0 前言
🔥 優質競賽項目系列,今天要分享的是
🚩 基于深度學習的植物識別算法研究與實現
🥇學長這里給一個題目綜合評分(每項滿分5分)
- 難度系數:4分
- 工作量:4分
- 創新點:4分
🧿 更多資料, 項目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
2 相關技術
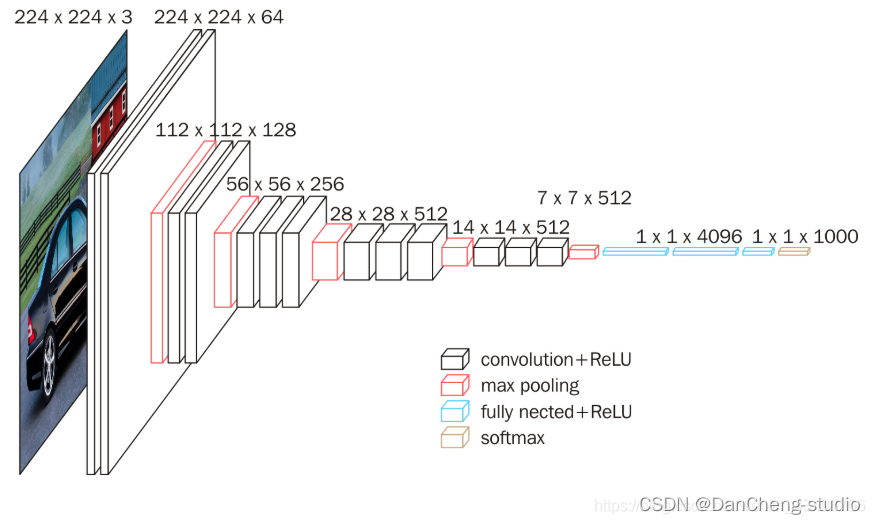
2.1 VGG-Net模型
Google DeepMind公司研究員與牛津大學計算機視覺組在2014年共同研發出了一種全新的卷積神經網絡–VGG-
Net。在同年舉辦的ILSVRC比賽中,該網絡結構模型在分類項目中取得了十分出色的成績,由于其簡潔性和實用性,使得其在當時迅速,飛快地成為了最受歡迎的卷積神經網絡模型。VGG-
Net卷積神經網絡在近年來衍生出了A-
E七種不同的層次結構,本次研究使用其中的D結構,也就是VGG-16Net結構,該結構中包含了13個卷積層,5個池化層和3個全連接層。針對所有的卷積層,使用相同的5x5大小的卷積核,針對所有的池化層,使用相同的3x3大小的池化核。VGG-
Net結構如圖所示。

2.2 VGG-Net在植物識別的優勢
在針對植物識別問題上,VGG-Net有著一些相較于其他神經網絡的優勢,主要包括以下幾點:
(1) 卷積核,池化核大小固定
網絡中所有的卷積核大小固定為3x3,所有的池化核大小固定為5x5。這樣在進行卷積和池化操作的時候,從數據中提取到的特征更加明顯,同時在層與層的連接時,信息的丟失會更少,更加方便后續對于重要特征的提取和處理。
(2) 特征提取更全面
VGG-
Net網絡模型中包含了13個卷積層。卷積層數目越多,對于特征的提取更加的全面。由于需要對于植物的姿態、顏色等進行判定,植物的特征較多,需要在提取時更加的全面,細致,才有可能得到一個更加準確的判定。VGG-
Net符合條件。
(3) 網絡訓練誤差收斂速度較快
VGG-
Net網絡在訓練時收斂速度相對較快,能夠較快地得到預期的結果。具有這一特點的原因有兩個,一個是網絡中每一個卷積層和池化層中的卷積核大小與池化核大小固定,另一個就是對于各個隱藏層的參數初始化方法使用專門針對ReLU激活函數的Kaiming正態初始化方法。
3 VGG-Net的搭建
本次研究基于Pytorch深度學習框架進行網絡的搭建,利用模塊化的設計思想,構建一個類,來對于整個的網絡進行結構上的封裝。這樣搭建的好處是可以隱藏實現的內部細節,提高代碼的安全性,增強代碼的復用效率,并且對于一些方法,通過在內部集成,可以方便之后對于其中方法的調用,提升代碼的簡潔性。
在網絡搭建完成后,將數據集傳入網絡中進行訓練,經過一段時間后即可得到植物識別的分類識別結果。
3.1 Tornado簡介
Tornado全稱Tornado Web
Server,是一個用Python語言寫成的Web服務器兼Web應用框架,由FriendFeed公司在自己的網站FriendFeed中使用,被Facebook收購以后框架在2009年9月以開源軟件形式開放給大眾。
(1) 優勢
- 輕量級web框架
- 異步非阻塞IO處理方式
- 出色的抗負載能力
- 優異的處理性能,不依賴多進程/多線程,一定程度上解決C10K問題
- WSGI全棧替代產品,推薦同時使用其web框架和HTTP服務器
(2) 關鍵代碼
? class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
? def get(self):
? self.render("index.html")
? def post(self):keras.backend.clear_session()img = Image.open(BytesIO(self.request.files['image'][0]['body']))img = imgb_img = Image.new('RGB', (224, 224), (255, 255, 255))size = img.sizeif size[0] >= size[1]:rate = 224 / size[0]new_size = (224, int(size[1] * rate))img = img.resize(new_size, Image.ANTIALIAS).convert("RGB")b_img.paste(img, (0, random.randint(0, 224 - new_size[1])))else:rate = 224 / size[1]new_size = (int(size[0] * rate), 224)img = img.resize(new_size, Image.ANTIALIAS).convert("RGB")b_img.paste(img, (random.randint(0, 224 - new_size[0]), 0))if self.get_argument("method", "mymodel") == "VGG16":Model = load_model("VGG16.h5")else:Model = load_model("InceptionV3.h5")data = orc_img(Model,b_img)self.write(json.dumps({"code": 200, "data": data}))def make_app():template_path = "templates/"static_path = "./static/"return tornado.web.Application([(r"/", MainHandler),], template_path=template_path, static_path=static_path, debug=True)?
? def run_server(port=8000):
? tornado.options.parse_command_line()
? app = make_app()
? app.listen(port)
? print("\n服務已啟動 請打開 http://127.0.0.1:8000 ")
? tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()4 Inception V3 神經網絡
GoogLeNet對網絡中的傳統卷積層進行了修改,提出了被稱為 Inception
的結構,用于增加網絡深度和寬度,提高深度神經網絡性能。從Inception V1到Inception
V4有4個更新版本,每一版的網絡在原來的基礎上進行改進,提高網絡性能。
4.1 網絡結構
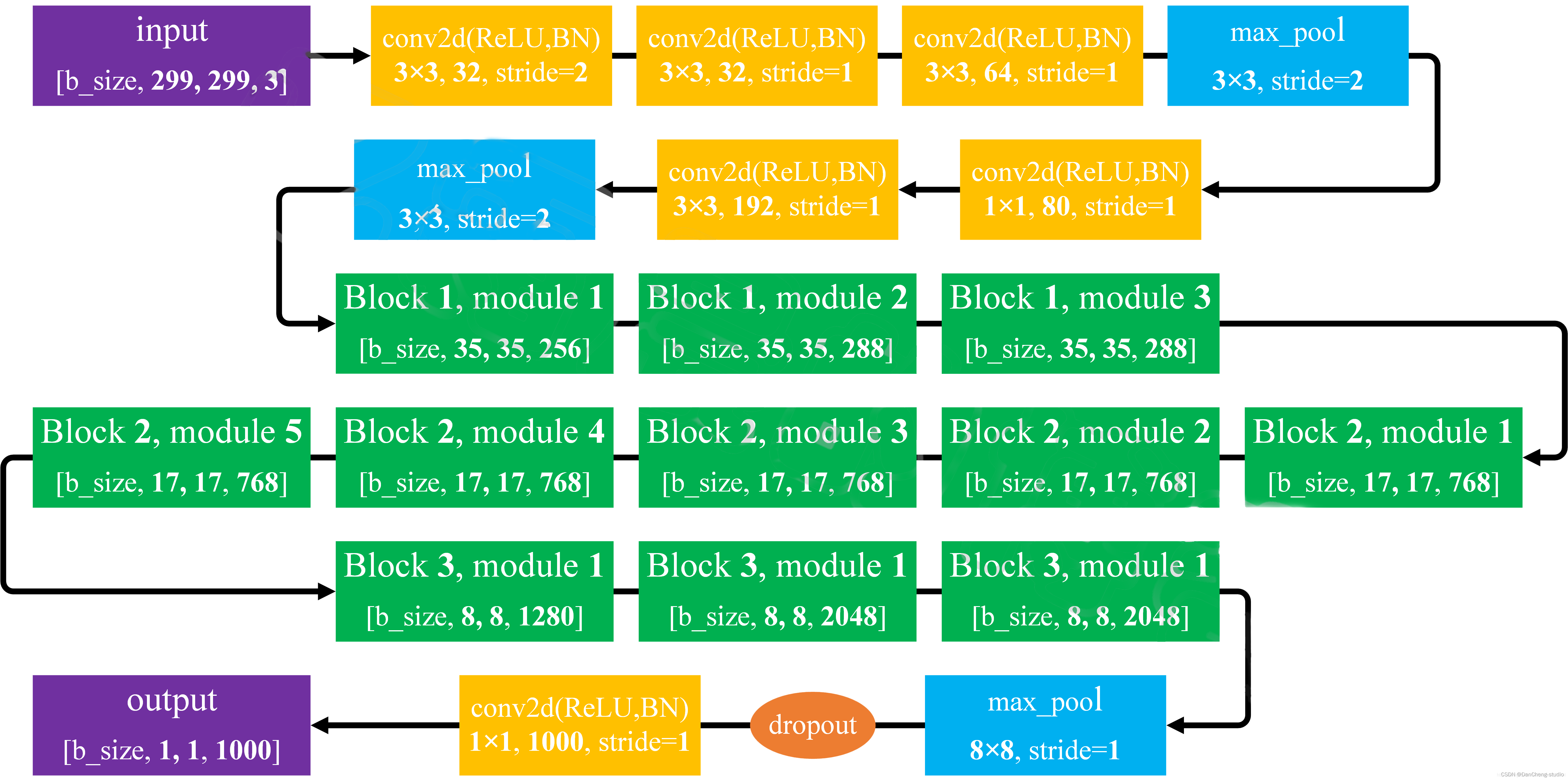
inception結構的作用(inception的結構和作用)
作用:代替人工確定卷積層中過濾器的類型或者確定是否需要創建卷積層或者池化層。即:不需要人為決定使用什么過濾器,是否需要創建池化層,由網絡自己學習決定這些參數,可以給網絡添加所有可能值,將輸入連接起來,網絡自己學習需要它需要什么樣的參數。
inception主要思想
用密集成分來近似最優的局部稀疏解(如上圖)
- 采用不同大小的卷積核意味著有不同大小的感受野,最后的拼接意味著不同尺度特征的融合。
- 之所以卷積核大小采用1x1、3x3和5x5,主要是為了方便對齊。設定卷積步長stride=1之后,只要分別設定padding = 0、1、2,采用same卷積可以得到相同維度的特征,然后這些特征直接拼接在一起。
- 很多地方都表明pooling挺有效,所以Inception里面也嵌入了pooling。
- 網絡越到后面特征越抽象,且每個特征涉及的感受野也更大,隨著層數的增加,3x3和5x5卷積的比例也要增加。
- 最終版inception,加入了1x1 conv來降低feature map厚度。
5 開始訓練
5.1 數據集
訓練圖像按照如下方式進行分類,共分為9文件夾。
5.2 關鍵代碼
?
from keras.utils import Sequenceimport math? class SequenceData(Sequence):
? def __init__(self, batch_size, target_size, data):# 初始化所需的參數self.batch_size = batch_sizeself.target_size = target_sizeself.x_filenames = datadef __len__(self):# 讓代碼知道這個序列的長度num_imgs = len(self.x_filenames)return math.ceil(num_imgs / self.batch_size)def __getitem__(self, idx):# 迭代器部分batch_x = self.x_filenames[idx * self.batch_size: (idx + 1) * self.batch_size]imgs = []y = []for x in batch_x:img = Image.open(x)b_img = Image.new('RGB', self.target_size, (255, 255, 255))size = img.sizeif size[0] >= size[1]:rate = self.target_size[0] / size[0]new_size = (self.target_size[0], int(size[1] * rate))img = img.resize(new_size, Image.ANTIALIAS).convert("RGB")b_img.paste(img, (0, random.randint(0, self.target_size[0] - new_size[1])))else:rate = self.target_size[0] / size[1]new_size = (int(size[0] * rate), self.target_size[0])img = img.resize(new_size, Image.ANTIALIAS).convert("RGB")b_img.paste(img, (random.randint(0, self.target_size[0] - new_size[0]), 0))img = b_imgif random.random() < 0.1:img = img.convert("L").convert("RGB")if random.random() < 0.2:img = img.rotate(random.randint(0, 20)) # 隨機旋轉一定角度if random.random() < 0.2:img = img.rotate(random.randint(340, 360)) # 隨 旋轉一定角度imgs.append(img.convert("RGB"))x_arrays = 1 - np.array([np.array(i) for i in imgs]).astype(float) / 255 # 讀取一批圖片batch_y = to_categorical(np.array([labels.index(x.split("/")[-2]) for x in batch_x]), len(labels))return x_arrays, batch_y?
5.3 模型預測
利用我們訓練好的 vgg16.h5 模型進行預測,相關代碼如下:
?
def orc_img(model,image):
? img =np.array(image)
? img = np.array([1 - img.astype(float) / 255])
? predict = model.predict(img)
? index = predict.argmax()
? print("CNN預測", index)
? target = target_name[index]index2 = np.argsort(predict)[0][-2]target2 = target_name[index2]index3 = np.argsort(predict)[0][-3]target3 = target_name[index3]return {"target": target,"predict": "%.2f" % (float(list(predict)[0][index]) * 64),"target2": target2,"predict2": "%.2f" % (float(list(predict)[0][index2]) * 64),}6 效果展示
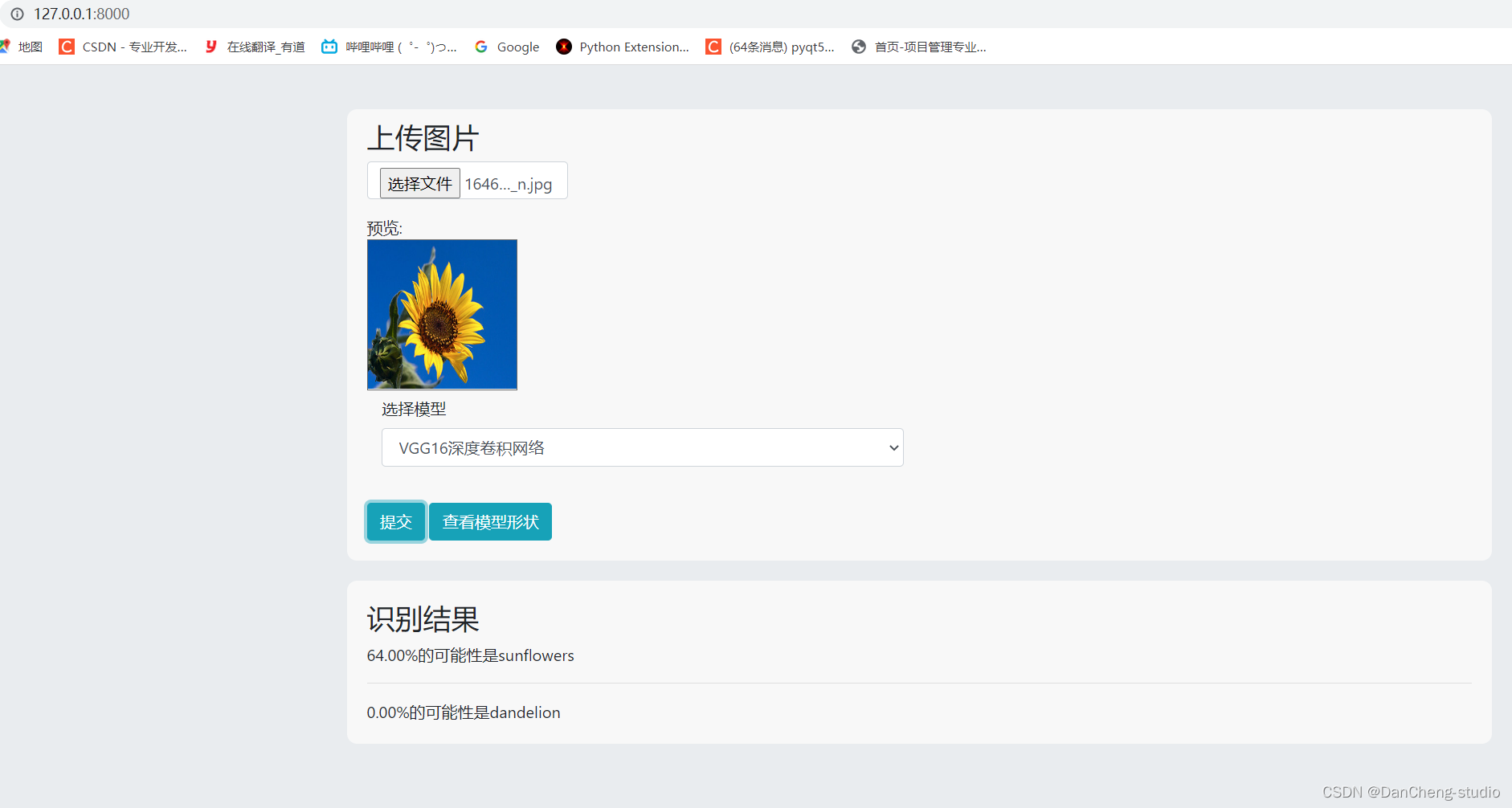
6.1 主頁面展示
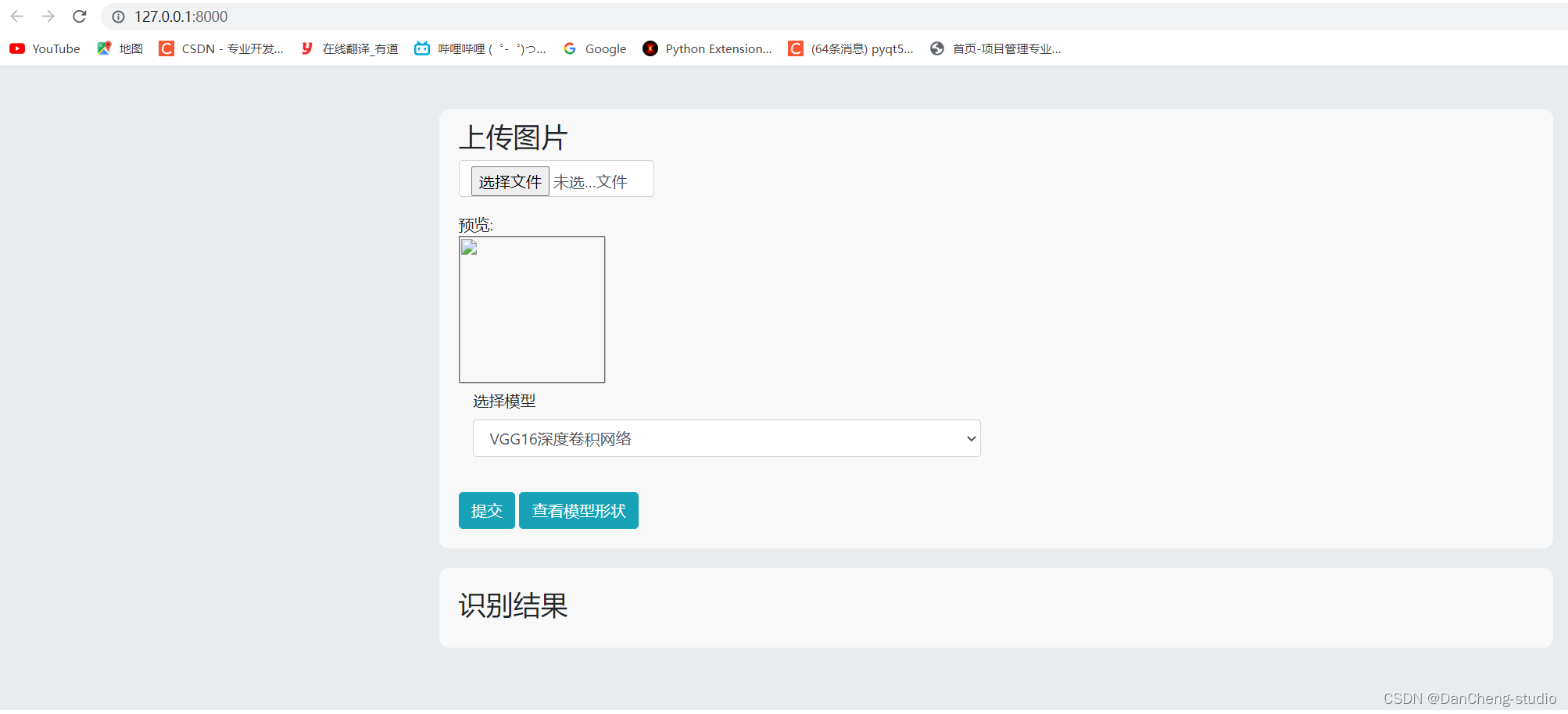
6.2 圖片預測

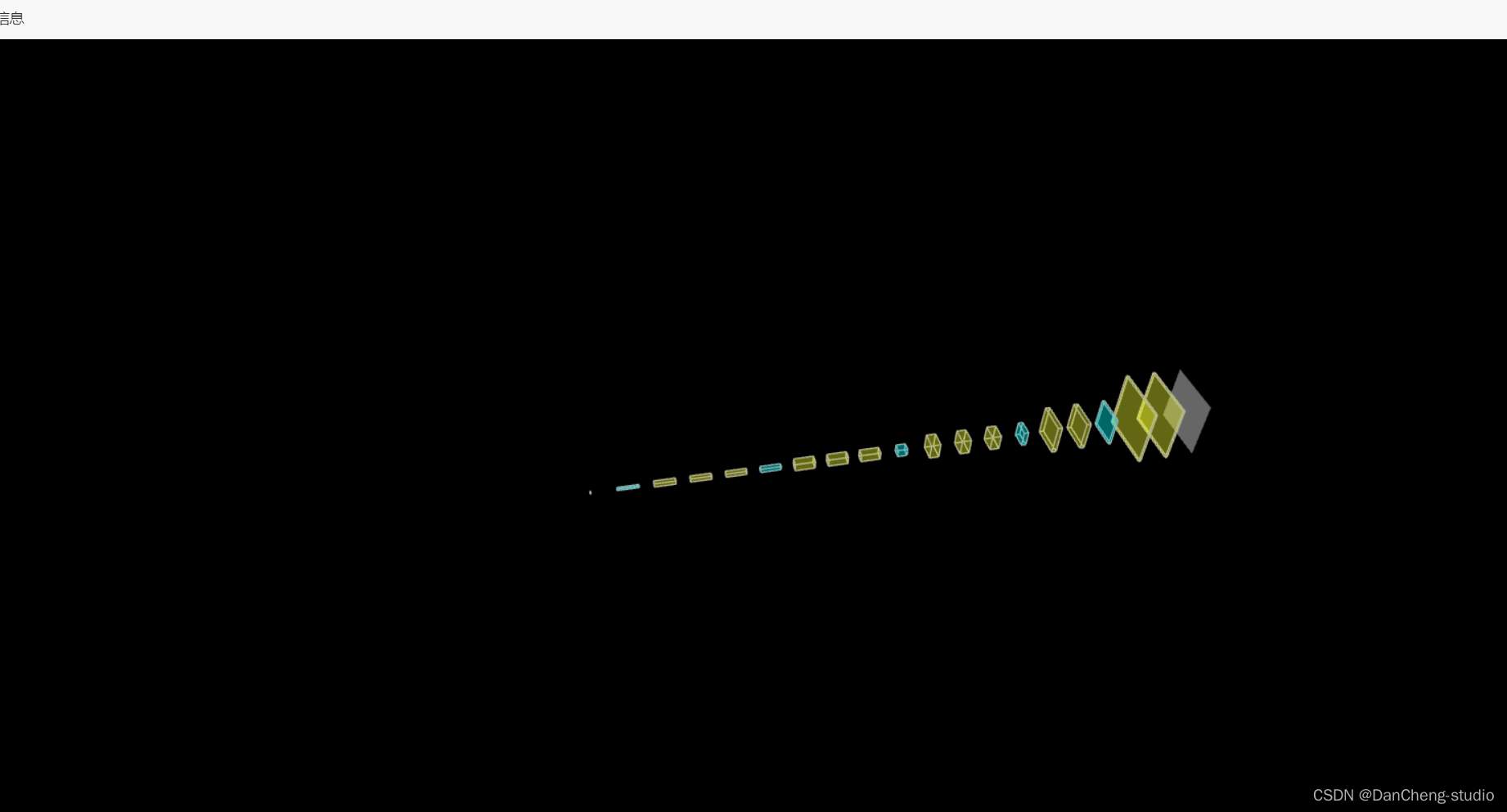
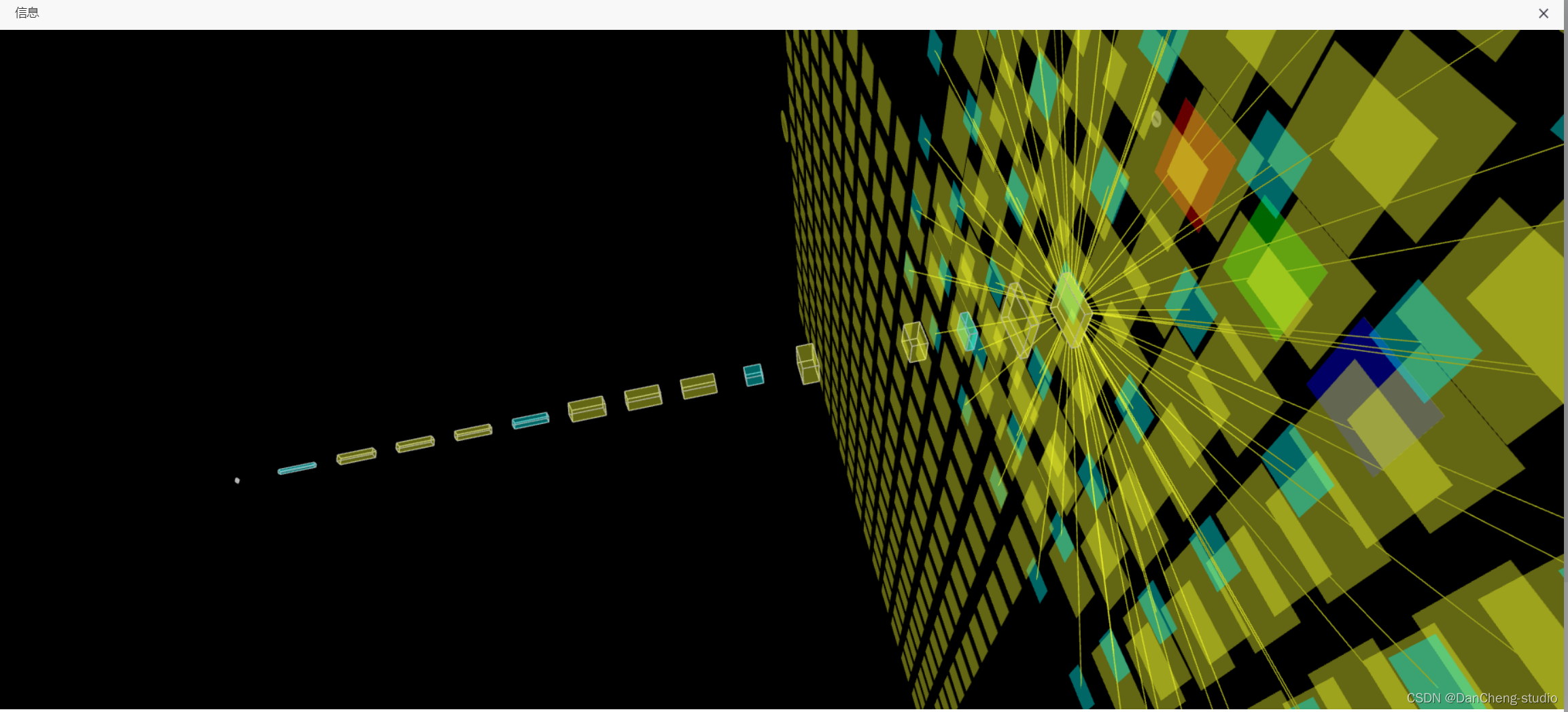
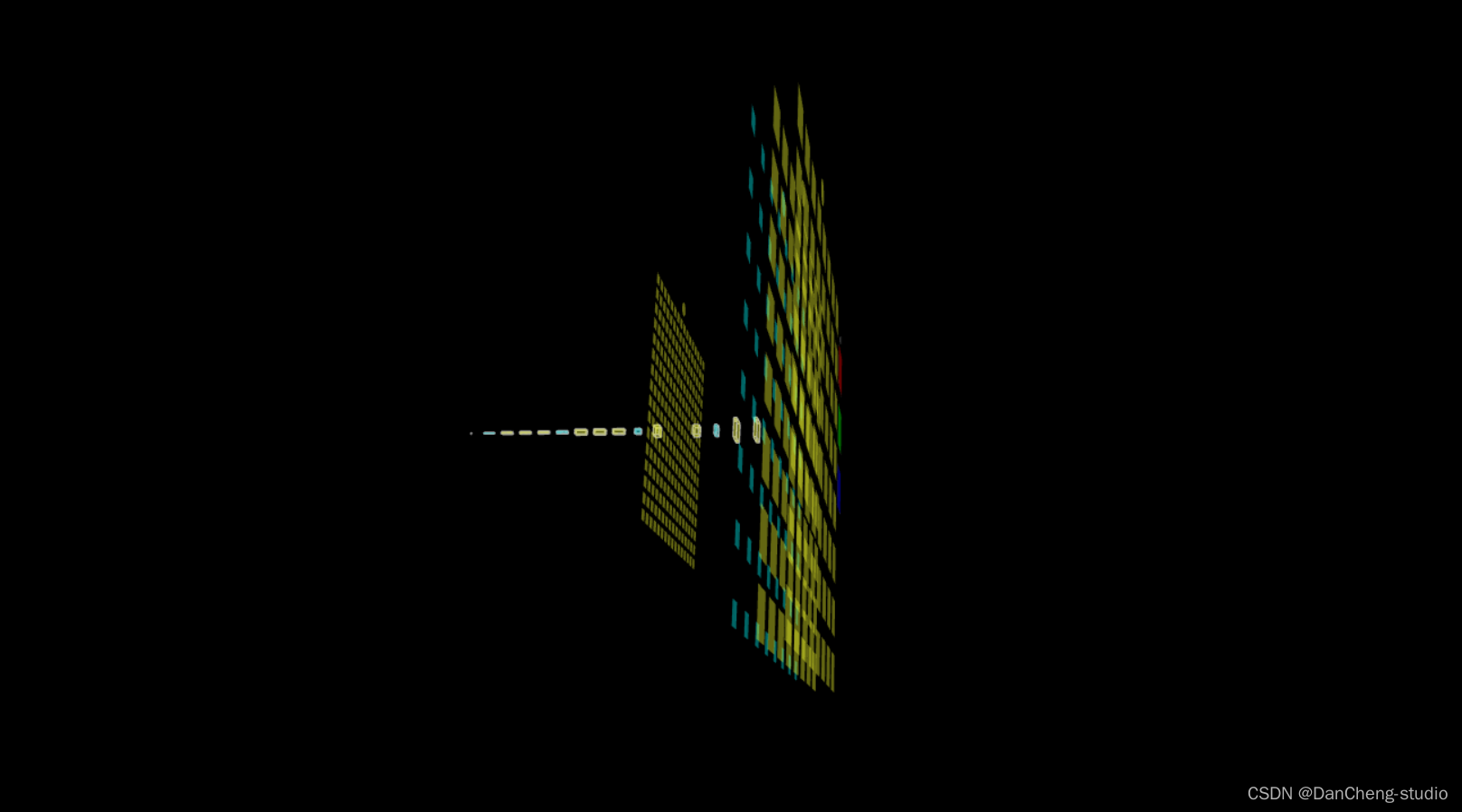
6.3 三維模型可視化
學長在web頁面上做了一個三維網絡結構可視化功能,可以直觀的看到網絡模型結構
7 最后
🧿 更多資料, 項目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
)
)



)






![[A133]uboot啟動流程](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[A133]uboot啟動流程)



_HTTP基礎知識,HTTP 請求、響應格式,方法,狀態碼)
shell腳本)

