hi,我是逸塵,一起學java吧
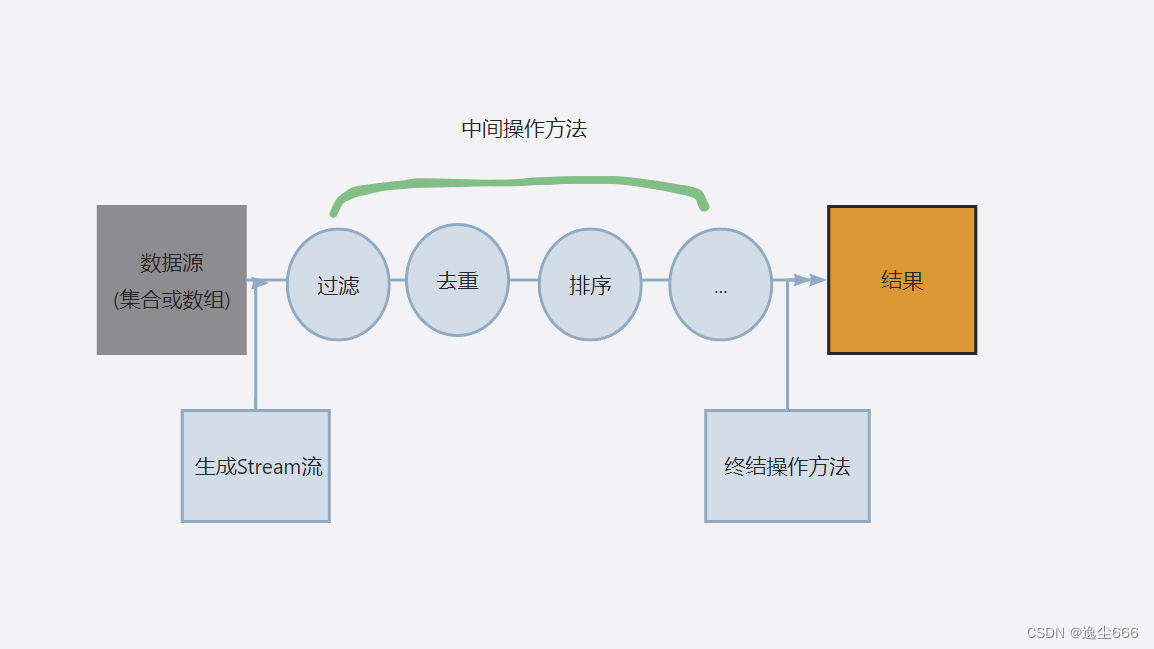
得益于Lambda所帶來的函數式編程,引入了一個全新的Stream流概念(就是都基本使用lambda的形式)。
流處理
我們首先理解什么是流處理,它類似于sql語句,可以執行非常復雜的過濾,映射,查找,收集等功能,且代碼很少,但是可讀性不高。字如其名,它的處理如同流淌的水一樣,或者可以理解為流水線一樣。
Stream流
Stream流也是流處理的一種,大多數流處理都是在Stream接口處理的,它是一個泛接口,所以它可以操作的元素是任意對象,他的操作可以用lambda去書寫(推薦)。
生成Stream流
Stream操作集合和數組的第一步是得到(生成)Stream流。
在Collection接口默認方法是stream()生成流。

 ?在數組中使用Arrays.stream(數組) /或Stream.of(數組);
?在數組中使用Arrays.stream(數組) /或Stream.of(數組);


?中間操作方法
其次我們就可以使用中間操作來處理這些元素對象。
這里舉出一些常見的API
- forEach : 逐一處理(遍歷)
- count:統計個數
- filter : 過濾元素 【數據過濾】
- distinct:去除重復元素?【數據過濾】
- limit : 取前幾個元素?【數據過濾】
- skip : 跳過前幾個?【數據過濾】
- map : 加工方法?【數據映射】
- allMatch:判斷流中的元素是否會全部符合某一個條件?【數據查找】
- concat:合并流
終結操作方法
終結操作方法調用以后流就無法使用了它是流的最后一個過程。
常見的有API有

單獨保存的操作方法
- collect() 方法配合collectors類將流的結果進行保存
處了stream流本身的方法我們還有兩個可以協助流操作的類
Collectors類
collectors是一個收集器類,可以將Stream流對象進行封裝,歸集,分組,是數據的收集,篩選出特殊的數據,可以復雜的統計。
1.toList()將流元素封裝到List集合 toSet()?toMap()類似
2.toCollection(Supplier<C> collectionFactory)?將流中的元素收集到指定類型的集合中的方法
即一個類型為?Supplier<C>?的函數式接口,其中?C?是要創建的集合類型。例如,如果我們想要創建一個?LinkedList?集合,可以這樣使用該方法:?
List<Integer> list = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));3.groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier)?
- 一個函數式接口?
classifier,表示如何對流中的元素進行分類。
例如,我們有一個字符串列表,并希望按照字符串長度分組:
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "peach", "grape","pear");
Map<Integer, List<String>> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(String::length));?在上面的代碼中,我們使用 String::length 函數式接口將字符串轉換為它的長度,并將其作為分類鍵。運行結果如下:
{4=[pear], 5=[apple, peach,grape], 6=[banana]}
需要注意的是,groupingBy() 方法返回的是一個 Map 對象,其中鍵是分類鍵.
Collectors.groupingBy() 方法還提供了第二個參數 downstream,用于進一步對分組的結果進行處理。例如,我們可以使用 Collectors.counting() 方法統計每個分組中元素的數量:
Map<Integer, Long> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(String::length, Collectors.counting()));上面的代碼中,我們使用 Collectors.counting() 方法作為 downstream 參數,統計了每個分組中元素的數量,并將結果封裝為 Long 類型。運行結果如下:
{4=1, 5=3, 6=1}
4.toConcurrentMap
將流中的元素收集到一個并發?Map?中的方法
ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> concurrentMap = Stream.of("a", "b", "c").collect(Collectors.toConcurrentMap(String::length,Function.identity()));在上面的例子中,我們使用 toConcurrentMap() 方法創建了一個并發 Map,它將字符串的長度作為鍵,字符串本身作為值。具體來說,這個方法接受兩個參數:
一個函數式接口 keyMapper,表示如何將流中的元素轉換成鍵;
一個函數式接口 valueMapper,表示如何將流中的元素轉換成值。
對于上述例子中的流,String::length 函數式接口將字符串轉換成它的長度,而 Function.identity() 函數式接口則將字符串映射成它本身。因此得到的結果為:
{1=a, 2=b, 3=c}
?5.以及averagingDouble計算元素平均值,maxBy返回符合條件的最大值,joining()按順序將元素連接成一個String類型數據,counting()統計個數等等
optional類
這是一個容器類
它的主要功能是針對NullpointerException空指針異常做處理,可以保證保存的值不為null。
of()返回一個value值等于參數的optional實例
ofNullable()是返回一個value值等于非null參數的optional實例
filter()是給定條件值匹配
empty()是靜態方法,返回一個空值的optional實例
案例?
我們上面的中間操作,其實是對我們的數據源進行加工。
這里我們簡單做了一個去重????????
package com.yd.yc;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Thirteen {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(6,88,4,5,22,22,6,66,7);//原數據printeach(list);//獲取stream,去重,收集器類重新封裝List<Integer> collect = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());printeach(collect);}//遍歷方法private static void printeach(List<Integer> list) {System.out.println("集合內容"+list);//逐一處理(遍歷)里面是lambdalist.stream().forEach(n-> System.out.println(n+""));}
}
某個公司的部門,分為開財務部門和開發部門,現在需要進行月中數據結算。
創建一張員工
| 部門 | 姓名 | 年齡 | 月工資 | 性別 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 開發部 | 張三 | 28 | 15000 | 男 |
| 開發部 | 李四 | 35 | 20000 | 女 |
| 開發部 | 王五 | 29 | 18000 | 男 |
| 財務部 | 趙六 | 33 | 16000 | 女 |
| 財務部 | 劉七 | 30 | 17000 | 男 |
| 財務部 | 陳八 | 27 | 14000 | 女 |
對應的是我們的員工實體類
public class Employee { private String name; private int age; private double monthlySalary; private String gender; private String department; public Employee(String name, int age, double monthlySalary, String gender, String department) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; this.gender = gender; this.department = department; } public String getName() { return name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public double getMonthlySalary() { return monthlySalary; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public String getDepartment() { return department; }
}分別篩選出2個部門的最高工資的員工信息,封裝成優秀員工對象topperformer
方案A
package com.yd.yc;import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;public class EmployeeTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Employee employee1 = new Employee("張三", 28, 15000, "男", "開發部");Employee employee2 = new Employee("李四", 35, 20000, "女", "開發部");Employee employee3 = new Employee("王五", 29, 18000, "男", "開發部");Employee employee4 = new Employee("趙六", 33, 16000, "女", "財務部");Employee employee5 = new Employee("劉七", 30, 17000, "男", "財務部");Employee employee6 = new Employee("陳八", 27, 44000, "女", "財務部");//測試//System.out.println(employee1.getName()); // 輸出:張三//System.out.println(employee2.getMonthlySalary()); // 輸出:20000.0ArrayList<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();employeeList.add(employee1);employeeList.add(employee2);employeeList.add(employee3);employeeList.add(employee4);employeeList.add(employee5);employeeList.add(employee6);//A方案//filter是過濾找到符合條件的元素//Collectors.maxBy去返回符合條件的最大值,Comparator.comparing(param),param : 這個參數是Function函數式對象,默認大,Comparator.reverseOrder()默認倒序Optional<Employee> result = employeeList.stream().filter(e -> "開發部".equals(e.getDepartment())).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getMonthlySalary)));//返回一個實體類對象Employee employee = result.get();System.out.println(employee.getName());//第二種寫法Employee resultOne= employeeList.stream().filter(e -> "財務部".equals(e.getDepartment())).max((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getMonthlySalary(), o2.getMonthlySalary())).get();//必須重寫toString才可以有內容System.out.println(resultOne);System.out.println(resultOne.getMonthlySalary());//包裝在一個優秀員工里List<Employee> topEmployees = new ArrayList<>();topEmployees.add(resultOne);topEmployees.add(employee);System.out.println(topEmployees);}
}
?方案B
//B方案Map<String, List<Employee>> groupedByDepartment = employeeList.stream()//分組.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDepartment));List<Employee> topEmployees = new ArrayList<>();for (List<Employee> departmentEmployees : groupedByDepartment.values()) {Employee topEmployee = departmentEmployees.stream().max(Comparator.comparingDouble(Employee::getMonthlySalary))//注意,如果一個部門沒有員工,那么這個方法將返回null//該方法在給定的流中找不到元素時返回一個默認值。.orElse(null);if (topEmployee != null) {topEmployees.add(topEmployee);}}System.out.println(topEmployees);
我們要注意的是stream流是方便操作集合/數組的手段,集合/數組才是開發中的目的。












)






SpringMVC的視圖)