前言
在C#第15天的學習中,我深入探索了類型轉換機制、對象比較原理和文件操作技術三大核心主題。這些知識是構建高效、健壯程序的關鍵基礎。本文完整保留我的課堂實踐代碼和命名體系,通過結構化梳理幫助大家掌握這些核心概念。所有代碼示例均來自我的實際操作,包含從基礎到進階的完整學習過程!
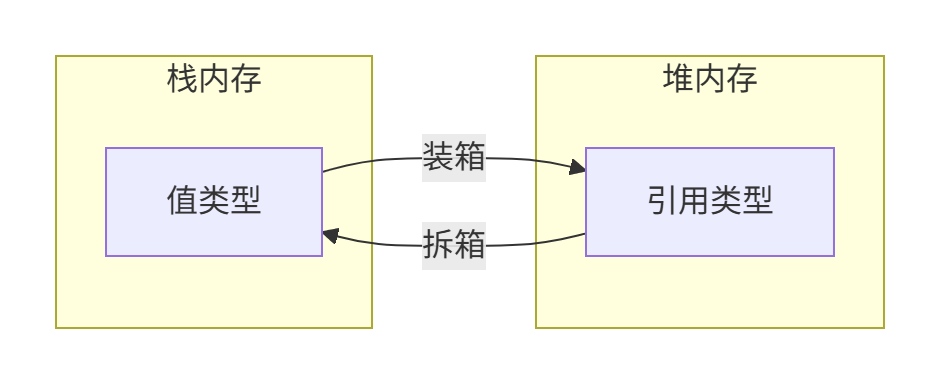
一、拆箱裝箱:值類型與引用類型的轉換
1. 基礎概念與實現
// 裝箱:值類型 → 引用類型
int a = 1;
object b = a; // 裝箱操作// 拆箱:引用類型 → 值類型
object c = 1;
int d = (int)c; // 拆箱操作2. 內存機制解析
3. 性能影響與最佳實踐
| ?操作? | ?性能開銷? | ?使用建議? |
|---|---|---|
| 裝箱 | 高(內存分配+數據復制) | 避免在循環中使用 |
| 拆箱 | 中(類型檢查+數據復制) | 確保類型兼容 |
| 泛型集合 | 無(避免裝箱拆箱) | 優先使用List |
二、Equals與==:對象比較的深層解析
1. 值類型比較
int x = 10;
int y = 10;// == 運算符比較
Console.WriteLine(x == y); // true// Equals方法比較
Console.WriteLine(x.Equals(y)); // true2. 引用類型比較
class Person
{public int Age { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public Person(int age, string name){Age = age;Name = name;}
}Person p1 = new Person(18, "張三");
Person p2 = new Person(18, "張三");// == 默認比較引用地址
Console.WriteLine(p1 == p2); // false// Equals默認比較引用地址
Console.WriteLine(p1.Equals(p2)); // false3. 重寫Equals實現值比較
class Person
{// ...其他代碼同上...// 重寫Equals方法public override bool Equals(object obj){// 類型檢查if (obj == null || GetType() != obj.GetType())return false;Person p = (Person)obj;return Age == p.Age && Name == p.Name;}// 重寫GetHashCode(推薦與Equals一起重寫)public override int GetHashCode(){return Age.GetHashCode() ^ Name.GetHashCode();}
}// 使用重寫后的Equals
Console.WriteLine(p1.Equals(p2)); // true4. 比較操作決策表
| ?比較場景? | ?推薦方式? | ?注意事項? |
|---|---|---|
| 值類型相等 | ==?或?Equals | 兩者行為相同 |
| 引用類型地址相等 | == | 默認行為 |
| 引用類型值相等 | 重寫?Equals | 需同時重寫?GetHashCode |
| 字符串內容相等 | ==?或?Equals | 字符串已特殊處理 |
三、文件IO操作:數據持久化技術
1. FileStream基礎操作
// 創建文件信息對象
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo("data.txt");// 寫入文件
using (FileStream writeStream = fi.OpenWrite())
{byte[] data = { 65, 66, 67, 68, 69 };writeStream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}// 讀取文件
using (FileStream readStream = fi.OpenRead())
{byte[] buffer = new byte[fi.Length];int bytesRead = readStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);foreach (byte b in buffer){Console.WriteLine(b);}
}2. StreamReader/Writer高級操作
// 獲取動態路徑
string path = Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(), "data.txt");// 寫入數據
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(path, true)) // true表示追加模式
{sw.WriteLine("張三今天打游戲了");sw.WriteLine("李四今天游泳了");sw.WriteLine("王五今天吃飯了");
}// 讀取數據
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path))
{string content = sr.ReadToEnd();string[] lines = content.Split('\n');foreach (string line in lines){if (line.Contains("張三")){Console.WriteLine("找到張三的記錄");}}
}3. 文件操作最佳實踐
?路徑處理?:
- 使用
Path.Combine()構建路徑 - 使用
Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()獲取當前目錄 - 避免硬編碼絕對路徑
- 使用
?資源管理?:
- 始終使用
using語句確保資源釋放 - 處理文件不存在異常
- 檢查磁盤空間
- 始終使用
?性能優化?:
- 使用緩沖區減少IO操作
- 異步讀寫大文件
- 批量處理小文件
四、綜合案例:學生成績管理系統
1. 學生類實現
class Student
{public string Name { get; set; }public int Score { get; set; }public Student(string name, int score){Name = name;Score = score;}// 重寫Equals實現值比較public override bool Equals(object obj){if (obj is Student other)return Name == other.Name && Score == other.Score;return false;}public override int GetHashCode(){return Name.GetHashCode() ^ Score;}
}2. 文件存儲與加載
class ScoreManager
{private List<Student> students = new List<Student>();private string filePath;public ScoreManager(string path){filePath = path;LoadData();}// 加載數據private void LoadData(){if (File.Exists(filePath)){using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(filePath)){string line;while ((line = sr.ReadLine()) != null){string[] parts = line.Split(',');if (parts.Length == 2 && int.TryParse(parts[1], out int score)){students.Add(new Student(parts[0], score));}}}}}// 保存數據public void SaveData(){using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(filePath)){foreach (Student s in students){sw.WriteLine($"{s.Name},{s.Score}");}}}// 添加學生public void AddStudent(Student student){students.Add(student);}// 查找學生public Student FindStudent(string name){return students.Find(s => s.Name == name);}
}3. 系統使用示例
// 初始化管理器
ScoreManager manager = new ScoreManager("scores.txt");// 添加學生
manager.AddStudent(new Student("張三", 90));
manager.AddStudent(new Student("李四", 85));// 保存數據
manager.SaveData();// 查找學生
Student found = manager.FindStudent("張三");
if (found != null)
{Console.WriteLine($"找到學生: {found.Name}, 成績: {found.Score}");
}// 比較學生
Student s1 = new Student("王五", 80);
Student s2 = new Student("王五", 80);
Console.WriteLine(s1.Equals(s2)); // true學習總結與進階建議
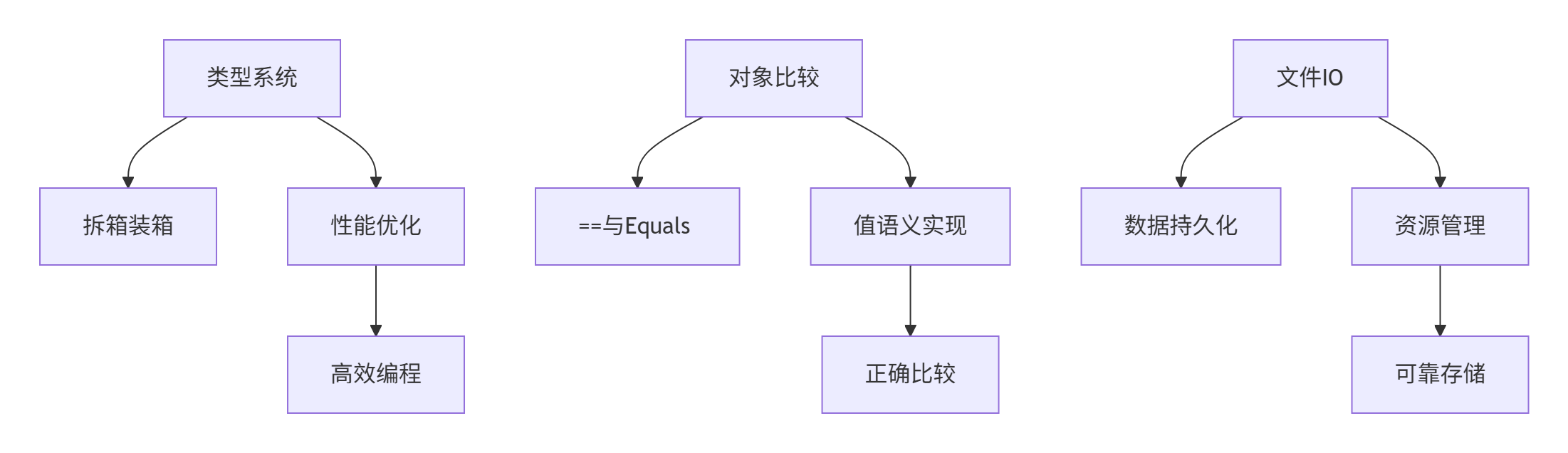
核心知識圖譜
關鍵編程原則
?類型轉換?:
- 避免不必要的裝箱拆箱
- 使用泛型集合替代非泛型集合
- 優先使用
as和is進行安全轉換
?對象比較?:
- 值類型直接使用
== - 引用類型按需重寫
Equals - 重寫
Equals時同步重寫GetHashCode
- 值類型直接使用
?文件操作?:
- 使用
using確保資源釋放 - 處理所有可能的IO異常
- 使用相對路徑增強可移植性
- 使用
實戰項目建議
?類型系統應用?:
- 實現高性能數值計算庫
- 開發類型安全的數據容器
- 創建泛型緩存系統
?對象比較實踐?:
- 實現深度比較工具
- 開發自定義集合類
- 創建對象差異檢測器
?文件IO實戰?:
- 開發配置管理系統
- 實現數據導入導出功能
- 創建日志記錄模塊
?編程箴言?
"理解類型轉換是性能優化的基礎,掌握對象比較是正確性的保障,善用文件IO是數據持久化的關鍵"

)

















)