樹沒有孩子,則直接令重新生成的樹的根結點的nextElement為originalNextElement、rightBrother為originalRightBrother;
??(4) 若重新生成的樹有孩子,則迭代新孩子,若這些新孩子都沒有孩子結點,則除最后一個新孩子外,每一個新孩子的nextElement為新的parent的elements的同索引元素,每一個新孩子的rightBrother為下一個新孩子;若這些新孩子有孩子結點,則nextElement和rightBrother都為null;
??(5) 若重新生成的樹有孩子,則設置新生成樹的根結點的rightBrother和nextElement為null;。
??對于本例,則是如下:
??(1) 被刪除的結點是結點[7],其父是[4,6]結點,因此originalLeftBrother=null,originalNextElement=8,originalRightBrother=[9,10]結點;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,第一個孩子結點是結點[1,2],因originalLeftBrother=null,因此不進行處理;
??(3) 重新生成樹后,最后一個孩子結點是[4,5,6],因此令其nextElement=originalNextElement=8,令其rightBrother=originalRightBrother=[9,10]結點;
??(4) 然后迭代新孩子,除最后一個新孩子外,只有一個孩子[1,2],于是child[1,2].nextElement=child[1,2].parent.elements[0]=3,child[1,2].rightBrother=child[1,2].parent.children[0+1]=child[4,5,6];
??(5) 最后設置新生成樹的根結點的rightBrother和nextElement為null。
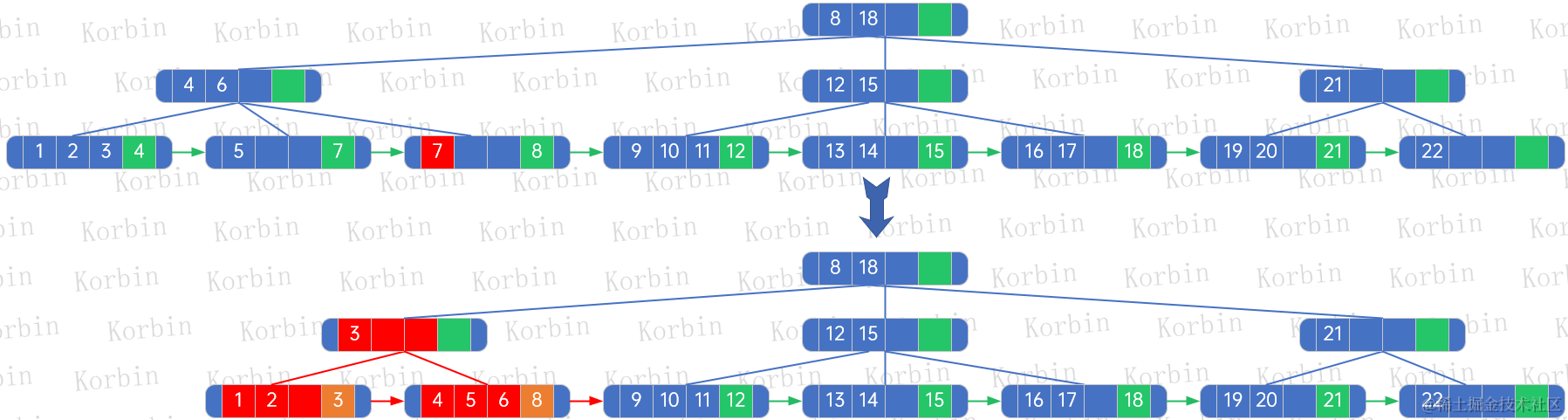
??然后刪除元素21,根據規則,直接與元素20替換即可,不需要進行其他變更:
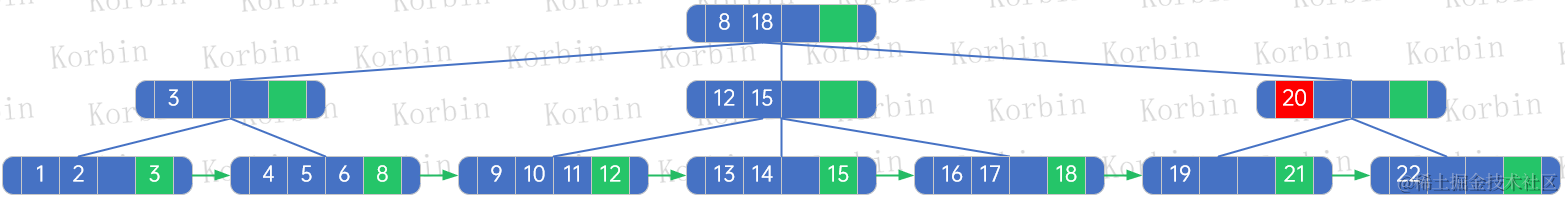
??然后刪除結點20,用元素19替換,然后按上述規則處理:
??(1) 被刪除的結點是結點[20],其父是[19]結點,因此originalLeftBrother=[16,17]結點,originalNextElement=null,originalRightBrother=null;
??(2) 重新生成樹后,該樹沒有孩子,因此令originalLeftBrother.rightBrother=重新生成的樹的根結點,即結點[19,22];
??(3) 重新生成樹后,該樹沒有孩子,因此令node[19,22].nextElement=originalNextElement=null,node[19,22].rightBrother=originalRightBrother=null;
??(4) 由于重新生成的樹沒有孩子,因此不做第四步處理;
??(5) 由于新生成的樹沒有孩子,因此不做第五步處理。
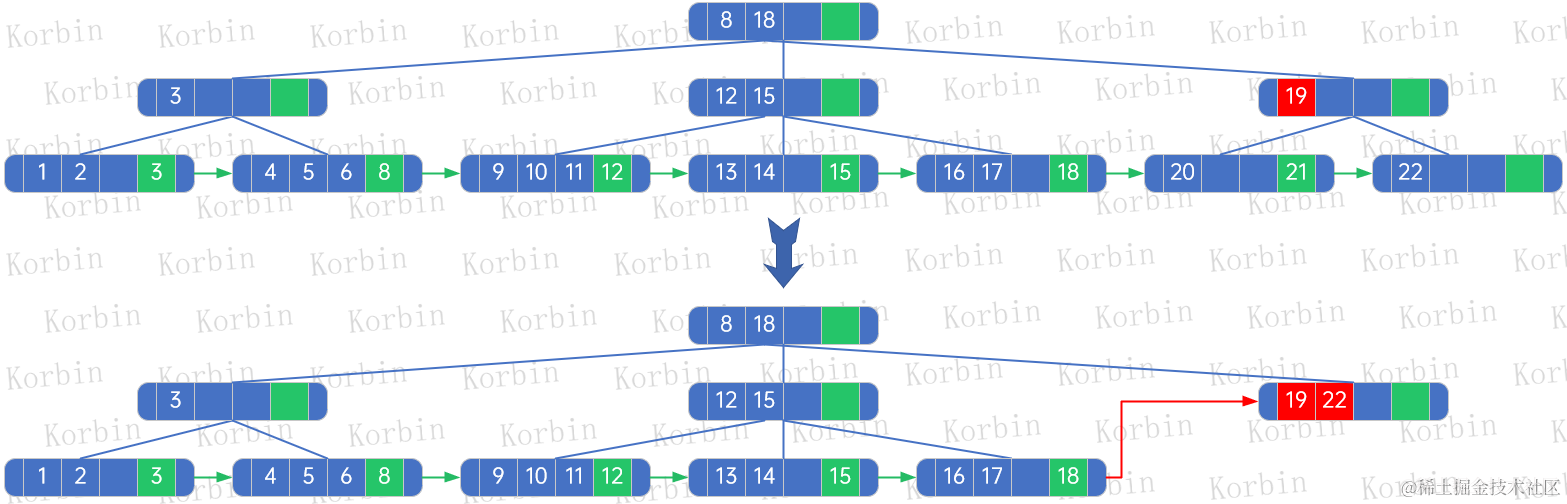
??然后繼續處理,這時被插入的結點變為結點[8,18],它沒有父結點,因此只需要重新構建樹即可,所有結點的nextElement和rightBrother都不需要調整:
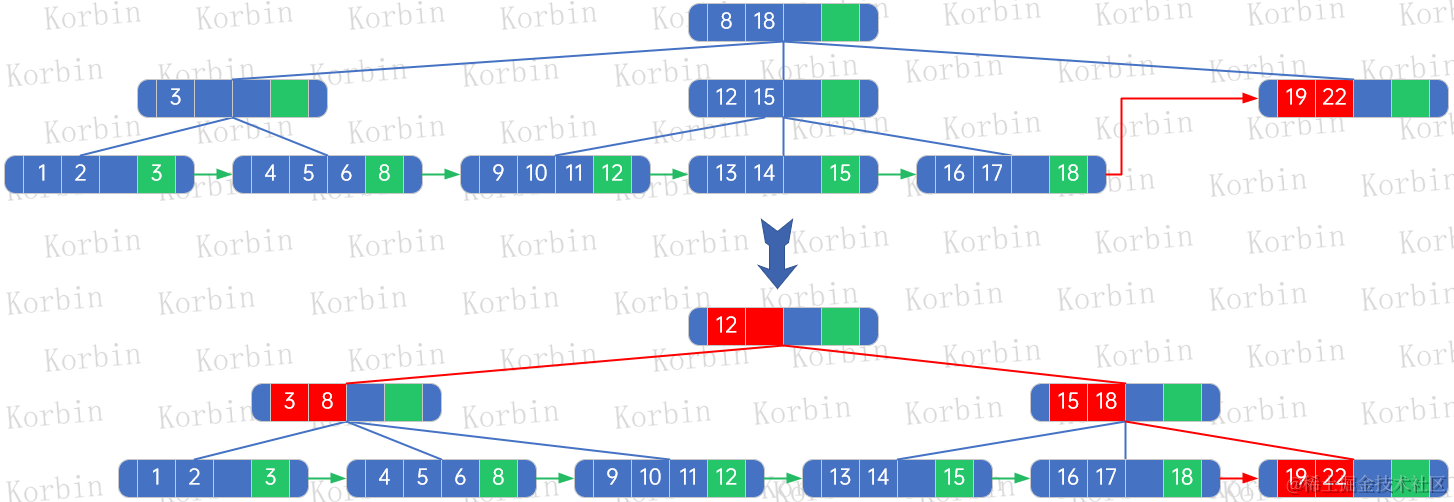
??其他元素的刪除都依上述規則處理即可。
7.5 代碼實現
??根據上文描述,結點定義代碼如下所示:
import lombok.Data;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;/*** multi way search tree node** @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-21 17:42:56**/
@Data
public class MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {/*** children, the array length must be 2 or 3 for 2-3 tree, and must be 2 or 3 or 4 for 2-3-4 tree**/private MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children;/*** elements, the array length must be 1 or 2 for 2-3 tree, and must be 1 or 2 or 3 for 2-3-4 tree**/private T[] elements;/*** left brother**/private MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> leftBrother;/*** next element value for inorder traversal**/private T nextElement;/*** parent node**/private MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> parent;/*** right brother**/private MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> rightBrother;/*** add an child**/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void addChild(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> child) {if (null == children) {children = (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[]) Array.newInstance(child.getClass(), 0);}MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] newChildren = Arrays.copyOf(children, children.length + 1);newChildren[newChildren.length - 1] = child;Arrays.sort(newChildren, (o1, o2) -> o1.getMaxElement().compareTo(o2.getMinElement()));this.children = newChildren;child.setParent(this);}/*** add an element**/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void addElement(T element) {if (null == elements) {elements = (T[]) Array.newInstance(element.getClass(), 0);}T[] newE = Arrays.copyOf(elements, elements.length + 1);newE[newE.length - 1] = element;Arrays.sort(newE);this.elements = newE;}/*** get all element**/public String getData() {if (null == elements) {return "null";} else {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();builder.append("[");for (int i = 0; i < elements.length - 1; i++) {builder.append(elements[i]).append(",");}builder.append(elements[elements.length - 1]).append("]");return builder.toString();}}/*** get max element**/public T getMaxElement() {return elements[elements.length - 1];}/*** get min element**/public T getMinElement() {return elements[0];}/*** remove an child**/public void removeChild(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> child) {if (this.children.length == 1) {this.children = null;} else {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] newChildren = Arrays.copyOf(children, children.length - 1);List<MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>> childList = new ArrayList<>();for (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> c : children) {boolean contains = false;for (T t : child.getElements()) {if (Arrays.asList(c.getElements()).contains(t)) {contains = true;break;}}if (!contains) {childList.add(c);}}childList.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.getMaxElement().compareTo(o2.getMinElement()));this.children = childList.toArray(newChildren);}}/*** remove an element**/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void removeElement(T element) {if (this.elements.length == 1) {this.elements = null;} else {T[] newE = (T[]) Array.newInstance(elements[0].getClass(), elements.length - 1);List<T> newArray = new ArrayList<>();for (T t : elements) {if (t.compareTo(element) != 0) {newArray.add(t);}}this.elements = newArray.toArray(newE);}}/*** set rightBrother** @param rightBrother right brother* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-29 10:19:26**/public void setRightBrother(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> rightBrother) {if (null != rightBrother) {rightBrother.setLeftBrother(this);}this.rightBrother = rightBrother;}@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();builder.append("Data is ").append(getData());if (null != parent) {builder.append(", parent is ").append(parent.getData());} else {builder.append(", parent is null");}if (null != children) {builder.append(", children is {");for (int i = 0; i < children.length - 1; i++) {builder.append(children[i].getData()).append(", ");}builder.append(children[children.length - 1].getData()).append("}");} else {builder.append(", children is null");}if (null != nextElement) {builder.append(", next element is ").append(nextElement);} else {builder.append(", next element is null");}if (null != rightBrother) {builder.append(", next brother is ").append(rightBrother.getData());} else {builder.append(", next brother is null");}return builder.toString();}}
??而樹的生成、元素的刪除、元素的查找代碼如下所示:
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;/*** multi way search way** @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-21 08:57:24**/
public class MultiWaySearchTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {/*** root node**/private MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> root = new MultiWaySearchTreeNode<>();/*** insert newNode into node** @param node node to insert* @param newNode node to be inserted* @param isBPlusTree is to create a B plus tree* @param maxChildrenNumber max child number, for 2-3 tree is 3, for 2-3-4 tree is 4* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-22 17:58:59**/private void checkAndMoveUp(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node, MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> newNode,int maxChildrenNumber, boolean isBPlusTree) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();node.addElement(newNode.getElements()[0]);// if new node's elements' length little or equals than maxChildrenNumber - 1, then just only add newNode's// children into nodeif (null != newNode.getChildren()) {for (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> child : newNode.getChildren()) {node.addChild(child);}}if (node.getElements().length > maxChildrenNumber - 1) {// if new node's elements' length greater than maxChildrenNumber - 1// 會影響parent的第一個孩子的leftBrother的leftBrother,和最后一個孩子的rightBrotherMultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalLeftBrother = node.getLeftBrother();MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalRightBrother = node.getRightBrother();T originalNextElement = node.getNextElement();rebuildTree(node, maxChildrenNumber);if (isBPlusTree) {resetIndex(node, originalLeftBrother, originalRightBrother, originalNextElement);}if (null == parent) {root = node;} else {// remove old nodeparent.removeChild(node);// check and move upcheckAndMoveUp(parent, node, maxChildrenNumber, isBPlusTree);}}}/*** create tree from array** @param array array* @param maxChildrenNumber max child number, for 2-3 tree is 3, for 2-3-4 tree is 4* @param isBPlusTree is to create a B plus tree* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-22 17:59:48**/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void createTreeFromArray(T[] array, int maxChildrenNumber, boolean isBPlusTree) {int length = array.length;if (length < maxChildrenNumber) {Arrays.sort(array);root.setElements(array);return;}// if length little than maxElementNumber(maxChildrenNumber - 1), then copy to rootT[] elements = (T[]) Array.newInstance(array[0].getClass(), maxChildrenNumber - 1);if (maxChildrenNumber - 1 >= 0) {System.arraycopy(array, 0, elements, 0, maxChildrenNumber - 1);}Arrays.sort(elements);root.setElements(elements);for (int i = maxChildrenNumber - 1; i < length; i++) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node = root;while (null != node) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children = node.getChildren();elements = node.getElements();if (null == children) {// has to move up// find the element which index is length - 2MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> newNode = new MultiWaySearchTreeNode<>();newNode.addElement(array[i]);checkAndMoveUp(node, newNode, maxChildrenNumber, isBPlusTree);break;} else {// if element to be inserted little than elements[0], then use elements[0]if (array[i].compareTo(elements[0]) < 0) {node = node.getChildren()[0];} else {// find from last to first, if element to be inserted greater than elements[j], then use// children[j + 1]for (int j = elements.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if (array[i].compareTo(elements[j]) > 0) {node = node.getChildren()[j + 1];break;}}}}}}}/*** delete an element from tree** @param element element to be deleted* @param maxChildrenNumber max children number* @param isBPlusTree is a B plus tree* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-23 17:07:04**/public void deleteElement(T element, int maxChildrenNumber, boolean isBPlusTree) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node = root;while (null != node && null != node.getElements()) {List<T> elementList = Arrays.asList(node.getElements());if (elementList.contains(element)) {int elementsLength = elementList.size();MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children = node.getChildren();if (null == children) {// if this node is leaf nodeif (elementsLength > 1) {// if node's elements' length greater than 1node.removeElement(element);} else {// if node's elements' length equals 1MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();if (null == parent) {// if this node is root nodenode.removeElement(element);} else {// if this node is not root node// delete this nodemoveAndMerge(node, maxChildrenNumber, isBPlusTree);}}} else {// find the index of elementT[] elements = node.getElements();int delIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < elementsLength; i++) {if (element.compareTo(elements[i]) == 0) {delIndex = i;break;}}// find the max value of the number delIndex child treeMultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> toReplaceNode = children[delIndex];while (null != toReplaceNode) {if (null != toReplaceNode.getChildren()) {toReplaceNode = toReplaceNode.getChildren()[toReplaceNode.getChildren().length - 1];} else {break;}}if (null == toReplaceNode) {// child must not be nullbreak;}T toReplaceElement = toReplaceNode.getMaxElement();// use the max value of the number delIndex child tree to replace this elementnode.removeElement(element);node.addElement(toReplaceElement);if (isBPlusTree) {toReplaceNode.setNextElement(toReplaceElement);}// if child's elements' length greater than 1if (toReplaceNode.getElements().length > 1) {toReplaceNode.removeElement(toReplaceElement);} else {// if child's elements' length equals 1moveAndMerge(toReplaceNode, maxChildrenNumber, isBPlusTree);}}break;} else if (element.compareTo(node.getMinElement()) < 0) {// if element little than node's first element, than node change to node's first childif (null == node.getChildren()) {break;} else {node = node.getChildren()[0];}} else if (null != node.getChildren()) {// find from last element to first elementfor (int j = elementList.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {// if element greater than element[j], than node change to node's j+1 childif (element.compareTo(node.getElements()[j]) > 0) {node = node.getChildren()[j + 1];break;}}} else {break;}}}/*** find node by element** @param element element* @return node* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-28 15:08:35**/public MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> findNodeByElement(T element) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node = root;while (null != node) {T[] elements = node.getElements();if (null == elements) {return null;}for (T e : elements) {if (element.compareTo(e) == 0) {return node;}}MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children = node.getChildren();if (null != children) {if (element.compareTo(node.getMinElement()) < 0) {node = children[0];} else {// find from last element to first elementfor (int j = elements.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {// if element greater than element[j], than node change to node's j+1 childif (element.compareTo(node.getElements()[j]) > 0) {node = node.getChildren()[j + 1];break;}}}}}return null;}/*** reset left brother's nextElement and rightBrother and move and merge** @param node node to move* @param maxChildrenNumber max children number* @param isBPlusTree is a B+ tree* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-30 22:53:36**/private void moveAndMerge(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node, int maxChildrenNumber, boolean isBPlusTree) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();// if is a B+ tree, then parent's first child's leftBrother's rightBrother has to reset, rebuild tree's new// last child's nextElement and rightBrother has to resetMultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] parentChildren = parent.getChildren();MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalLeftBrother = parentChildren[0].getLeftBrother();MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalRightBrother = parentChildren[parentChildren.length - 1].getRightBrother();T originalNextElement = parentChildren[parentChildren.length - 1].getNextElement();parent.removeChild(node);moveAndMerge(parent, null, maxChildrenNumber);if (isBPlusTree) {resetIndex(parent, originalLeftBrother, originalRightBrother, originalNextElement);}}/*** move and merge,add all elements of parent's all children but not node into parent, add all children of parent's* all children but not node into parent, and then rebuild the tree** @param parent parent* @param node one child of parent or null* @param maxChildrenNumber max children number* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-27 16:17:39**/private void moveAndMerge(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> parent, MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node, int maxChildrenNumber) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children = parent.getChildren();if (null != children) {for (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> child : children) {if (null == node || child.getMinElement().compareTo(node.getMinElement()) != 0) {for (T element : child.getElements()) {// add all children's element into parentparent.addElement(element);}if (null != child.getChildren()) {// add all grand children into parentfor (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> grandChild : child.getChildren()) {parent.addChild(grandChild);}}// remove this childparent.removeChild(child);}}T[] elements = parent.getElements();int elementsLength = elements.length;// rebuild this treeif (elementsLength <= maxChildrenNumber - 1) {if (elementsLength == 3) {// if elements' length is 3, just need to build tree use these three elementsrebuildTree(parent, 3);} else {// iterate grand parentMultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> grandParent = parent.getParent();if (null != grandParent) {// if grand parent is not nullmoveAndMerge(grandParent, parent, maxChildrenNumber);}}} else {rebuildTree(parent, maxChildrenNumber);}}}/*** rebuild a tree** @param node to rebuild node* @param maxChildrenNumber max children number* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-28 20:53:34**/private void rebuildTree(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node, int maxChildrenNumber) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] children = node.getChildren();T[] elements = node.getElements();int elementsLength = elements.length;int shardNumber = (elementsLength % (maxChildrenNumber - 1) == 0 ? elementsLength / (maxChildrenNumber - 1) :elementsLength / (maxChildrenNumber - 1) + 1);List<MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>> rebuildNodeList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < shardNumber; i++) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> newNode = new MultiWaySearchTreeNode<>();for (int j = 0; j < maxChildrenNumber - 1; j++) {int index = i * (maxChildrenNumber - 1) + j;if (index < elementsLength) {newNode.addElement(elements[index]);node.removeElement(elements[index]);}}rebuildNodeList.add(newNode);}for (int i = 0; i < rebuildNodeList.size() - 1; i++) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> newNode = rebuildNodeList.get(i);node.addElement(newNode.getMaxElement());newNode.removeElement(newNode.getMaxElement());node.addChild(newNode);}node.addChild(rebuildNodeList.get(rebuildNodeList.size() - 1));int startChildIndex = 0;// rebuild childif (null != children) {for (MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> newNode : rebuildNodeList) {int childrenSize = startChildIndex + newNode.getElements().length + 1;for (int i = startChildIndex; i < childrenSize && i < children.length; i++) {newNode.addChild(children[i]);node.removeChild(children[i]);startChildIndex++;}}}}/*** reset next element and right brother** @param node to reset node's parent* @param originalLeftBrother node's or first child of it's parent's left brother* @param originalRightBrother node's or last child of it's parent's right brother* @param originalNextElement node's or last child of it's parent's next element* @author Korbin* @date 2023-12-04 15:40:09**/private void resetIndex(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> node, MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalLeftBrother,MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> originalRightBrother, T originalNextElement) {MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T>[] newParentChildren = node.getChildren();if (null != newParentChildren) {// rebuild tree has childrenif (null != originalLeftBrother) {// set right brother of original first child's left brother as new parent children's first nodeoriginalLeftBrother.setRightBrother(newParentChildren[0]);}if (null == newParentChildren[newParentChildren.length - 1].getChildren()) {// set right brother of new parent children's last child as original last child's right brothernewParentChildren[newParentChildren.length - 1].setRightBrother(originalRightBrother);// set next element of new parent children's last child as original last child's next elementnewParentChildren[newParentChildren.length - 1].setNextElement(originalNextElement);} else {newParentChildren[newParentChildren.length - 1].setNextElement(null);newParentChildren[newParentChildren.length - 1].setRightBrother(null);}// set all but last child of new parent's children's next element and right brotherT[] newElements = node.getElements();for (int i = 0; i < newParentChildren.length - 1; i++) {if (null == newParentChildren[i].getChildren()) {newParentChildren[i].setRightBrother(newParentChildren[i + 1]);newParentChildren[i].setNextElement(newElements[i]);} else {newParentChildren[i].setNextElement(null);newParentChildren[i].setRightBrother(null);}}node.setNextElement(null);node.setRightBrother(null);} else {// rebuild tree does not have childrenif (null != originalLeftBrother) {originalLeftBrother.setRightBrother(node);}// set right brother of new parent as original last child's right brothernode.setRightBrother(originalRightBrother);// set next element of new parent as original last child's next elementnode.setNextElement(originalNextElement);}}/*** set root** @param root root node* @author Korbin* @date 2023-11-27 16:20:42**/public void setRoot(MultiWaySearchTreeNode<T> root) {this.root = root;}}

“軟件工程教育”論壇 成功召開)




)





)
)





