歡迎大家關注全網生信學習者系列:
- WX公zhong號:生信學習者
- Xiao hong書:生信學習者
- 知hu:生信學習者
- CDSN:生信學習者2
介紹
中介分析(Mediation Analysis)是一種統計方法,用于研究一個自變量(通常是獨立變量或預測變量)如何通過一個或多個中介變量(也稱為中介因素或中介機制)影響因變量(通常是響應變量或結果變量)。中介分析的目的是揭示變量之間的內在關系,特別是自變量對因變量的間接效應,以及這種效應是如何通過中介變量傳遞的。
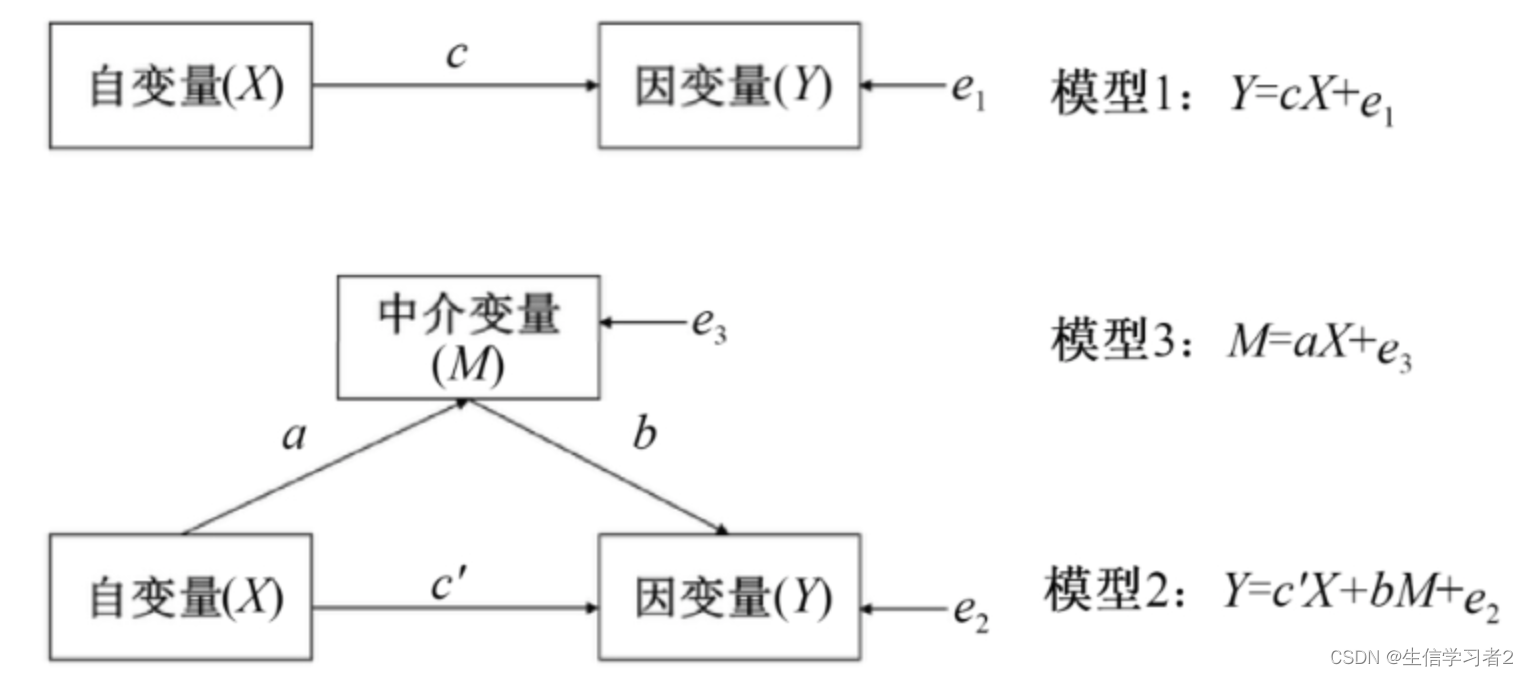
評估識別出的與結局變量顯著相關的標記物如炎癥細胞因子cytokines、腸道微生物gut microbiota和短鏈脂肪酸SCFA是否能夠在伴侶數目number of partners和HIV-1血清轉化HIV-1 seroconversion之間起到中介作用。
自然效應模型(Natural Effect Model)是一種統計方法,用于估計在自然情況下(即在沒有干預或隨機分配的情況下)變量之間的因果關系。在流行病學和臨床研究中,這種模型特別有用,因為它可以幫助研究者了解不同因素對健康結果的自然影響。以下是中介分析的變量解析:
-
exposure variables (自變量X): consisting of sexual exposure groups
-
mediators (中介變量M): biomarkers (cytokines, gut microbiota, SCFA)
-
outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
加載R包
library(readr)
library(openxlsx)
library(tidyverse)
library(microbiome)
library(mia)
library(compositions)
library(medflex)
library(ggsci)
library(ggpubr)
導入數據
大家通過以下鏈接下載數據:
- 百度網盤鏈接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fz5tWy4mpJ7nd6C260abtg
- 提取碼: 請關注WX公zhong號_生信學習者_后臺發送 復現gmsb 獲取提取碼
df_v1 <- read_csv("./data/GMSB-data/df_v1.csv", show_col_types = FALSE)bias_corr_species <- read_csv("./data/GMSB-data/results/outputs/bias_corr_species.csv")sig_species_raw1 <- read.xlsx("./data/GMSB-data/results/outputs/res_ancombc2.xlsx", sheet = 1)
sig_species_raw2 <- read.xlsx("./data/GMSB-data/results/outputs/res_ancombc2.xlsx", sheet = 2) # 趨勢分析結果
ne_trend_test <- readRDS("./data/GMSB-data/rds/ne_trend_test.rds")
數據預處理
-
提取差異物種豐度表
-
合并分組變量和差異物種豐度表
df_v1 <- df_v1 %>%dplyr::filter(group1 != "missing",druguse != "missing")# Microbiome data
bias_corr_species <- bias_corr_species %>%dplyr::rowwise() %>%dplyr::filter(grepl("Species:", species)|grepl("Genus:", species)) %>%dplyr::mutate(species = ifelse(grepl("Genus:", species), paste(strsplit(species, ":")[[1]][2], "spp."),strsplit(species, ":")[[1]][2])) %>%dplyr::ungroup() # Significant taxa by group
sig_species1 <- sig_species_raw1 %>%dplyr::filter(p_val < 0.05) %>%.$taxon# Significant taxa by status
sig_species2 <- sig_species_raw2 %>%dplyr::filter(p_statussc < 0.05) %>%.$taxonsig_species <- sort(base::intersect(sig_species1, sig_species2))# Subset significant taxa
df_da_species <- bias_corr_species %>%dplyr::filter(species %in% sig_species)
df_da_species <- t(df_da_species)
colnames(df_da_species) <- df_da_species[1, ]
df_da_species <- data.frame(df_da_species[-1, , drop = FALSE], check.names = FALSE) %>%rownames_to_column("sampleid") %>%dplyr::mutate(across(-1, as.numeric))# Exposure, outcome, confounders, and potential mediators
# cytokines overlap: sCD14 and sCD163
# SCFA overlap: none
df_causal <- df_v1 %>%dplyr::select(sampleid, recept_anal, group1, status, druguse, cd14, cd163) %>%dplyr::left_join(df_da_species, by = "sampleid")
df_causal$status <- factor(df_causal$status)
df_causal$group1 <- factor(df_causal$group1)
df_causal$druguse <- factor(df_causal$druguse)
df_causal <- data.frame(df_causal)head(df_causal)
| sampleid | recept_anal | group1 | status | druguse | cd14 | cd163 | Dehalobacterium.spp. | Bacteroides.spp. | ||
| 1 | F-1 | 5 | g3 | nc | yes | 1681.160 | 665.6528 | NA | 0.1151280 | |
| 2 | F-2 | 6 | g4 | nc | yes | 1178.440 | 336.1164 | -0.1870557 | -1.0903494 | |
| 3 | F-3 | 3 | g3 | nc | yes | 1717.935 | 495.9060 | NA | -0.3093994 | |
| 4 | F-4 | 7 | g4 | nc | yes | 1271.675 | 536.5375 | NA | -3.3221487 | |
| 5 | F-5 | 4 | g3 | nc | yes | 929.645 | 472.6636 | -1.1128170 | -1.2803083 | |
| 6 | F-6 | 4 | g3 | nc | no | 1103.670 | 382.0072 | NA | 1.8015313 |
函數
-
constrain_est:提取約束線性模型的beta值 -
l_infty:計算l_infty norm值 -
trend_test:趨勢檢驗
# Estimate coefficients under constraints
constrain_est <- function(beta_hat, vcov_hat, contrast, solver = "ECOS") {beta_opt <- CVXR::Variable(rows = length(beta_hat), cols = 1, name = "beta")obj <- CVXR::Minimize(CVXR::matrix_frac(beta_opt - beta_hat, vcov_hat))cons <- suppressMessages(contrast %*% beta_opt >= 0)problem <- CVXR::Problem(objective = obj, constraints = list(cons))suppressMessages(result <- try(CVXR::solve(problem, solver = solver), silent = TRUE))if (inherits(result, "try-error")) {beta_opt <- rep(0, length(beta_hat))} else {beta_opt <- as.numeric(result$getValue(beta_opt))}return(beta_opt)
}# Compute the l_infty norm for a pattern
l_infty <- function(beta_opt, node) {l <- max(abs(beta_opt[node]),abs(beta_opt[node] - beta_opt[length(beta_opt)]),na.rm = TRUE)return(l)
}# Trend test
trend_test <- function(beta_hat, vcov_hat, contrast, solver = "ECOS",node, B = 1000) {beta_opt <- constrain_est(beta_hat = beta_hat,vcov_hat = vcov_hat,contrast = contrast,solver = solver)l_opt <- l_infty(beta = beta_opt, node = node)beta_null <- MASS::mvrnorm(n = B, mu = rep(0, length(beta_hat)), Sigma = vcov_hat)l_null <- apply(beta_null, 1, function(x) {beta_trend <- constrain_est(beta_hat = x, vcov_hat = vcov_hat, contrast = contrast,solver = solver)l_trend <- l_infty(beta = beta_trend, node = node)})p_trend <- 1/B * sum(l_null > l_opt)res <- list(estimate = beta_opt,test_statistic = l_opt,p_value = p_trend)return(res)
}contrast_mat <- matrix(c(1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0,0, -1, 1),nrow = 3, byrow = TRUE)
Cytokine mediators
炎癥細胞因子作為中介變量
All cytokines
-
多重插補
medflex::neImpute():- 使用
medflex::neImpute()函數進行多重插補。 - status是響應變量,而group1, cd14, cd163, druguse是預測變量。
- family = binomial(“logit”)指定了使用邏輯斯蒂回歸模型,適用于二分類結果的變量。
- nMed = 2表示生成兩個不同的插補數據集。
group1生成了group10和group11兩個插補數據集。- 這個步驟是為了處理數據中的缺失值,通過生成多個完整的數據集來模擬缺失數據的可能值。
- 使用
-
構建自然效應模型
Natural effects model:- 使用
medflex::neModel()函數來擬合自然效應模型。 - 公式status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse定義了模型,其中status是響應變量,group10, group11, druguse是預測變量。
group10和group11來自medflex::neImpute()函數的多重插補。 - family = binomial(“logit”)再次指定了模型的分布族和鏈接函數。expData = df_exp指定了使用經過多重插補的數據集來進行模型擬合。
- se = "robust"表示使用穩健的標準誤差估計,這有助于在模型估計中減少異方差性的影響。
- 使用
-
中介分析使用
Natural effects model:- exposure variables (自變量X): consisting of sexual exposure groups
- mediators (中介變量M): cytokines
- outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
- adjusted variable (混淆變量): druguse
- NDE: natural direct effect(自變量X不經過中介變量M直接對因變量Y的效應大小)
- NIE: natural indirect effect(自變量X僅通過中介變量M間接對因變量Y的效應大小)
df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, cd14, cd163, druguse) %>%drop_na()df_exp <- medflex::neImpute(status ~ group1 + cd14 + cd163 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), nMed = 2, data = df)ne_mod <- medflex::neModel(status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")summ <- summary(ne_mod)
df_summ <- data.frame(summ$coefficients)# Trend test
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nde <- trend_test(
# beta_hat = summ$coefficients[2:4, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[2:4, 2:4],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
#
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nie <- trend_test(
# beta_hat = summ$coefficients[5:7, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[5:7, 5:7],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
#
# ne_trend_test <- base::append(
# ne_trend_test,
# list(cyto_nde = trend_nde, cyto_nie = trend_nie))# Outputs
types <- c("nde", "nie")
groups <- c("g2", "g3", "g4")
res <- data.frame(type = rep(types, each = length(groups)),group = rep(groups, length(types)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA,trend_p = NA)res$estimate <- round(df_summ$Estimate[2:7], 2)
res$se <- round(df_summ$Std..Error[2:7], 2)
res$p <- round(df_summ$Pr...z..[2:7], 3)
res$trend_p[3] <- round(ne_trend_test$cyto_nde$p_value, 3)
res$trend_p[6] <- round(ne_trend_test$cyto_nie$p_value, 3)head(res)
| type | group | estimate | se | p | trend_p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nde | g2 | 1.92 | 0.64 | 0.003 | NA |
| 2 | nde | g3 | 2.56 | 0.61 | 0.000 | NA |
| 3 | nde | g4 | 3.55 | 0.70 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 4 | nie | g2 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.284 | NA |
| 5 | nie | g3 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.168 | NA |
| 6 | nie | g4 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.023 | 0.007 |
結果:炎癥細胞因子cytokines在不同分組的直接和間接效應的結果
-
nde直接效應:具體來說,對于沒有
druguse的受試者,增加從第1組到另一組的暴露【同時保持sCD14和sCD163在同一水平】顯著增加了血清轉化的幾率。第2、3、4組的優勢比為exp(1.92) = 6.82; Exp (2.56) = 12.94, Exp (3.55) = 34.81; -
nie間接效應,對于未
druguse的受試者,將sCD14和sCD163的水平從第1組觀察到的水平轉移到第4組可能看到的水平,同時在任何給定組保持暴露不變,增加血清轉化的幾率,比值比為exp(0.33) = 1.39。炎癥因子水平從g1組水平轉變成g4組,則對應HIV-1血清風險增加。
Individual cytokines
單個細胞因子的中介分析
features <- c("cd14", "cd163")
groups <- c("g2", "g3", "g4")
res_nde <- data.frame(type = "nde",feature = rep(features, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(features)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA)
res_nie <- data.frame(type = "nie",feature = rep(features, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(features)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA)for (i in seq_along(features)) {df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, druguse, all_of(features[i])) %>%drop_na()t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ group1 + ", features[i], " + druguse"))df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula, family = binomial("logit"), data = df)ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")summ <- summary(ne_mod)idx <- seq_along(groups) + (i - 1) * length(groups)res_nde[idx, "estimate"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Estimate"], 2)res_nde[idx, "se"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Std. Error"], 2)res_nde[idx, "p"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Pr(>|z|)"], 3)res_nie[idx, "estimate"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Estimate"], 2)res_nie[idx, "se"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Std. Error"], 2)res_nie[idx, "p"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Pr(>|z|)"], 3)
}res <- rbind(res_nde, res_nie)head(res)
| type | feature | group | estimate | se | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nde | cd14 | g2 | 1.99 | 0.64 | 0.002 |
| 2 | nde | cd14 | g3 | 2.59 | 0.61 | 0.000 |
| 3 | nde | cd14 | g4 | 3.66 | 0.69 | 0.000 |
| 4 | nde | cd163 | g2 | 2.01 | 0.65 | 0.002 |
| 5 | nde | cd163 | g3 | 2.69 | 0.62 | 0.000 |
| 6 | nde | cd163 | g4 | 3.76 | 0.71 | 0.000 |
Microbial species
炎癥細胞因子作為中介變量
All species
-
中介分析使用
Natural effects model:- exposure variables (自變量X): consisting of sexual exposure groups
- mediators (中介變量M): gut microbiota
- outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
- adjusted variable (混淆變量): druguse
# Natural effects model
all_species <- colnames(df_causal)[8:16]
df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, druguse, all_of(all_species))
df[is.na(df)] <- 0t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ group1 + ", paste0(all_species, collapse = " + "), " + druguse"))
df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula,family = binomial("logit"), nMed = length(all_species), data = df)ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")summ <- summary(ne_mod)
df_summ <- data.frame(summ$coefficients)# Trend test
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nde <- trend_test(beta_hat = summ$coefficients[2:4, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[2:4, 2:4],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nie <- trend_test(beta_hat = summ$coefficients[5:7, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[5:7, 5:7],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
#
# ne_trend_test <- base::append(ne_trend_test,
# list(species_nde = trend_nde, species_nie = trend_nie))# Outputs
type <- c("nde", "nie")
groups <- c("g2", "g3", "g4")
res <- data.frame(type = rep(types, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(type)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA,trend_p = NA)
res$estimate <- round(df_summ$Estimate[2:7], 2)
res$se <- round(df_summ$Std..Error[2:7], 2)
res$p <- round(df_summ$Pr...z..[2:7], 3)
res$trend_p[3] <- round(ne_trend_test$species_nde$p_value, 3)
res$trend_p[6] <- round(ne_trend_test$species_nie$p_value, 3)head(res)
| type | group | estimate | se | p | trend_p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nde | g2 | 2.08 | 0.68 | 0.002 | NA |
| 2 | nde | g3 | 2.61 | 0.64 | 0.000 | NA |
| 3 | nde | g4 | 3.58 | 0.71 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 4 | nie | g2 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.879 | NA |
| 5 | nie | g3 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.264 | NA |
| 6 | nie | g4 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.045 | 0.033 |
Individual species
features <- sort(all_species)
groups <- c("g2", "g3", "g4")
res_nde <- data.frame(type = "nde",feature = rep(features, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(features)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA)
res_nie <- data.frame(type = "nie",feature = rep(features, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(features)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA)for (i in seq_along(features)) {df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, druguse, all_of(features[i])) %>%drop_na()t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ group1 + ", features[i], " + druguse"))df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula, family = binomial("logit"), data = df)ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")summ <- summary(ne_mod)idx = seq_along(groups) + (i - 1) * length(groups)res_nde[idx, "estimate"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Estimate"], 2)res_nde[idx, "se"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Std. Error"], 2)res_nde[idx, "p"] <- round(summ$coefficients[2:4, "Pr(>|z|)"], 3)res_nie[idx, "estimate"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Estimate"], 2)res_nie[idx, "se"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Std. Error"], 2)res_nie[idx, "p"] <- round(summ$coefficients[5:7, "Pr(>|z|)"], 3)
}res <- rbind(res_nde, res_nie)head(res)
| type | feature | group | estimate | se | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nde | A.muciniphila | g2 | -0.62 | 1.37 | 0.649 |
| 2 | nde | A.muciniphila | g3 | 1.57 | 0.88 | 0.076 |
| 3 | nde | A.muciniphila | g4 | 3.46 | 1.37 | 0.012 |
| 4 | nde | B.caccae | g2 | 0.90 | 1.03 | 0.382 |
| 5 | nde | B.caccae | g3 | 2.09 | 0.95 | 0.028 |
| 6 | nde | B.caccae | g4 | 3.28 | 1.20 | 0.006 |
Combine cytokines and DA species
-
中介分析使用
Natural effects model:- exposure variables (自變量X): consisting of sexual exposure groups
- mediators (中介變量M): cytokines & gut microbiota
- outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
- adjusted variable (混淆變量): druguse
# Natural effects model
all_mediators <- c(all_species, "cd14", "cd163")
df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, druguse, all_of(all_mediators))
df[is.na(df)] <- 0t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ group1 + ", paste0(all_mediators, collapse = " + "), " + druguse"))
df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula,family = binomial("logit"), nMed = length(all_mediators), data = df)ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ group10 + group11 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")summ <- summary(ne_mod)
df_summ <- data.frame(summ$coefficients)# Trend test
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nde <- trend_test(beta_hat = summ$coefficients[2:4, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[2:4, 2:4],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
# set.seed(123)
# trend_nie <- trend_test(beta_hat = summ$coefficients[5:7, "Estimate"],
# vcov_hat = ne_mod$vcov[5:7, 5:7],
# contrast = contrast_mat,
# node = 3, B = 1000)
#
# ne_trend_test <- base::append(ne_trend_test,
# list(all_nde = trend_nde, all_nie = trend_nie))# Outputs
types <- c("nde", "nie")
groups <- c("g2", "g3", "g4")
res <- data.frame(type = rep(types, each = length(groups)), group = rep(groups, length(types)), estimate = NA, se = NA, p = NA,trend_p = NA)
res$estimate <- round(df_summ$Estimate[2:7], 2)
res$se <- round(df_summ$Std..Error[2:7], 2)
res$p <- round(df_summ$Pr...z..[2:7], 3)
res$trend_p[3] <- round(ne_trend_test$all_nde$p_value, 3)
res$trend_p[6] <- round(ne_trend_test$all_nie$p_value, 3)head(res)
| type | group | estimate | se | p | trend_p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nde | g2 | 1.81 | 0.64 | 0.005 | NA |
| 2 | nde | g3 | 2.38 | 0.61 | 0.000 | NA |
| 3 | nde | g4 | 3.16 | 0.68 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 4 | nie | g2 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.241 | NA |
| 5 | nie | g3 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.087 | NA |
| 6 | nie | g4 | 0.74 | 0.24 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
Additional analysis: treating the exposure as continuous
-
中介分析使用
Natural effects model:- exposure variables (自變量X): recept_anal
- mediators (中介變量M): cytokines & gut microbiota
- outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
- adjusted variable (混淆變量): druguse
# Natural effects model
all_mediators <- c(all_species, "cd14", "cd163")
df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, recept_anal, druguse, all_of(all_mediators))
df[is.na(df)] <- 0t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ recept_anal + ", paste0(all_mediators, collapse = " + "), " + druguse"))
df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula,family = binomial("logit"), nMed = length(all_mediators), data = df)
ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ recept_anal0 + recept_anal1 + druguse,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")
summ <- summary(ne_mod)
df_summ <- data.frame(summ$coefficients)df_summ
| Estimate | Std…Error | z.value | Pr…z… | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | -1.92892873 | 0.419607493 | -4.596984 | 4.286515e-06 |
| recept_anal0 | 0.08028533 | 0.040929531 | 1.961550 | 4.981487e-02 |
| recept_anal1 | 0.00831693 | 0.004785597 | 1.737909 | 8.222692e-02 |
| druguseyes | 1.17852596 | 0.434863654 | 2.710105 | 6.726201e-03 |
Additional analysis: substance usage as the mediator
-
中介分析使用
Natural effects model:-
exposure variables (自變量X): recept_anal
-
mediators (中介變量M): druguse
-
outcome variable (因變量Y): HIV-1 seroconversion status
-
# Natural effects model
df <- df_causal %>%dplyr::select(status, group1, druguse)
df[is.na(df)] <- 0t_formula <- as.formula(paste0("status ~ group1 + druguse"))
df_exp <- neImpute(t_formula,family = binomial("logit"), data = df)
ne_mod <- neModel(status ~ group10 + group11,family = binomial("logit"), expData = df_exp, se = "robust")
summ <- summary(ne_mod)
df_summ <- data.frame(summ$coefficients)df_summ
| Estimate | Std…Error | z.value | Pr…z… | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | -3.01328264 | 0.59597082 | -5.056091 | 4.279374e-07 |
| group10g2 | 2.07838397 | 0.65668493 | 3.164964 | 1.551023e-03 |
| group10g3 | 2.71549102 | 0.62579799 | 4.339245 | 1.429728e-05 |
| group10g4 | 3.88678487 | 0.70600884 | 5.505292 | 3.685567e-08 |
| group11g2 | 0.07609705 | 0.07185271 | 1.059070 | 2.895679e-01 |
| group11g3 | 0.18057639 | 0.11016834 | 1.639095 | 1.011934e-01 |
| group11g4 | 0.17817557 | 0.12483109 | 1.427333 | 1.534839e-01 |

全面學習指南,初學者入門,一看就懂!)









00)







