之前我們編程都是在應用層,只需在地址結構體中傳 地址與端口號。然后協議棧在傳輸層,與網絡層幫我們進行數據的封裝。但這里我們要學的是在鏈路層進行編程

這里我想說一下,當數據到達鏈路層,有三個分支:ARP,IP,RARP 當數據湊夠IP,到達網絡層又有四個分支:ICMP,IGMP,TCP,UDP
當數據到達傳輸層,只看端口,不看分支
步入正題:
知識點1【原始套接字】
1、概述
原始套接字,是實現與系統核心的套接字,可以接受本機網卡上所有的數據幀(只要到達網卡的數據幀都可以收到)。
當我們利用標準套接字(SOCK_DGRAM,SOCK_STREAM),都需要借助傳輸層協議,然后借助網絡層協議,再到達網絡核心。
而原始套接字,可以直接到達網絡層,或者系統核心,而我們這里要學習的,就是直接到達系統核心,在系統核心上進行編程的。

補充

2、創建原始套接字
int socket(PF_PACKET,SOCK_RAW,protocol)
//第三個參數沒有固定
-
函數介紹
功能
創建鏈路層的原始套接字
參數
protocol:指定可以接受或發送的數據包類型
ETH_P_IP:IPV4數據包
ETH_P_ARP:ARP數據包
ETH_P_ALL:任何協議類型的數據包
返回值
成功:>0 鏈路層套接字
失敗:<0 出錯
代碼演示

代碼運行結果

這里我想說一下,因為我們實操偏底層的代碼,因此
所有的原始套接字都需要加sudo權限來執行可執行文件./a.out
這里補充一下,如果要使用宏ETH_P_…宏需要包含頭文件
#include <netinet/ether.h>
知識點2【數據包】

大家可以看到每個分支都有編號,我們下面將介紹

上圖,是頭部的添加以及解析流程。
1、UDP報文

UDP是傳輸層協議,因此它的數據是它的上一層:應用層
UDP的頭部是8個字節
0-15 源端口
16-31 目的端口
32-47 UDP數據長度
48-63 UDP檢驗和
一定要對報文有印象,這是我們組包和解包的前提
2、TCP報文
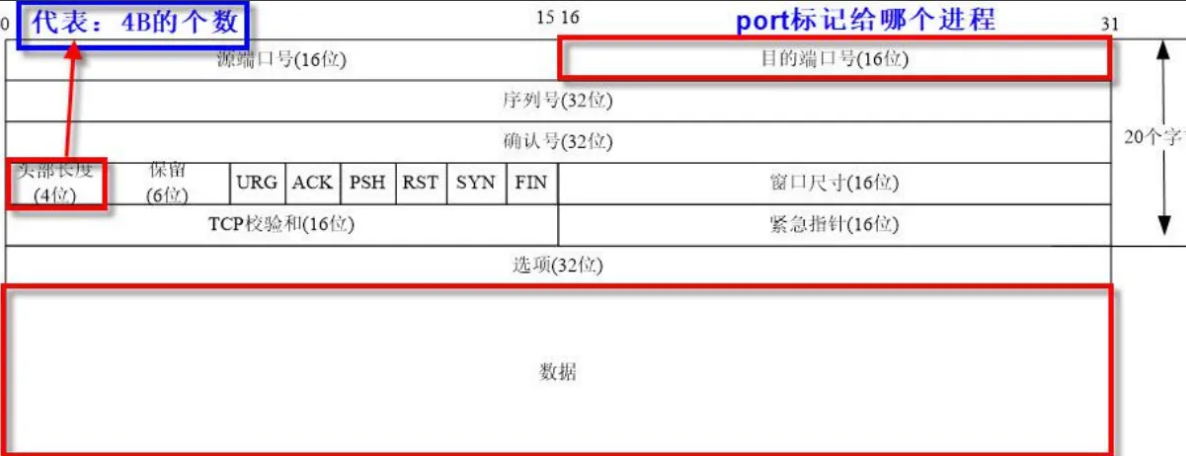
我們可以看到頭部長度4位,最大也只能表示15.
但是TCP就算不算選項,也需要20個字節,該如何存儲呢?
此時最大是15,只需要讓15中的每一個1,代表4B即可。這樣最多可以表示64個字節。
數據是源自應用層
0-15 源端口號
16-31 目的端口號
96-99 頭部長度
3、IP報文

數據包是來自傳輸層 的數據
0-3 版本:區分IPv4與IPv6 4→IPv4 6→IPv6
4-7 首部長度:數值0-15,單位是4B
16-31 總長度:頭部長度+來自傳輸層的數據 總長度
72-79 協議類型
1:ICMP
2:IGMP
6:TCP
17:UDP
96-127 源IP地址
128-159 目的IP地址
4、mac報文

數據包是來自網絡層的數據
0-47 目的mac地址
48-95 源mac地址
96-111 類型
0x0806 ARP數據包
0x0800 IP數據包
0x8035 RARP數據包
5、ICMP報文
我們的ping命令

不同的類型值和代碼值的組合代表不同的功能
8 0代表請求
0 8代表應答
知識點3【利用原始套接字捕獲網絡數據】
原始套接字使用 recvfrom函數 接收
這里我補充一下,原始套接字實在鏈路層,我們在鏈路層收數據,recvfrom的參數有地址結構體指針,這里就無需傳參了→NULL,因為傳參也沒有用,不經過網絡層,傳輸層,無法利用其協議,因此需要用戶自行解包。
代碼演示

代碼運行結果

這里運行之后 由于recvfrom帶阻塞仍能 源源不斷的收到數據,為什么呢?
這是因為我們xshell使用windows終端控制Linux終端,需要反復通信,因此會不斷發送數據
1、分析mac報文頭部

xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx\0
我們知道mac地址存儲時冒分法,16進制,并且高位補零。如上,因此如果打印成為字符串的形式總計18個字節
下面我們展示分析過程(提取mac報文頭部)
代碼演示
// 接收數據while (1){// recvfrom 收到的是一個完整的幀數據unsigned char buf[1500] = "";int len = recvfrom(fd_sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, NULL, NULL);if (len < 0){perror("recvfrom");_exit(-1);}printf("len == %d\\n", len);// 分析mac報文頭部char mac_src_addr[18] = "";char mac_dst_addr[18] = "";//提取源mac地址sprintf(mac_src_addr, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",buf[0], buf[1], buf[2], buf[3], buf[4], buf[5]);//提取目的mac地址sprintf(mac_dst_addr, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",buf[0 + 6], buf[1 + 6], buf[2 + 6], buf[3 + 6], buf[4 + 6], buf[5 + 6]);//這里補充說明:網絡字節序大端存儲,buf[0]存儲高位數據,因此需要按照上面方法提取//提取類型unsigned short mac_type = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)(buf + 12)));//遍歷printf("%s---->%s, ",mac_src_addr,mac_dst_addr);switch (mac_type){case 0x0800:printf("type:IP\\n");break;case 0x0806:printf("type:ARP\\n");break;case 0x8035:printf("type:RARP\\n");break;default:break;}}
代碼運行結果

我們查看一下5a和ef分別是誰?

這里我們驗證了,我們一直收到的數據 就是虛擬機和主機進行的通信
2、分析IP報文頭部
要分析ip頭部,需要先跳過mac頭
這里看一下IP的格式

10進制點分發,我們用字符串提取,16個字節(按照最多的算)
代碼演示
//分析IP報文頭部//跳過mac地址報文頭部unsigned char *ip = buf + 14;//這里一定要是無符號的//提取源IP與目的IPchar src_ip_addr[16] = "";char dst_ip_addr[16] = "";//提取IP的方法1//sprintf(src_ip_addr,"%d.%d.%d.%d",ip[12],ip[13],ip[14],ip[15]);//sprintf(dst_ip_addr,"%d.%d.%d.%d",ip[12 + 4],ip[13 + 4],ip[14 + 4],ip[15 + 4]);//提取IP的方法二inet_ntop(AF_INET,ip + 12,src_ip_addr,sizeof(src_ip_addr));inet_ntop(AF_INET,ip + 12,dst_ip_addr,sizeof(dst_ip_addr));printf("\\t%s---->%s, ",src_ip_addr,dst_ip_addr);//提取類型unsigned char ip_type = ip[9];switch (ip_type){case 1:printf("type:ICMP, ");break;case 2:printf("type:IGMP, ");break;case 6:printf("type:TCP, ");break;case 17:printf("type:UCP, ");break;default:break;}//提取一下版本與首部長度unsigned char version = ip[0];unsigned char len_head = ip[0];version >>= 4;len_head &= 0x0F;printf("version :%d, len_head = %d\\n",version,len_head * 4); //注意這里一定不要用%c遍歷,因為%c默認會遍歷其ASCII碼值,而并非數值}
代碼運行結果

代碼中的注意事項:
1、當遍歷char 類型數據的時候,要顯示數值使用%d,如果要顯示ascll碼才使用%c
2、ip無符號字符數組類型,buf也是無符號字符數組類型
3、ip的提取有兩種方式一種是組包法(sprintf),另一種是inet_ntop()法
3、分析TCP和UDP報文頭部
代碼演示(含 數據遍歷)
//分析TCP報文//從IP報文位置跳轉到TCP報文位置char *tcp = ip + ip_len_head;//提取目的端口號和源端口號unsigned short src_port_id_tcp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)tcp));unsigned short dst_port_id_tcp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)(tcp + 2)));printf("\\t\\t%hu---->%hu\\n",src_port_id_tcp,dst_port_id_tcp);//提取數據內容//跳轉到數據報文位置char tcp_len_head = (tcp[12]>>4) * 4;char *data_udp = tcp + tcp_len_head;printf("%s\\n",data_udp);
代碼運行結果

4、整體代碼
由于 數據內容遍歷影響 結果的查看,我們這里不遍歷數據
#include <stdio.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h> //socket()
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/ether.h> //ETH_P_ALLint main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// 創建原始套接字int fd_sock = socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL));if (fd_sock < 0){perror("sock");_exit(-1);}printf("fd_sock == %d\\n", fd_sock);// 接收數據while (1){// recvfrom 收到的是一個完整的幀數據unsigned char buf[1500] = "";int len = recvfrom(fd_sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, NULL, NULL);if (len < 0){perror("recvfrom");_exit(-1);}printf("len == %d\\n", len);// 分析mac報文頭部char mac_src_addr[18] = "";char mac_dst_addr[18] = "";// 提取源mac地址sprintf(mac_src_addr, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",buf[0], buf[1], buf[2], buf[3], buf[4], buf[5]);// 提取目的mac地址sprintf(mac_dst_addr, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",buf[0 + 6], buf[1 + 6], buf[2 + 6], buf[3 + 6], buf[4 + 6], buf[5 + 6]);// 這里補充說明:網絡字節序大端存儲,buf[0]存儲高位數據,因此需要按照上面方法提取// 提取類型unsigned short mac_type = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)(buf + 12)));// 遍歷printf("%s---->%s, ", mac_src_addr, mac_dst_addr);switch (mac_type){case 0x0800:printf("type:IP\\n");// 分析IP報文頭部// 跳過mac地址報文頭部unsigned char *ip = buf + 14; // 這里一定要是無符號的// 提取源IP與目的IPchar src_ip_addr[16] = "";char dst_ip_addr[16] = "";// 提取IP的方法1// sprintf(src_ip_addr,"%d.%d.%d.%d",ip[12],ip[13],ip[14],ip[15]);// sprintf(dst_ip_addr,"%d.%d.%d.%d",ip[12 + 4],ip[13 + 4],ip[14 + 4],ip[15 + 4]);// 提取IP的方法二inet_ntop(AF_INET, ip + 12, src_ip_addr, sizeof(src_ip_addr));inet_ntop(AF_INET, ip + 12, dst_ip_addr, sizeof(dst_ip_addr));printf("\\t%s---->%s, ", src_ip_addr, dst_ip_addr);// 提取一下版本與首部長度unsigned char version = ip[0];unsigned char ip_len_head = ip[0];version >>= 4;ip_len_head &= 0x0F;ip_len_head *= 4;printf("IP_version :%d, IP_len_head = %d, ", version, ip_len_head);// 注意這里一定不要用%c遍歷,因為%c默認會遍歷其ASCII碼值,而并非數值// 提取類型unsigned char ip_type = ip[9];switch (ip_type){case 1:printf("type:ICMP\\n");break;case 2:printf("type:IGMP\\n");break;case 6:printf("type:TCP\\n");//分析TCP報文//從IP報文位置跳轉到TCP報文位置char *tcp = ip + ip_len_head;//提取目的端口號和源端口號unsigned short src_port_id_tcp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)tcp));unsigned short dst_port_id_tcp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)(tcp + 2)));printf("\\t\\t%hu---->%hu\\n",src_port_id_tcp,dst_port_id_tcp);//提取數據內容//跳轉到數據報文位置char tcp_len_head = (tcp[12]>>4) * 4;char *data_tcp = tcp + tcp_len_head;//printf("%s\\n",data_udp);break;case 17:printf("type:UCP\\n");//分析UDP報文//從IP報文位置跳轉到UDP報文位置char *udp = ip + ip_len_head;//提取目的端口號和源端口號unsigned short src_port_id_udp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)udp));unsigned short dst_port_id_udp = ntohs(*((unsigned short *)(udp + 2)));printf("\\t\\t%hu---->%hu\\n",src_port_id_udp,dst_port_id_udp);//提取數據內容//跳轉到數據報文位置char *data_udp = udp + 8;//printf("%s\\n",data_udp);break;default:break;}break;case 0x0806:printf("type:ARP\\n");break;case 0x8035:printf("type:RARP\\n");break;default:break;}}// 關閉套接字close(fd_sock);return 0;
}代碼運行結果

結束
代碼重在練習!
代碼重在練習!
代碼重在練習!
今天的分享就到此結束了,希望對你有所幫助,如果你喜歡我的分享,請點贊收藏夾關注,謝謝大家!!!



)

 的最佳實踐)

--多文件上傳)


與TTS的深度融合)

 打包詳解)



主要應用在什么方面?涉及到具體知識是什么?)


