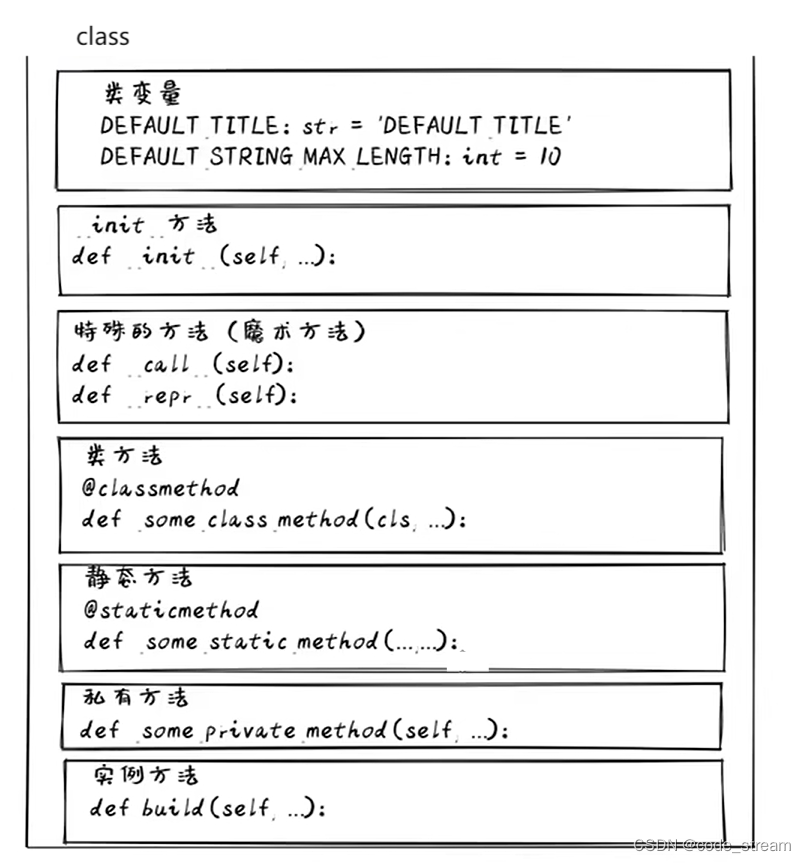
理想的類結構
@Property裝飾器
# 傳統寫法
class Square1:def __init__(self):self.__side = Nonedef get_side(self):return self.__sidedef set_side(self, side):assert side >= 0, '邊長不能為負數!'self.__side = sidedef del_side(self):# del self.__sideself.__side = 0 # 這里并不打算真的去刪除# Pythonic寫法
class Square2:def __init__(self):self.__side = None@propertydef side(self):return self.__side@side.setterdef side(self, side):assert side >= 0, '邊長不能為負數!'self.__side = side@side.deleterdef side(self):# del self.__sideself.__side = 0 # 這里并不打算真的去刪除s = Square2()
s.side = 10
print(s.side) # 10
del s.side
print(s.side) # 0公有化與私有化
# 在Python類里面,"屬性和方法"默認都是公有的(public)
class Person:def __init__(self, name: str, age: int):self._name = name # _ 類似與 C++ 的 protected,特點:_name 可以在類內部使用,也可以被繼承self.__age = age # __ 類似與 C++ 的 private,特點:__age 可以在類內部使用,但不可以被繼承@propertydef name(self):return self._name@name.setterdef name(self, name):self._name = name@propertydef age(self):return self.__age@age.setterdef age(self, name):self.__age = nameclass Teacher(Person): # 繼承Person類@propertydef info(self):return self._name, self.__age # 報錯,不存在 __age 屬性t = Teacher('Jack', 35)
print(t.info)屬性控制
# 屬性控制,可用于攔截或日志
class Person:# 控制獲取屬性def __getattribute__(self, item):print(f'getting attribute [{item}]')return super().__getattribute__(item) # 調用父級(object)的方法# 控制設置屬性def __setattr__(self, key, value):print(f'setting attribute [{key}] to [{value}]')super().__setattr__(key, value) # 調用父級(object)的方法person = Person()
person.name = 'Jack' # 觸發"__setattr__"方法
print(person.name) # 觸發"__getattribute__"方法"""
運行結果:setting attribute [name] to [Jack]
getting attribute [name]
Jack"""MRO
"""
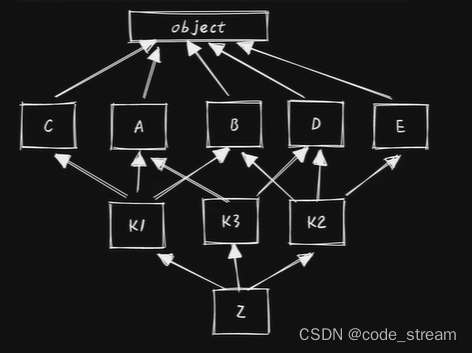
MRO: Method Resolution Order(方法解析順序)
作用:用于類的繼承樹的方法搜索順序在單繼承的情況下,我們可以很好的理解"類的繼承樹的方法順序"
但是在多繼承下,"類的繼承樹的方法順序"就顯得尤為復雜了(在 Python3 里面,使用了C3線性化的算法進行排序)
通常情況下,我們可以使用類的 mro() 方法來直接查看"類的繼承樹的方法順序"
"""class A(object):passclass B(object):passclass C(object):passclass D(object):passclass E(object):passclass K1(C, A, B):passclass K2(A, D):passclass K3(B, D, E):passclass Z(K1, K2, K3):passprint(Z.mro())
# [
# <class '__main__.Z'>,
# <class '__main__.K1'>,
# <class '__main__.C'>,
# <class '__main__.K2'>,
# <class '__main__.A'>,
# <class '__main__.K3'>,
# <class '__main__.B'>,
# <class '__main__.D'>,
# <class '__main__.E'>,
# <class 'object'>
# ]可迭代對象
# 利用迭代對象進行迭代,本質是用時間換取空間
# 在迭代進行的那一刻,數據才被產生或處理,從而大幅降低了內存空間的占用print('\n-----------------------------')# 可迭代對象的迭代
lst = [66, 77, 88]
for num in lst:print(num, end=' ')print('\n-----------------------------')# 上面 for 循環的迭代原理如下
iter_obj = lst.__iter__()
print(iter_obj.__next__(), end=' ')
print(iter_obj.__next__(), end=' ')
print(iter_obj.__next__(), end=' ')print('\n-----------------------------')# 自定義可迭代對象
class Fibonacci: # 斐波那契數"""F0 = 0F1 = 1Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2 (n >= 2)0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, ..."""def __init__(self, n):self.__n = nself.__previous = 0self.__current = 1self.__count = 0def __iter__(self):return selfdef __next__(self):if self.__count >= self.__n:raise StopIterationself.__count += 1return_value = self.__previousself.__previous, self.__current = self.__current, self.__previous + self.__currentreturn return_value# 自定義可迭代對象的迭代
for num in Fibonacci(12):print(num, end=' ')print('\n-----------------------------')"""
運行結果:-----------------------------
66 77 88
-----------------------------
66 77 88
-----------------------------
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89
-----------------------------"""__getitem__()方法
"""
在創建一個可迭代的對象序列時,可以用__iter__()和__next__()方法
如果沒有這兩個方法,我們還可以通過__getitem__()方法和__len__()方法進行創建序列
如果__getitem__()方法和__len__()方法也沒有的話,解釋器會拋出 TypeError 的錯誤!而__getitem__()方法與上面的__iter__()方法正好相反
它是以空間換取時間:1.先占用內存,布置好數據2.隨機查找的時間復雜度 O(1)
"""from datetime import date, timedeltaclass DateRange:def __init__(self, start_dt, end_dt):self.start_dt = start_dtself.end_dt = end_dtself._range_values = self._get_range_values()def _get_range_values(self):data = []current_dt = self.start_dtwhile current_dt <= self.end_dt:data.append(current_dt)current_dt += timedelta(days=1)return datadef __len__(self):print("You are using the method of len().")return len(self._range_values)def __getitem__(self, index):print("You are using the symbol of [] to get item.")return self._range_values[index]my_date_range = DateRange(date(2024, 6, 1), date(2024, 6, 3))
print(len(my_date_range))for my_date in my_date_range:print(my_date)"""
迭代原理:
在 DateRange 類中,盡管我們沒有顯式地定義__iter__(),但由于定義了__getitem__和__len__,因此你仍然可以在for循環中使用my_date_range對象。
Python 會自動為我們處理迭代過程,使用你定義的__getitem__來獲取日期,直到索引超出由__len__指定的范圍。
總結起來,for循環在 Python 中確實是通過迭代對象來工作的,但迭代對象不一定需要顯式地定義__iter__()。
如果對象定義了__getitem__和__len__(并且表現出序列的特性),Python將為你提供一個隱式的迭代器,使得你可以在for循環中使用該對象。運行結果:You are using the method of len().
3
You are using the symbol of [] to get item.
2024-06-01
You are using the symbol of [] to get item.
2024-06-02
You are using the symbol of [] to get item.
2024-06-03
You are using the symbol of [] to get item."""__contains__()方法
class Product: # 產品def __init__(self, name: str, price: float, num: int) -> None:self.name = nameself.price = priceself.num = numclass Promotion: # 促銷方案def __init__(self, lower_num: int, upper_num: int, rate: float) -> None:self.__lower_num = lower_numself.__upper_num = upper_numself.__rate = rate@propertydef rate(self) -> float:return self.__ratedef __contains__(self, product: Product) -> bool:return self.__lower_num <= product.num <= self.__upper_numdef get_total_price(products: [Product], promotions: [Promotion]) -> float:total_price = 0for product in products:promotion = [promotion for promotion in promotions if product in promotion][0] # in 觸發 __contains__()方法total_price += product.price * promotion.ratereturn total_priceif __name__ == '__main__':top_promotion = Promotion(100, 199, 0.5) # 最好促銷方案average_promotion = Promotion(50, 99, 0.8) # 一般促銷方案none_promotion = Promotion(0, 49, 1.0) # 沒有優惠的促銷方案promotions = (top_promotion, average_promotion, none_promotion)products = (Product('cart', 89188.90, 188),Product('computer', 7999.99, 66),Product('toy', 13.60, 27),)total_price = round(get_total_price(products, promotions), 2)print(total_price) # 51009.04動態處理對象屬性
class Person:def __init__(self, name: str) -> None:self.name = namedef __getattribute__(self, attr):print("All operations that get attribute trigger this function to execute.")return super().__getattribute__(attr)def __getattr__(self, attr):print(f"You're trying to get attribute [{attr}], but the attribute is not defined.")return '空空如也'def __setattr__(self, key, value):print(f"You are setting the [{key}] attribute to [{value}].")super().__setattr__(key, value)person = Person('Jack')
print(person.name)
# You are setting the [name] attribute to [Jack].
# All operations that get attribute trigger this function to execute.
# Jackperson.age = 33
print(person.age)
# You are setting the [age] attribute to [33].
# All operations that get attribute trigger this function to execute.
# 33# 如果嘗試獲取沒有定義過的屬性,會觸發 __getattr__() 方法
print(person.hobby)
# All operations that get attribute trigger this function to execute.
# You're trying to get attribute [hobby], but the attribute is not defined.
# 空空如也__call__()方法
class MyPrint:def __call__(self, text: str, end=''):print(text, end=end)return selfmy_print = MyPrint()
print(callable(my_print)) # True
my_print("你好呀")("我很好")("那就好")("都很好") # 你好呀我很好那就好都很好__str__()與__repr__()
class Person:def __init__(self, name: str, hobby: [str]) -> None:self.name = nameself.hobby = hobbydef __str__(self):return f"{self.name} like {','.join(self.hobby)}"def __repr__(self):return f"Person(name={self.name}, hobby={self.hobby}"person = Person('Jack', ['football', 'basketball'])
print(person) # 調用 __str__()方法
print(str(person)) # 調用 __str__()方法
print(repr(person)) # 調用 __repr__()方法"""
__str__()方法是用于普通人群、客戶看
__repr__()方法是用于機器、開發人員看運行結果:Jack like football,basketball
Jack like football,basketball
Person(name=Jack, hobby=['football', 'basketball']"""深拷貝
import copylist1 = [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]
list2 = copy.deepcopy(list1)print(list1, id(list1))
print(list2, id(list2))# [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]] 2016821662784
# [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]] 2016821293952import copyclass A:def __repr__(self):return f"A: {id(self)}"class B:def __init__(self, a: A) -> None:self.a = aself.b = selfself.c = 1def __repr__(self):return f"B: {id(self.a)}, {id(self.b)}, {id(self.c)}"a1 = A()
b1 = B(a1)memo = {}
b2 = copy.deepcopy(b1, memo=memo)print(a1)
print(b1)
print(b2)b2.c = 3print(a1)
print(b1)
print(b2)"""
運行結果:(內存地址)A: 2124853485392
B: 2124853485392, 2124853487120, 140716077503272
B: 2124853487056, 2124851868688, 140716077503272
A: 2124853485392
B: 2124853485392, 2124853487120, 140716077503272
B: 2124853487056, 2124851868688, 140716077503336"""
抽象類與方法
from abc import abstractmethod, ABCMeta# 抽象類
class Component(metaclass=ABCMeta):@abstractmethoddef bind_data(self): # 抽象方法pass@abstractmethoddef render(self): # 抽象方法pass# 具體類
class ProductListComponent(Component):def bind_data(self): # 具體實現return ['computer', 'life']def render(self): # 具體實現for item in self.bind_data():print(f'--- {item.upper()} ---')product_list_component = ProductListComponent()
product_list_component.render()數據類
"""
我們知道,在C/C++/C#語言里面,都有結構體Struct,它作為數據的載體,我們使用它處理數據很方便
在python里面,同樣提供了類似的東西,就是數據類————@dataclass
數據類,在Python3.7版本開始以標準庫方式提供為什么要用數據類呢?
因為使用普通的類進行數據的封裝與處理,往往需要經過很多繁瑣且無意義的工作,比如使用__init__()方法聲明數據等等
而使用數據類,將能幫助我們減少這些繁瑣的操作,將精力集中在處理數據本身上
"""class Person:def __init__(self, name: str, age: int) -> None:self.name = nameself.age = agedef __repr__(self) -> str:return f"{self.name}({self.age})"obj1 = Person("Jack", 28)
obj2 = Person("John", 35)
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
print(obj1 == obj2)
# Jack(28)
# John(35)
# Falsefrom dataclasses import dataclass@dataclass
class People:name: strage: intobj1 = People("Jack", 28)
obj2 = People("John", 35)
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
print(obj1 == obj2)
# People(name='Jack', age=28)
# People(name='John', age=35)
# False官方文檔:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/dataclasses.html
元類
# 所有類的祖宗————type# int類
num = 3
print(type(num))
print(type(type(num)))
print(type(type(type(num))))
# <class 'int'>
# <class 'type'>
# <class 'type'># str類
name = "Jack"
print(type(name))
print(type(type(name)))
print(type(type(type(name))))
# <class 'str'>
# <class 'type'>
# <class 'type'># bool類
flag = True
print(type(flag))
print(type(type(flag)))
print(type(type(type(flag))))
# <class 'bool'>
# <class 'type'>
# <class 'type'># Object類
print(type(object))
print(type(type(object)))# <class 'type'>
# <class 'type'># 自定義類
class MyClass:passobj = MyClass()print(type(obj))
print(type(type(obj)))
print(type(type(type(obj))))
print('=' * 16)
# <class '__main__.MyClass'>
# <class 'type'>
# <class 'type'># 通過類的祖宗type創建一個類(類對象)
# 1. 定義類里面要實現的方法
def __repr__(self):return f"{self.__class__.__name__}(wheel={self.wheel}, type={self.size})"# 2. 通過type()創建類對象
# --- 參數: ( 類的名稱、(要繼承的父類...)、{ 要定義的屬性: ... } )
Vehicle = type('Vehicle', (), {'wheel': 4, '__repr__': __repr__, })
Bus = type('Bus', (Vehicle,), {'size': 'big', })
Truck = type('Truck', (Vehicle,), {'size': 'extremely big', })# 類的實例
bus = Bus()
truck = Truck()
print(bus)
print(truck)
# Bus(wheel=4, type=big)
# Truck(wheel=4, type=extremely big)class MetaAutoAttributes(type):def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):# 在這里我們可以修改或添加attrs中的屬性attrs['auto_attribute'] = 'This is an automatically added attribute'# 調用父類的__new__方法來創建類return super().__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs)# 使用自定義元類class MyClass(metaclass=MetaAutoAttributes):pass# 創建MyClass的實例
obj = MyClass()# 訪問自動添加的屬性
print(obj.auto_attribute) # 輸出: This is an automatically added attribute推薦閱讀:https://www.cnblogs.com/JetpropelledSnake/p/9094103.html
函數裝飾器
import timedef timer(func):start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間func()end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")def show():print('showing...')time.sleep(0.5)timer(show)# showing...
# 耗時:0.5006642000516877import timedef timer(func):start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間res = func()end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")return resdef show():print('showing...')time.sleep(0.5)return "OK"result = timer(show)
print(result)# showing...
# 耗時:0.5005822000093758
# OKimport timedef timer(func):def inner(*args, **kwargs):start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間res = func(*args, **kwargs)end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")return resreturn innerdef show(name: str) -> str:print(f'{name} is showing...')time.sleep(0.5)return "OK"show = timer(show)
result = show('Jack')
print(result)
print(show.__name__) # 不完美的偽裝# Jack is showing...
# 耗時:0.5001411000266671
# OK
# innerimport time
import functoolsdef timer(func):@functools.wraps(func) # 完美偽裝def inner(*args, **kwargs):start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間res = func(*args, **kwargs)end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")return resreturn innerdef show(name: str) -> str:print(f'{name} is showing...')time.sleep(0.5)return "OK"show = timer(show)
result = show('Jack')
print(result)
print(show.__name__) # 完美偽裝# Jack is showing...
# 耗時:0.5001411000266671
# OK
# showimport time
import functoolsdef timer(func):@functools.wraps(func)def inner(*args, **kwargs):start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間res = func(*args, **kwargs)end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")return resreturn inner@timer # 使用語法糖
def show(name: str) -> str:print(f'{name} is showing...')time.sleep(0.5)return "OK"# 不再使用原生的 show = timer(show) ,而是使用語法糖
result = show('Jack')
print(result)
print(show.__name__)# Jack is showing...
# 耗時:0.5002126999897882
# OK
# show含參裝飾器
import time
import functoolsdef timer(appearance=False): # 是否開啟外觀模式,默認不開啟def outer(func):@functools.wraps(func)def inner(*args, **kwargs):if appearance:print("=" * 16)start = time.perf_counter() # 統計時間res = func(*args, **kwargs)end = time.perf_counter()print(f"耗時:{end - start}")if appearance:print("=" * 16)return resreturn innerreturn outer@timer(appearance=True)
def show(name: str) -> str:print(f'{name} is showing...')time.sleep(0.5)return "OK"result = show('Jack')
print(result)# ================
# Jack is showing...
# 耗時:0.5003457000711933
# ================
# OK類裝飾器
# 裝飾功能:給被裝飾的類,添加兩個方法
class Entity:def __call__(self, cls):# 聲明第一個方法def __repr__(self) -> str:return f'{cls.__qualname__}' # __qualname__ 用于獲取類或函數的完全限定名稱,即包括模塊名稱和嵌套結構# 聲明第二個方法def is_adult(self) -> bool:return self.age > 18# 給被裝飾的類,添加上面兩個方法cls.__repr__ = __repr__cls.is_adult = is_adultreturn cls@Entity() # Entity() 實例化一個對象. 對象 + __call__() 方法 == 函數()
class User:def __init__(self, name, age):self.name = ageself.age = age# 本質:User = obj(User)
# 本質:User = clsuser = User('Jack', 35)
print(user)
print(user.is_adult())
# User
# True上下文管理器
# 傳統操作
file = open('test.txt', 'w')
try:file.write('This is a test file.')
except Exception as e:print(e)
finally:file.close()# 利用上下文管理器with操作
with open('test.txt', 'w') as file:file.write('This is a test file.')# 查看是否已經關閉文件(資源)
print(file.closed) # True# 自定義上下文管理器
class FileManager:def __init__(self, filename: str, mode: str) -> None:self.filename = filenameself.mode = modeself.file = None # 初始化文件對象def __enter__(self):print('>>> Open', self.filename)self.file = open(self.filename, self.mode)print(">>> file object:", self.file) # 測試return self.filedef __exit__(self, error_type, error_value, traceback):if self.file:print('>>> Close', self.filename)self.file.close()with FileManager('test.txt', 'r') as file:print(">>> file object:", file) # 測試print("==========<File Content>==========")print(file.read())print("==========<File Content>==========")# >>> Open test.txt
# >>> file object: <_io.TextIOWrapper name='test.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp936'>
# >>> file object: <_io.TextIOWrapper name='test.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp936'>
# ==========<File Content>==========
# This is a test file.
# ==========<File Content>==========
# >>> Close test.txtclass Sequence: # 順序-sequencedef __init__(self, start: int, end: int) -> None:self.start = startself.end = enddef __enter__(self):self.data = list(range(self.start, self.end))return self.data# 參數:異常類型,異常值,異常回溯。 返回值:True(停止異常繼續往外拋出)def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):# 判斷是否為索引越界的錯誤類型if isinstance(exc_val, IndexError): # isinstance(66, int) ==> 66 是不是 int 類的實例(對象),如果是,返回值True,如果不是,返回值Falseprint(f'索引超出范圍:[{self.start}, {self.end})')return Truewith Sequence(1, 10) as seq:print(seq[5]) # 6print(seq[15]) # 索引超出范圍:[1, 10)import timeclass Timer:def __enter__(self):self.start = time.perf_counter()self.end = 0def elapsed():return self.end - self.startreturn elapseddef __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):self.end = time.perf_counter()with Timer() as timer:print('Start to do sth.')time.sleep(1)print('Stop to do sth.')print("運行時間:", timer())# Start to do sth.
# Stop to do sth.
# 運行時間: 1.0006713000002492)
)










)






