前言
之前看了些App啟動流程的文章,但是看得很淺顯,隔了沒多久就忘了,自己抓耳撓腮的終于看完了,看得頭疼哦。因為很多是個人理解,大哥們主打一個7分信,2分思考,1分懷疑哈。
主要看的源碼是Android 9 的源碼,因為很多framework的代碼在AS里面看需要配置,我沒配好,于是找了幾個網站,最后綜合下來用的這個
Android社區 - https://www.androidos.net.cn
一、啟動方式
App啟動分為冷啟動和熱啟動
- 冷啟動:點擊桌面圖標,手機系統不存在該應用進程,這時系統會重新fork一個子進程來加載Application并啟動Activity,這個啟動方式就是冷啟動。
- 熱啟動:應用的熱啟動比冷啟動簡單得多,開銷也更低。在熱啟動中,因為系統里已有該應用的進程,所以系統的所有工作就是將您的 Activity 帶到前臺。?
二、App冷啟動的簡要流程
這是找的網上的圖片: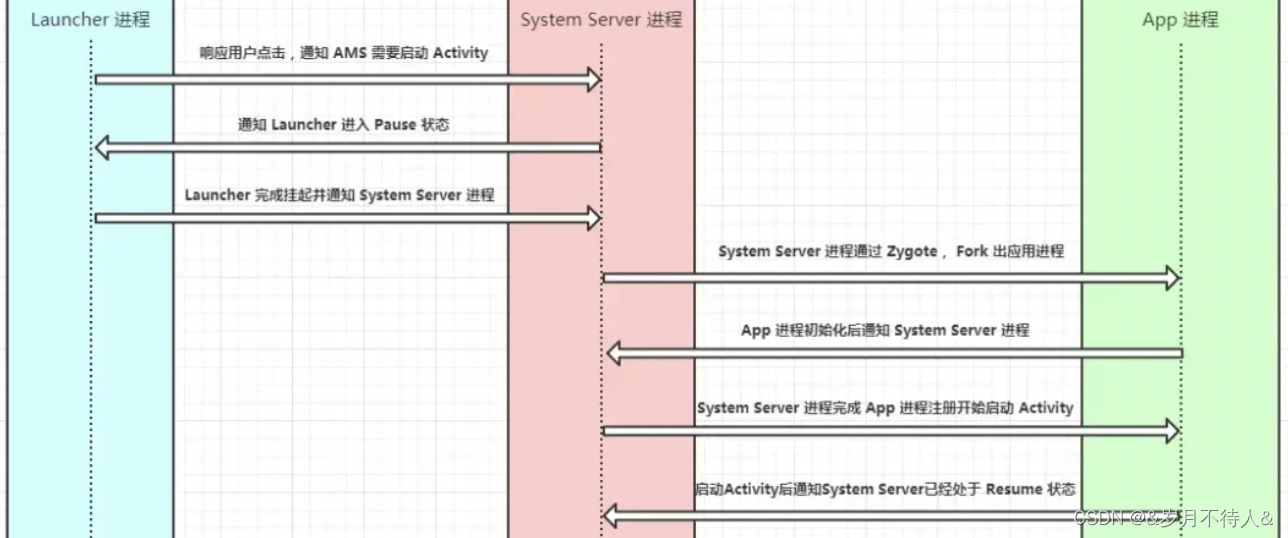
?如果只是了解,純應付簡單的面試,上面這張圖就夠了。
簡單地講,從?用戶手指觸摸點擊桌面圖標到 Activity啟動?可以用下面 4 步概括:
1.啟動進程
點擊圖標發生在Launcher應用的進程,startActivity()函數最終是由Instrumentation通過Android的Binder跨進程通信機制 發送消息給 system_server 進程; 在 system_server 中,啟動進程的操作在ActivityManagerService。AMS發現ProcessRecord不存在時,就會執行Process.start(),最終是通過 socket 通信告知 Zygote 進程 fork 子進程(app進程,這兒用的Socket)
第一步:Activity的startActivity方法
源碼位置:

源碼
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {this.startActivity(intent, null);}@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {if (options != null) {startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);} else {// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with// applications that may have overridden the method.startActivityForResult(intent, -1);}}@Overridepublic void startActivityForResult(String who, Intent intent, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options) {Uri referrer = onProvideReferrer();if (referrer != null) {intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REFERRER, referrer);}options = transferSpringboardActivityOptions(options);Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, who,intent, requestCode, options);//關鍵代碼if (ar != null) {mMainThread.sendActivityResult(mToken, who, requestCode,ar.getResultCode(), ar.getResultData());}cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);}第二步:Instrumnetation調用ActivityManager.getService().startActivity()方法
源碼位置:
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {···try {intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);int result = ActivityManager.getService()//關鍵代碼.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,requestCode, 0, null, options);checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);} catch (RemoteException e) {throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);}return null;}ActivityManager.java
public static IActivityManager getService() {return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();}private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {@Overrideprotected IActivityManager create() {final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);return am;}};第三步:ActivityManagerService里的調用
@Overridepublic final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,UserHandle.getCallingUserId());}@Overridepublic final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, null,"startActivityAsUser");}
第四步:mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait()方法
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, WaitResult outResult,Configuration globalConfig, Bundle bOptions, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, int userId,IActivityContainer iContainer, TaskRecord inTask, String reason) {···int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, container,inTask, reason);···}int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,ActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified,ActivityRecord[] outActivity, ActivityStackSupervisor.ActivityContainer container,TaskRecord inTask, String reason) {···mLastStartActivityResult = startActivity(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode,callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, mLastStartActivityRecord,container, inTask);···return mLastStartActivityResult;}private int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,ActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified,ActivityRecord[] outActivity, ActivityStackSupervisor.ActivityContainer container,TaskRecord inTask) {···return startActivity(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags, true,options, inTask, outActivity);}private int startActivity(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {···try {mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();result = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, outActivity);} finally {···}···}private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {···if (mDoResume) {final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =mStartActivity.getTask().topRunningActivityLocked();if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {···} else {···mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack, mStartActivity,mOptions);}} else {···}···}
這里面最后調用了mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked方法,這個mSupervisor就是ActivityStackSupervisor,在后面systemserver通知創建activity時也會用到。
第五步:resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked方法里調用targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked,然后又在ActivityStack的代碼里回調到?ActivityStackSupervisor ;
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {if (targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);}···return false;}
//ActivityStack
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {···try {···result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);} finally {···}···return result;}private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {···if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {···} else {···mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);}···}第六步:ActivityStackSupervisor 回調到 ActivityManagerService,這里會判斷要啟動 App 的進程是否存在,存在則通知進程啟動 Activity,否則就先將進程創建出來;
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {···if (app != null && app.thread != null) {try {···// 如果進程已存在,則通知進程啟動組件,然后returnrealStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);return;} catch (RemoteException e) {···}}// 否則先將進程創建出來mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);}
致此,熱啟動就走到這里,但是我們主要看冷啟動,接著往下走
第七步:Process#start()啟動進程
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting,boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {return startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags, hostingType,hostingName, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */, keepIfLarge,null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */, null /* entryPointArgs */,null /* crashHandler */);}final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {···startProcessLocked(app, hostingType, hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);···}private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {···ProcessStartResult startResult;if (hostingType.equals("webview_service")) {···} else {startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, entryPointArgs);}···}
ActivityManagerService 通過 socket 通信告知 Zygote 進程 fork 子進程,即 app 進程;到這兒,啟動進程的代碼就完成了。
關于如何fork進程,我下面對Zygote進程會詳細說。
2.開啟主線程
app進程創建后,首先是反射調用android.app.ActivityThread類的main方法,main()函數里會初始化app的運行時環境,然后去創建 ApplicationThread,Looper,Handler 對象,并開啟主線程消息循環Looper.loop()。
主要代碼:
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();//main()方法public static void main(String[] args) {...Looper.prepareMainLooper();//這里面涉及looper,后面講handler機制展開剖析ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();thread.attach(false, startSeq);//進行 Binder 通信,通知system_server進程執行 if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();}if (false) {Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(newLogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));}Looper.loop();throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");}
ActivityThread的main()調用 ActivityThread#attach(false) 方法進行 Binder 通信,通知system_server進程執行 ActivityManagerService里的attachApplication(mAppThread) 方法,用于初始化Application和Activity。
核心代碼:
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {sCurrentActivityThread = this;mSystemThread = system;if (!system) {ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {ensureJitEnabled();}});android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>",UserHandle.myUserId());RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();//ActivityManagerServicetry {mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);} catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();}
...}看其中的mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);這里就使用到了AIDL,最后走進了AMS里面的attachApplication()方法。
3.創建并初始化 Application和Activity
核心代碼:ActivityManagerService.java,這里面的代碼量很大,請看注釋內容。
@Overridepublic final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {synchronized (this) {int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);//1.關鍵代碼,往里走Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);}}
//2.attachApplicationLocked里的thread調用bindApplication方法
//IApplicationThread 在ActivtyThread里是一個Private的內部類,
//里面實現了bindApplication方法。里面最終回通過mH.sendMessage方法(handler)把事件分發出去
//sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
//3.那么在Activity里的Handler里,通過handleMessage方法收到msg.what為BIND_APPLICATION去創建app在system_server進程中,ActivityManagerService的attachApplication(mAppThread)里依次初始化了Application和Activity,分別有2個關鍵函數:
第一個:?thread#bindApplication() 方法通知主線程Handler 創建 Application 對象、綁定 Context 、執行 Application#onCreate() 生命周期,先講application的創建
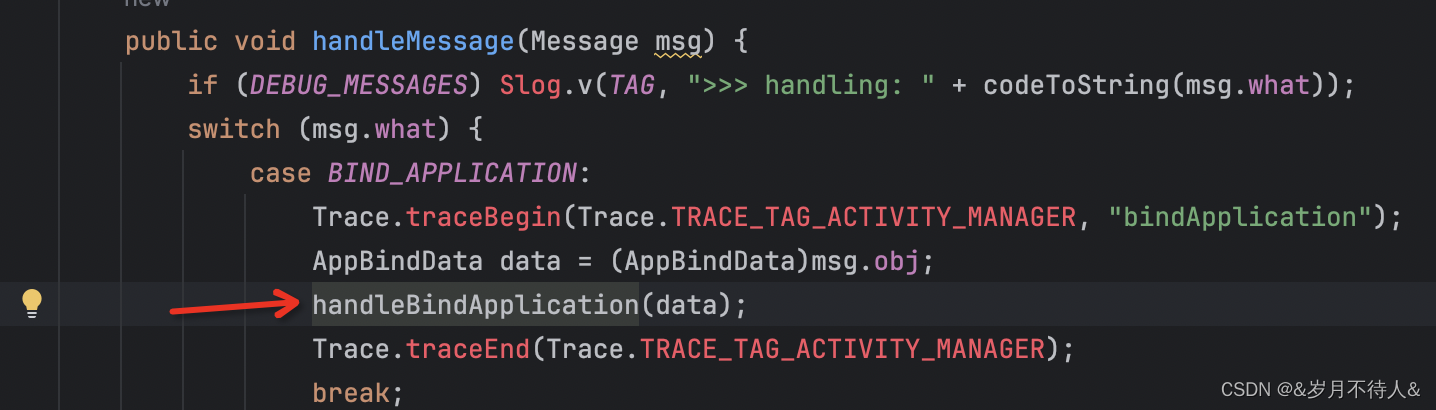
handleBindApplication核心代碼
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) { Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);//創建Application對象 mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);//調用Application.onCreate,執行application的生命周期
} 在ActivityThread創建的時候,會將自己的ApplicationThread綁定到AMS中:
ActivityThread.main()
└── ActivityThread.attach()
? ? └── IActivityManager.attachApplication(mAppThread)
? ? ? ? └── Binder.transact()執行流程從應用進程進入到系統進程:
ActivityManagerService.onTransact()
└── ActivityManagerService.attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread)
?????└── IApplicationThread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo ...)(切到ActivityThread里面的ApplicationThread)?????????????└── Binder.transact()
然后在ApplicationThread里
ApplicationThread.onTransact()
└── ApplicationThread.bindApplication()
? ? └── ActivityThread.H.handleMessage(BIND_APPLICATION)
? ? ? ? └── ActivityThread.handleBindApplication()
? ? ? ? ? ? └── Application.onCreate()
第二個:Activity的創建(在AMS里的bindAppliocation方法里)
- mStackSupervisor的attachApplicationLocked() 方法中調用realStartActivityLocked()方法,
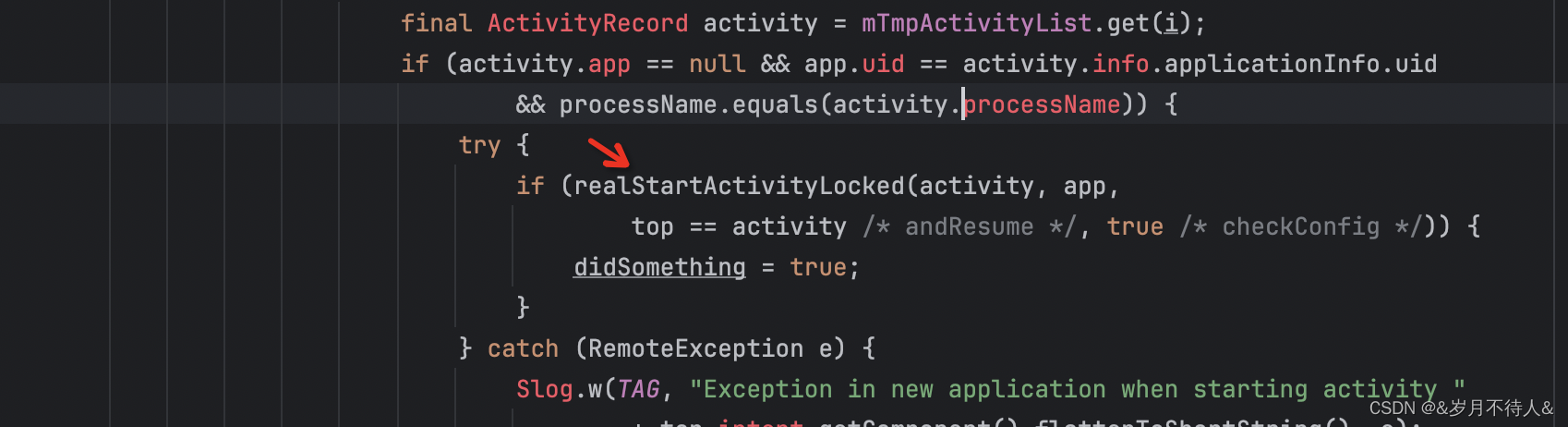
ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked()表示要啟動一個Activity,ActivityRecord作為參數。從ActivityRecord中提取出Token對象,作為跨進程調用的參數,通過IApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity()傳遞到應用進程。進而通過主線程Handler消息通知創建 Activity 對象。
是的,一個讓我百思不得解的地方終于找到了,因為android 9.0以前,realStartActivityLocked里面是:
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {···try {···app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global and// override configs.mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);···} catch (RemoteException e) {···}···}
我在9.0里找不到啊,后面仔細閱讀代碼,才發現改了:
try里的代碼:
clientTransaction.addCallback(LaunchActivityItem.obtain(new Intent(r.intent),System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global// and override configs.mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,r.persistentState, results, newIntents, mService.isNextTransitionForward(),profilerInfo));final ActivityLifecycleItem lifecycleItem;if (andResume) {lifecycleItem = ResumeActivityItem.obtain(mService.isNextTransitionForward());} else {lifecycleItem = PauseActivityItem.obtain();}clientTransaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(lifecycleItem);?但是最后還是會走到相同的方法里去創建activity。
關于9.0后這塊代碼的詳情可以去看這個博客
android AMS—— 生命周期管理 - 簡書
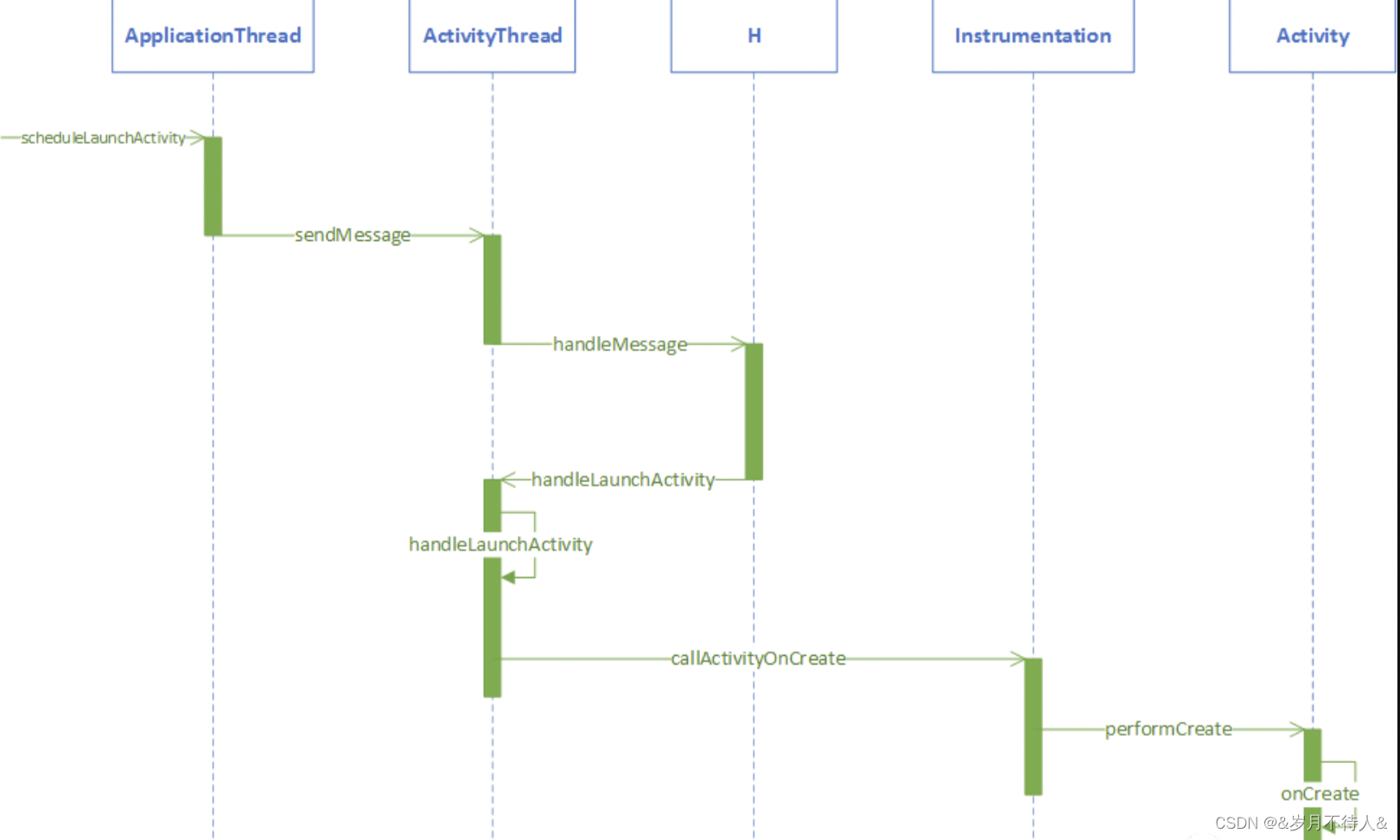
Activity對象,是通過ActivityThread的handleLaunchActivity()中的performLaunchActivity()創建的
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) { Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
}然后再調用 mInstrumentation()?Activity#onCreate() 生命周期。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) { ...代碼量很大,我就不貼了
//創建activityif (r.isPersistable()) {mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);} else {mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);}
}ActiviyThread(app進程)的方法調用:(9.0以前)
ApplicationThread.onTransact()
└── ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity(...token, ...)
? ? // token將被封裝進ActivityClientRecord這個數據結構中
? ? └── ActivityThread.H.handleMessage()
? ? ? ? └── ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(LAUNCH_ACTIVITY)
? ? ? ? ? ? └── ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord, ...)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? // 從ActivityRecord取出token,下面的r就是record
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? └──mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
創建activity流程圖?
 ?
?
4.布局&繪制
后面看了源碼補上
啟動流程圖
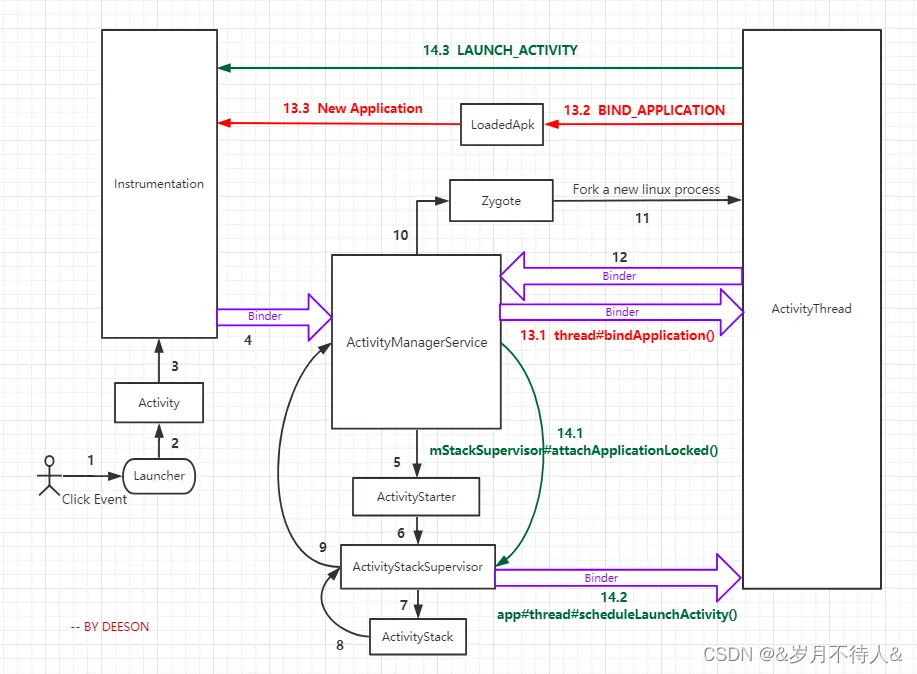
三、zygote進程
- Zygote進程是所有的android進程的父進程,包括SystemServer和各種應用進程都是通過Zygote進程fork出來的。Zygote(孵化)進程相當于是android系統的根進程,后面所有的進程都是通過這個進程fork出來的
- 雖然Zygote進程相當于Android系統的根進程,但是事實上它也是由Linux系統的init進程啟動的。
各個進程的先后順序
init進程 --> Zygote進程 --> SystemServer進程 -->各種應用進程
進程作用說明
init進程:Android手機開機Linux內核啟動后,會加載system/core/init/init.rc文件,啟動init進程,他是linux的根進程,android系統是基于linux系統的,因此可以算作是整個android操作系統的第一個進程;
作用:
- 各種復雜工作
- 負責開關機畫面
- 文件系統的創建和掛載
- 啟動Zygote(孵化器)進程
- 啟動ServiceManager,它是Binder服務管理器,管理所有Android系統服務
Zygote進程:android系統的根進程,主要作用:可以作用Zygote進程fork出SystemServer進程和各種應用進程;
SystemService進程:主要是在這個進程中啟動系統的各項服務,比如ActivityManagerService,PackageManagerService,WindowManagerService服務等等;
各種應用進程:啟動自己編寫的客戶端應用時,一般都是重新啟動一個應用進程,有自己的虛擬機與運行環境;
啟動流程
Zygote進程mian方法主要執行邏輯:
- 初始化DDMS;調用enableDdms(),設置DDMS可用,可以發現DDMS啟動的時機還是比較早的,在整個Zygote進程剛剛開始要啟動額時候就設置可用,初始化各種參數
- 注冊Zygote進程的socket通訊;(registerZygoteSocket)
- 初始化Zygote中的各種類,資源文件,OpenGL,類庫,Text資源等等;(preload)
- 初始化完成之后fork出SystemServer進程;()
- fork出SystemServer進程之后,關閉socket連接;
public static void main(String argv[]) {try {//設置ddms可以用RuntimeInit.enableDdms();SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();boolean startSystemServer = false;String socketName = "zygote";registerZygoteSocket(socketName);//注冊preload();//初始化if (startSystemServer) {startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);//啟動systemService}closeServerSocket();//關閉socket連接} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {caller.run();} catch (RuntimeException ex) {Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);closeServerSocket();throw ex;} }
四、SystemService進程
SystemServer是由zygote進程fork出來的第一個進程,SystemServer和Zygote是Android Framework最重要的2個進程。?
SystemServer進程主要的作用是在這個進程中啟動各種系統服務,他是通過創建SystemServiceManager對象去啟動服務的,他啟動的服務比如ActivityManagerService,PackageManagerService,WindowManagerService服務,以及各種系統性的服務其實都是在SystemServer進程中啟動的,而當我們的應用需要使用各種系統服務的時候其實也是通過與SystemServer進程通訊獲取各種服務對象的句柄的。它的啟動函數為main函數。
tips:SertemServer進程在嘗試啟動服務之前會首先嘗試與Zygote建立socket通訊,只有通訊成功之后才會開始嘗試啟動服務;
SystemService的執行main()方法,里面會直接走到run方法里面去。
源碼位置:
public static void main(String[] args) {new SystemServer().run();}run方法里代碼量挺大的:
1.設置系統當前時間為該時間點。
2.設置系統的語言環境等
3.設置虛擬機運行內存,加載運行庫,設置SystemServer的異步消息
4.準備主線程循環,初始化本地服務,初始化context,啟動各種服務
5.開啟loop循環
private void run() {if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);}//時間if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");}//語言Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());///虛擬機if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);}}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);}// Mmmmmm... more memory!VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();// 系統服務器必須一直運行,所以需要// 盡可能高效地使用內存。 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure// we've defined it before booting further.Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without// explicitly specifying a user.Environment.setUserRequired(true);// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);//準備主循環線程(本線程)。android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);Looper.prepareMainLooper();// 初始化原生服務.System.loadLibrary("android_servers");// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.// This call may not return.performPendingShutdown();// 初始化系統上下文。通過ActivityThread.systemMain方法創建context的createSystemContext();// 創建系統服務管理器。mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);//將SystemServiceManager對象保存SystemServer進程中的一個數據結構中。 LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);// Start services.try {//startBootstrapServices() 主要用于啟動系統Boot級服務,例如ActivityManagerService,PowerManagerService,PackageManagerService//startCoreServices() 主要用于啟動系統核心的服務,BatteryService(電池相關服務),UsageStatsService,WebViewUpdateService服務等//startOtherServices() 主要用于啟動一些非緊要或者是非需要及時啟動的服務startBootstrapServices();startCoreServices();startOtherServices();} catch (Throwable ex) {Slog.e("System", "******************************************");Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);throw ex;}// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");}// Loop forever.Looper.loop();throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}五、總結
1.在Android中,通過包名和Activity類名就可以打開一個APP。實際上,項目里的startActivity()方法并不是真正創建進程、拉起APP的地方。而是通過一系列的調用,把請求傳遞給SystemServer的AMS。AMS收到來自客戶端的請求后,再通知zygote進程來fork一個新進程,來啟動App的。
2.這個過程涉及到3個進程:App進程、AMS(SystemServer進程)、zygote進程。
- App進程(ActivityThread)與AMS通過Binder機制進行跨進程通信(AIDL)。
- AMS(SystemServer進程)與zygote通過Socket進行跨進程通信。
- 應用啟動是一個跨進程的復雜工作,應用啟動流程基本是圍繞著SystemServer進程的ActivityManagerService和應用進程的ActivityThread展開。
3.在Android系統中,任何一個Activity(任何一個四大組件)的啟動都是由SystemServer進程(AMS)和App進程(主要是ActivityThread)相互配合來完成的。在ActivityThread的main方法中,調用 ActivityThread的attach(false) 方法進行 Binder 通信,通知system_server進程執行 ActivityManagerService的attachApplication(mAppThread) 方法,用于初始化Application和Activity。
4.對于Activity,在App進程中,主要是通過ActivityThread的,而在System Server中,則是使用AMS通過ActivityRecord來維護Activity運行時的狀態信息,第一次啟動某個Activity時,AMS會創建ActivityRecord記錄該Activity的信息,比如ActivityRecord里的ActivityState代表了該Activity目前處于什么生命周期。在Activity類中有一個IBinder類型的屬性:private IBinder mToken;,這個主要是作為系統進程(AMS)里Activity的唯一標識,當我們展示Dialog的時候,WindowManagerGlobal#addView()也是通過這個token來得知彈窗View要添加到哪個Activity里。ActivityRecord的構造函數里會創建這個appToken。
5.系統進程維護的是ActivityRecord,應用進程維護的是Activity,兩者之間的映射關系就是利用Token來維系的。app進程的Activity在創建的時候,就被賦予了一個Token,拿著這個Token才能完成后續與系統進程的通信。例如在發生Activity切換時,app進程會將上一個Activity的Token(AMS.startActivity()的參數resultTo)傳遞給系統進程,系統進程會根據這個Token找到ActivityRecord,對其完成調度后,再通知應用進程執行Activity的生命周期方法。
6.Instrumentation:每個Activity都持有一個Instrumentation,它是由ActivityThread創建出來的一個單例。 這個類就是完成對Application和Activity初始化和生命周期的工具類,ActivityThread要創建或執行Activity生命周期方法時,都需要通過Instrumentation來進行具體的操作。
關于App開機到啟動App的流程圖,當然,本文主要講的是Framework層的代碼
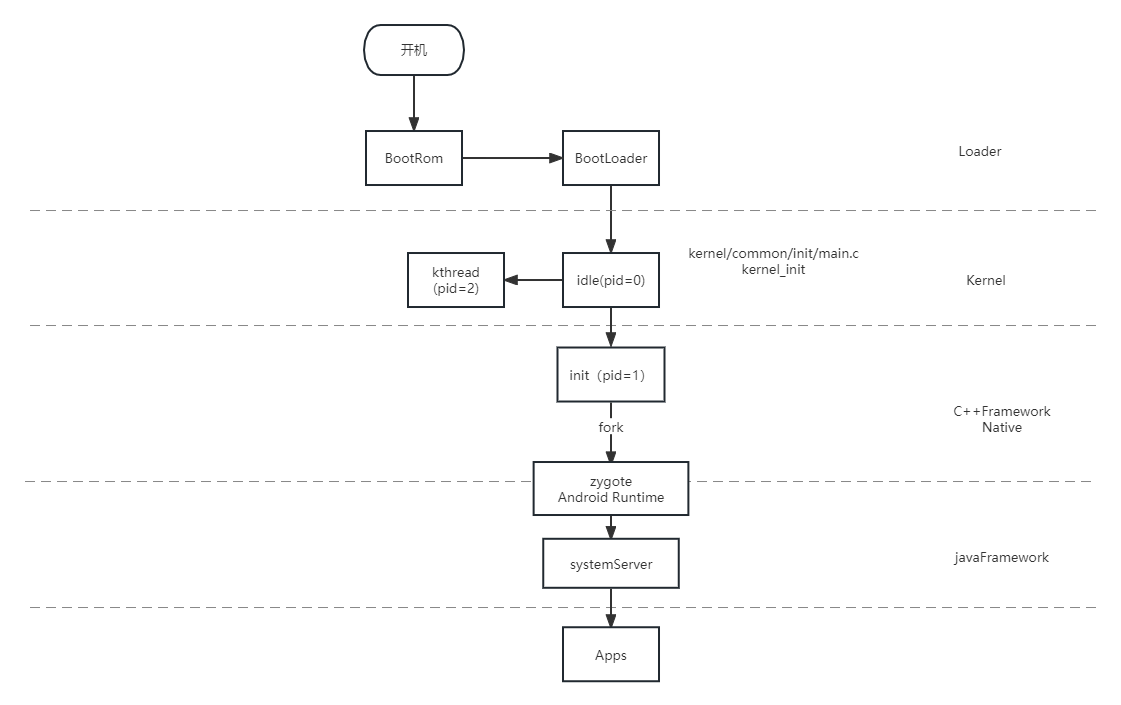
文章可以去看這個:android啟動流程-從開機到zygote創建_android的啟動流程-CSDN博客?
源碼閱讀真的好心累哦,上面我貼的代碼里,其實很多源碼我沒有貼出來,只貼了主流程的一些代碼。?
與君共勉,加油


【8-18】)


—— 抽象類、接口、Object類和內部類)













