多線程基礎
線程:一個程序內部的一條執行流程,只有一條執行流程就是單線程
java.lang.Thread代表線程
主線程退出,子線程存在,進程不會退出
可以使用jconsole查看
創建線程
有多個方法可以創建線程
-
繼承Thread類
- 優點:編碼簡單
- 缺點:無法繼承其他類,不利于功能的擴展
-
實現Runnable接口
- 優點:任務類只是實現了接口,可以繼續繼承其他類、實現其他接口,擴展性強
- 缺點:需要多創建一個Runnable對象
-
實現Callable接口和FutureTask類
- 優點:可以返回線程執行結束之后的結果
- 缺點:編碼復雜
執行為什么是start()?
使用run不是多線程, 相當于直接調用方法 還是單線程
start->start0(本地方法 JVM調用 C/C++實現的)
方法一
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//main是主線程執行的//新建了一個t線程Thread t = new primeThread();//啟動線程 start自動調用run方法 必須要調用start方法//如果是t.run() 相當于直接調用方法 還是單線程t.start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("主線程");Thread.sleep(500);}}
}class primeThread extends Thread{public primeThread(){}@Overridepublic void run() {//描述線程的執行的任務for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("子線程");try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
方法二
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//runnable只是一個任務對象Runnable target = new prime1Thread();//需要線程對象接受任務對象 開辟新的線程new Thread(target).start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("主線程");Thread.sleep(500);}}
}class prime1Thread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("子線程");try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}//可以使用匿名內部類
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//需要線程對象進行調用任務對象開辟新的線程new Thread(()-> {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("子線程");try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} }}).start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("主線程");Thread.sleep(500);}}
}
方法三
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//創建一個Callable對象Callable<String> myCallable = new MyCallable(100);// 把Callable的對象封裝成一個FutureTask對象(任務對象)// 未來任務對象的作用?// 1、是一個任務對象,實現下Runnable對象// 2、可以在線程執行完畢之后,用未來任務對象調用get方法獲取線程執行完畢的結果//也可以使用匿名內部類FutureTask<String> stringFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(myCallable);new Thread(stringFutureTask).start();//獲取結果會阻塞線程System.out.println(stringFutureTask.get());}
}//泛型
class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{private int n;public MyCallable(int n) {this.n = n;}@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {sum+=i;}return sum+"";}
}
線程方法
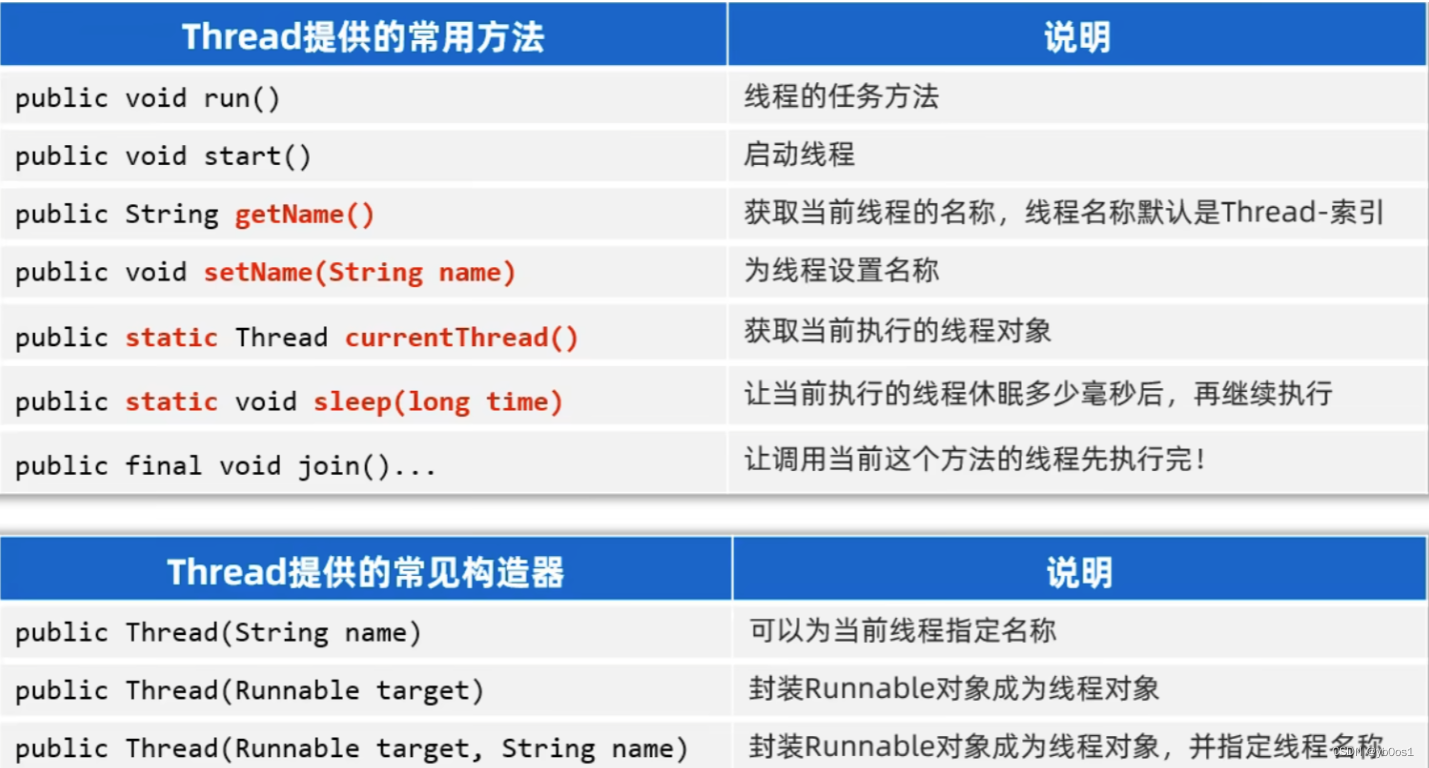
setPriority()更改線程的優先級getPriority()獲取線程的優先級interrupt中斷線程,并不是真正的結束線程 所以一般用于中斷正在休眠的線程yield線程的禮讓,不一定禮讓成功(和join相反,線程的插隊)
public class Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread1("1號線程");
// t1.setName("1號線程");//啟動之前取名字t1.start();t1.join();
// System.out.println(t1.getName());Thread t2 = new Thread1("2號線程");
// t2.setName("2號線程");//啟動之前取名字t2.start();t2.join();//t2線程執行完成之后才能繼續往下執行
// System.out.println(t2.getName());Thread t3 = new Thread1("3號線程");t3.start();t3.join();Thread m = Thread.currentThread();m.setName("最牛逼的名字");
// System.out.println(m.getName());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(m.getName()+"輸出"+(i+1));}}
}class Thread1 extends Thread{public Thread1(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic void run() {Thread t= Thread.currentThread();for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("子線程"+t.getName()+"輸出:"+(i+1));}}
}
線程終止
- 當線程執行完成時,自動退出
- 使用變量來控制run方法退出的方式停止線程
守護線程
當所有的用戶線程都退出時,守護線程自動退出
垃圾回收機制
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//子線程設置為守護線程myDaemonThread myDaemonThread = new myDaemonThread();myDaemonThread.setDaemon(true);myDaemonThread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 執行");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}/*
守護線程:
當用戶線程退出后 子線程也自動退出*/
class myDaemonThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在執行");try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
線程安全
概念
多個線程同時操作同一個共享資源的時候可能出現業務安全問題
模擬線程安全問題
package Thread_;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread xiaoHong = new DrawThread("小紅");Thread xiaoMing = new DrawThread("小明");xiaoMing.start();xiaoHong.start();}
}
class Account{private static double moneys = 100000;private Account(){}public static double getMoneys() {return moneys;}public static void setMoneys(double moneys) {Account.moneys = moneys;}public static boolean drawMoneys(double moneys){String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();if (moneys>Account.getMoneys()){System.out.println(name+"來取錢,錢不夠");return false;}Account.moneys-=moneys;System.out.println(name+"來取錢,取錢成功,剩余"+Account.moneys);return true;}
}class DrawThread extends Thread{public DrawThread(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic void run() {Account.drawMoneys(100000.0);}
}
線程同步
認識線程同步
多個線程實現先后依次訪問共享資源
**加鎖:**每次只允許一個線程加鎖,加鎖之后才能訪問,訪問完畢之后自動解鎖,然后其他線程才能再加鎖繼續
方法一:同步代碼塊
把訪問共享資源的核心代碼給上鎖,保證線程安全
synchronized(同步鎖){訪問共享資源的核心代碼
}
對于當前同時執行的線程來說,同步鎖必須是同一把(同一對象)
鎖對象的選擇:
- 實例對象:使用
this - 靜態對象:使用
類型.class
public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Account acc1 = new Account(100000);Thread xiaoHong = new DrawThread("小紅",acc1);Thread xiaoMing = new DrawThread("小明",acc1);xiaoMing.start();xiaoHong.start();Account acc2 = new Account(100000);Thread daGang = new DrawThread("大綱",acc2);Thread daLi = new DrawThread("大力",acc2);daGang.start();daLi.start();}
}class Account {private double moneys;public Account() {}public Account(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}public double getMoneys() {return moneys;}public void setMoneys(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}public void drawMoneys(double moneys) throws InterruptedException {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();/** 兩個人同時競爭lock這個對象(這把鎖),只有一個人能夠得到* 上鎖之后另外一個人要等待開鎖** 但是這個lock對于所有的對象是一個鎖* 一個對象上鎖的時候 和該對象無關的對象也無法進入核心代碼* 非static建議使用 this* static建議使用 ClassName.class* */synchronized (this) {
// Thread.sleep(5000); 測試if (moneys > this.getMoneys()) {System.out.println(name + "來取錢,錢不夠");} else {this.moneys -= moneys;System.out.println(name + "來取錢,取錢" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);}}}
}class DrawThread extends Thread {private Account acc;public DrawThread(String name,Account acc) {super(name);this.acc = acc;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {acc.drawMoneys(100000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
方法二:同步方法
訪問共享資源的核心方法給上鎖
修飾符 synchronized 返回值類型 方法名稱(形參列表){操作共享資源的代碼
}
public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Account acc1 = new Account(100000);Thread xiaoHong = new DrawThread("小紅", acc1);Thread xiaoMing = new DrawThread("小明", acc1);xiaoMing.start();xiaoHong.start();Account acc2 = new Account(100000);Thread daGang = new DrawThread("大綱", acc2);Thread daLi = new DrawThread("大力", acc2);daGang.start();daLi.start();}
}class Account {private double moneys;public Account() {}public Account(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}public double getMoneys() {return moneys;}public void setMoneys(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}/*有一個隱含的鎖 實例方法是 this 靜態方法是 類型.class*/public synchronized void drawMoneys(double moneys) throws InterruptedException {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();if (moneys > this.getMoneys()) {System.out.println(name + "來取錢,錢不夠");} else {this.moneys -= moneys;System.out.println(name + "來取錢,取錢" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);}}
}class DrawThread extends Thread {private Account acc;public DrawThread(String name, Account acc) {super(name);this.acc = acc;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {acc.drawMoneys(100000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}

方法三:Lock鎖
Lock鎖是IDK5開始提供的一個新的鎖定操作,通過它可以創建出鎖對象進行加鎖和解鎖,更靈活、更方便、更強大
Lock是接口,不能直接實例化,可以采用它的實現類**ReentrantLock**來構建Lock鎖對象。
package Thread_;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Account acc1 = new Account(100000);Thread xiaoHong = new DrawThread("小紅", acc1);Thread xiaoMing = new DrawThread("小明", acc1);xiaoMing.start();xiaoHong.start();Account acc2 = new Account(100000);Thread daGang = new DrawThread("大綱", acc2);Thread daLi = new DrawThread("大力", acc2);daGang.start();daLi.start();}
}class Account {/*創建了一個鎖對象 每一個賬戶都有一個自己的鎖對象不允許二次賦值*/private final Lock lk = new ReentrantLock();private double moneys;public Account() {}public Account(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}public double getMoneys() {return moneys;}public void setMoneys(double moneys) {this.moneys = moneys;}public void drawMoneys(double moneys) throws InterruptedException {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();try {lk.lock();if (moneys > this.getMoneys()) {System.out.println(name + "來取錢,錢不夠");} else {this.moneys -= moneys;System.out.println(name + "來取錢,取錢" + moneys + "成功,剩余" + this.moneys);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lk.unlock();//無論try中代碼是否有錯誤 都會解鎖}}
}class DrawThread extends Thread {private Account acc;public DrawThread(String name, Account acc) {super(name);this.acc = acc;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {acc.drawMoneys(100000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
釋放鎖的時機
- 當前線程的同步方法、同步代碼塊執行結束
- 當前線程在同步方法、同步代碼塊中遇到
break、return - 當前線程在同步方法、同步代碼塊中出現了未處理的
Error或者Exception,導致異常結束 - 當前線程在同步方法、同步代碼塊中執行了線程對象的
wait()方法,當前線程暫停 釋放鎖,等待喚醒
不釋放鎖
Thread.sleep()、Thread.yeild不會釋放鎖suspend()掛起方法,也不會釋放鎖suspend、resume控制線程,不推薦使用
線程死鎖
多個線程都占用了對方的鎖資源,但是不肯相讓,導致了死鎖
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new MyDeadThread(false)).start();new Thread(new MyDeadThread(true)).start();}
}
class MyDeadThread implements Runnable{private boolean flag;private static Object o1 = new Object();private static Object o2 = new Object();public MyDeadThread() {}public MyDeadThread(boolean flag) {this.flag = flag;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){/*flag=true 占用o1鎖 搶奪o2鎖flag=false 占用o2鎖 搶奪o1鎖如果兩個線程 一個占用o1 一個占用o2 那么就造成死鎖*/if (flag){synchronized (o1){System.out.println("o1");synchronized (o2){System.out.println("o2");}}}else {synchronized (o2){System.out.println("o2");synchronized (o1){System.out.println("o1");}}}}}
}
線程通信
當多個線程共同操作共享資源的時候,線程間通過某種方式相互告知自己的狀態,相互協調,避免無效的資源爭奪
生產者消費者模型
- 生產者線程負責生產數據
- 消費者線程負責消費生產者生產的數據
- 生產者生產完數據應該等待,通知消費者消費;消費者消費完數據也應該等待,通知生產者生產

public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Desk desk = new Desk();//3個生產者new Thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"廚師1").start();new Thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"廚師2").start();new Thread(()-> {while (true){desk.put();}},"廚師3").start();//2個消費者new Thread(()-> {while (true){desk.get();}},"吃貨1").start();new Thread(()-> {while (true){desk.get();}},"吃貨2").start();}
}import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Desk {private final List<String>list = new ArrayList<>();//這個五個人是同一把鎖public synchronized void put(){try {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();if (list.isEmpty()){list.add(name+"做的肉包子");System.out.println(name+"做的肉包子");Thread.sleep(500);}//等待自己 喚醒別人 先喚醒后等待//只能線程對象調用this.notify();this.wait();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public synchronized void get(){try {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();if (!list.isEmpty()){System.out.println(name + "吃了"+list.remove(0));Thread.sleep(500);}//等待自己 喚醒別人 先喚醒后等待//只能線程對象調用this.notify();this.wait();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
線程池
概念
可以復用線程的技術
**不使用線程池:**用戶每發起一個請求,后臺就需要創建一個新線程來處理,下次新任務來了肯定又要創建新線程處理的,而創建新線程的開銷是很大的,并且請求過多時,肯定會產生大量的線程出來,這樣會嚴重影響系統的性能。
使用ExecutorService創建線程池
使用ExecutorService的實現類ThreadPoolExecutor創建一個線程池對象(JDK5.0之后提供代表線程池的接口:ExecutorService)

corePoolSize:指定線程池的核心線程的數量maximumPoolSize:指定線程池的最大線程的數量keepAliceTime:指定臨時線程的存活時間unit:指定臨時線程存貨時間的單位(秒、分、時、天)workQueue:指定線程池的任務隊列threadFactory:指定線程池的線程工廠handler:指定線程池的任務拒絕策略(線程都在忙,任務隊列也滿了的時候,新任務來了該怎么處理)
/*ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)*/ExecutorService poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 8, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());什么時候創建臨時對象?
新任務提交時發現核心線程都在忙,任務隊列也滿了,并且還可以創建臨時線程,才會創建
什么時候會開始拒絕新任務?
核心線程和臨時線程都在忙,任務隊列也滿了
新任務拒絕策略
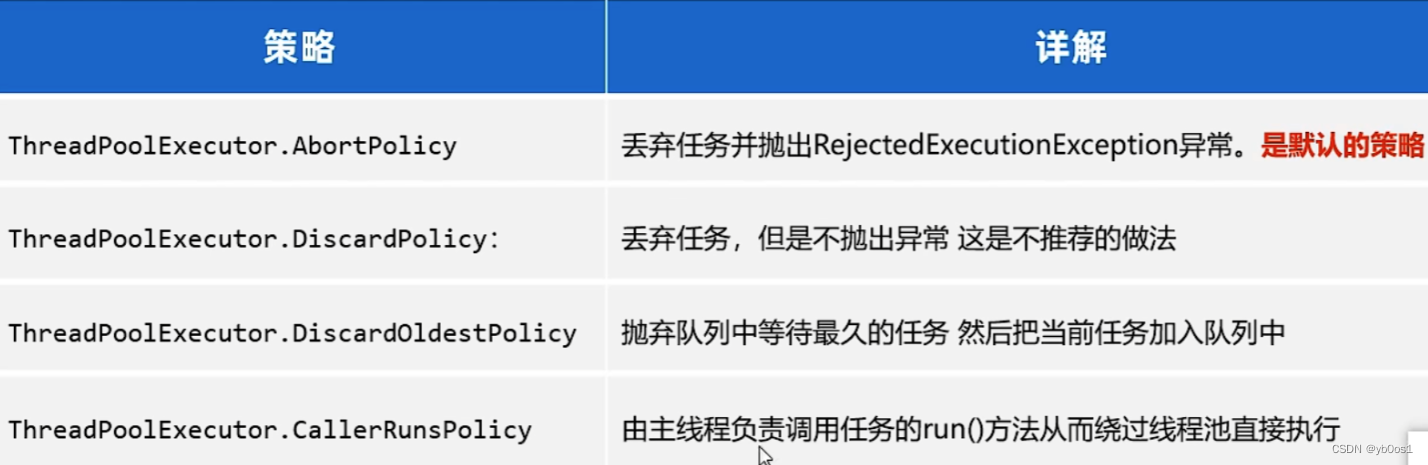
處理Runnable任務

import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class _ThreadPool {public static void main(String[] args) {/*ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)*/ExecutorService poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5,8, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());MyRunnable myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable();MyRunnable myRunnable2 = new MyRunnable();MyRunnable myRunnable3 = new MyRunnable();//三個核心線程在忙poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable1);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable2);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);//任務隊列占滿poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);//可以創建兩個臨時線程poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);//拒絕新任務poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);// poolExecutor.shutdown();//等任務執行完后關閉線程池
// poolExecutor.shutdownNow();//立刻關閉線程池}
}class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();System.out.println(name + "666");try {Thread.sleep(100000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
處理Callable任務

import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class _ThreadPool {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {/*ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)*/ExecutorService poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5,8, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());Future<String>f1 = poolExecutor.submit(new MyCallable(100));Future<String>f2 = poolExecutor.submit(new MyCallable(200));Future<String>f3 = poolExecutor.submit(new MyCallable(300));Future<String>f4 = poolExecutor.submit(new MyCallable(400));System.out.println(f1.get());System.out.println(f2.get());System.out.println(f3.get());System.out.println(f4.get());}
}class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {private int n;public MyCallable(int n) {this.n = n;}@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {sum+=i;}return Thread.currentThread().getName()+"計算出1-"+n+"的和為"+sum;}
}
使用Executors創建線程池(大型并發系統不建議)
(線程池的工具類)調用方法返回不同特點的線程池對象
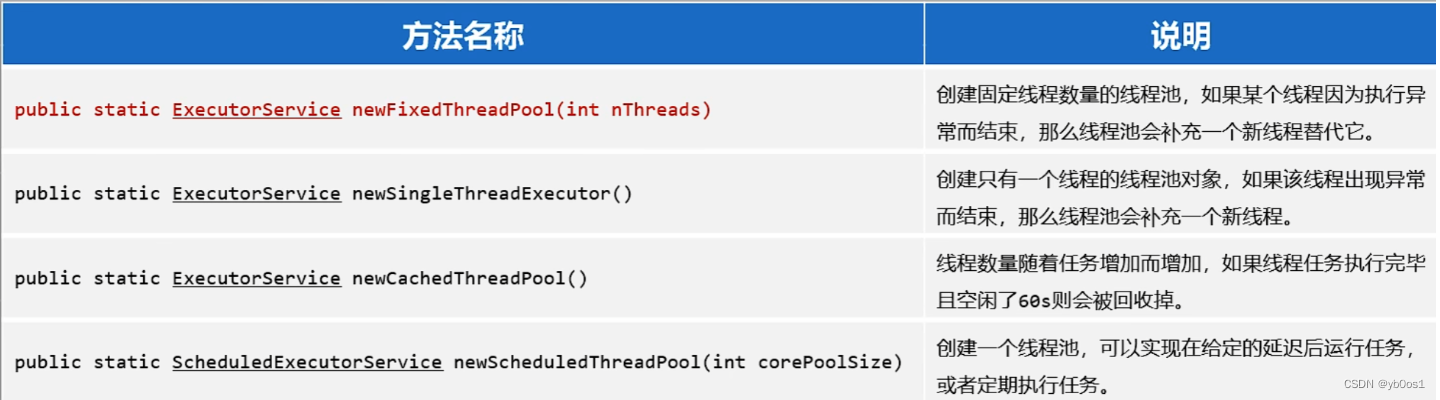
- FixedThreadPool、SingleThreadExecutor允許請求隊列長度為Integer.MAX_VALUE
- CachedThreadPool允許創建線程數量為Integer.MAX_VALUE
這些方法的底層,都是通過線程池的實現類ThreadPoolExecutor創建的線程池對象
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
核心線程配置數量
- 計算密集型的任務:CPU核數+1
- IO密集型的任務:CPU核數*2
并發和并行
并發的含義
進程中的線程是由CPU負責調度執行的,但是CPU能同時處理線程的數量是有限的。
為了保證全部線程都能往前執行,CPU會輪詢為系統的每個線程服務,由于CPU切換速度很快,給我們的感覺就是這些線程在同時執行,這就是并發
并行的含義
同一時刻上,同時有多個線程在被CPU調度執行
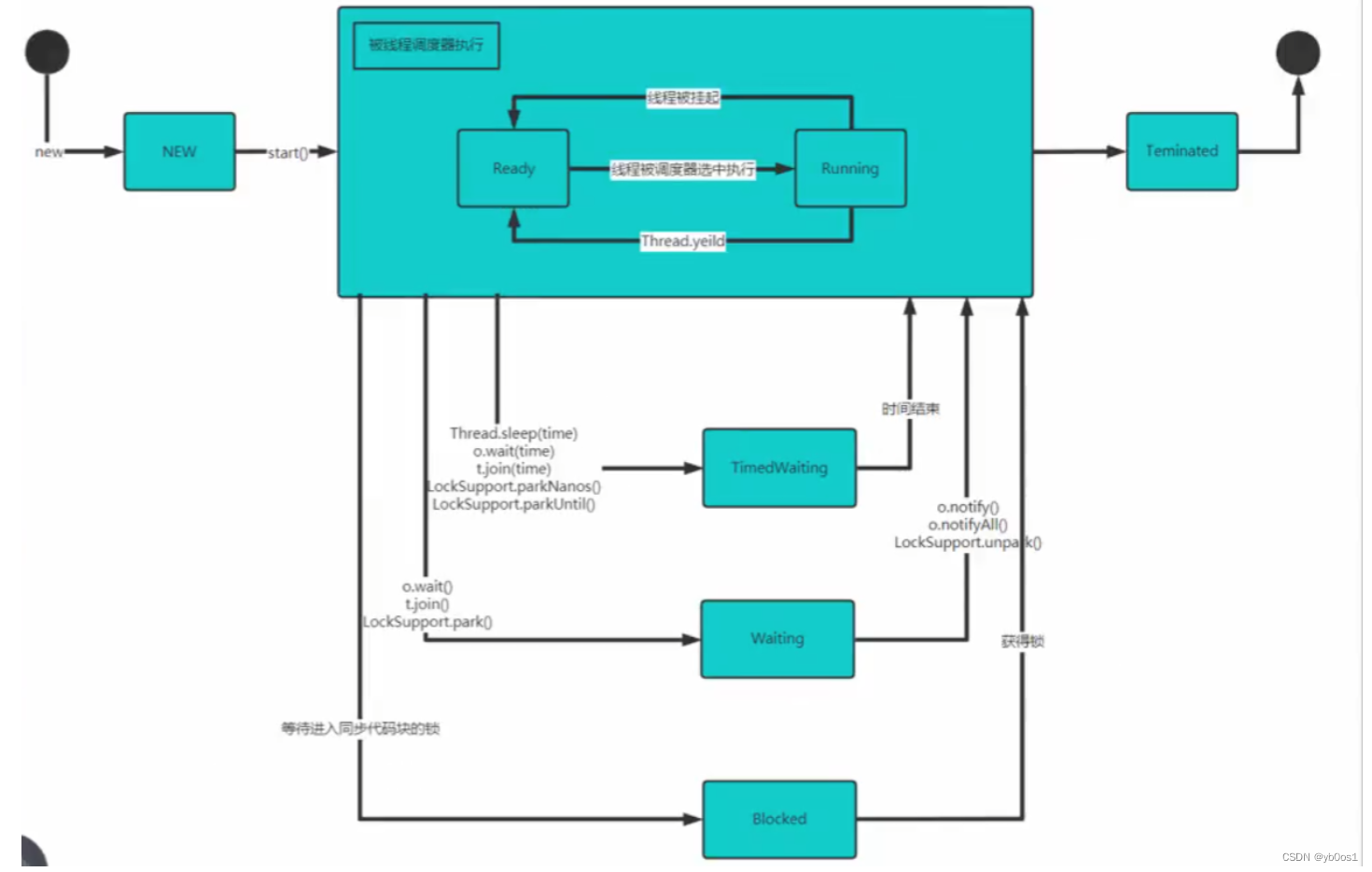
線程生命周期
也就是線程從生到死的過程,經歷的各種狀態以及狀態轉換
理解線程這些狀態有利于提高并發編程的理解能力

擴展:悲觀鎖和樂觀鎖
悲觀鎖:一開始就加鎖,沒有安全感,每次只能一個線程進入,訪問完畢后再解鎖。線程安全 性能較差
樂觀鎖:一開始不上鎖,認為沒問題,等出現線程安全的時候才開始控制。線程安全 性能較好
//樂觀鎖
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class Demo7 {//一個靜態變量,100個線程,每個線程對其加100次public static void main(String[] args) {Runnable mRunnable = new MRunnable2();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {//100個線程執行相同的任務new Thread(mRunnable).start();}}
}class MRunnable2 implements Runnable {
// private int count;//整數修改的樂觀鎖:原子類,private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("count====>" + (count.incrementAndGet()));}}
}
多線程練習
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {/*** 目標:有100份禮品,小紅,小明兩人同時發送,當剩下的禮品小于10份的時候則不再送出,* 利用多線程模擬該過程并將線程的名稱打印出來。并最后在控制臺分別打印小紅,小明各自送出多少分禮物。*/ArrayList<String> gifts = new ArrayList<>();String[] names = {"口紅", "包包", "腰帶", "剃須刀", "香水", "衣服"};Random r = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {gifts.add(names[r.nextInt(names.length)] + (i + 1));}sendThread xm = new sendThread(gifts, "小明");sendThread xh = new sendThread(gifts, "小紅");xm.start();xh.start();xm.join();xh.join();System.out.println("小明送出去" + xm.getCount());System.out.println("小紅送出去" + xh.getCount());}
}class sendThread extends Thread {private ArrayList<String> gifts;private int count;public int getCount() {return count;}public void setCount(int count) {this.count = count;}public sendThread() {}public sendThread(ArrayList<String> gifts, String name) {super(name);this.gifts = gifts;}@Overridepublic void run() {Random r = new Random();String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();while (true) {synchronized (gifts) {int length = gifts.size();if (length < 10)break;String s = gifts.remove(r.nextInt(length));System.out.println(name + "送出禮物" + s);++count;}}}
}
網絡編程基礎
可以讓設備中的程序與網絡上其他設備中的程序進行數據交互(實現網絡通信的)
java.net.*的包下
網絡通信三要素
- IP地址:設備在網絡中的地址,是唯一的標識
- 端口號:應用程序在設備中唯一的標識
- 協議:連接和數據在網絡中傳輸的規則
java獲取Ip地址:InetAddress
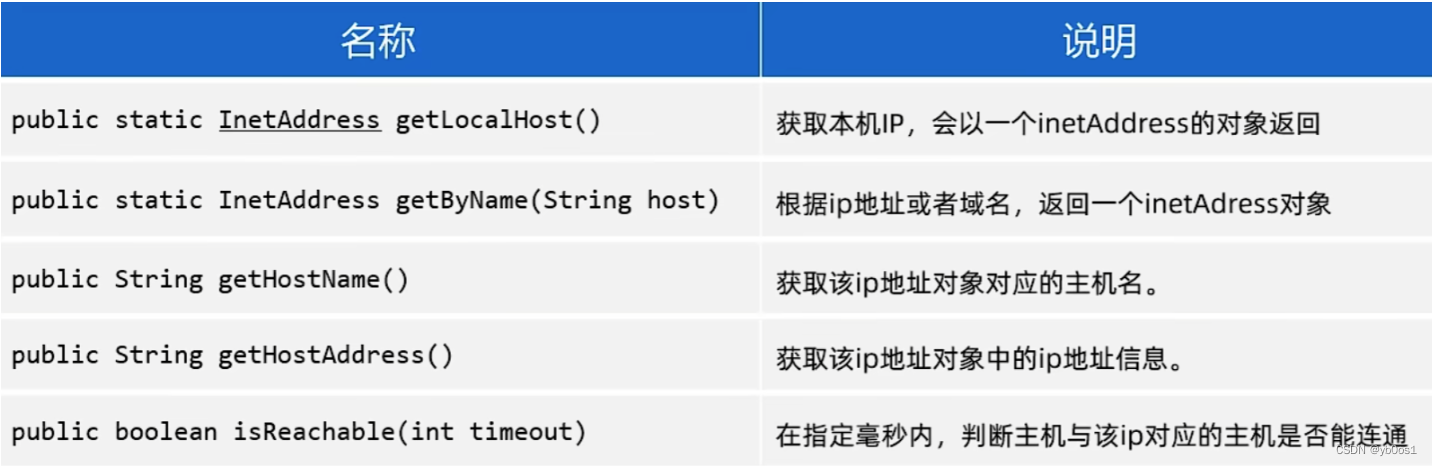
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;public class GetIP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//本機InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();System.out.println(ip.getHostName());System.out.println(ip.getHostAddress());//指定InetAddress ipBaiDu = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");System.out.println(ipBaiDu.getHostName());System.out.println(ipBaiDu.getHostAddress());//本機ping 百度System.out.println(ipBaiDu.isReachable(6000));}
}
UDP通信
java.net.DatagramSocket實現UDP通信

一發一收
Client
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//創建客戶端 以及客戶端端口DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);String data = "我是客戶端,哈哈哈";byte[]bytes = data.getBytes();//創建數據包DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(),5555);//發送數據socket.send(packet);System.out.println("客戶端數據發送完畢");//釋放資源socket.close();}
}
Serve
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;public class Serve {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("===服務端啟動===");//創建服務端 注冊服務端端口DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(5555);byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*64];//64KB UDP一個數據包最大為64KB//創建一個用來接收數據的數據包對象DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);//接受數據socket.receive(packet);//從字節數組中獲取接受的數據int len = packet.getLength();String data = new String(buffer,0,len);System.out.println(data);//獲取客戶端的IP 端口System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress());System.out.println(packet.getPort());//釋放資源socket.close();}
}
多發多收
可以多個用戶同時發送
Client
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//創建客戶端 以及客戶端端口(默認隨機分配)DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {System.out.println("請輸入消息://exit是退出");String msg = sc.nextLine();if (msg.equals("exit")){System.out.println("歡迎下次光臨");break;}byte[]bytes = msg.getBytes();//創建數據包DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(),5555);//發送數據socket.send(packet);}socket.close();}
}
Serve
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;public class Serve {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("===服務端啟動===");//創建服務端 注冊服務端端口DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(5555);byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*64];//64KB UDP一個數據包最大為64KB//創建一個用來接收數據的數據包對象DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);while (true) {//接受數據socket.receive(packet);//從字節數組中獲取接受的數據int len = packet.getLength();String data = new String(buffer,0,len);System.out.println(data);//獲取客戶端的IP 端口System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress());System.out.println(packet.getPort());System.out.println("----------------");}}
}
TCP通信
客戶端:java.net.Socket
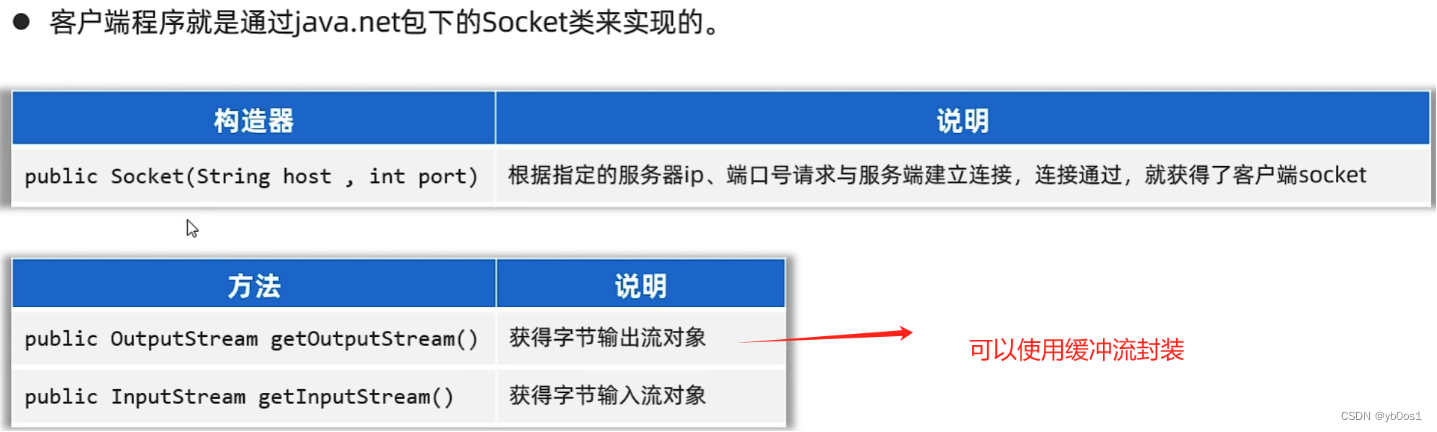
一發一收
client
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;public class ClientTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//創建socket對象Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 5555);//從socket通信管道中得到一個字節輸出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//封裝成數據輸出流DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(os);//寫入數據dataOutputStream.writeUTF("你好呀!");//關閉數據流dataOutputStream.close();//關閉socketsocket.close();}
}
serve
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;public class ServeTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{System.out.println("--服務端啟動--");//創建服務端對象 綁定端口ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5555);//等待連接Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//接受數據InputStream ds = socket.getInputStream();//封裝DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(ds);//接受數據String s = dataInputStream.readUTF();System.out.println(s);//客戶端ip地址System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());dataInputStream.close();socket.close();}
}
多發多收
client
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Scanner;public class ClientTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//創建socket對象Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 5555);//從socket通信管道中得到一個字節輸出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//封裝成數據輸出流DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(os);Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {//寫入數據System.out.println("請說:");String s = sc.nextLine();if (Objects.equals(s, "exit")){System.out.println("歡迎下次光臨");break; }dataOutputStream.writeUTF(s);dataOutputStream.flush();}//關閉數據流dataOutputStream.close();//關閉socketsocket.close();}
}
serve
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;public class ServeTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{System.out.println("--服務端啟動--");//創建服務端對象 綁定端口ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5555);//等待連接Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//接受數據InputStream ds = socket.getInputStream();//封裝DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(ds);//接受數據while (true) {try {String s = dataInputStream.readUTF();System.out.println(s);//客戶端ip地址
// System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"離線");break;}}dataInputStream.close();socket.close();}
}
多個客戶端連接一個服務端
服務端:
- 主線程負責接受客戶端連接
- 子線程負責具體每一個客戶端
client
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;public class ClientTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true){String s = sc.nextLine();if (s.equals("exit")){System.out.println("歡迎下次光臨");dos.close();socket.close();break;}dos.writeUTF(s);dos.flush();}}
}
serve
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.SocketAddress;public class ServeTCP {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服務端開啟...");ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);while (true) {Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"上線了");new Thread(new SocketThread(socket)).start();}}
}class SocketThread implements Runnable{private Socket socket;public SocketThread(Socket socket){this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {SocketAddress remoteSocketAddress = socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();try {InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);while (true) {try {String s = dis.readUTF();System.out.println(remoteSocketAddress+"發送:"+s);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(remoteSocketAddress+"下線了");socket.close();dis.close();break;}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
案例:群聊
client
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;public class ClientChat {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);new ClientThread(socket).start();OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {String s = sc.nextLine();if (s.equals("exit")) {System.out.println("歡迎下次光臨");socket.close();dos.close();break;}dos.writeUTF(s);dos.flush();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}class ClientThread extends Thread {private Socket socket;public ClientThread(Socket socket) {this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);while (true) {try {String msg = dis.readUTF();System.out.println(msg);} catch (Exception e) {dis.close();socket.close();break;}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
serve
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;public class ServeChat {public static final List<Socket> onlineUsers = new ArrayList<>();public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{System.out.println("==服務器啟動==");ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);while (true) {Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();onlineUsers.add(socket);new ServeReaderThread(socket).start();}}
}class ServeReaderThread extends Thread {private Socket socket;public ServeReaderThread(Socket socket) {this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);while (true) {try {String msg = dis.readUTF();System.out.println(msg);sendAllOnlineUsers(socket,msg);} catch (Exception e) {ServeChat.onlineUsers.remove(socket);socket.close();dis.close();System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress() + "下線");break;}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private void sendAllOnlineUsers(Socket socket,String msg) throws Exception {for (Socket onlineUser : ServeChat.onlineUsers) {SocketAddress remoteSocketAddress = socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();if (Objects.equals(onlineUser.getRemoteSocketAddress(),remoteSocketAddress)){continue;}OutputStream os = onlineUser.getOutputStream();DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);dos.writeUTF(remoteSocketAddress+"說:"+msg);dos.flush();}}
}
案例:簡易BS架構
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;public class Serve {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);while (true){Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"上線了");new CThread(socket).start();}}
}class CThread extends Thread{private Socket socket;public CThread(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(os);/*服務器必須給瀏覽器相應Http協議規定的格式*/ps.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");ps.println("Content-Type:text/html;charset=UTF-8");ps.println();//必須換行ps.println("<div style='color:red;font-size:120px;'>java666</div>");ps.close();socket.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
改進:線程池
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class Serve {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(16 * 2, 16 * 2, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(8), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());while (true){Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"上線了");pool.execute(new CThread(socket));}}
}class CThread implements Runnable{private Socket socket;public CThread(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(os);/*服務器必須給瀏覽器相應Http協議規定的格式*/ps.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");ps.println("Content-Type:text/html;charset=UTF-8");ps.println();//必須換行ps.println("<div style='color:red;font-size:120px;'>java666</div>");ps.close();socket.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
案例:多用戶即時通信系統
需求分析
- 用戶登錄
- 拉取在線用戶
- 無異常退出
- 私聊
- 群聊
- 發文件
- 服務器推送新聞
java高級
單元測試
就是針對最小的功能單元(方法),編寫測試代碼對其進行正確性測試
junit單元測試框架
- 可以靈活的編寫測試代碼,可以針對某個方法執行測試,也支持一鍵完成對全部的方法自動化測試
- 不需要程序員去分析測試結果,會自動生成測試報告
具體使用
public class Demo {public static void printNumber(String name){if (name==null)return;System.out.println("名字長度:"+name.length());}public static int getMaxIndex(String data){if (data==null)return -1;return data.length();}
}
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;/*
測試類*/
public class DemoTest {@Beforepublic void test1(){System.out.println("---------Before---------");}@Afterpublic void test2(){System.out.println("---------After---------");}@AfterClasspublic static void test3(){System.out.println("---------AfterClass---------");}@BeforeClasspublic static void test4(){System.out.println("---------BeforeClass---------");}/*公開 無返回值*/@Test //測試方法public void testPrintNumber(){Demo.printNumber("admin");Demo.printNumber(null);}@Test //測試方法public void testGetMaxIndex(){//斷言機制:可以通過預測業務方法的結果來測試 bugSystem.out.println(Demo.getMaxIndex("admin"));System.out.println(Demo.getMaxIndex(null));//斷言機制:可以通過預測業務方法的結果來測試 bugAssert.assertEquals("有bug",4,Demo.getMaxIndex("admin"));}
}


以下是學習框架源碼的時候會用到,開發幾乎不會用
反射
認識反射
加載類,并允許以編程的方式解剖類中的各個成分(成員變量、方法、構造器等)
步驟
- 加載類,獲取類的字節碼:Class對象
- 獲取類的構造器:Constructor對象
- 獲取類成員變量:Field對象
- 獲取類成員方法:Method對象
獲取類的字節碼
- Class c1 = 類名.class
- 調用Class提供的方法
public static Class forName(String package);全類名 - Object的方法 對象.getClass()
獲取類的構造器

import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class c = Cat.class;Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor();System.out.println(constructor.getName()+"--"+constructor.getParameterCount());Cat o = (Cat) constructor.newInstance();System.out.println(o);Constructor declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);System.out.println(declaredConstructor.getName()+"--"+declaredConstructor.getParameterCount());declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);//打破修飾符的限制Cat o1 = (Cat)declaredConstructor.newInstance("學習", 5);}
} class Cat{private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public Cat() {}private Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public Cat(String name) {this.name = name;}
}
獲取類的成員變量

import java.lang.reflect.Field;public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class c = Cat.class;Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();for (Field field : fields) {System.out.println(field.getName()+"--"+field.getType());}Field name = c.getDeclaredField("name");System.out.println(name.getName()+"--"+name.getType());Cat cat = new Cat();name.setAccessible(true);name.set(cat,"貓貓");System.out.println(name.get(cat));}
}class Cat{public static int a;public static final String COUNTRY ="中國";private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public Cat() {}private Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public Cat(String name) {this.name = name;}
}
獲取類的成員方法

作用、應用場景
基本作用:可以得到一個類全部成分對其操作;可以破壞封裝性;適合做java的框架
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {Student stu = new Student("小明", 18, 82.5);Teacher tea = new Teacher("大強", 58);saveObject(stu);saveObject(tea);}public static void saveObject(Object obj) throws Exception {Class o = obj.getClass();String cname = o.getSimpleName();PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("./out/obj.txt",true));ps.println("---------"+cname+"---------");Field[] fields = o.getDeclaredFields();for (Field field : fields) {field.setAccessible(true);String name = field.getName();String value = field.get(obj)+"";ps.println(name+":"+value);}ps.close();}
}
class Student{private String name;private int age;private double sorce;public Student(String name, int age, double sorce) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.sorce = sorce;}
}class Teacher{private String name;private int age;public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}
}
注解
就是java中特殊的標記,比如@override、@Test等
作用:讓其他程序根據注解信息來決定怎么執行程序
注解可以用在類、方法、構造器、成員變量、參數等等
自定義注解
public @interface 注解名稱{public 屬性類型 屬性名() default 默認值;
}
只有一個注解 且為 value 可以省略不寫value
注解原理
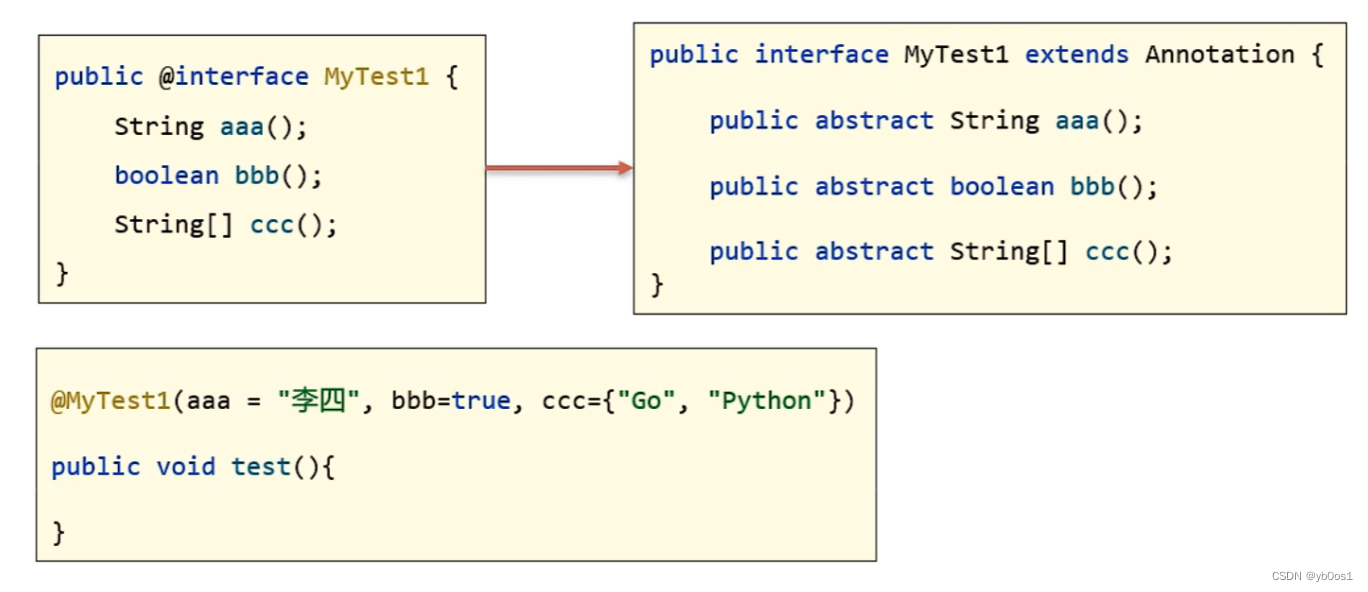
注解本質就是一個接口,java中所有的注解都是繼承了Annotation的接口
@注解(…)其實就是一個實現類對象,實現了該注解以及Annotation的接口
元注解
修飾注解的注解

注解的解析
就是判斷類上、方法上、成員變量上是否存在注解,并把注解里的內容給解析出來。
要解析誰的注解,就要先拿到誰
Class、Method、Field,Constructor、都實現了AnnotatedElement接口,它們都擁有解析注解的能力。

package annotation;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})//當前被修飾的注解只能使用在類上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTest{String value();double aaa() default 100;String[] bbb();
}package annotation;@MyTest(value = "大強",aaa = 199.9,bbb={"css","java","html"})public class Demo {
@MyTest(value = "小明",aaa = 99.9,bbb={"java","html"})void test(){}
}package annotation;import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;public class AnnotationTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class c = Demo.class;Method test = c.getDeclaredMethod("test");if (c.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest.class)) {MyTest myTest = (MyTest) c.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyTest.class);System.out.println(myTest.value());System.out.println(myTest.aaa());System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myTest.bbb()));}if (test.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest.class)) {MyTest myTest = test.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyTest.class);System.out.println(myTest.value());System.out.println(myTest.aaa());System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myTest.bbb()));}}
}應用場景
模擬junit
package annotation;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class TestTest {@MyTest2public void test1(){System.out.println("==test1==");}public void test2(){System.out.println("==test2==");}public void test3(){System.out.println("==test3==");}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class c = TestTest.class;Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method method : methods) {if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest2.class)){method.invoke(new TestTest());}}}
}
動態代理
概念
對象做的事情太多的話,可以通過代理來轉移部分職責

package proxy;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class ProxyUtil {public static Star createProxy(BigStar bigStar) {/*參數1:指定一個類加載器參數2:指定生成的代理是什么樣子,也就是有什么方法參數3:指定生成的代理對象要干什么事情*/return (Star) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyUtil.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Star.class}, new InvocationHandler() {@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//代理對象要做的事情 會在這里寫代碼if (method.getName().equals("sing")){System.out.println("準備話筒,收錢20w");}else if (method.getName().equals("dance")){System.out.println("準備場地,收錢1000w");}return method.invoke(bigStar,args);}});}
}
package proxy;public class BigStar implements Star {private String name;public BigStar() {}public BigStar(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String sing(String name) {System.out.println(this.name+"正在唱"+name+"歌~~~");return "謝謝!謝謝~";}@Overridepublic void dance() {System.out.println(name+"正在跳舞~~~");}
}
package proxy;public interface Star {public String sing(String name);public void dance();
}
package proxy;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {BigStar s = new BigStar("楊超越");Star starProxy = ProxyUtil.createProxy(s);String rs = starProxy.sing("好日子");System.out.println(rs);System.out.println("--------------------------");starProxy.dance();}
}
坦克大戰
java坐標系
下圖說明了Java坐標系。坐標原點位于左上角,以像素為單位。在Java坐標系中,第一個是x坐標,表示當前位置為水平方向,距離坐標原點x個像素;第二個是y坐標,表示當前位置為垂直方向,距離坐標原點y個像素。
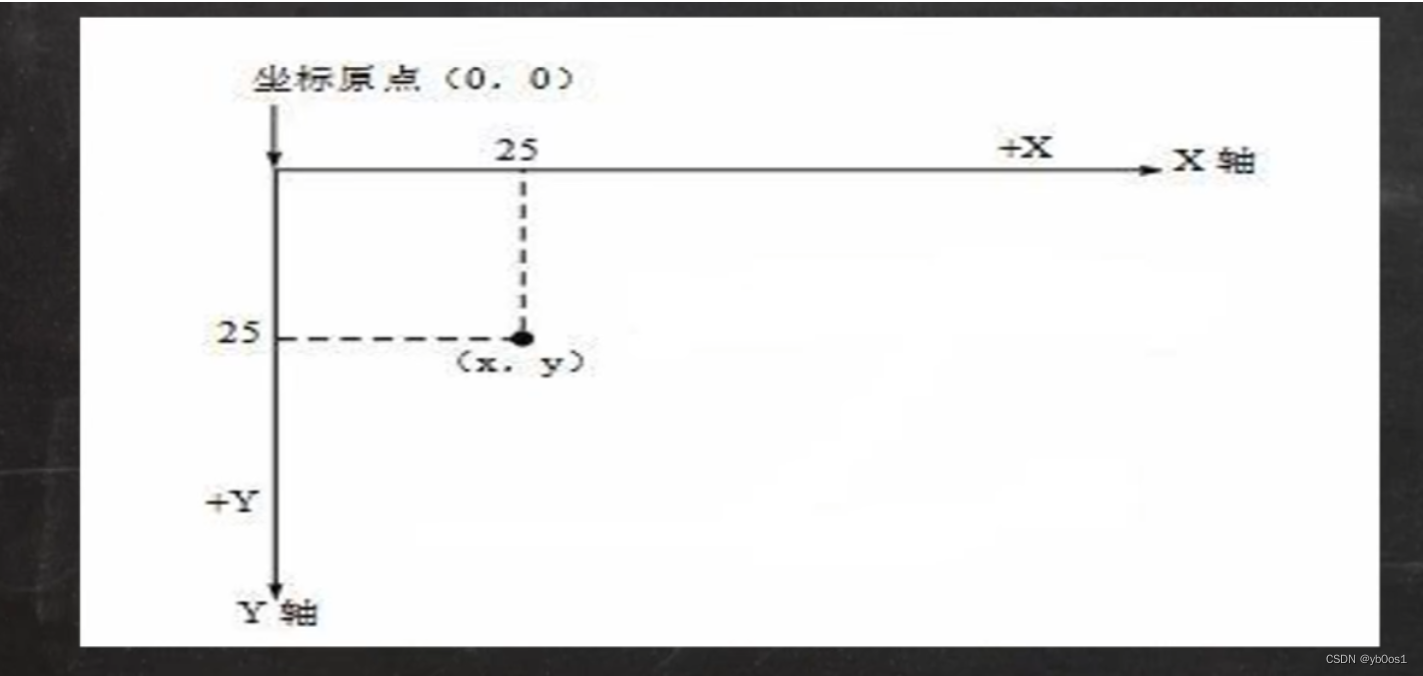
package tankeGame;import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;public class Draw extends JFrame {//JFrame 對應窗口 可以理解為一個畫框private MyPanel mp =null;//定義一個畫板public Draw(){//初始化畫板mp = new MyPanel();//畫板放入窗口this.add(mp);//設置窗口大小this.setSize(1000,800);//可以顯示this.setVisible(true);//點窗口的× 程序退出this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);}public static void main(String[] args) {new Draw();}
}//1.定義一個MyPanel繼承JPanel,這個就是畫板 畫圖形
class MyPanel extends JPanel{/*MyPanel:畫板(面板)對象Graphics g:畫筆paint調用時機:1.組件第一次在屏幕中顯示的時候,系統自動調用2.窗口最小化 再最大化3.窗口大小發生變化4.repaint函數被調用*/@Overridepublic void paint(Graphics g) {//繪圖的方法super.paint(g);//調用父類的方法完成初始化//畫一個圓g.drawOval(10,10,100,100);//畫直線g.drawLine(10,10,60,60);//畫矩形g.drawRect(10,10,100,100);//填充矩形//設置畫筆顏色g.setColor(Color.BLUE);g.fillRect(50,50,100,100);g.fillOval(200,200,50,60);//畫圖片//1.加載圖片資源Image image = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getImage("d:/shangan.png");//2.畫圖片g.drawImage(image,300,300,300,300,this);//畫字符串g.setColor(Color.cyan);g.setFont(new Font("隸書",Font.BOLD,50));//位置是字體的左下角g.drawString("yb0os1",500,100);}
}
事件處理機制
委派事件模型
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.KeyListener;//事件控制 鍵盤控制小球的移動
//畫筆
public class BallMove extends JFrame {private DrawBall ball = null;public BallMove() {ball = new DrawBall();this.add(ball);this.setVisible(true);this.setSize(500, 400);this.addKeyListener(ball);//JFame對象可以監聽ball上面發生的鍵盤事件this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);}public static void main(String[] args) {new BallMove();}
}//畫板
//KeyListener 監聽器 監聽鍵盤事件
class DrawBall extends JPanel implements KeyListener {int x = 10;int y = 10;@Override//有字符輸出時 該方法會觸發public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {}@Override//當某個鍵被按下時 該方法會觸發public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
// System.out.println((char) e.getKeyChar() + "被按下");//根據用戶按下的不同鍵,來處理小球的移動//java中給每一個鍵分配一個值switch (e.getKeyCode()){case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN://向下的箭頭++y;break;case KeyEvent.VK_UP://向上的--y;break;case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT://向左--x;break;case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT://向右++x;break;}//重繪面板this.repaint();}@Override//當某個鍵被松開時 該方法會觸發public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {}@Overridepublic void paint(Graphics g) {super.paint(g);g.fillOval(x, y, 20, 20);}
}








)




)



】)

