文章目錄
- JUC原子類
- 1.JUC中的Atomic原子操作包
- 1.1. 基本原子類(Basic Atomic Classes)
- 1.2. 數組原子類(Array Atomic Classes)
- 1.3. 引用原子類(Reference Atomic Classes)
- 4. 字段更新原子類(Field Updater Atomic Classes)
- 2.基礎原子類(Atomic Integer)
- 2.1.基本方法
- 2.2.案例代碼
- 3.數組原子類
- 3.1.基本方法
- 3.2.案例代碼
- 4.AtomicInteger線程安全原理
- 5.對象操作原子性
- 5.1引用類型原子類
- 5.2.案例代碼
- 6.屬性更新原子類
- 6.1.屬性更新原子類
- 6.2.案例代碼
JUC原子類
在多線程并發執行過程中,例如++ ,–,這類運算符都是不具備原子性的,通常我們會使用synchronized將其變為同步操作,但是這樣會導致性能上的下降。JDK為這些不安全的操作提供了一些原子類,JDK原子類基于CAS輕量級原子操作實現,使得運行效率變得很高。
1.JUC中的Atomic原子操作包
Java中的java.util.concurrent.atomic包提供了一系列的原子操作類,用于在多線程環境下進行原子操作。這些類通常用于實現線程安全的計數器、標志位、引用等,并且比使用synchronized關鍵字或者volatile變量實現的方式更高效。
根據操作目標的數據類型,可以將JUC包的原子類分為以下4類,基本原子類,數組原子類,引用原子類,字段更新原子類
1.1. 基本原子類(Basic Atomic Classes)
這些類用于對基本數據類型進行原子操作,如int、long、boolean等。
-
AtomicBoolean:提供了對boolean類型值的原子更新操作,使用CAS算法來保證原子性。
AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(true); atomicBoolean.getAndSet(false); // 設置新值并返回舊值 -
AtomicInteger:提供了對int類型值的原子更新操作,同樣使用CAS算法。
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); atomicInteger.incrementAndGet(); // 原子地將當前值加一,并返回增加后的值 -
AtomicLong:提供了對long類型值的原子更新操作。
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0L); atomicLong.compareAndExchange(0L, 1L); // 如果當前值等于預期值,則更新為新值
1.2. 數組原子類(Array Atomic Classes)
這些類用于對數組中的元素進行原子操作。
-
AtomicIntegerArray:提供了對int數組中元素的原子更新操作。
AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(5); atomicIntArray.getAndIncrement(0); // 原子地將指定索引位置的元素加一,并返回原值 -
AtomicLongArray:提供了對long數組中元素的原子更新操作。
AtomicLongArray atomicLongArray = new AtomicLongArray(5); atomicLongArray.addAndGet(0, 10L); // 原子地將指定索引位置的元素加上給定的值,并返回增加后的值 -
AtomicReferenceArray:提供了對引用類型數組中元素的原子更新操作。
AtomicReferenceArray<String> atomicRefArray = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(new String[]{"a", "b", "c"}); atomicRefArray.compareAndSet(1, "b", "new_value"); // 如果當前值等于預期值,則更新為新值
1.3. 引用原子類(Reference Atomic Classes)
這些類用于對引用類型數據進行原子操作。
-
AtomicReference:提供了對引用類型值的原子更新操作。
AtomicReference<String> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>("initial_value"); atomicReference.getAndSet("new_value"); // 設置新值并返回舊值
4. 字段更新原子類(Field Updater Atomic Classes)
這些類用于對指定類的指定字段進行原子更新操作,通常用于性能優化。
-
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:用于對指定類的指定volatile int字段進行原子更新操作。
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<MyClass> updater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyClass.class, "fieldName"); updater.incrementAndGet(instance); // 原子地將指定實例的字段值加一,并返回增加后的值 -
AtomicLongFieldUpdater:用于對指定類的指定volatile long字段進行原子更新操作。
AtomicLongFieldUpdater<MyClass> updater = AtomicLongFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyClass.class, "fieldName"); updater.compareAndSet(instance, 0L, 1L); // 如果當前值等于預期值,則更新為新值 -
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:用于對指定類的指定volatile引用字段進行原子更新操作。
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyClass, String> updater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyClass.class, String.class, "fieldName"); updater.getAndSet(instance, "new_value"); // 設置新值并返回舊值
這些原子類提供了一系列的原子操作方法,可以確保在多線程環境下的操作是線程安全的,避免了使用synchronized關鍵字或者volatile變量所帶來的性能開銷。
2.基礎原子類(Atomic Integer)
2.1.基本方法
- get(): 獲取當前的值。
- set(int newValue): 設置為指定的值。
- getAndSet(int newValue): 設置為指定的值,并返回舊值。
- incrementAndGet(): 將當前值加 1,并返回增加后的值。
- decrementAndGet(): 將當前值減 1,并返回減少后的值。
- getAndIncrement(): 返回當前值,并將其加 1。
- getAndDecrement(): 返回當前值,并將其減 1。
- compareAndSet(int expect, int update): 如果當前值等于期望值,則設置為新值,并返回 true,否則返回 false。
2.2.案例代碼
通過調用Atomict提供的API 實現了原子性 修改數據
@Test
@DisplayName("測試AtomicInteger")
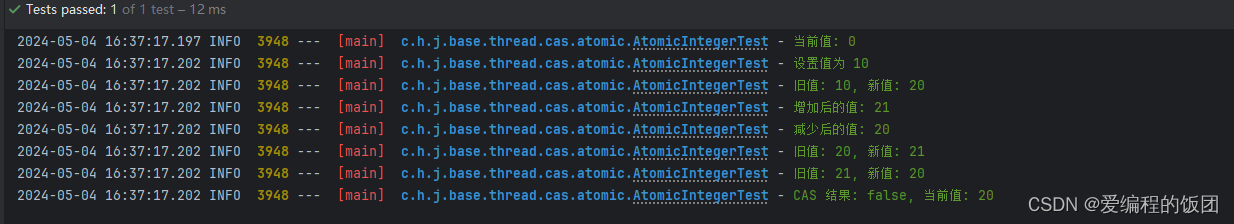
public void testAtomicInteger() {log.info("當前值: {}", counter.get());counter.set(10);log.info("設置值為 10");int oldValue = counter.getAndSet(20);log.info("舊值: {}, 新值: {}", oldValue, counter.get());log.info("增加后的值: {}", counter.incrementAndGet());log.info("減少后的值: {}", counter.decrementAndGet());oldValue = counter.getAndIncrement();log.info("舊值: {}, 新值: {}", oldValue, counter.get());oldValue = counter.getAndDecrement();log.info("舊值: {}, 新值: {}", oldValue, counter.get());boolean success = counter.compareAndSet(18, 30);log.info("CAS 結果: {}, 當前值: {}", success, counter.get());}
上面的操作是在單線程的環境下,下面我通過多線程來實現 數據的一個自增操作
@Test
@DisplayName("多線程實現自增運算")
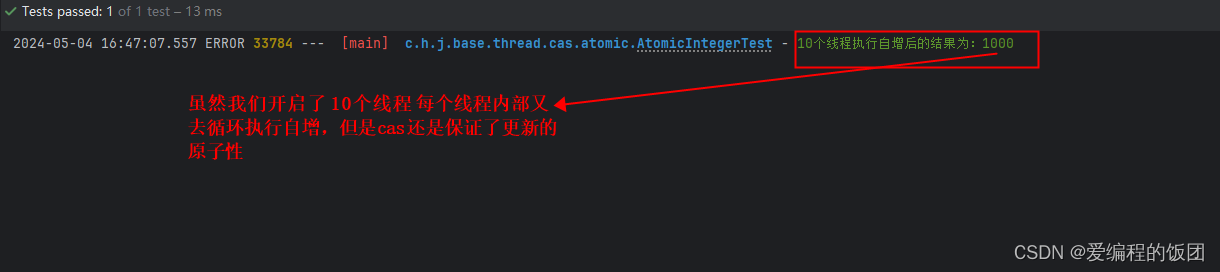
public void test() throws InterruptedException {ArrayList<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>();CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {threads.add(new Thread(()->{// 每個線程進行 100次自增運算for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {counter.incrementAndGet();}latch.countDown();}));}// 全部啟動線程threads.forEach(Thread::start);// 等待全部線程執行結束latch.await();//打印最終結果log.error("10個線程執行自增后的結果為:{}", counter.get());
}
3.數組原子類
3.1.基本方法
- get(int index): 獲取指定索引處的值。
- set(int index, int newValue): 設置指定索引處的值。
- getAndSet(int index, int newValue): 設置指定索引處的值,并返回舊值。
- incrementAndGet(int index): 將指定索引處的值加 1,并返回增加后的值。
- decrementAndGet(int index): 將指定索引處的值減 1,并返回減少后的值。
- addAndGet(int index, int delta): 將指定索引處的值加上給定的增量,并返回增加后的值。
- compareAndSet(int index, int expect, int update): 如果指定索引處的值等于期望值,則設置為新值,
3.2.案例代碼
// 數組原子類
private static final AtomicIntegerArray array = new AtomicIntegerArray(5);@Test
@DisplayName("測試數組原子類")
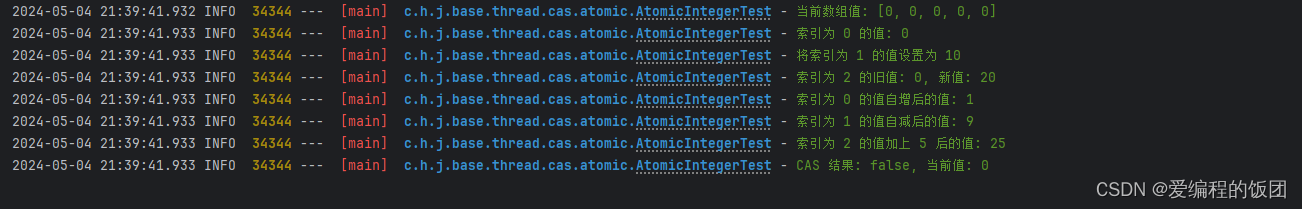
public void testAtomicIntegerArray() {// 1. get(int index)log.info("當前數組值: {}", array.toString());// 2. get(int index)log.info("索引為 0 的值: {}", array.get(0));// 3. set(int index, int newValue)array.set(1, 10);log.info("將索引為 1 的值設置為 10");// 4. getAndSet(int index, int newValue)int oldValue = array.getAndSet(2, 20);log.info("索引為 2 的舊值: {}, 新值: {}", oldValue, array.get(2));// 5. incrementAndGet(int index)log.info("索引為 0 的值自增后的值: {}", array.incrementAndGet(0));// 6. decrementAndGet(int index)log.info("索引為 1 的值自減后的值: {}", array.decrementAndGet(1));// 7. addAndGet(int index, int delta)log.info("索引為 2 的值加上 5 后的值: {}", array.addAndGet(2, 5));// 8. compareAndSet(int index, int expect, int update)boolean success = array.compareAndSet(3, 18, 30);log.info("CAS 結果: {}, 當前值: {}", success, array.get(3));
}
運行以上程序,結果如下:
4.AtomicInteger線程安全原理
基礎原子類(以AtomicInteger為例),主要是通過CAS自旋 + volatile相結合的方案實現,既保證了變量操作線程的原子性,有避免了synchronized重量級鎖的開銷,使得Java程序的效率得到大幅度提升。
下面簡單 以AtomicInteger源碼 分析一下 原子類的CAS自旋 + volatile相結合的方案(JDK 17發生 了變化)
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;// 使用Unsafe類獲取Unsafe實例,用于執行CAS操作private static final Unsafe U = Unsafe.getUnsafe();// VALUE字段的偏移量private static final long VALUE = U.objectFieldOffset(AtomicInteger.class, "value");// 使用volatile關鍵字保證多線程間的可見性private volatile int value;// 構造方法,初始化AtomicInteger的值public AtomicInteger(int initialValue) {value = initialValue;}// 構造方法,默認初始值為0public AtomicInteger() {}// 獲取當前值public final int get() {return value;}// 設置新值public final void set(int newValue) {value = newValue;}// 延遲設置新值,使用setRelease方法public final void lazySet(int newValue) {U.putIntRelease(this, VALUE, newValue);}// 獲取并設置新值,返回舊值public final int getAndSet(int newValue) {return U.getAndSetInt(this, VALUE, newValue);}// 比較并設置新值,如果當前值等于期望值,則設置為新值,返回設置前的值public final boolean compareAndSet(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.compareAndSetInt(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 下面的方法實現了自增、自減、加法運算,并返回相應的結果,以及更新當前值的功能,使用CAS操作保證原子性// 自增并獲取當前值public final int getAndIncrement() {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, 1);}// 自減并獲取當前值public final int getAndDecrement() {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, -1);}// 加上指定的值并獲取當前值public final int getAndAdd(int delta) {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, delta);}// 自增并獲取更新后的值public final int incrementAndGet() {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, 1) + 1;}// 自減并獲取更新后的值public final int decrementAndGet() {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, -1) - 1;}// 加上指定的值并獲取更新后的值public final int addAndGet(int delta) {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, delta) + delta;}// 下面的方法為類型轉換方法,用于轉換為其他基本數據類型// 返回int值public final String toString() {return Integer.toString(get());}// 返回當前值的int表示public int intValue() {return get();}// 返回當前值的long表示public long longValue() {return (long)get();}// 返回當前值的float表示public float floatValue() {return (float)get();}// 返回當前值的double表示public double doubleValue() {return (double)get();}// JDK 9之后的新增方法,使用plain、opaque、acquire、release等方法增加了對內存操作的控制// 返回當前值,使用非volatile內存語義public final int getPlain() {return U.getInt(this, VALUE);}// 設置新值,使用非volatile內存語義public final void setPlain(int newValue) {U.putInt(this, VALUE, newValue);}// 返回當前值,使用opaque內存語義public final int getOpaque() {return U.getIntOpaque(this, VALUE);}// 設置新值,使用opaque內存語義public final void setOpaque(int newValue) {U.putIntOpaque(this, VALUE, newValue);}// 返回當前值,使用acquire內存語義public final int getAcquire() {return U.getIntAcquire(this, VALUE);}// 設置新值,使用release內存語義public final void setRelease(int newValue) {U.putIntRelease(this, VALUE, newValue);}// 使用compareAndExchange方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回舊值public final int compareAndExchange(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.compareAndExchangeInt(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 使用compareAndExchangeAcquire方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回舊值public final int compareAndExchangeAcquire(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.compareAndExchangeIntAcquire(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 使用compareAndExchangeRelease方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回舊值public final int compareAndExchangeRelease(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.compareAndExchangeIntRelease(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 使用weakCompareAndSetInt方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回操作是否成功public final boolean weakCompareAndSetVolatile(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.weakCompareAndSetInt(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 使用weakCompareAndSetIntAcquire方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回操作是否成功public final boolean weakCompareAndSetAcquire(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.weakCompareAndSetIntAcquire(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}// 使用weakCompareAndSetIntRelease方法實現CAS操作,設置新值,返回操作是否成功public final boolean weakCompareAndSetRelease(int expectedValue, int newValue) {return U.weakCompareAndSetIntRelease(this, VALUE, expectedValue, newValue);}
}// 其中自旋操作在UnSafe中實現 /*** Atomically adds the given value to the current value of a field* or array element within the given object {@code o}* at the given {@code offset}.** @param o object/array to update the field/element in* @param offset field/element offset* @param delta the value to add* @return the previous value* @since 1.8*/@IntrinsicCandidatepublic final int getAndAddInt(Object o, long offset, int delta) {int v;do {v = getIntVolatile(o, offset);} while (!weakCompareAndSetInt(o, offset, v, v + delta));return v;}@IntrinsicCandidatepublic native int getIntVolatile(Object o, long offset);// 比較期望值 并設置@IntrinsicCandidatepublic final boolean weakCompareAndSetInt(Object o, long offset,int expected,int x) {return compareAndSetInt(o, offset, expected, x);}5.對象操作原子性
基礎原子類型 只能保證一個變量的原子操作,但是當需要對多個變量操作時,CAS無法保證原子性操作,這個時候可以使用AtomicReference(原子引用類型),保證對象引用的原子性。
簡單來說,如果需要同時保證多個變量操作原子性,可以把多個變量放入一個對象中進行操作
5.1引用類型原子類
-
AtomicReference :基礎引用原子類
get():獲取當前存儲在AtomicReference中的對象。set():設置AtomicReference中的對象為指定值。compareAndSet():如果當前存儲在AtomicReference中的對象等于預期值,則將AtomicReference中的對象設置為新值。getAndSet():獲取當前存儲在AtomicReference中的對象,并設置AtomicReference中的對象為新值。
-
AtomicStampedReference:原子更新帶有整數標記的引用。此類可以用于解決CAS操作的ABA問題。ABA問題是指在使用CAS進行原子更新時,如果被更新的數據從A變成了B,然后又變回了A,這樣的狀態變化可能會導致誤判。
AtomicStampedReference通過引入版本號(或時間戳)來解決這個問題,它將每次更新都與一個標記相關聯,以便在比較時不僅考慮引用對象的值,還要考慮其標記。主要方法:
boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference, int expectedStamp, int newStamp):如果當前引用和標記都與預期值匹配,則原子地將引用和標記的值設置為新值。
-
AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新帶有標記位的引用。與
AtomicStampedReference類似,但是標記是一個布爾值,只有兩種狀態(true或false)。這個類通常用于簡單的標記,而不需要額外的版本信息。主要方法:
boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference, boolean expectedMark, boolean newMark):如果當前引用和標記都與預期值匹配,則原子地將引用和標記的值設置為新值。
下面主要介紹一下AtomicReference
5.2.案例代碼
@Test@DisplayName("測試基礎引用原子類型")public void test2() {// 創建一個初始值為null的AtomicReference對象AtomicReference<Student> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>(null);Student student = new Student("張三",21);// 設置AtomicReference中的對象值為atomicReference.set(student);log.error("當前AtomicReference中的對象值為: " + atomicReference.get());// 比較并設置操作,如果當前對象值等于"student",則設置為"新的student"boolean success = atomicReference.compareAndSet(student,new Student("李四",21));if (success) {log.error("對象值成功被修改為: " + atomicReference.get());} else {log.error("對象值未被修改,當前值為: " + atomicReference.get());}// 獲取并設置操作,獲取當前對象值并設置為"王五 32"Student studentOld = atomicReference.getAndSet(new Student("王五", 32));log.error("獲取到的舊對象值為: " + studentOld);log.error("當前AtomicReference中的對象值為: " + atomicReference.get());}@Getter@Setter@ToStringclass Student{private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}}

注意:使用原子應用類型AtomicReference操作包裝了Student,只能保證Student引用的原子的操作,對被包裝的Student對象的字段修改時并不能保證原子性(說白了,student.setName() 這種是不具備原子性的 new Student(“xxx”,232) 這種 通過包裝統一更新的 是具備原子性的)
6.屬性更新原子類
屬性更新原子類是Java并發包提供的一組類,用于原子性地更新對象中的屬性值。這些類通常用于保證多線程環境下的線程安全性,避免競態條件和數據不一致性問題。
6.1.屬性更新原子類
屬性類更新原子類有以下三個
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新整型字段的值。
static <T> AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<T> newUpdater(Class<T> tClass, String fieldName):創建一個新的原子整型字段更新器。int get(T obj):獲取指定對象中字段的當前值。void set(T obj, int newValue):設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。int getAndSet(T obj, int newValue):獲取并設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新長整型字段的值。
static <T> AtomicLongFieldUpdater<T> newUpdater(Class<T> tClass, String fieldName):創建一個新的原子長整型字段更新器。long get(T obj):獲取指定對象中字段的當前值。void set(T obj, long newValue):設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。long getAndSet(T obj, long newValue):獲取并設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<T, V>:原子更新引用類型字段的值。
static <T,V> AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<T,V> newUpdater(Class<T> tClass, Class<V> vClass, String fieldName):創建一個新的原子引用類型字段更新器。V get(T obj):獲取指定對象中字段的當前值。void set(T obj, V newValue):設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。V getAndSet(T obj, V newValue):獲取并設置指定對象中字段的值為指定的新值。
使用屬性更新原子類保障安全性的主要流程 大致分為兩部
- 更新的對象的屬性必須是 public volatile修飾符
- 因為對象的屬性修改類型原子類都是抽象類,所以每次每次使用都必須使用靜態方法
6.2.案例代碼
@Test@DisplayName("屬性更新原子類")public void test3() {AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Data> updater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Data.class, "value");Data data = new Data(10);// 獲取并輸出當前值log.error("初始值:{}",updater.get(data));// 嘗試原子性地將值更新為20updater.set(data, 20);log.error("更新后的值:{}",updater.get(data));// 嘗試原子性地獲取并更新值為30int oldValue = updater.getAndSet(data, 30);log.error("原來的值:{}", oldValue);log.error("更新后的值:{}", updater.get(data));}class Data {public volatile int value; // 要更新的字段必須是 volatile 的public Data(int value) {this.value = value;}}
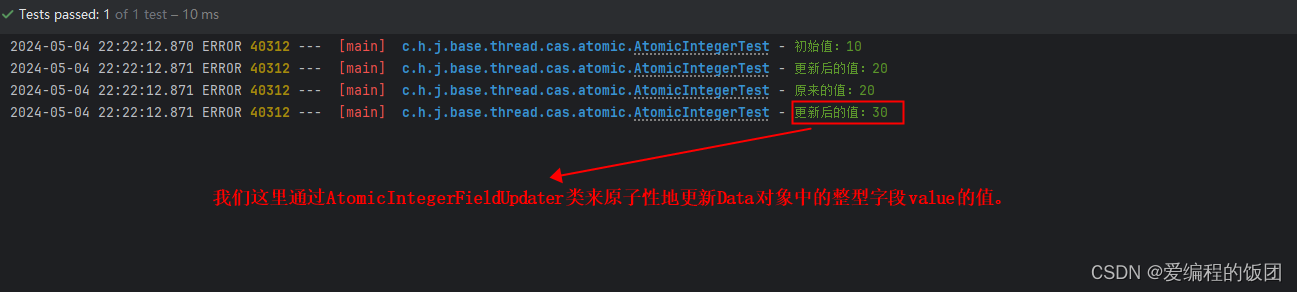
這個代碼了如何使用AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater類來原子性地更新Data對象中的整型字段value的值。



)









Java Web攔截器作用和用法)
)

暨第六屆CCPC河南省大學生程序設計競賽 problem K. 樹上問題)


![61、內蒙古工業大學、內蒙科學技術研究院:CBAM-CNN用于SSVEP - BCI的分類方法[腦機二區還是好發的]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/61、內蒙古工業大學、內蒙科學技術研究院:CBAM-CNN用于SSVEP - BCI的分類方法[腦機二區還是好發的])