?代理是指授權代理人在一定范圍內代表其向第三方進行處理有關事務。
1 代理模式
需求:1)將業務代碼與非業務代碼分離,在不改變代碼結構的基礎上,為其添加新的功能。2)為系統中的某些操作做同一處理,例如進行鑒權、監控、日志、統計等。
1.1 代理模式介紹
增加一個代理對象,在客戶端和目標對象之間起到中介作用,去掉客戶不能看到的內容和服務,或者添加客戶想要的額外服務。
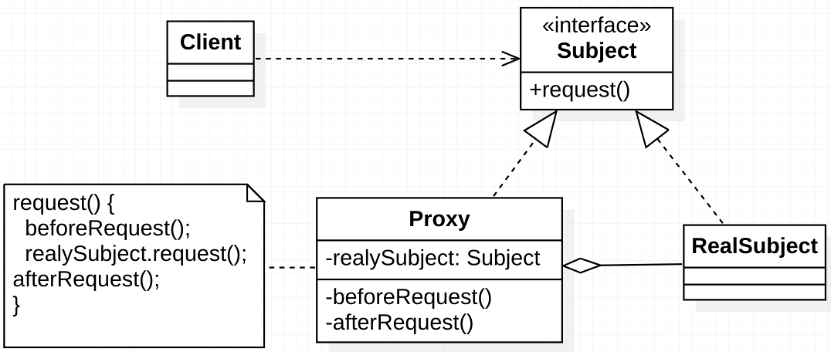
圖 代理模式UML
public class StaticProxy {public static void main(String[] args) {Subject request = new SimpleRequest();Subject proxy = new LogProxy(request);proxy.request("applet","123456");}private interface Subject {void request(String source,String token);}private static class LogProxy implements Subject {private final Subject subject;private LogProxy(Subject subject) {this.subject = subject;}@Overridepublic void request(String source, String token) {System.out.println("記錄訪問日志,source=" + source + ",token=" + token);subject.request(source,token);}}private static class SimpleRequest implements Subject {@Overridepublic void request(String source, String token) {System.out.println("接收請求:" + source + "," + token);}}}| 代理模式 | 側重控制對目標對象的訪問,及擴展不同于目標對象緯度的功能。 |
| 裝飾模式 | 側重于增強目標對象本身的功能,是繼承方案的一個代替。 |
表 代理模式與裝飾模式對比
1.1.1 動態代理
靜態代理模式,需要為每個目標對象創建一個代理類,會造成系統中類的數量增多,而且當這些代理類提供的功能相同時,將會造成代碼的冗余。動態代理是指在運行時動態創建代理對象。
| JDK | JDK自帶的一種動態代理方法,要求被代理類必須要實現接口。 原理:動態生成實現目標接口的代理類,調用代理方法時,通過反射的形式來調用目標對象方法。 |
| CGLIB | 是CGLIB提供的一種動態代理方法。被代理類可為普通類及接口。 原理:動態生成繼承目標類的代理類,通過fastclass 的策略來找到目標方法。 與JDK方式對比,其動態生成的類會比較多,但執行效率會比反射更快。 |
表 Java中兩種動態代理
JDK 方式:
public class JdkDynamicProxy {private interface Subject {void request(String source,String token);}private static class RealRequest implements Subject{@Overridepublic void request(String source, String token) {System.out.println("請求網絡");}}private static class RequestIntercept implements InvocationHandler {private final Subject subject;private RequestIntercept(Subject subject) {this.subject = subject;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {System.out.println("請求參數:" + Arrays.asList(args));Object result = method.invoke(subject, args);System.out.println("記錄訪問日志");return result;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Subject realSubject = new RealRequest();Subject subject = (Subject) Proxy.newProxyInstance(JdkDynamicProxy.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Subject.class}, new RequestIntercept(realSubject));subject.request("小程序","1344");}}CGLIB方式
public class CglibDynamicProxy {private static class RealRequest {public RealRequest() {}public void request(String source, String token) {System.out.println("請求成功,source=" + source + ",token=" + token);}}private static class RequestIntercept implements MethodInterceptor {@Overridepublic Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {System.out.println("攔截請求:" + Arrays.asList(objects));Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);System.out.println("記錄請求日志");return result;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();enhancer.setSuperclass(RealRequest.class);enhancer.setCallback(new RequestIntercept());RealRequest realRequest = (RealRequest) enhancer.create();realRequest.request("小程序","1344");}
}1.1.2 遠程代理
使得客戶端可以訪問遠程機,將網絡細節隱藏起來,客戶端可完全認為被代理的遠程對象是局域的而非遠程的。
遠程代理對象承擔了大部份網絡通信工作,并負責對遠程業務方法的調用。
RMI,Remote Method Invocation,遠程方法調用,是JDK 實現的一種遠程代理。
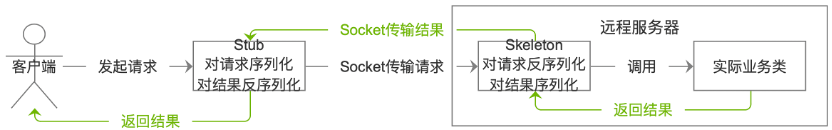
表 RMI 內部實現步驟
客戶端通過一個樁(Stub),相當于代理類對象,與遠程主機上的業務對象進行通信。而遠程主機端有個Skeleton(骨架)對象來負責與Stub對象通信。
遠程機部署代碼:
public interface RemoteService extends Remote {String service(String requestInfo) throws RemoteException;}public class RemoteServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteService{public RemoteServiceImpl() throws RemoteException{}@Overridepublic String service(String requestInfo) throws RemoteException {System.out.println("請求:" + requestInfo);return "RemoteService提供遠程服務:" + requestInfo;}
}public class JNDIPublisher {public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, MalformedURLException {RemoteService remoteService = new RemoteServiceImpl();int port = 8080;String serviceName = "rmi://localhost:" + port + "/remoteService";LocateRegistry.createRegistry(port);Naming.rebind(serviceName,remoteService);}}客戶端代碼:
public class RmiLocal {public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, NotBoundException, RemoteException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {String serviceName = "rmi://localhost:" + 8080 + "/remoteService";reflectRemote(serviceName);interfaceRemote(serviceName);}// 這種方式仍然需要導入遠程服務提供的接口,RemoteServiceprivate static void reflectRemote(String serviceName) throws MalformedURLException, NotBoundException, RemoteException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {Remote lookup = Naming.lookup(serviceName);Method method = lookup.getClass().getMethod("service", String.class);Object result = method.invoke(lookup, "反射方式");System.out.println("反射方式,遠程調用結果:" + result);}private static void interfaceRemote(String serviceName) throws MalformedURLException, NotBoundException, RemoteException{RemoteService remoteService = (RemoteService)Naming.lookup(serviceName);String result = remoteService.service("接口方式");System.out.println("接口方式,遠程調用結果:" + result);}}1.1.3 虛擬代理
主要目標是延遲對象的創建或者復雜計算,直到它們實際需要被創建或計算。這可以提高性能,降低資源消耗。
public class VirtualAgent {private interface Image {void display();}private static class RealImage implements Image {private String path;public RealImage(String path) {System.out.println("創建一個圖片需要許多資源,耗費時間較長");this.path = path;}@Overridepublic void display() {System.out.println("展示圖片:" + path);}}private static class ProxyImage implements Image {private volatile Image image;private String path;public ProxyImage(String path) {System.out.println("虛擬對象,需要資源及時間都很少,用于延遲真實對象的創建與訪問");this.path = path;}@Overridepublic void display() {if (image == null) {synchronized (ProxyImage.class) {if (image == null) image = new RealImage(path);}}image.display();}}public static void main(String[] args) {Image[] images = new Image[10];// 在網頁加載過程,先加載這些圖片,為了防止陷入卡頓,不直接創建圖片,而是先創建虛擬對象System.out.println("網頁加載中...");for (int i = 0; i < images.length; i++) {images[i] = new ProxyImage(i + ".png");}System.out.println("網頁加載完成--------");// 當網頁加載完成后,可以依次加載真實圖片了for (Image image : images) {image.display();}}}1.1.4 緩存代理
為某些目標操作的結果提供臨時的存儲空間,讓后續相同的操作及相同的參數可以直接共享這些結果,而不必再執行計算,以此來提高系統性能。
public class CacheProxy {private static class CacheMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {private final static Map<MethodKey,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>();@Overridepublic Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {MethodKey methodKey = MethodKey.getKey(method, args);Object result = resultMap.get(methodKey);if (result != null) {return result;} else {Object result2 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, args);resultMap.put(methodKey,result2);return result2;}}}// 根據method 及 參數來生成keyprivate static class MethodKey {private static final Map<String,MethodKey> methodKeyMap = new HashMap<>();private String code;private MethodKey(String code) { this.code = code;}public static MethodKey getKey(Method method, Object[] objects) {String hasCode = "method:" + method.hashCode();if (objects != null) hasCode += "args:" + Arrays.hashCode(objects);MethodKey methodKey = methodKeyMap.get(hasCode);if (methodKey == null) {synchronized (MethodKey.class) {methodKey = new MethodKey(hasCode);methodKeyMap.put(hasCode,methodKey);}}return methodKey;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return code;}}private static class ComplexCompute {public ComplexCompute() {}long compute(long num) {System.out.println("執行復雜計算,參數" + num);return num * 2345;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();enhancer.setSuperclass(ComplexCompute.class);enhancer.setCallback(new CacheMethodInterceptor());ComplexCompute compute = (ComplexCompute) enhancer.create();System.out.println(compute.compute(23));System.out.println("----------");System.out.println(compute.compute(123));System.out.println("----------");System.out.println(compute.compute(23));}}1.2 優缺點
優點:
- 能動態擴展對象的功能,而不需要修改原有代碼,符合開閉原則。
- 能對目標對象的方法訪問進行控制與保護。
- 將耗費系統資源及時間較多的對象延遲到真正需要使用時再創建,能提高系統性能及系統對客戶的友好度。
- 能調用遠程對象方法,而不需要考慮復雜的實現細節。
- 能對運行結果進行緩存,提高系統運行效率。
缺點:
- 增加了代理對象,可能會造成請求的處理速度變慢。
- 增加了類的數量,讓系統變得更復雜。
![[實例] Unity Shader 逐像素漫反射與半蘭伯特光照](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[實例] Unity Shader 逐像素漫反射與半蘭伯特光照)













|武忠祥老師每日一題 5月24日)



)
