目錄
一、List 介紹
?二、線性表
三、自己實現 ArrayList
3.1 顯示元素
3.2 增
3.2.1 默認在數組后面新增元素
3.2.2 在指定位置中新增元素
3.3 查
3.4 取值
3.5 改
3.5.1 把 pos 位置的元素修改成 value
3.5.2 刪除某個元素
3.5.3 清空
四、認識 ArrayList
4.0 說明
4.1 成員變量?
?4.2 構造方法
4.2.1 指定順序表的初始容量
4.2.2 無參構造方法
4.2.3 利用其他 Collection 構建 ArrayList
4.3 常用方法
4.4 ArrayList 的遍歷
4.4.1 for 循環 + get()方法
4.4.2 foreach
4.4.3 迭代器
五、練習
5.1 刪除
5.2 楊輝三角
5.3 綜合練習——洗牌
六、二維表
七、ArrayList 的問題與思考
一、List 介紹
在 java.util 包下一些重要的接口和類中,我們本次講到的是紅色線框的部分。
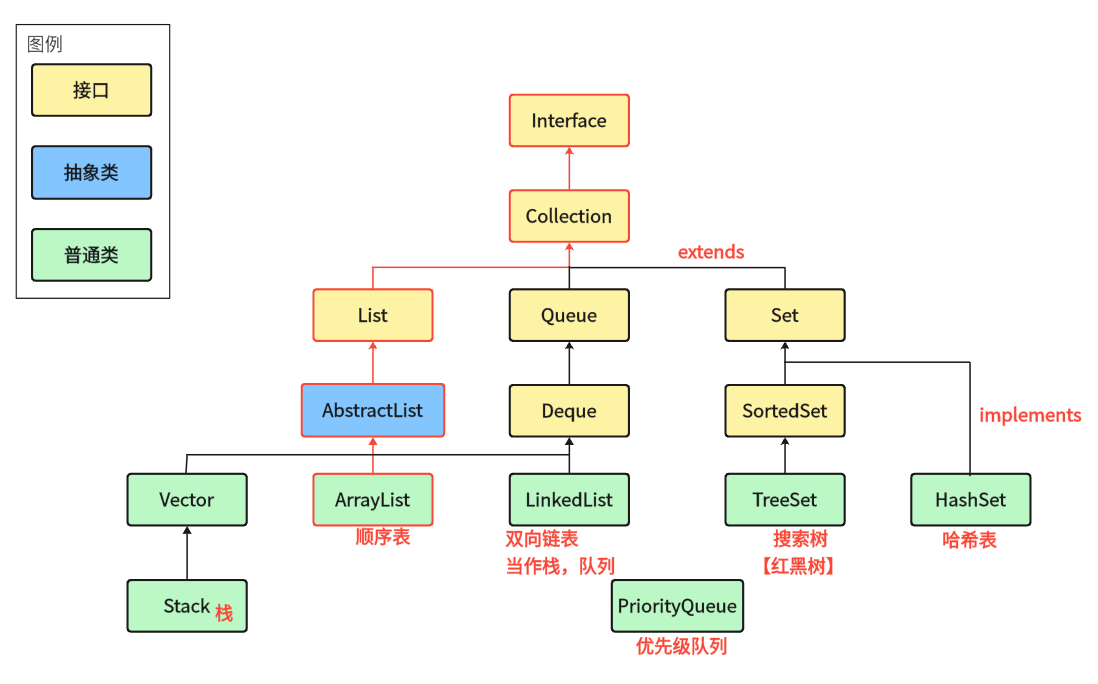
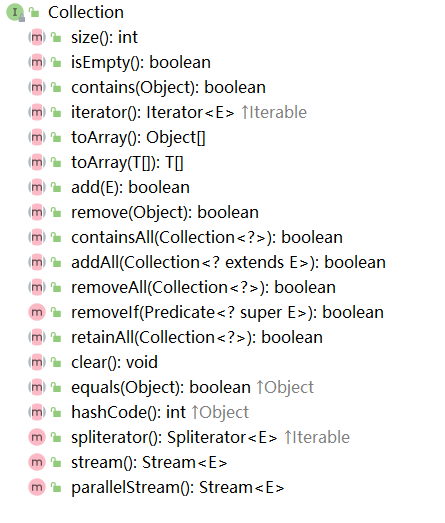
????????在集合框架中,List 是一個接口,繼承自 Collection 接口,而 Collection 接口又繼承自 Iterable 接口。而他們之間的關系是“extends 擴展”的關系,即 List 擴展了 Collection 的功能,如 List 接口的方法比?Collection 的要多:
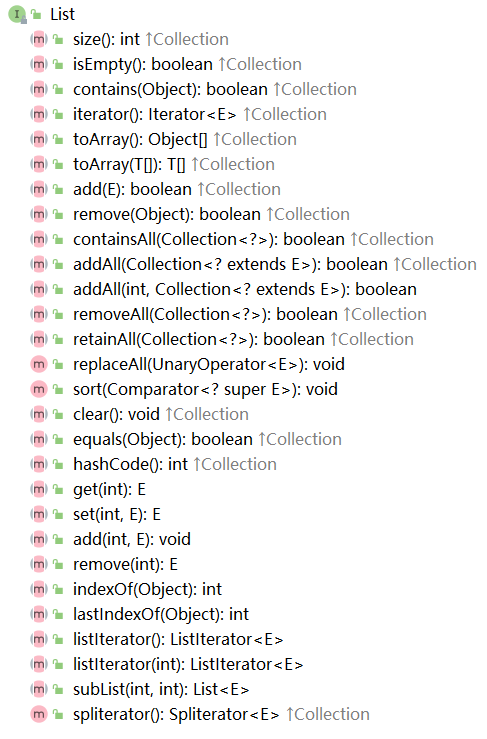
????????此外因為 List 是一個接口,因此不能直接被用來實例化;如果要使用,必須實例化 List 的實現類,即 ArrayList 和 LinkedList。
二、線性表
一般順序表如下圖(此外還有 棧和隊列 這2個受限線性表)
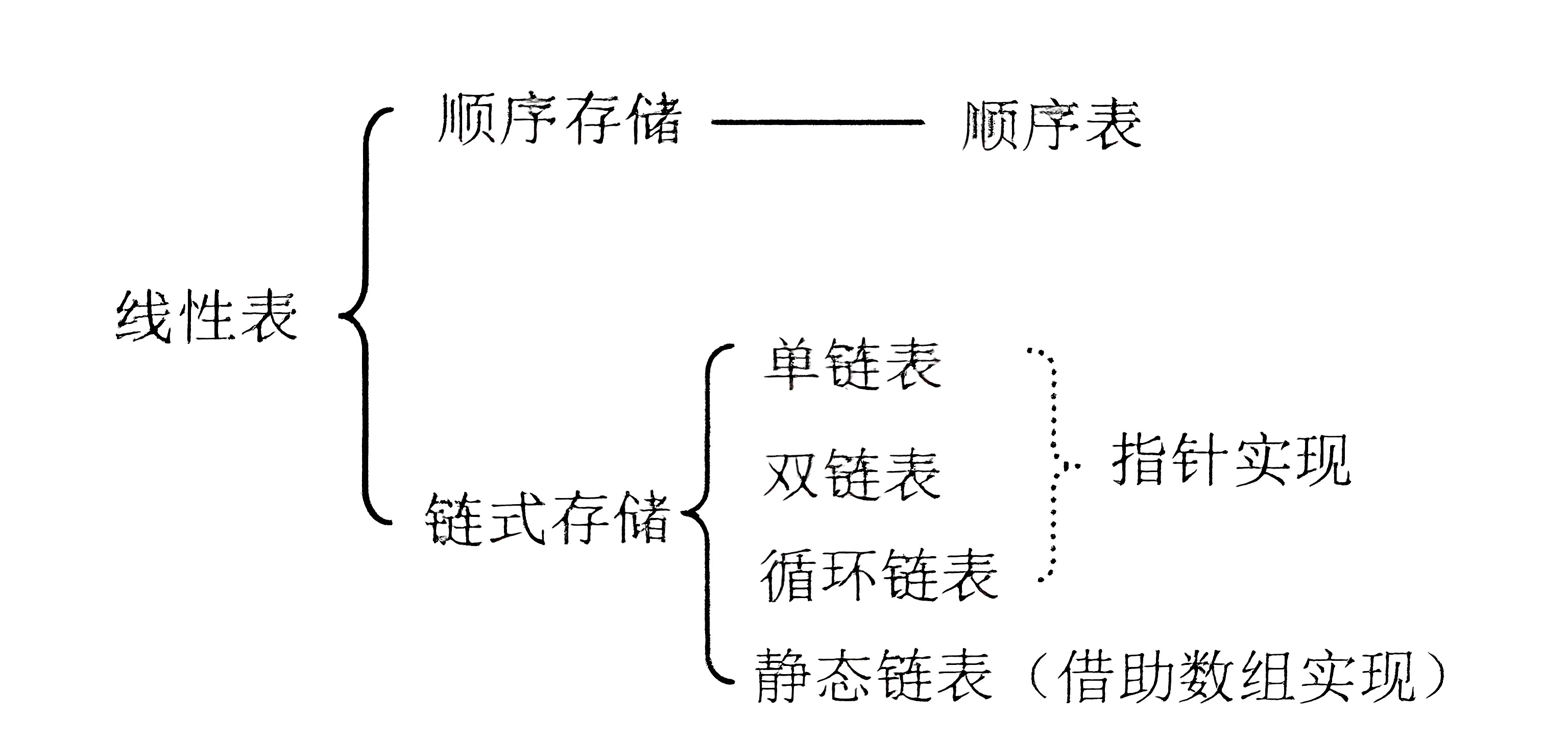
????????站在數據結構的角度上來看,List 是一個線性表,即 n 個具有相同類型元素的有限序列,在該序列上可以執行 增刪改查 以及變量等操作。
????????線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,也可以說是連續的一條直線;但是在物理結構上并不一定是連續的,現象表在物理上存儲時,通常以數組和鏈式結構的形式存儲。
三、自己實現 ArrayList
????????自己實現對數組進行增刪查改的操作。新建一個 MyArrayList 類文件,存放整型數組和有效數據長度兩個字段(有效數據長度與圖書管理系統的用法一致)。
????????定義一個名為 IList 的總接口,該接口可實現對數組進行增刪查改等的操作。MyArrayList 類實現該接口并重寫增刪查改等方法。
3.1 顯示元素
package test;public interface IList{// 新增元素,默認在數組最后新增void add(int data);// 在 pos 位置新增元素void add(int pos, int data);// 判定是否包含某個元素boolean contains(int toFind);// 查找某個元素對應的位置int indexOf(int toFind);// 獲取 pos 位置的元素int get(int pos);// 給 pos 位置的元素設為 valuevoid set(int pos, int value);//刪除第一次出現的關鍵字keyvoid remove(int toRemove);// 獲取順序表長度int size();// 清空順序表void clear();// 打印順序表,注意:該方法并不是順序表中的方法,為了方便看測試結果給出的void display();
}package test;import java.util.Arrays;public class MyArrayList implements IList{private int[] arr;private int usedSize;private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 定義一個常量,表示數組的容量public MyArrayList(){arr = arr[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; // 實例化 MyArrayList 同時調用構造方法給數組進行初始化}@Overridepublic void add(int data) {}@Overridepublic void add(int pos, int data) {}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {return false;}@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {}@Overridepublic int get(int pos) {}@Overridepublic void set(int pos, int value) {}@Overridepublic void remove(int toRemove) {}@Overridepublic int size() {return this.usedSize;}@Overridepublic void clear() {}@Overridepublic void display() {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");}// 不能使用 foreach 遍歷數組,因為我們只需要顯示usedSize范圍內的元素}
}?測試類先測試能否將數組元素遍歷顯示:
package test;public class Test{public staic void main(String[] args){MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();IList iList = new MyArrayList(); // 向上轉型System.out.println(myArrayList.size());System.out.println(iList.size());System.out.println("----------------------");myArrayList.display();iList.display();}
}上面代碼的輸出結果是:
0
0
----------------------
Process finished with exit code 0
因為此時 usedSize 為0,無法顯示任何數組中的元素。
實例化可以有兩種方法:
????????如果用接口引用當前對象,只要實現這個接口的對象都能引用,意味著可以向上轉型并發生動態綁定和多態;但缺點在于通過這個接口,只能調用這個接口當中包含的方法,不能調用對象中特有的方法。
? ? ? ? 而如果用當前對象引用當前對象,可以調用對象中的所有方法。
獲取當前順序表的長度用 .size() 方法。
3.2 增
3.2.1 默認在數組后面新增元素
實現條件:
1、在新增之前,數組是否已經滿了?
2、如果數組滿了,如何對數組進行擴容?
思路:
1、在接口中編寫一個判斷數組是否已滿的方法,并在 MyArrayList 中重寫該方法。
public interface IList{// 在新增元素之前,需要對數組判斷是否已滿boolean isFull();// 其余方法(略)
}public class MyArrayList{// 新增判滿方法public boolean isFull(){return this.usedSize == this.arr.length;}}?2、使用 Arrays 的復制數組的方法將數組原來的內容復制到新定義長度的數組中。
public class MyArrayList{// 新增判滿方法public boolean isFull(){return this.usedSize == this.arr.length;}private void grow(){this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr, 2*this.arr.length);}}3、實現:如果滿了,擴容 --> 將 data 賦值給?usedSize 為下標的元素 --> 有效數組長度+1
public class MyArrayList{// 新增判滿方法public boolean isFull(){return this.usedSize == this.arr.length;}private void grow(){this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr, 2*this.arr.length);}@Overridepublic void add(int data) {if (isFull()){// 如果滿了,需要擴容grow();}this.arr[this.usedSize] = data;this.usedSize++;}
}public class Test{public static void main(String[] args){MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();myArrayList.add(1);myArrayList.add(2);myArrayList.add(3);myArrayList.display();}
}3.2.2 在指定位置中新增元素
實現條件:
1、指定的位置不能是負數,且指定的位置前一個元素必須不能為空。
????????(順序表中的除第1個元素外,每個元素必須有唯一一個直接前驅)
2、數組已經滿了的話,也是需要擴容的。
思路:
1、 對于指定位置不合法,我們可以編寫一個類,使得這個類繼承于運行時的異常接口,并重載構造方法:
package test;public class PosIllegalException extends RuntimeException{public PosIllegalException(){}public PosIllegalException(String mes){super(mes)}
}2、在 MyArrayList 中新增一個檢查 pos 的方法,如果 pos 不合法,則 拋出異常
public class MyArrayList implements IList{private void checkPos(int pos) throws PosIllegalException {if (pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize){throw new PosIllegalException("Pos位置不合法!!!")}}
}3、實現插入新元素:
public class MyArrayList implements IList{private void checkPos(int pos) throws PosIllegalException {if (pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize){throw new PosIllegalException("Pos位置不合法!!!")}}@Overridepublic void add(int pos, int data){try {// 檢查pos是否合法checkPos(pos);// 擴容if (isFull()){grow();}// 挪動元素for (int i = usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--){arr[i + 1] = arr[i];}arr[pos] = data;this.usedSize++;}catch (PosIllegalException e){System.out.println("插入pos元素的位置不合法!!");e.printStackTrace();}}
}public class Test{public static void main(String[] args) {MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();myArrayList.add(1);myArrayList.add(2);myArrayList.add(3);myArrayList.add(4);myArrayList.add(5);myArrayList.add(2,66);myArrayList.add(7,4);myArrayList.display();}
}輸出結果:
插入pos元素的位置不合法!!
1 2 66 3 4 5 test.PosIllegal: Pos位置不合法!!!
?? ?at test.MyArrayList.checkPos(MyArrayList.java:34)
?? ?at test.MyArrayList.add(MyArrayList.java:40)
?? ?at test.test.main(test.java:24)
3.3 查
判斷是否包含每個元素 contains 和 查找某個元素對應的位置 indexOf 方法:
public class MyArrayList implements IList{@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if (arr[i] == toFind){return true;}}return false;}@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if (arr[i] == toFind){return i;}}return -1;}
}3.4 取值
實現條件:
1、pos 超出合法范圍,pos 不能小于0,不能大于 usedSize,也不能等于 usedSize,下標為?usedSize 的位置沒有元素。
2、如果下標為 pos 的元素為空?
思路:
1、因為上面寫的 checkPos 方法在 pos 等于?usedSize 的時候不會拋出異常,因此我們需要重寫一個 checkPos2 方法:
public class MyArrayList implements IList {private void checkPos2(int pos) throws PosIllegalException{if (pos < 0 || pos >= usedSize){throw new PosIllegalException("Pos位置不合法!!!");}}
}2、編寫一個元素為空異常的類
package test;public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{public EmptyException(){}public EmptyException(String msg){super(msg);}
}3、判斷元素是否為空
public class MyArrayList implements IList{public boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize == 0;}private void checkEmpty(){if (isEmpty()){throw new EmptyException("順序表為空!!!");}}
}4、實現取值
public class MyArrayList implements IList{public boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize == 0;}private void checkEmpty(){if (isEmpty()){throw new EmptyException("順序表為空!!!");}}@Overridepublic int get(int pos) {try{checkEmpty();checkPos2(pos);return arr[pos];}catch (EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (PosIllegalException e){e.printStackTrace();}return -1;}
}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();myArrayList.add(1);myArrayList.add(2);System.out.println(myArrayList.get(2));}
}輸出結果:
test.PosIllegalException: Pos位置不合法!!!
?? ?at test.MyArrayList.checkPos2(MyArrayList.java:78)
?? ?at test.MyArrayList.get(MyArrayList.java:94)
?? ?at test.test.main(test.java:9)
-1
3.5 改
3.5.1 把 pos 位置的元素修改成 value
實現條件:
1、如果為空就不能修改;?
2、檢查 pos 位置的合法性。
public class MyArrayList implements IList {@Overridepublic void set(int pos, int value) {try{checkEmpty();checkPos2(pos);arr[pos] = value;}catch (EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (PosIllegalException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}3.5.2 刪除某個元素
實現條件:
1、判斷是否為空,本來就是空的不用刪除;
2、?從 pos 位置到最后一個下標,將最后一個元素覆蓋到前面一個元素。
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();myArrayList.add(1);myArrayList.add(2);myArrayList.add(3);myArrayList.add(4);myArrayList.add(5);myArrayList.remove(3);myArrayList.display();}
}3.5.3 清空
????????對于基本數據類型的數組,直接將有效數組長度賦值為0,對后續操作并無影響。比如清空之后再新增元素,即調用 add(int data),那么會將 data 的值覆蓋到 arr[0] 上,即使原本內存中已經在 arr[0] 上存放了值也會被覆蓋掉。
????????但是對于引用類型,存放的是引用,如果沒有及時將引用變量置空,那么那份被引用的空間將一直無法被內存回收,因此容易造成內存泄漏。
public class MyArrayList implements IList{@Overridepublic void clear() {this.usedSize = 0; // 對于基本數據類型,該方法不會造成內存泄漏// 但是對于引用類型,存放的是引用,因為沒有被置為空,其引用的對象不能被內存回收,也就一直占用著那份內存,容易造成內存泄漏// 所以如果是引用類型,需要以下操作:/*for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {arr[i] = null;}this.usedSize = 0;*/}
}
到這里所有的操作都已實現,下面是 MyArrayList 的完整代碼
package test_8_5;import java.util.Arrays;public class MyArrayList implements IList{private int[] arr;private int usedSize;private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;public MyArrayList(){arr = new int[this.DEFAULT_CAPACITY];}public boolean isFull(){return this.usedSize == this.arr.length;}@Overridepublic void add(int data) {if (isFull()){// 如果滿了,需要擴容grow();}this.arr[this.usedSize] = data;this.usedSize++;}private void grow(){this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr,2*this.arr.length);}private void checkPos(int pos) throws PosIllegalException {if (pos < 0 || pos > usedSize){throw new PosIllegalException("Pos位置不合法!!!");}}@Overridepublic void add(int pos, int data) {try{checkPos(pos);if (isFull()){grow();}usedSize += 1;for (int i = usedSize-1; i > pos; i--) {arr[i] = arr[i-1];}arr[pos] = data;}catch (PosIllegalException e){System.out.println("插入pos元素的位置不合法!!");e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if (arr[i] == toFind){return true;}}return false;}@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {if (arr[i] == toFind){return i;}}return -1;}private void checkPos2(int pos) throws PosIllegalException{if (pos < 0 || pos >= usedSize){throw new PosIllegalException("Pos位置不合法!!!");}}public boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize == 0;}private void checkEmpty(){if (isEmpty()){throw new EmptyException("順序表為空!!!");}}@Overridepublic int get(int pos) {try{checkEmpty();checkPos2(pos);return arr[pos];}catch (EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (PosIllegalException e){e.printStackTrace();}return -1;}@Overridepublic void set(int pos, int value) {try{checkEmpty();checkPos2(pos);arr[pos] = value;}catch (EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (PosIllegalException e){e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic void remove(int toRemove) {try{checkEmpty();int pos = indexOf(toRemove);if (pos == -1){return;}for (int i = pos; i < usedSize -1; i++) { // -1是為了防止arr[i+1]的時候越界arr[i] = arr[i+1];}usedSize--;}catch (EmptyException e){e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic int size() {return this.usedSize;}@Overridepublic void clear() {this.usedSize = 0; // 對于基本數據類型,該方法不會造成內存泄漏// 但是對于引用類型,存放的是引用,因為沒有被置為空,其引用的對象不能被內存回收,也就一直占用著那份內存,容易造成內存泄漏// 所以如果是引用類型,需要以下操作:/*for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {arr[i] = null;}this.usedSize = 0;*/}@Overridepublic void display() {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");}// 不能使用 foreach 遍歷數組,因為我們只需要顯示usedSize范圍內的元素}
}
四、認識 ArrayList
4.0 說明
1. ArrayList 是以泛型方式實現的,使用時必須要先實例化;
2. ArrayList 實現了 RandomAccess 接口,表明 ArrayList 支持隨機訪問;
3. ArrayList 實現了 Cloneable 接口,表明 ArrayList 是可以 clone 的;
4. ArrayList 實現了 Serializable 接口,表明 ArrayList 是支持序列化的;
5. 和 Vector 不同,ArrayList 不是線程安全的,在單線程下可以使用,在多線程中可以選擇Vector 或者 CopyOnWriteArrayList;
6. ArrayList 底層是一段連續的空間,并且可以動態擴容,是一個動態類型的順序表。
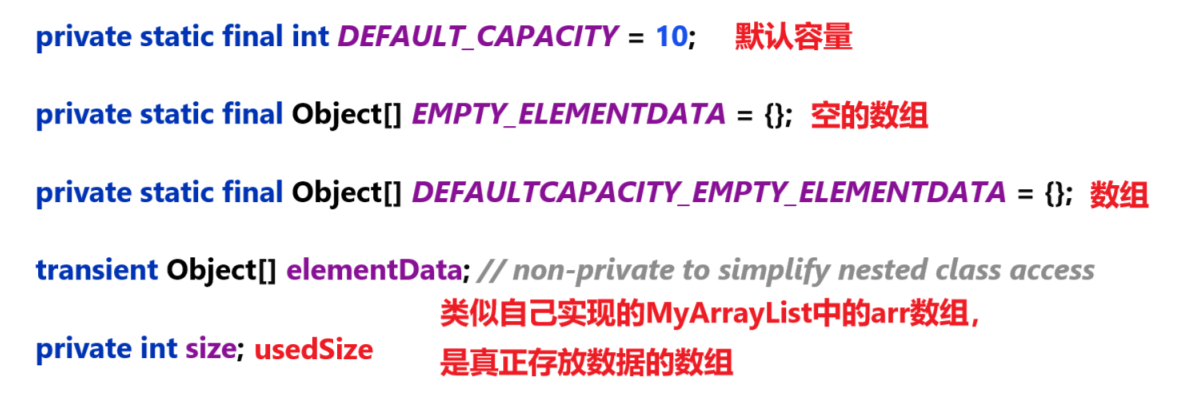
4.1 成員變量?
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class accessprivate int size;// ……
}上面的成員變量中與我們剛剛編寫的 MyArrayList 中的具有相似性:
?4.2 構造方法
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
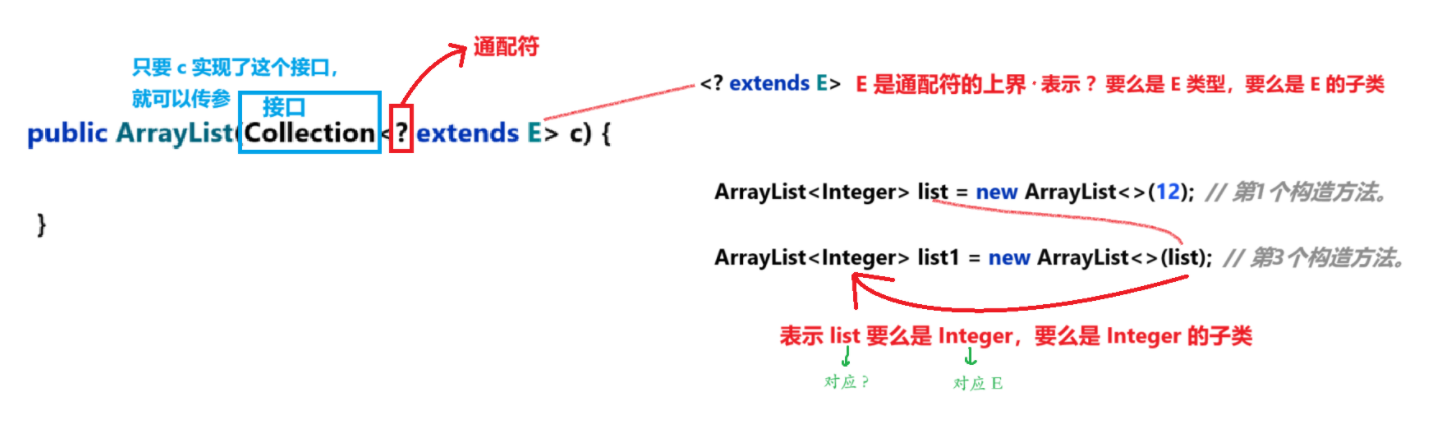
{public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);}}public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);} else {// replace with empty array.this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}
}4.2.1 指定順序表的初始容量
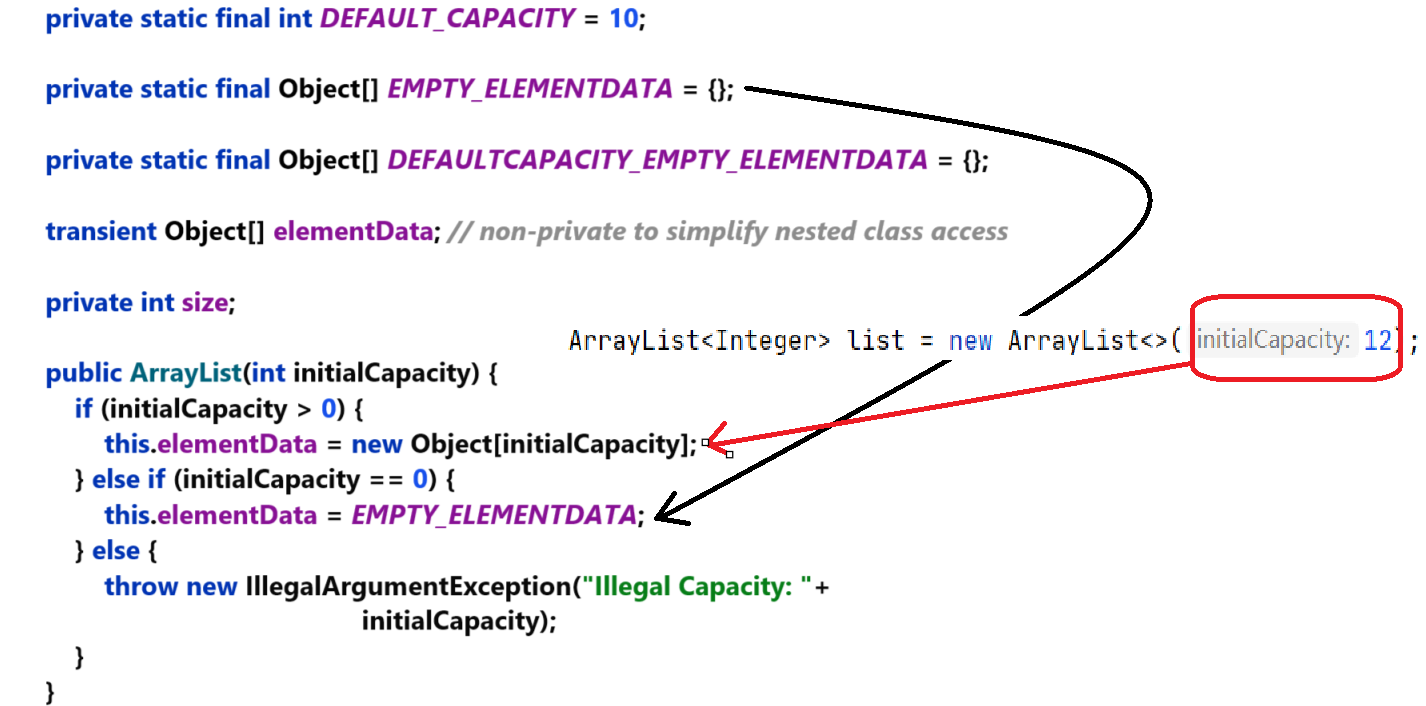
????????如果在實例化順序表時傳入一個整數作為參數,那么會調用第一個構造方法。根據傳入參數的大小決定順序表的容量:如果大于0,創建與參數大小一樣的數組;如果等于0,給空數組;再否則拋出初始容量不合法的異常。
如:ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(12); 構造一個具有12個容量的列表。
4.2.2 無參構造方法

如:ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 構造一個空的列表,推薦寫法。
??這個構造方法,其實并沒有給分配內存,為什么還可以進行 add 的操作?
????????分析源碼得到的結論是,第一次使用 add 方法的時候分配內存大小為 10,如果后面再操作發現容量滿了,那么就是 1.5 倍進行擴容。理解為,初始容量為10,若滿了,將擴容為15。
1. 檢測是否真正需要擴容,如果是調用grow準備擴容
2. 預估需要庫容的大小
????????初步預估按照1.5倍大小擴容
????????如果用戶所需大小超過預估1.5倍大小,則按照用戶所需大小擴容
????????真正擴容之前檢測是否能擴容成功,防止太大導致擴容失敗
3. 使用copyOf進行擴容
4.2.3 利用其他 Collection 構建 ArrayList
4.3 常用方法
| 方法 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| size() | 獲取有效元素個數 |
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 將 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 刪除 index 位置元素,該元素之后的元素統一往前搬移一個位 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 刪除遇到的第一個 o |
| E get(int index) | 獲取下標 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 將下標 index 位置元素設置為 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判斷 o 是否在線性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一個 o 所在下標 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一個 o 的下標 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
????????與上面自己實現的 myArrayList 中的方法大相徑庭,此處需要留意的是 addAll()、remove()、subList()、set() 方法。
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 第2個構造方法。list.add(4);list.add(9);list.add(0);list.add(1);list.add(1,0);System.out.println(list); // [4, 0, 9, 0, 1]ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();list1.add(2);list1.addAll(list);System.out.println(list1); // [2, 4, 0, 9, 0, 1]list1.remove(0);System.out.println(list1); // [4, 0, 9, 0, 1]list1.remove(new Integer(0));System.out.println(list1); // [4, 9, 0, 1]}
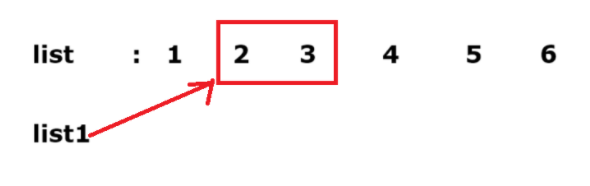
}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 截取部分 listArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 第2個構造方法。list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);list.add(6);System.out.println(list); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]List<Integer> list1 = list.subList(1,3);System.out.println(list1); // [2, 3]System.out.println("-----------------");list1.set(0,666);System.out.println(list1); // 預期輸出 [666, 3],運行之后達到預期System.out.println(list); // 預期沒有變化 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],運行結果得到 [1, 666, 3, 4, 5, 6]}
}????????由上一個代碼運行結果可見,使用 subList 截取本質上是將下標為 1 的引用給了 list1,而不是復制了一份。因此使用 set 修改 list1 本質上是修改 list。
4.4 ArrayList 的遍歷
????????上面舉的例子可以直接輸出表的內容是因為 ArrayList 中重寫了 toString 方法。下面將通過3種遍歷方法來訪問順序表的數據。
4.4.1 for 循環 + get()方法
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);list.add(6);for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + " "); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 }}
}4.4.2 foreach
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);list.add(6);// for (int x: list) // 拆箱操作for (Integer x: list) {System.out.print(x + " ");}}
}4.4.3 迭代器
????????有兩種迭代器,一種是 interator,另一種是 listInterator (兩者首字母都是小寫),其不同在于后者拓展了前者的功能。
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("------迭代器 iterator 循環------");Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("------迭代器 listIterator 循環------");ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator();while (it2.hasNext()){System.out.print(it2.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("------迭代器 listIterator 循環------");System.out.println(" ·拓展功能,指定位置倒著輸出");ListIterator<Integer> it3 = list.listIterator(list.size());while (it3.hasPrevious()){System.out.print(it3.previous() + " ");} // 6 5 4 3 2 1}
}五、練習
5.1 刪除
輸入兩行字符串,從 str1 中刪除所有包含?str2 的字符,得到新的字符串。(大小寫敏感)
要求:使用 ArrayList,相比使用 StringBuilder 的方法,性能有所提高。
示例1:
輸入:
str1 :? Welcome to China!
str2 :? ?come
輸出:Wl t?China!
示例2:
輸入:
str1 :? Today is Tuesday.
str2 :? ?days
輸出:To i Tue.
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);String str1 = in.nextLine();String str2 = in.nextLine();ArrayList<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {char ch = str1.charAt(i);if (!str2.contains(ch + "")){list.add(ch);}}for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i));}}
}一個小技巧:str2.contains(ch+"");
在不改變原來的意義前提下,將字符變字符串
????????contains() 方法的參數需要是字符串類型的數據,但是 ch 是字符類型的,那么 加一個 "",就使得 ch 變成了字符串,且沒有新增任何不該存在的值。
5.2 楊輝三角
給定一個非負整數?numRows,生成「楊輝三角」的前?numRows?行。

在 leetcode 上給出的模板中,返回類型要求是?List<List<Integer>> (?!這是個什么東東)
【那么,我們這里插入一個知識點(六、二維表),為了排版好看,請跳轉到相應位置。】
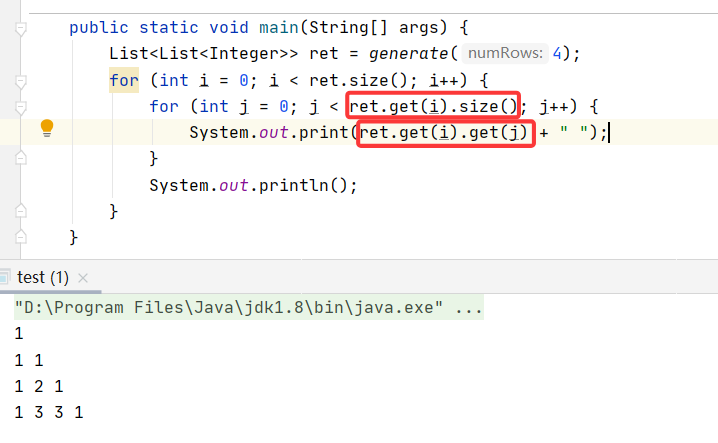
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();// 處理楊輝三角第一行List<Integer> startRow = new ArrayList<>();startRow.add(1);ret.add(startRow);// 從第2行開始循環新增一維數組for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>(); // 當前行// 第一列的元素肯定是1curRow.add(1);// 處理中間List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i-1); // 當前行的上一行for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) { // 也是從第2列開始,列數要小于行數,因為對角線右邊沒有值int val1 = preRow.get(j);int val2 = preRow.get(j-1);curRow.add(val1 + val2);}// 最后一列也是1curRow.add(1);ret.add(curRow); // 最后將當前行給二維數組}return ret;
}測試:
5.3 綜合練習——洗牌
描述:
新買的一副撲克牌,去掉大小王剩52張牌,總共有花色4種:? ? ? ?,每種花色共13張牌;
洗牌;
3位玩家隨機抽取5張牌。
步驟:
1、自定義類型:Card
屬性:花色、牌號
package playCard;public class Card {private String suit;private int rank;public Card(String suit, int rank) {this.suit = suit;this.rank = rank;}@Overridepublic String toString() {/*return "Card{" +"suit='" + suit + '\'' +", rank=" + rank +'}';*/return "{" + suit + rank + "} ";}
}2、設置牌號和花色對應,生成按順序的52張牌
package playCard;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class CardDemo {private static final String[] suits = {"?","?","?","?"};public List<Card> buyCards(){List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>(); // 相當于紙牌盒,用于存放for(int i = 1; i <= 13; i++){ // 1~13號牌for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++){ // 4種花色String suit = suits[j];int rank = i;Card card = new Card(suit, rank); // 花色對應牌號生成一張牌cardList.add(card); // 將生成的牌放到紙牌盒}}return cardList;}
}package playCard;import java.util.List;public class Play {public static void main(String[] args) {CardDemo cardDemo = new CardDemo();List<Card> cardList = cardDemo.buyCards();System.out.println(cardList);}
}
輸出結果:
[{?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} ]
3、洗牌
????????原理:從最后一張牌(下標為51)開始,與前面下標為 0~50的隨機一張牌進行交換,交換完之后到下一張(下標為50);也可以從第一張牌開始與后面的牌進行交換,但因為生成隨機數下標一般是從0開始,所以采用第一種方法。
package playCard;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;public class CardDemo {// 略public void shuffle(List<Card> cardList){Random random = new Random();for (int i = cardList.size() -1; i > 0; i--) {int j = random.nextInt(i); // 生成0~i-1范圍的隨機數swap(cardList,i,j);}}private void swap(List<Card> cardList, int i, int j){/*料想的交換:Card tmp = cardList[i];cardList[i] = cardList[j];cardList[j] = tmp;但因為 cardList 不是數組,因此無法進行上面的操作*/Card tmp = cardList.get(i);cardList.set(i,cardList.get(j));cardList.set(j,tmp);}
}package playCard;import java.util.List;public class Play {public static void main(String[] args) {CardDemo cardDemo = new CardDemo();// 買52張牌,展示List<Card> cardList = cardDemo.buyCards();System.out.println(cardList);System.out.println("洗牌后:");// 洗牌cardDemo.shuffle(cardList);System.out.println(cardList);}
}輸出示例:
[{?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} ]
洗牌后:
[{?5} , {?7} , {?12} , {?3} , {?12} , {?5} , {?10} , {?7} , {?3} , {?5} , {?1} , {?2} , {?2} , {?10} , {?9} , {?5} , {?6} , {?8} , {?2} , {?4} , {?12} , {?13} , {?11} , {?4} , {?4} , {?3} , {?7} , {?6} , {?3} , {?9} , {?2} , {?13} , {?6} , {?11} , {?6} , {?10} , {?7} , {?1} , {?1} , {?12} , {?8} , {?4} , {?10} , {?13} , {?8} , {?13} , {?9} , {?11} , {?8} , {?1} , {?9} , {?11} ]
4、發牌
原理:每個玩家相當于一張表,整個牌桌就相當于存了三張表的二維表。
package playCard;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;public class CardDemo {// ......public List<List<Card>> play(List<Card> cardList){List<Card> player1 = new ArraysList<>(); // 每個玩家手里的牌List<Card> player2 = new ArraysList<>();List<Card> player3 = new ArraysList<>();List<List<Card>> desk = new ArraysList<>(); // 牌桌desk.add(player1);desk.add(player2);desk.add(player3);for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){Card card = cardList.remove(i);// 把對應的牌放到玩家的手上,那紙牌盒上的牌就少了desk.get(j).add(card);}}return desk;}
}package playCard;import java.util.List;public class Play{public static void main(String[] args){// ......List<List<Card>> desk = cardDemo.play(cardList);for(int i = 0; i < desk.size(); i++){System.out.println("第" + (i+1) + "個玩家的牌:" + desk.get(i));}System.out.println("剩余的牌:");System.out.println(cardList);}
}輸出示例:
[{?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?1} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?2} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?3} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?4} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?5} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?6} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?7} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?8} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?9} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?10} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?11} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?12} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} , {?13} ]
洗牌后:
[{?11} , {?2} , {?2} , {?12} , {?1} , {?4} , {?8} , {?5} , {?9} , {?13} , {?8} , {?7} , {?3} , {?7} , {?13} , {?1} , {?1} , {?6} , {?4} , {?9} , {?7} , {?7} , {?5} , {?3} , {?8} , {?8} , {?11} , {?12} , {?10} , {?5} , {?4} , {?9} , {?9} , {?10} , {?10} , {?13} , {?6} , {?3} , {?13} , {?2} , {?10} , {?12} , {?11} , {?5} , {?6} , {?1} , {?6} , {?12} , {?4} , {?2} , {?3} , {?11} ]
第1個玩家的牌:[{?11} , {?1} , {?9} , {?3} , {?1} ]
第2個玩家的牌:[{?2} , {?4} , {?13} , {?7} , {?6} ]
第3個玩家的牌:[{?2} , {?8} , {?8} , {?13} , {?4} ]
剩下的牌:
[{?12} , {?5} , {?7} , {?1} , {?9} , {?7} , {?7} , {?5} , {?3} , {?8} , {?8} , {?11} , {?12} , {?10} , {?5} , {?4} , {?9} , {?9} , {?10} , {?10} , {?13} , {?6} , {?3} , {?13} , {?2} , {?10} , {?12} , {?11} , {?5} , {?6} , {?1} , {?6} , {?12} , {?4} , {?2} , {?3} , {?11} ]
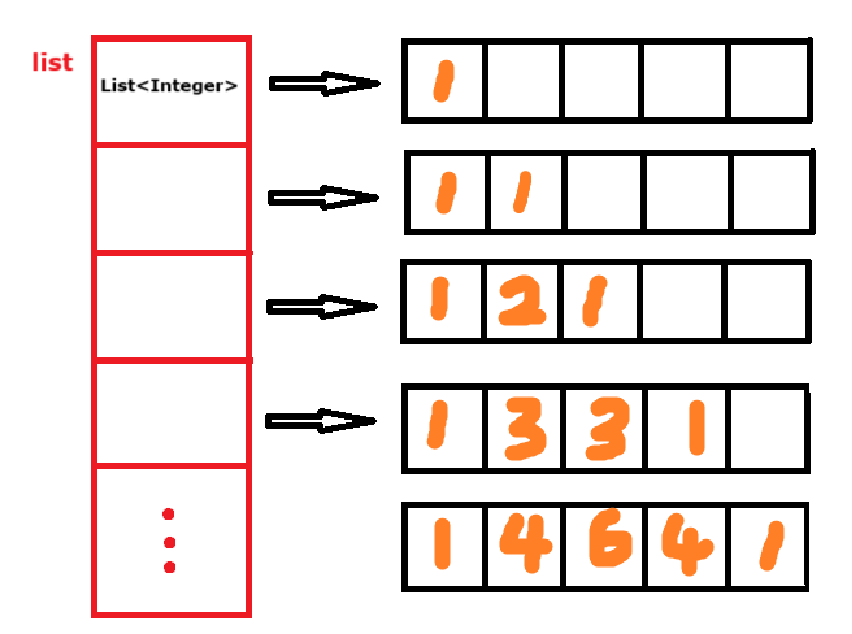
六、二維表
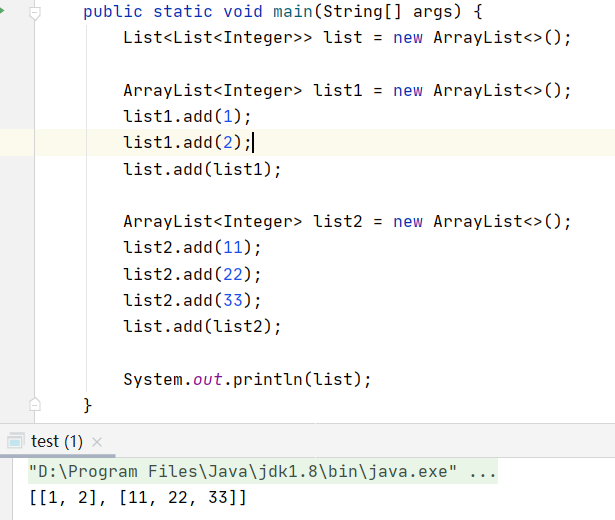
List<List<Integer>>? 類似于二維數組,其初始化方法如下:
七、ArrayList 的問題與思考
對于順序表,其優點是查找速度快。但它有以下的缺點:
1. ArrayList 底層使用連續的空間,任意位置插入或刪除元素時,需要將該位置后序元素整體往前或者往后搬移,故時間復雜度為 O(N)
2. 增容需要申請新空間,拷貝數據,釋放舊空間。會有不小的消耗。
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增長,勢必會有一定的空間浪費。例如當前容量為100,滿了以后增容到200,我們再繼續插入了5個數據,后面沒有數據插入了,那么就浪費了95個數據空間。
為了解決上面的問題,產生了鏈表。
)



![[GESP202309 四級] 2023年9月GESP C++四級上機題題解,附帶講解視頻!](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[GESP202309 四級] 2023年9月GESP C++四級上機題題解,附帶講解視頻!)

)



:Spring Boot + AI +DeepSeek實現智能合同數據問答助手?(附完整源碼))

![[sqlserver] 分析SQL Server中執行效率較低的SQL語句](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[sqlserver] 分析SQL Server中執行效率較低的SQL語句)






視頻的處理與保存)