文章目錄
- 前言
- 目標
- 環境背景
- U-Boot如何自動調起菜單
- U-Boot添加自定義命令
- 實踐
前言
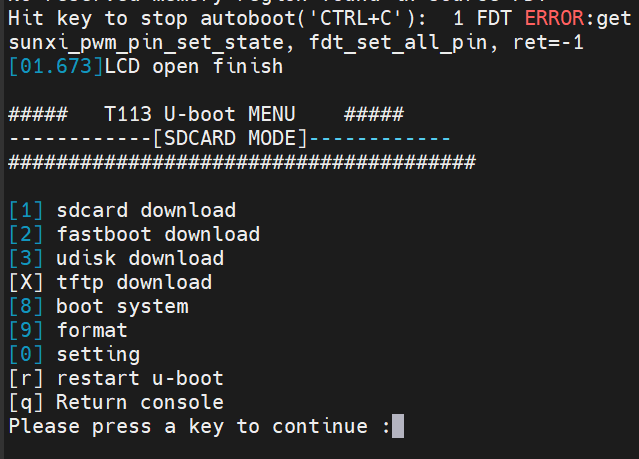
在某個廠家的開發板中,在進入它的U-Boot后,會自動彈出一個菜單頁面,輸入對應的選項就會執行對應的功能。如SD卡鏡像更新、顯示設置等:
目標
本文主要分析U-Boot在程序中的執行順序,又如何在U-Boot階段調起菜單?相信大家都試過,在U-Boot倒數結束前按任意按鍵后,會進入U-Boot命令行模式。
這里先留一個問題:如何做到按鍵按下后,調啟的是自己的U-Boot菜單,而不再是進入冷冰冰的命令行模式?
環境背景
本文介紹所用的U-Boot版本:2018
U-Boot如何自動調起菜單
U-Boot的入口程序文件是<u-boot>/common/main.c,入口函數main_loop():
/* We come here after U-Boot is initialised and ready to process commands */
/* 在U-Boot初始化并準備好處理命令之后,我們來到這里。 */
void main_loop(void)
{const char *s;bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_MAIN_LOOP, "main_loop"); #ifdef CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLEenv_set("ver", version_string); /* set version variable */ #endif /* CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE */cli_init(); //命令初始化有關,初始化 hush shell 相關的變量run_preboot_environment_command(); //獲取環境變量 perboot 的內容#if defined(CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP)update_tftp(0UL, NULL, NULL); #endif /* CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP */s = bootdelay_process(); //此函數會讀取環境變量 bootdelay 和 bootcmd 的內容if (cli_process_fdt(&s))cli_secure_boot_cmd(s);autoboot_command(s); //開啟倒計時,并在倒計時結束前檢測是否有按鍵按下cli_loop(); //命令行處理函數(即進入U-Boot命令行)panic("No CLI available");
}
關鍵函數是autoboot_command(),該函數的實現在<u-boot>/common/autoboot.c:
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "<UNDEFINED>");if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) { // 倒計時過程中,沒有按鍵按下
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
#endifrun_command_list(s, -1, 0); // 倒計時結束后,啟動內核#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif}#ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEYif (menukey == CONFIG_MENUKEY) {s = env_get("menucmd");if (s)run_command_list(s, -1, 0);}
#endif /* CONFIG_MENUKEY */
}
進入autoboot_command()后,先看第一個if:
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{...if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay))...
}
這里有三個條件:
stored_bootdelay != -1:stored_bootdelay是倒數的總時間,就是常見的3秒、5秒不等;s:傳進來的參數s不能為空;!abortboot(stored_bootdelay):該函數會從stored_bootdelay開始倒計時,期間判斷是否有按鍵按下。函數實現如下,倒計時過程中若檢測到按鍵按下,則令abort=1。無按鍵按下,則abort=0。最后返回abort。
static int __abortboot(int bootdelay)
{int abort = 0;unsigned long ts;#ifdef CONFIG_MENUPROMPTprintf(CONFIG_MENUPROMPT);
#elseprintf("Hit any key to stop autoboot: %2d ", bootdelay);
#endif/** Check if key already pressed*/if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press */(void) getc(); /* consume input */puts("\b\b\b 0");abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */}while ((bootdelay > 0) && (!abort)) {--bootdelay;/* delay 1000 ms */ts = get_timer(0);do {if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press */abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */bootdelay = 0; /* no more delay */
# ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEYmenukey = getc();
# else(void) getc(); /* consume input */
# endifbreak;}udelay(10000);} while (!abort && get_timer(ts) < 1000);printf("\b\b\b%2d ", bootdelay);}putc('\n');return abort;
}
剛剛說了,abortboot()函數執行期間有按鍵按下的話,abortboot()會返回1,那就不會進入第一個if,程序會接著往下運行直至該函數運行結束。autoboot_command()結束后繼續返回到main_loop(),隨后立刻執行cli_loop(),進入我們所熟悉的U-Boot命令行模式。
void main_loop(void)
{...autoboot_command(s); //檢查倒計時是否結束cli_loop(); //命令行處理函數
}
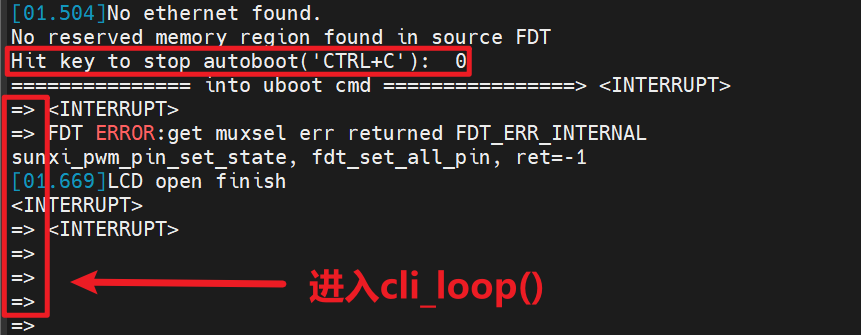
至此,就實現了U-Boot倒數期間,有按鍵按下,則進入U-Boot的命令行模式。
現在繼續回到第一個if:
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{...if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) { // 倒計時過程中,沒有按鍵按下
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
#endifrun_command_list(s, -1, 0); // 倒計時結束后,啟動內核#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif}...
}
如果在autoboot倒計時結束前,一直沒有按鍵按下呢?那abortboot()最后會返回0,第一個if的三個條件全部滿足。進入if,run_command_list()執行一系列命令后,啟動內核。注意,這里的現象是直接啟動內核,run_command_list()后的程序不再執行。
解析到這里,我們得出一個結論:在autoboot倒計時中,如果有按鍵按下的話,會進入U-Boot的命令行模式。無按鍵按下則在倒計時結束后直接啟動內核。
那現在可以回答第一個問題,如何做到按下按鍵后,是自啟動U-Boot菜單,而不是進入U-Boot命令行呢?答案是在執行cli_loop()之前,我們可以在autoboot檢測到按鍵按下后,調用run_command()函數執行menu命令,從而調起菜單。
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "<UNDEFINED>");if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) {
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
#endifrun_command_list(s, -1, 0);#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif}//啟動菜單run_command("menu", 0);#ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEYif (menukey == CONFIG_MENUKEY) {s = env_get("menucmd");if (s)run_command_list(s, -1, 0);}
#endif /* CONFIG_MENUKEY */
}
U-Boot添加自定義命令
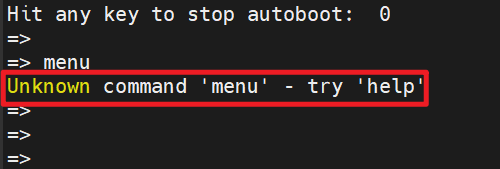
難道通過run_command()執行menu命令后,菜單就自己出來了?這是一個理所當然的猜想。實際上U-Boot根本不認識menu命令:
接下來看看如何添加U-Boot命令,參考一下別人的代碼:
int do_brightness(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{int rcode = 0;ulong side;ulong bright;switch (argc) {case 3:side = simple_strtoul(argv[1], NULL, 10);bright = simple_strtoul(argv[2], NULL, 10);if ((side >= 0) && (side <= 3) &&(bright >= 0) && (bright <= 1000)) {vcxk_setbrightness(side, bright);rcode = 0;} else {printf("parameters out of range\n");printf("Usage:\n%s\n", cmdtp->usage);rcode = 1;}break;default:printf("Usage:\n%s\n", cmdtp->usage);rcode = 1;break;}return rcode;
}U_BOOT_CMD(bright, 3, 0, do_brightness,"sets the display brightness\n"," <side> <0..1000>\n side: 0/3=both; 1=first; 2=second\n"
);
先看最底下的U_BOOT_CMD,這是一個宏,用來添加U-Boot命令:
#define U_BOOT_CMD(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help) \U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, NULL)
- _name:命令的名字
- _maxargs:添加的命令最多有幾個參數
- _rep:是否重復(1重復,0不重復),指在U-Boot命令行按下Enter鍵的時候,重復執行上次的命令
- _cmd:執行函數(即執行該命令后,運行哪個函數)
- _usage:短幫助信息
- _help:長幫助信息
再來看看執行函數do_brightness的聲名:
int (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *const argv[]);
- cmdtp:Table entry describing the command (see above).
- flag:A bitmap which may contain the following bit
- CMD_FLAG_REPEAT - The last command is repeated.
- CMD_FLAG_BOOTD - The command is called by the bootd command.
- CMD_FLAG_ENV - The command is called by the run command.
- argc:執行命令時,傳入的參數數量
- argv:傳入的參數
實踐
下面,添加一個U-Boot菜單,不過只作打印,沒有實際功能。
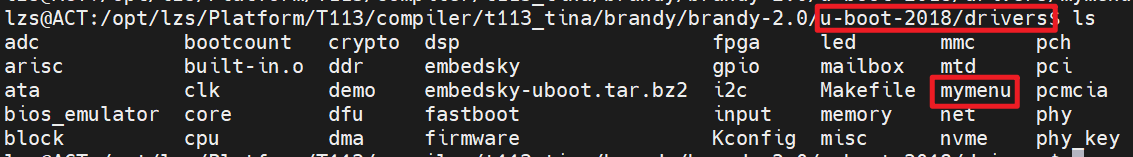
在<u-boot>/drivers下創建一個名為mymenu的文件夾:
在mymenu文件夾下創建mymenu.c,內容如下:
#include <common.h>
#include <command.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <cli.h>
#include <fs.h>static int do_mymenu(struct cmd_tbl_s *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *const argv[])
{if(argc != 2)return 0;if(!strcmp(argv[1], "pageone"))printf("\n======== pageone ========\n"); else if(!strcmp(argv[1], "pagetwo"))printf("\n======== pagetwo ========\n"); elseprintf("\n======== pageone ========\n"); printf("== [1] xxxxxx\n");printf("== [2] xxxxxx\n");printf("== [3] xxxxxx\n");printf("== [4] xxxxxx\n");printf("=========================\n\n");return 0;
}U_BOOT_CMD(mymenu, 2, 1, do_mymenu,"here is uboot mymenu\n","here is uboot mymenu, make in 2024-05-15\n"
);
還需在mymenu文件夾下創建一個Makefile文件,內容如下:
obj-y += mymenu.o
最后修改<u-boot>/drivers/下的Makefile,在結尾加上如下內容,表示要編譯mymenu路徑下的文件:
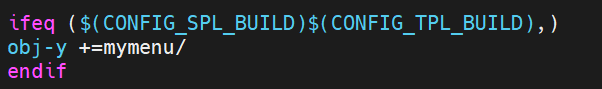
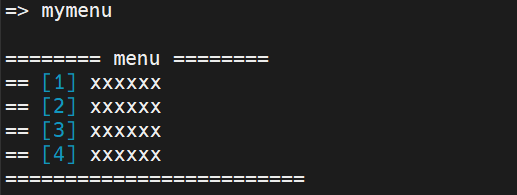
編譯U-Boot,更新U-Boot,重啟單板,在U-Boot倒計時結束前,按任意按鍵進入U-Boot命令行,輸入mymenu后,可以看到命令被正確識別,對應的函數也執行成功:
那如何做到按任意按鍵后直接調起菜單呢?上面有說過,可以在autoboot檢測到按鍵按下后,調用run_command()函數執行mymenu命令,從而調起菜單。
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "<UNDEFINED>");if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) {
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
#endifrun_command_list(s, -1, 0);#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif}//啟動菜單run_command("mymenu", 0);#ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEYif (menukey == CONFIG_MENUKEY) {s = env_get("menucmd");if (s)run_command_list(s, -1, 0);}
#endif /* CONFIG_MENUKEY */
}
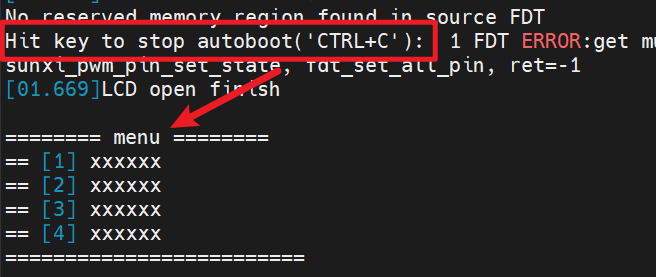
剩下的菜單程序編寫就是根據實際功能來開發了。

增加護盾強度)


)





:Linux系統文件類型與文件權限)
)
)






