0 背景
為了更好的檢測linux kernel中內存out-of-bounds、mem-corruption、use-after-free、invaild-free等問題,調研了kfence功能(該功能在linux kernel 5.12引入),幫助研發更好的分析與定位這類內存錯誤的問題。
一、kfence介紹
1.1 什么是kfence
kfence是Linux kernel中用于檢測內存錯誤的工具,如檢測out-of-bounds、mem-corruption、use-after-free、invaild-free等,利用該工具盡早發現項目中存在的內存錯誤問題,幫助研發人員快速定位分析這些問題。
1.2 kfence與kasan區別
| 檢測范圍 | 檢測原理 | 性能影響 | 適用場景 | |
| kfence | 小于1個page(4KB)的slab內存分配 | 1)采用page fence和canary pattern機制檢測內存out-of-bounds 2)采用data page的狀態標志(如已釋放的data page標記free)檢測內存use-after-free | 對內存的影響: kfence采用以大量內存開銷換取較小的性能干擾的思路,占用的內存較高,但可設定任意較小的num_objects來節約內存; 其他情況(全量模式及動態開啟)則需消耗GB級別的內存。 對性能的影響: 采樣模式下,對性能影響較小; 全量模式,對性能影響較大。 | 采樣模式下,由于性能開銷較小,可以在量產階段使用 |
| ksan | 適用整個kernel的內存分配,包括所有的slab、page、堆棧和全局內存等 | 采用shadow memory檢測機制 | 開銷較大 | 由于性能開銷大,一般在研發階段使用 |
二、kfence如何使用
kfence是linux kernel 5.12版本才引入,低內核版本想使用kfence工具,第一步需要功能移植(詳見第四節)。
2.1 打開kfence功能開關
CONFIG_KFENCE=y // kfence enable
CONFIG_KFENCE_SAMPLE_INTERVAL=500 // 采樣時間間隔,每隔500ms做檢測
CONFIG_KFENCE_NUM_OBJECTS=63 // kfence內存池size?以上宏控配置可以根據自己的需求來做配置。
2.2 debug
宏控配置的方式不夠靈活,不利于debug。因此,內核向用戶空間提供了一些節點,方便用戶動態調整配置:
??/sys/module/kfence/parameters/check_on_panic?
Y:更多的DEBUG信息
N:在生產環境中,減少系統崩潰時的額外開銷/sys/module/kfence/parameters/deferrable
Y:KFENCE可以延遲執行某些內存檢測操作,以減少對系統性能的影響
N:KFENCE 不會延遲執行內存檢測操作,而是立即執行/sys/kernel/debug/kfence/stats // 記錄kfence內存檢測的狀態信息??/sys/kernel/debug/kfence/objects? // 提供關于 KFENCE 管理的內存對象的信息echo -1 > /sys/module/kfence/parameters/sample_interval // 動態調整內存檢測的采樣時間間隔;0:表示關閉kfence功能,-1:所有符合(slab類型篩選)條件的內存均將進入kfence的監控范圍內
echo 100 > /sys/module/kfence/parameters/skip_covered_thresh // 當某個內存區域的訪問頻率超過這個閾值時,KFENCE 可能會選擇跳過對該區域的檢測2.3 查詢相關日志信息
當kfence捕獲到內存錯誤問題時,可以 cat /sys/kernel/debug/kfence/stats節點,查看total bugs計數會增加:
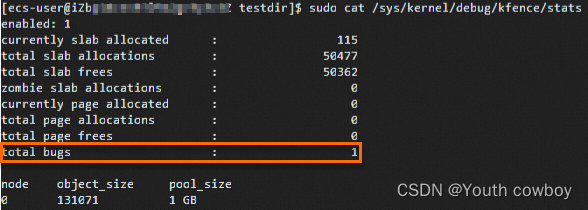
系統會將信息打印在dmesg,通過dmesg | grep -i kfence查詢kfence相關的錯誤日志信息:

2.4?如何獨立收集這些錯誤信息
在kfence捕獲到內存錯誤,將日志輸出到dmesg附近做hook,將日志獲取到。詳見3.2節。
三、kfence實現原理
3.1 檢測原理
3.1.1 slub/slab hook實現
需要在slub/slab的malloc、free流程中加入kfence模塊的hook,這樣在內存分配與釋放流程中才能走kfence的malloc、free流程,實現對內存錯誤的監控。
1)kfence alloc實現流程
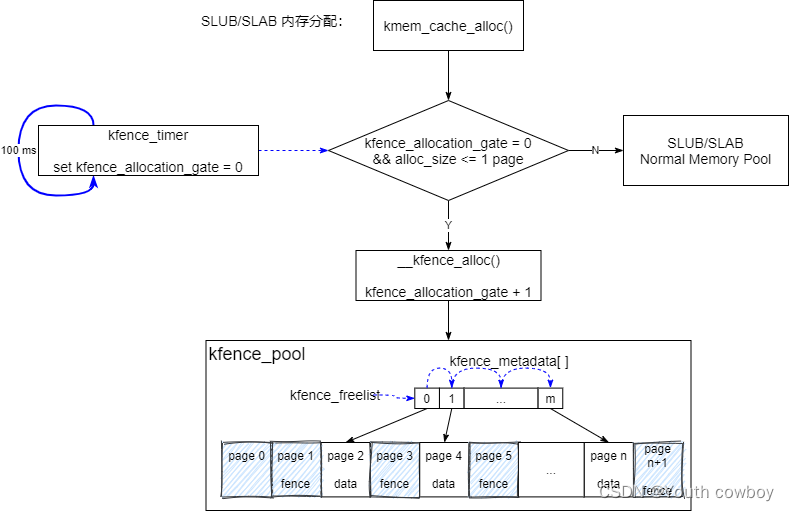
在初始化階段,kfence創建了自己的專有檢測內存池 kfence_pool,詳見3.3。
kmem_cache_alloc--->__kmem_cache_alloc_lru---> slab_alloc--->slab_alloc_node--->kfence_alloc,kfence alloc代碼實現,詳見3.4節。
2)kfence free實現流程
__kmem_cache_free--->__do_kmem_cache_free--->__cache_free--->__kfence_free,kfence free代碼實現,詳見3.5節。
3.1.2 use-after-free
obj 被 free 以后,對應 data page 也會被設置成不可訪問狀態。當被訪問時,立刻會觸發異常。

3.1.3 out-of-bounds或mem-corruption
內存訪問越界,可分為data page頁外訪問越界(out-of-bounds)和頁內訪問越界(mem-corruption)。
data page頁外訪問越界:
從 kfence_pool內存池中分配一個內存對象 obj,不管 obj 的實際大小有多大,都會占據一個 data page, data page 的兩邊加上了 fence page 電子柵欄,利用 MMU 的特性把 fence page 設置成不可訪問。如果對 data page 的訪問越過了 page 邊界, 即訪問page fence,就會立刻觸發異常,這種就稱為data page頁外訪問越界。
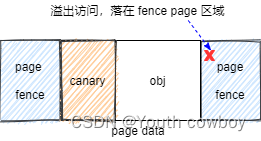
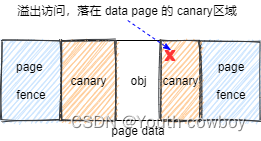
data page頁內訪問越界:
大部分情況下 obj 是小于一個 page 的,對于 data page 剩余空間系統使用 canary pattern 進行填充。這種操作是為了檢測超出了 obj 但還在 data page 范圍內的溢出訪問,這種就稱為data page頁內訪問越界。
頁內訪問越界發生時不會立刻觸發,只能在 obj free 時,通過檢測 canary pattern 被破壞來檢測到有 canary 區域的溢出訪問,這種異常訪問也被叫做mem-corruption.
3.1.4 invalid-free
當obj free 時,會檢查記錄的 malloc 信息,判斷是不是一次異常的 free,如內存重復釋放。
3.2 異常如何觸發&日志打印
1)use-after-free:KFENCE_ERROR_UAF類型的內存錯誤
當某個模塊的代碼中觸發了use-after-free,會走kernel原生的流程,調用kfence的kfence_handle_page_fault函數,進行錯誤日志的收集與打印。
// kernel/arch/arm/mm/fault.c /** Oops. The kernel tried to access some page that wasn't present.*/
static void
__do_kernel_fault(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long addr, unsigned int fsr,struct pt_regs *regs)
{const char *msg;/** Are we prepared to handle this kernel fault?*/if (fixup_exception(regs))return;/** No handler, we'll have to terminate things with extreme prejudice.*/if (addr < PAGE_SIZE) {msg = "NULL pointer dereference";} else {if (is_translation_fault(fsr) &&kfence_handle_page_fault(addr, is_write_fault(fsr), regs))return;msg = "paging request";}die_kernel_fault(msg, mm, addr, fsr, regs);
}
kfence_handle_page_fault函數中判斷是KFENCE_ERROR_OOB或KFENCE_ERROR_UAF類型的錯誤,調用kfence_report_error將錯誤的日志打印到dmesg.
bool kfence_handle_page_fault(unsigned long addr, bool is_write, struct pt_regs *regs)
{const int page_index = (addr - (unsigned long)__kfence_pool) / PAGE_SIZE;struct kfence_metadata *to_report = NULL;enum kfence_error_type error_type;unsigned long flags;if (!is_kfence_address((void *)addr))return false;if (!READ_ONCE(kfence_enabled)) /* If disabled at runtime ... */return kfence_unprotect(addr); /* ... unprotect and proceed. */atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_BUGS]);// 判斷是KFENCE_ERROR_OOB(data page頁外越界訪問)還是KFENCE_ERROR_UAF(use-after-free)類型的錯誤// 如果page_index是奇數,說明是fence page被訪問,KFENCE_ERROR_OOB類型錯誤// 如果page_index是偶數,說明是data page釋放后被訪問,KFENCE_ERROR_UAF類型錯誤if (page_index % 2) {/* This is a redzone, report a buffer overflow. */struct kfence_metadata *meta;int distance = 0;meta = addr_to_metadata(addr - PAGE_SIZE);if (meta && READ_ONCE(meta->state) == KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED) {to_report = meta;/* Data race ok; distance calculation approximate. */distance = addr - data_race(meta->addr + meta->size);}meta = addr_to_metadata(addr + PAGE_SIZE);if (meta && READ_ONCE(meta->state) == KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED) {/* Data race ok; distance calculation approximate. */if (!to_report || distance > data_race(meta->addr) - addr)to_report = meta;}if (!to_report)goto out;raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&to_report->lock, flags);to_report->unprotected_page = addr;error_type = KFENCE_ERROR_OOB;/** If the object was freed before we took the look we can still* report this as an OOB -- the report will simply show the* stacktrace of the free as well.*/} else {to_report = addr_to_metadata(addr);if (!to_report)goto out;raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&to_report->lock, flags);error_type = KFENCE_ERROR_UAF;/** We may race with __kfence_alloc(), and it is possible that a* freed object may be reallocated. We simply report this as a* use-after-free, with the stack trace showing the place where* the object was re-allocated.*/}out:if (to_report) {kfence_report_error(addr, is_write, regs, to_report, error_type);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&to_report->lock, flags);} else {/* This may be a UAF or OOB access, but we can't be sure. */// 無法判斷是哪種類型的內存錯誤kfence_report_error(addr, is_write, regs, NULL, KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID);}return kfence_unprotect(addr); /* Unprotect and let access proceed. */
}2)out-of-bounds(頁外訪問越界):KFENCE_ERROR_OOB類型的內存錯誤
同上
3)out-of-bounds(頁內訪問越界):KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION類型的內存錯誤
在kfence allock階段初始化canary區域(詳見3.4),kfence free階段去檢測canary區域是否被訪問過或破壞,如果被破壞,傳入KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION類型的參數,調用kfence_report_error函數,打印錯誤日志信息。
static void kfence_guarded_free(void *addr, struct kfence_metadata *meta, bool zombie)
{....../* Check canary bytes for memory corruption. */for_each_canary(meta, check_canary_byte);......
}/* __always_inline this to ensure we won't do an indirect call to fn. */
static __always_inline void for_each_canary(const struct kfence_metadata *meta, bool (*fn)(u8 *))
{// pageaddr為這塊data page的首地址const unsigned long pageaddr = ALIGN_DOWN(meta->addr, PAGE_SIZE);unsigned long addr;/** We'll iterate over each canary byte per-side until fn() returns* false. However, we'll still iterate over the canary bytes to the* right of the object even if there was an error in the canary bytes to* the left of the object. Specifically, if check_canary_byte()* generates an error, showing both sides might give more clues as to* what the error is about when displaying which bytes were corrupted.*//* Apply to left of object. */// 檢查左邊的canary區域for (addr = pageaddr; addr < meta->addr; addr++) {if (!fn((u8 *)addr))break;}/* Apply to right of object. */// 檢查右邊的canary區域for (addr = meta->addr + meta->size; addr < pageaddr + PAGE_SIZE; addr++) {if (!fn((u8 *)addr))break;}
}/* Check canary byte at @addr. */
static inline bool check_canary_byte(u8 *addr)
{struct kfence_metadata *meta;unsigned long flags;// 如果data page的canary區域沒被訪問過或破壞,直接返回,否則,調用kfence_report_error函數,打印錯誤日志信息if (likely(*addr == KFENCE_CANARY_PATTERN(addr)))return true;atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_BUGS]);// 根據內存地址找到元數據對象meta = addr_to_metadata((unsigned long)addr);raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&meta->lock, flags);// 傳入KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION類型的參數,調用kfence_report_error函數,打印錯誤日志信息kfence_report_error((unsigned long)addr, false, NULL, meta, KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&meta->lock, flags);return false;
}/** Get the canary byte pattern for @addr. Use a pattern that varies based on the* lower 3 bits of the address, to detect memory corruptions with higher* probability, where similar constants are used.*/
#define KFENCE_CANARY_PATTERN(addr) ((u8)0xaa ^ (u8)((unsigned long)(addr) & 0x7))4)invalid-free:KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE類型的內存錯誤
kfence free階段去檢測本次內存釋放是否為invalid-free,調用kfence_report_error函數,傳入KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE類型的參數,打印錯誤日志信息。
static void kfence_guarded_free(void *addr, struct kfence_metadata *meta, bool zombie)
{......// 如果內存塊沒有被分配就釋放(包含了double-free)或內存塊分配與釋放時的地址不一樣,認為本次釋放是invalid-freeif (meta->state != KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED || meta->addr != (unsigned long)addr) {/* Invalid or double-free, bail out. */atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_BUGS]);// 調用kfence_report_error函數,傳入KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE類型的參數,打印錯誤日志信息kfence_report_error((unsigned long)addr, false, NULL, meta,KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&meta->lock, flags);return;}......
}下面看如何打印錯誤的日志信息,kfence_report_error錯誤的日志信息會打印到dmesg.
#define pr_err printkvoid kfence_report_error(unsigned long address, bool is_write, struct pt_regs *regs,const struct kfence_metadata *meta, enum kfence_error_type type)
{....../* Print report header. */switch (type) {// 打印data page頁外訪問越界的錯誤日志信息到dmesgcase KFENCE_ERROR_OOB: {const bool left_of_object = address < meta->addr;pr_err("BUG: KFENCE: out-of-bounds %s in %pS\n\n", get_access_type(is_write),(void *)stack_entries[skipnr]);pr_err("Out-of-bounds %s at 0x%p (%luB %s of kfence-#%td):\n",get_access_type(is_write), (void *)address,left_of_object ? meta->addr - address : address - meta->addr,left_of_object ? "left" : "right", object_index);break;}// 打印use-after-free的錯誤日志信息到dmesgcase KFENCE_ERROR_UAF:pr_err("BUG: KFENCE: use-after-free %s in %pS\n\n", get_access_type(is_write),(void *)stack_entries[skipnr]);pr_err("Use-after-free %s at 0x%p (in kfence-#%td):\n",get_access_type(is_write), (void *)address, object_index);break;// 打印data page頁內(canary區域內存破壞)訪問越界的錯誤日志信息到dmesgcase KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION:pr_err("BUG: KFENCE: memory corruption in %pS\n\n", (void *)stack_entries[skipnr]);pr_err("Corrupted memory at 0x%p ", (void *)address);print_diff_canary(address, 16, meta);pr_cont(" (in kfence-#%td):\n", object_index);break;case KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID:pr_err("BUG: KFENCE: invalid %s in %pS\n\n", get_access_type(is_write),(void *)stack_entries[skipnr]);pr_err("Invalid %s at 0x%p:\n", get_access_type(is_write),(void *)address);break;// 打印invalid-free的錯誤日志信息到dmesgcase KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE:pr_err("BUG: KFENCE: invalid free in %pS\n\n", (void *)stack_entries[skipnr]);pr_err("Invalid free of 0x%p (in kfence-#%td):\n", (void *)address,object_index);break;}......
}
3.3 kfence init
kfence初始化主要做了幾件事情:
1)判斷kfence_sample_interval采樣間隔是否為0,設置為0,說明kfence功能disable
2)分配kfence pool內存池,默認內存塊是255,分配(255+1)*2 = 512個page,包括255個data page,256個fence page,1個不可用的data page(放在第一個位置,記為page 0)
3)初始化metadata數組,記錄每個data page內存塊狀態信息
4)初始化freelist空閑鏈表,記錄data page內存塊的是否可分配
5)將所有fence page和page 0設置為不可訪問
// mm/kfence/core.cvoid __init kfence_init(void)
{stack_hash_seed = get_random_u32();/* Setting kfence_sample_interval to 0 on boot disables KFENCE. */// 1. 采樣間隔為0,kfence disableif (!kfence_sample_interval)return;// 2. 初始化kfence pool內存池if (!kfence_init_pool_early()) {pr_err("%s failed\n", __func__);return;}kfence_init_enable();
}
static bool __init kfence_init_pool_early(void)
{unsigned long addr;if (!__kfence_pool)return false;addr = kfence_init_pool();......
}#define KFENCE_POOL_SIZE ((CONFIG_KFENCE_NUM_OBJECTS + 1) * 2 * PAGE_SIZE) // 默認為256*2個page
static struct list_head kfence_freelist = LIST_HEAD_INIT(kfence_freelist); // 空閑鏈表,記錄空閑的內存塊
struct kfence_metadata kfence_metadata[CONFIG_KFENCE_NUM_OBJECTS]; // metadata數組,記錄data page內存塊狀態信息
/** Initialization of the KFENCE pool after its allocation.* Returns 0 on success; otherwise returns the address up to* which partial initialization succeeded.*/
static unsigned long kfence_init_pool(void)
{unsigned long addr;struct page *pages;int i;if (!arch_kfence_init_pool())return (unsigned long)__kfence_pool;addr = (unsigned long)__kfence_pool;// 將虛擬地址轉換為物理地址pages = virt_to_page(__kfence_pool);/** Set up object pages: they must have PG_slab set, to avoid freeing* these as real pages.** We also want to avoid inserting kfence_free() in the kfree()* fast-path in SLUB, and therefore need to ensure kfree() correctly* enters __slab_free() slow-path.*/// 默認分配512個pagefor (i = 0; i < KFENCE_POOL_SIZE / PAGE_SIZE; i++) {struct slab *slab = page_slab(nth_page(pages, i));if (!i || (i % 2))continue;__folio_set_slab(slab_folio(slab));
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCGslab->memcg_data = (unsigned long)&kfence_metadata[i / 2 - 1].objcg |MEMCG_DATA_OBJCGS;
#endif}/** Protect the first 2 pages. The first page is mostly unnecessary, and* merely serves as an extended guard page. However, adding one* additional page in the beginning gives us an even number of pages,* which simplifies the mapping of address to metadata index.*/for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) {if (unlikely(!kfence_protect(addr)))return addr;addr += PAGE_SIZE;}for (i = 0; i < CONFIG_KFENCE_NUM_OBJECTS; i++) {struct kfence_metadata *meta = &kfence_metadata_init[i];/* Initialize metadata. */INIT_LIST_HEAD(&meta->list);raw_spin_lock_init(&meta->lock);// 記錄內存塊狀態為unusedmeta->state = KFENCE_OBJECT_UNUSED;// 記錄內存塊地址meta->addr = addr; /* Initialize for validation in metadata_to_pageaddr(). */// 加入空閑鏈表list_add_tail(&meta->list, &kfence_freelist);/* Protect the right redzone. */// 將fence page設置為不可訪問if (unlikely(!kfence_protect(addr + PAGE_SIZE)))goto reset_slab;// 下一個data page的首地址addr += 2 * PAGE_SIZE; // 每個page data間隔8KB,因為中間隔了一個fence page}/** Make kfence_metadata visible only when initialization is successful.* Otherwise, if the initialization fails and kfence_metadata is freed,* it may cause UAF in kfence_shutdown_cache().*/smp_store_release(&kfence_metadata, kfence_metadata_init);return 0;reset_slab:for (i = 0; i < KFENCE_POOL_SIZE / PAGE_SIZE; i++) {struct slab *slab = page_slab(nth_page(pages, i));if (!i || (i % 2))continue;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCGslab->memcg_data = 0;
#endif__folio_clear_slab(slab_folio(slab));}return addr;
}3.4 kfence alloc
Kfence alloc主要做了以下幾個事情:
1)從kfence pool內存池中找到空閑內存塊(data page)
2)向data page canary區域寫入固定的數據,便于在free階段做檢測
void *__kfence_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s, size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{unsigned long stack_entries[KFENCE_STACK_DEPTH];size_t num_stack_entries;u32 alloc_stack_hash;/** Perform size check before switching kfence_allocation_gate, so that* we don't disable KFENCE without making an allocation.*/// 如果申請的內存超過1個page(4KB),直接返回NULLif (size > PAGE_SIZE) {atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_SKIP_INCOMPAT]);return NULL;}/** Skip allocations from non-default zones, including DMA. We cannot* guarantee that pages in the KFENCE pool will have the requested* properties (e.g. reside in DMAable memory).*/if ((flags & GFP_ZONEMASK) ||(s->flags & (SLAB_CACHE_DMA | SLAB_CACHE_DMA32))) {atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_SKIP_INCOMPAT]);return NULL;}/** Skip allocations for this slab, if KFENCE has been disabled for* this slab.*/// 標志位設置了 ?SLAB_SKIP_KFENCE?,說明對于該 slab 已經禁用了 KFENCE,直接返回 NULL/*除此之外,還有以下標志位SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT?:用于標記 slab 是可回收的,即可以被內存回收機制重新使用。??SLAB_PANIC?:在出現內存分配失敗時,會觸發內核崩潰轉儲,用于故障排除。 ??SLAB_CONSISTENCY_CHECKS?:啟用一致性檢查,用于檢測內存污染或其他問題。??SLAB_RED_ZONE?:在分配的內存塊兩端添加紅色區域,用于檢測寫越界操作。??SLAB_STORE_USER?:在 slab 元數據中存儲用戶定義的數據。 ??SLAB_DEBUG_OBJECTS?:用于開啟額外的對象調試功能。*/if (s->flags & SLAB_SKIP_KFENCE)return NULL;// kfence_allocation_gate > 1,說明還沒到下一輪采樣時間點if (atomic_inc_return(&kfence_allocation_gate) > 1)return NULL;
#ifdef CONFIG_KFENCE_STATIC_KEYS/** waitqueue_active() is fully ordered after the update of* kfence_allocation_gate per atomic_inc_return().*/if (waitqueue_active(&allocation_wait)) {/** Calling wake_up() here may deadlock when allocations happen* from within timer code. Use an irq_work to defer it.*/irq_work_queue(&wake_up_kfence_timer_work);}
#endifif (!READ_ONCE(kfence_enabled))return NULL;num_stack_entries = stack_trace_save(stack_entries, KFENCE_STACK_DEPTH, 0);/** Do expensive check for coverage of allocation in slow-path after* allocation_gate has already become non-zero, even though it might* mean not making any allocation within a given sample interval.** This ensures reasonable allocation coverage when the pool is almost* full, including avoiding long-lived allocations of the same source* filling up the pool (e.g. pagecache allocations).*/alloc_stack_hash = get_alloc_stack_hash(stack_entries, num_stack_entries);if (should_skip_covered() && alloc_covered_contains(alloc_stack_hash)) {atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_SKIP_COVERED]);return NULL;}return kfence_guarded_alloc(s, size, flags, stack_entries, num_stack_entries,alloc_stack_hash);
}static void *kfence_guarded_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cache, size_t size, gfp_t gfp,unsigned long *stack_entries, size_t num_stack_entries,u32 alloc_stack_hash)
{// 以kfence_metadata結構體管理元數據struct kfence_metadata *meta = NULL;unsigned long flags;struct slab *slab;void *addr;const bool random_right_allocate = prandom_u32_max(2);const bool random_fault = CONFIG_KFENCE_STRESS_TEST_FAULTS &&!prandom_u32_max(CONFIG_KFENCE_STRESS_TEST_FAULTS);/* Try to obtain a free object. */// 從kfence list中獲取空閑的內存塊raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&kfence_freelist_lock, flags);if (!list_empty(&kfence_freelist)) {meta = list_entry(kfence_freelist.next, struct kfence_metadata, list);list_del_init(&meta->list);}......meta->addr = metadata_to_pageaddr(meta);/* Unprotect if we're reusing this page. */// 如果該data page被標記為已釋放狀態,則取消該標記if (meta->state == KFENCE_OBJECT_FREED)kfence_unprotect(meta->addr);/** Note: for allocations made before RNG initialization, will always* return zero. We still benefit from enabling KFENCE as early as* possible, even when the RNG is not yet available, as this will allow* KFENCE to detect bugs due to earlier allocations. The only downside* is that the out-of-bounds accesses detected are deterministic for* such allocations.*/if (random_right_allocate) {/* Allocate on the "right" side, re-calculate address. */meta->addr += PAGE_SIZE - size;meta->addr = ALIGN_DOWN(meta->addr, cache->align);}addr = (void *)meta->addr;/* Update remaining metadata. */metadata_update_state(meta, KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED, stack_entries, num_stack_entries);/* Pairs with READ_ONCE() in kfence_shutdown_cache(). */WRITE_ONCE(meta->cache, cache);meta->size = size;meta->alloc_stack_hash = alloc_stack_hash;raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&meta->lock, flags);alloc_covered_add(alloc_stack_hash, 1);/* Set required slab fields. */slab = virt_to_slab((void *)meta->addr);slab->slab_cache = cache;
#if defined(CONFIG_SLUB)slab->objects = 1;
#elif defined(CONFIG_SLAB)slab->s_mem = addr;
#endif/* Memory initialization. */// 初始化 canary區域for_each_canary(meta, set_canary_byte);/** We check slab_want_init_on_alloc() ourselves, rather than letting* SL*B do the initialization, as otherwise we might overwrite KFENCE's* redzone.*/if (unlikely(slab_want_init_on_alloc(gfp, cache)))memzero_explicit(addr, size);if (cache->ctor)cache->ctor(addr);if (random_fault)kfence_protect(meta->addr); /* Random "faults" by protecting the object. */atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_ALLOCATED]);atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_ALLOCS]);return addr;
}
下面看下是如何向data page的canary區域寫入固定的數據:
/* Write canary byte to @addr. */
static inline bool set_canary_byte(u8 *addr)
{*addr = KFENCE_CANARY_PATTERN(addr);return true;
}3.5 kfence free
kfence free主要做了以下事情:
1) data page釋放后,將狀態設置為‘不可訪問狀態’
2)檢查data page的canary區域是否被破壞
3)將釋放的內存還回到kfence pool內存池或空閑鏈表
void __kfence_free(void *addr)
{// 地址轉換為 ?struct kfence_metadata? 結構體指針 ?meta?。// 這里的 ?struct kfence_metadata? 是內存分配元數據結構,用于追蹤內存分配和釋放的相關信息。struct kfence_metadata *meta = addr_to_metadata((unsigned long)addr);#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCGKFENCE_WARN_ON(meta->objcg);
#endif/** If the objects of the cache are SLAB_TYPESAFE_BY_RCU, defer freeing* the object, as the object page may be recycled for other-typed* objects once it has been freed. meta->cache may be NULL if the cache* was destroyed.*/// 碼判斷了 ?meta? 對應的緩存是否存在,并且緩存的標志為 ?SLAB_TYPESAFE_BY_RCU?,// 如果滿足條件,則調用 ?call_rcu? 來延遲釋放對象。這是因為一些緩存類型在被釋放后可能會// 立即被重新利用,因此需要通過 RCU 機制來確保安全釋放。if (unlikely(meta->cache && (meta->cache->flags & SLAB_TYPESAFE_BY_RCU)))call_rcu(&meta->rcu_head, rcu_guarded_free);else// 否則,立即釋放內存kfence_guarded_free(addr, meta, false);
}static void kfence_guarded_free(void *addr, struct kfence_metadata *meta, bool zombie)
{struct kcsan_scoped_access assert_page_exclusive;unsigned long flags;bool init;raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&meta->lock, flags);if (meta->state != KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED || meta->addr != (unsigned long)addr) {/* Invalid or double-free, bail out. */atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_BUGS]);kfence_report_error((unsigned long)addr, false, NULL, meta,KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&meta->lock, flags);return;}/* Detect racy use-after-free, or incorrect reallocation of this page by KFENCE. */kcsan_begin_scoped_access((void *)ALIGN_DOWN((unsigned long)addr, PAGE_SIZE), PAGE_SIZE,KCSAN_ACCESS_SCOPED | KCSAN_ACCESS_WRITE | KCSAN_ACCESS_ASSERT,&assert_page_exclusive);if (CONFIG_KFENCE_STRESS_TEST_FAULTS)kfence_unprotect((unsigned long)addr); /* To check canary bytes. *//* Restore page protection if there was an OOB access. */// if (meta->unprotected_page) {memzero_explicit((void *)ALIGN_DOWN(meta->unprotected_page, PAGE_SIZE), PAGE_SIZE);kfence_protect(meta->unprotected_page);meta->unprotected_page = 0;}/* Mark the object as freed. */// data page釋放后,需要將狀態設置為‘不可訪問狀態’,若被訪問,立即觸發use-after-free異常metadata_update_state(meta, KFENCE_OBJECT_FREED, NULL, 0);init = slab_want_init_on_free(meta->cache);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&meta->lock, flags);alloc_covered_add(meta->alloc_stack_hash, -1);/* Check canary bytes for memory corruption. */// 檢查data page的canary區域是否被破壞,即是否被訪問過for_each_canary(meta, check_canary_byte);/** Clear memory if init-on-free is set. While we protect the page, the* data is still there, and after a use-after-free is detected, we* unprotect the page, so the data is still accessible.*/if (!zombie && unlikely(init))memzero_explicit(addr, meta->size);/* Protect to detect use-after-frees. */kfence_protect((unsigned long)addr);kcsan_end_scoped_access(&assert_page_exclusive);// 如果不是僵死進程,則將釋放的內存還回到kfence pool內存池或空閑鏈表if (!zombie) {/* Add it to the tail of the freelist for reuse. */raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&kfence_freelist_lock, flags);KFENCE_WARN_ON(!list_empty(&meta->list));list_add_tail(&meta->list, &kfence_freelist);raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&kfence_freelist_lock, flags);atomic_long_dec(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_ALLOCATED]);atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_FREES]);} else {/* See kfence_shutdown_cache(). */atomic_long_inc(&counters[KFENCE_COUNTER_ZOMBIES]);}
}
3.6 metadata
metadata用于記錄內存塊的狀態。
3.7?核心數據結構
/* Alloc/free tracking information. */
// 用于跟蹤分配和釋放的信息
struct kfence_track {pid_t pid; // 進行分配/釋放內存操作的進程IDint cpu; // 進行操作時的CPUu64 ts_nsec; // 記錄內存分配或釋放時間點int num_stack_entries; // 函數調用棧數量unsigned long stack_entries[KFENCE_STACK_DEPTH]; // 函數調用棧存放數組
};/* KFENCE error types for report generation. */
// 異常類型定義
enum kfence_error_type {KFENCE_ERROR_OOB, /* Detected a out-of-bounds access. */KFENCE_ERROR_UAF, /* Detected a use-after-free access. */KFENCE_ERROR_CORRUPTION, /* Detected a memory corruption on free. */KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID, /* Invalid access of unknown type. */KFENCE_ERROR_INVALID_FREE, /* Invalid free. */
};/* KFENCE object states. */
// 定義元數據對象的狀態
enum kfence_object_state {KFENCE_OBJECT_UNUSED, /* Object is unused. */KFENCE_OBJECT_ALLOCATED, /* Object is currently allocated. */KFENCE_OBJECT_FREED, /* Object was allocated, and then freed. */
};/* KFENCE metadata per guarded allocation. */
// 用于記錄data page的信息
struct kfence_metadata {struct list_head list; /* Freelist node; access under kfence_freelist_lock. */struct rcu_head rcu_head; /* For delayed freeing. *//** Lock protecting below data; to ensure consistency of the below data,* since the following may execute concurrently: __kfence_alloc(),* __kfence_free(), kfence_handle_page_fault(). However, note that we* cannot grab the same metadata off the freelist twice, and multiple* __kfence_alloc() cannot run concurrently on the same metadata.*/raw_spinlock_t lock;/* The current state of the object; see above. */enum kfence_object_state state; // 內存塊的狀態/** Allocated object address; cannot be calculated from size, because of* alignment requirements.** Invariant: ALIGN_DOWN(addr, PAGE_SIZE) is constant.*/unsigned long addr; // data page內存塊的地址/** The size of the original allocation.*/size_t size; // 原始size/** The kmem_cache cache of the last allocation; NULL if never allocated* or the cache has already been destroyed.*/struct kmem_cache *cache; // 用于分配小塊內存的高速緩存,減少頻繁地分配和釋放內存的開銷/** In case of an invalid access, the page that was unprotected; we* optimistically only store one address.*/unsigned long unprotected_page;/* Allocation and free stack information. */struct kfence_track alloc_track; // 記錄內存分配的信息struct kfence_track free_track; // 記錄內存釋放的信息/* For updating alloc_covered on frees. */u32 alloc_stack_hash; // 使用 ?alloc_stack_hash? 來比較分配和釋放時的棧信息哈希值,可以提高對釋放操作的準確性和安全性
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCGstruct obj_cgroup *objcg;
#endif
};
四、如何移植kfence
kfence功能在linux kernel 5.12被引入,低內核版本要使用kfence,需做功能移植,如Alibaba Cloud Linux 3在內核版本5.10.134-16支持kfence功能。
功能移植,主要分為三個模塊,如下:
1)移植框架代碼
這部分是kfence功能代碼,主要文件,如下:
include/linux/kfence.h
init/main.c
lib/Kconfig.debug
lib/Kconfig.kfence
mm/Makefile
mm/kfence/Makefile
mm/kfence/core.c
mm/kfence/kfence.h
mm/kfence/report.c
2)移植ARM平臺代碼
這部分是kfence在arm平臺的hook代碼,主要文件,如下:
arch/arm64/Kconfig
arch/arm64/include/asm/kfence.h
arch/arm64/mm/fault.c
arch/arm64/mm/mmu.c
3)移植slub模塊中的hook代碼
這部分是kfence在slub內存分配器的hook代碼,主要文件,如下:
include/linux/slub_def.h
mm/kfence/core.c
mm/slub.c





)


: input delay約束和output delay約束)










