一、Playbook基礎
1.1 Playbook定義
Playbook其實是Ansible服務的一個配置文件,Ansible使用Playbook的YAML語言配置編寫成操作需求,實現對遠端主機或策略部署,實現對遠端主機的控制與管理。
1.2 Playbook組成
Tasks:任務,即通過 task 調用 ansible 的模板將多個操作組織在一個 playbook 中運行
Variables:變量
Templates:模板
Handlers:處理器,當changed狀態條件滿足時,(notify)觸發執行的操作
Roles:角色
1.3 Playbook劇本詳解
vim test1.yaml
---
#yaml文件以---開頭,以表明這是一個yaml文件,可省略(但是如果兩個YAML配置疊加的話,要以此為分割)
- name: first play
#定義一個play的名稱,可省略gather_facts: false
#設置不進行facts信息收集,這可以加快執行速度,可省略hosts: webservers
#指定要執行任務的被管理主機組,如多個主機組用冒號分隔remote_user: root
#指定被管理主機上執行任務的用戶tasks:
#定義任務列表,任務列表中的各任務按次序逐個在hosts中指定的主機上執行- name: test connection
#自定義任務名稱ping:
#使用 module: [options] 格式來定義一個任務- name: disable selinuxcommand: '/sbin/setenforce 0'
#command模塊和shell模塊無需使用key=value格式ignore_errors: True
#如執行命令的返回值不為0,就會報錯,tasks停止,可使用ignore_errors忽略失敗的任務- name: disable firewalldservice: name=firewalld state=stopped
#使用 module: options 格式來定義任務,option使用key=value格式- name: install httpdyum: name=httpd state=latest- name: install configuration file for httpdcopy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#這里需要一個事先準備好的/opt/httpd.conf文件notify: "restart httpd"
#如以上操作后為changed的狀態時,會通過notify指定的名稱觸發對應名稱的handlers操作- name: start httpd serviceservice: enabled=true name=httpd state=startedhandlers:
#handlers中定義的就是任務,此處handlers中的任務使用的是service模塊- name: restart httpd
#notify和handlers中任務的名稱必須一致service: name=httpd state=restarted
#Ansible在執行完某個任務之后并不會立即去執行對應的handler,而是在當前play中所有普通任務都執行完后再去執行handler,這樣的好處是可以多次觸發notify,但最后只執行一次對應的handler,從而避免多次重啟。1.4 Playbook命令?
//運行playbook
ansible-playbook test01.yaml
//補充參數:
-k(–ask-pass):用來交互輸入ssh密碼
-K(-ask-become-pass):用來交互輸入sudo密碼
-u:指定用戶
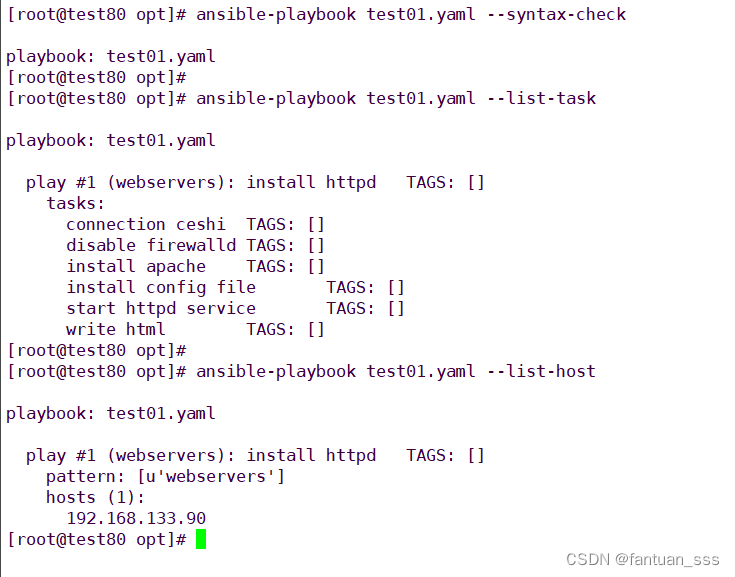
ansible-playbook test01.yaml --syntax-check #檢查yaml文件的語法是否正確
ansible-playbook test01.yaml --list-task #檢查tasks任務
ansible-playbook test01.yaml --list-hosts #檢查生效的主機
ansible-playbook test01.yaml --start-at-task='install httpd' #指定從某個task開始運行
1.5 Playbook安裝并啟動httpd服務
cd /opt/
vim test01.yaml
---
- name: install httpdgather_facts: falsehosts: webserversremote_user: roottasks:- name: connection ceshiping:- name: disable firewalldservice: name=firewalld state=stopped- name: install apacheyum: name=httpd state=latest- name: install config filecopy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf- name: start httpd serviceservice: enabled=true name=httpd state=started- name: write htmlcopy: src=/opt/index.html dest=/var/www/html/index.htmlnotify: "restart httpd"handlers:- name: restart httpdservice: name=httpd state=restarted
echo 123 > index.html
cat index.html?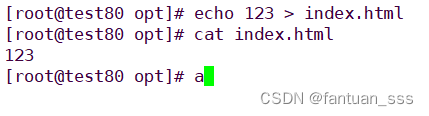
ansible-playbook test01.yaml --syntax-checkansible-playbook test01.yaml --list-taskansible-playbook test01.yaml --list-hostansible-playbook test01.yaml
 ?
?
1.6?變量的定義和引用
cd /opt
vim test02.yaml---
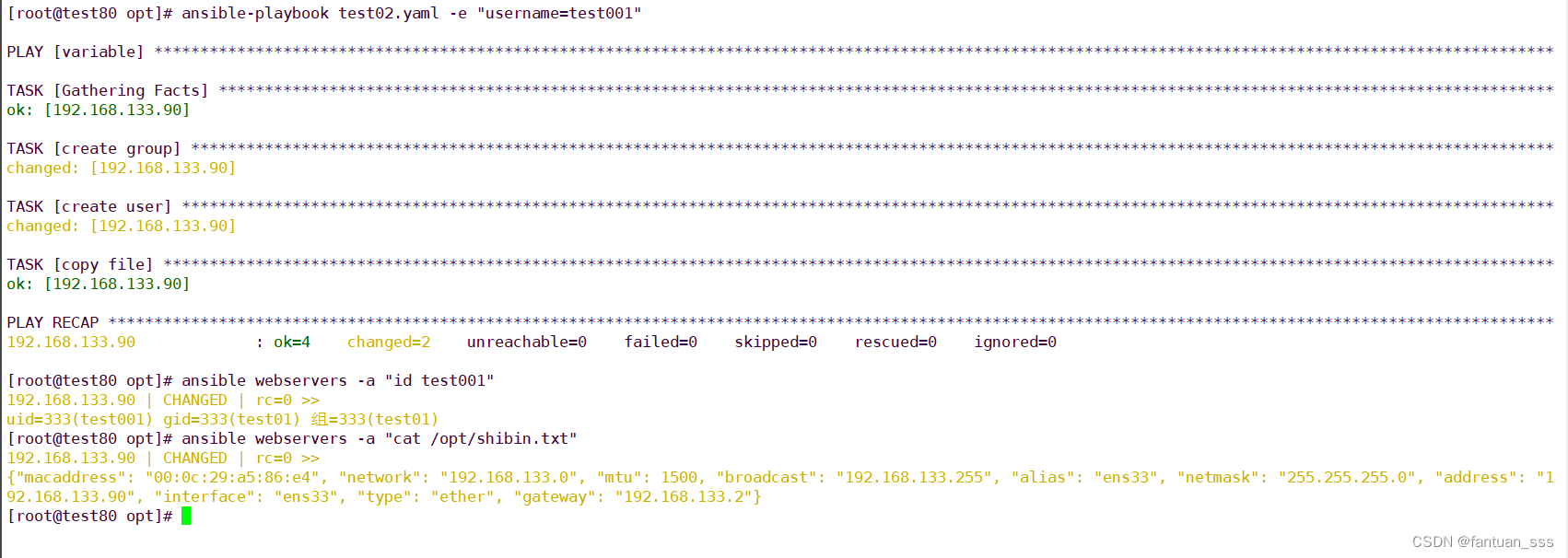
- name: variablehosts: webserversremote_user: rootvars:- groupname: test01- username: nginxtasks:- name: create groupgroup: name={{groupname}} system=yes gid=333- name: create useruser: name={{username}} uid=333 group={{groupname}}- name: copy filecopy: content="{{ansible_default_ipv4}}" dest=/opt/shibin.txt-e選項指定ymal配置文件中變量username,因為指定了在yaml文件中指定的username為"nginx",實際命令中指定為"test001"最終是以-e選項指定的username生效;
注意:命令行中的變量優先級高于YAML配置文件中的變量優先級。
ansible-playbook test02.yaml -e "username=test001"
 ?
?
1.7?指定遠程主機sudo切換用戶?
cd /opt
vim test03.yaml---
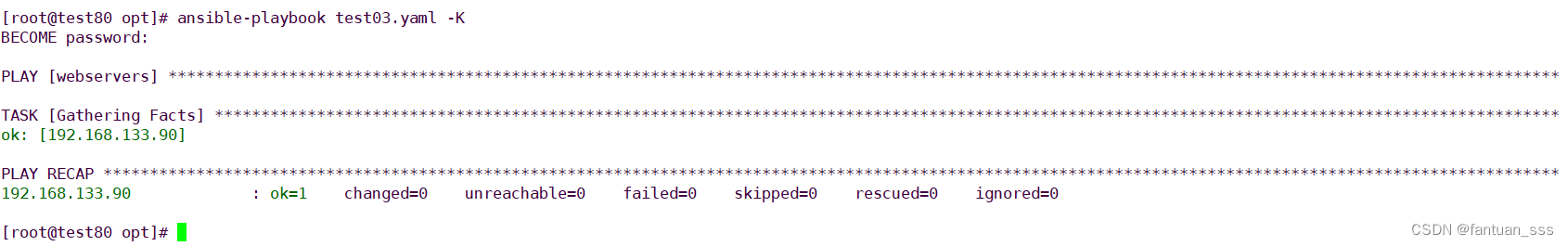
- hosts: webserversremote_user: zhangsan become: yes become_user: root
ansible-playbook test03.yml -K ?
?
這里紅色顯示sudo提權失敗,可以去遠端主機的配置文件(/etc/sudoers)中修改zhangsan用戶的權限
 ???
???
? ?
?
?1.8 When(條件判斷)
cd /opt
vim test04.yaml---
- name: reboot hosthosts: dbserversremote_user: roottasks:- name: shutdown hostcommand: /sbin/shutdown -r nowwhen: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "192.168.133.10"
 ?
?
由于判斷條件為主機地址為192.168.133.10才執行Shutdown操作,所以主機地址為192.168.133.100的主機跳過Playbook?
1.9 迭代
1.9.1?創建文件夾
cd /opt
vim test05.yaml- name: test05hosts: webserverstasks:- name: create directoriesfile: path={{item}} state=touchwith_items:- /opt/shibin/s1.txt- /opt/shibin/s2.txt- /opt/shibin/s3.txt- /opt/shibin/s4.txt注意:需提前在webservers里的主機上創建好目錄/opt/shibin?
ansible-playbook test05.yaml
1.9.2??創建文件夾并建立用戶
cd /opt
vim test06.yaml---
- name: test06hosts: webserversgather_facts: falsetasks:- name: create directoriesfile:path: "{{item}}"state: directorywith_items:- /tmp/test1- /tmp/test2- name: add usersuser: name={{item.name}} state=present groups={{item.groups}}with_items:- name: test1groups: wheel- name: test2groups: rootansible-playbook test06.yaml
 二、Templates模塊
二、Templates模塊
Jinja是基于Python的模板引擎。Template類是Jinja的一個重要組件,可以看作是一個編譯過的模板文件,用來產生目標文本,傳遞Python的變量給模板去替換模板中的標記。
2.1?準備模板文件并設置引用的變量
yum install -y httpdcp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /opt/httpd.conf.j2vim /opt/httpd.conf.j2-42行修改- Listen {{http_port}}
-95行修改- ServerName {{server_name}}
-119行修改- DocumentRoot "{{root_dir}}" 
2.2?修改主機清單內的變量
vim /etc/ansible/hosts -19- [webservers]
-20- 192.168.133.90 http_port=192.168.133.90:80 server_name=www.test1.com:80 root_dir=/etc/httpd/htdocs
#注意 root_dir要和前面的server_name空格 不可另起一行,否則報錯UNREACHABLE!-34- [dbservers]
-35- 192.168.133.100 http_port=192.168.133.100:80 server_name=www.test2.com:80 root_dir=/etc/httpd/htdocs
#注意 root_dir要和前面的server_name空格 不可另起一行,否則報錯UNREACHABLE!2.3?編寫Playbook劇本
vim apache.yaml
---
- hosts: allremote_user: rootvars:- package: httpd- service: httpdtasks:- name: create dirfile: path=/etc/httpd/htdocs state=directory- name: install httpd packageyum: name={{package}} state=latest- name: install configure filetemplate: src=/opt/httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confnotify: "restart httpd"- name: start httpd serverservice: name={{service}} enabled=true state=startedhandlers:- name: restart httpdservice: name={{service}} state=restartedansible-playbook apache.yaml
 ?
?
?三、Tags模塊
可以在一個playbook中為某個或某些任務定義“標簽”,在執行此playbook時通過ansible-playbook命令使用--tags選項能實現僅運行指定的tasks。
playbook還提供了一個特殊的tags為always。作用就是當使用always當tags的task時,無論執行哪一個tags時,定義有always的tags都會執行。
cd /opt
vim test07.yaml---
- hosts: webserversremote_user: roottasks:- name: Copy hosts filecopy: src=/etc/hosts dest=/opt/hoststags: "shibin"- name: touch filefile: path=/opt/testhost state=touchtags: "always"ansible-playbook test07.yaml --tags="shibin"?

?四、Roles模塊
Ansible為了層次化、結構化地組織Playbook,使用了角色(roles),roles可以根據層次型結構自動裝載變量文件、task以及handlers等。簡單來講,roles就是通過分別將變量、文件、任務、模塊及處理器放置于單獨的目錄中,并可以便捷地include它們。roles一般用于基于主機構建服務的場景中,但也可以用于構建守護進程等場景中。
4.1 Roles目錄詳解

4.2?在Playbook中使用Roles步驟
4.2.1?環境準備
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/ -p
#創建以 roles 命名的目錄mkdir /etc/ansible/group_vars/ -p
touch /etc/ansible/group_vars/all
#創建全局變量目錄mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql
#在 roles 目錄中分別創建以各角色名稱命令的目錄mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta}
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta}
#在每個角色命令的目錄中分別創建files、handlers、tasks、templates、meta、defaults和vars目錄,用不到的目錄可以創建為空目錄,也可以不創建touch /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
#在每個角色的 handlers、tasks、meta、defaults、vars 目錄下創建 main.yml 文件,千萬不能自定義文件名4.2.2?修改yml文件?
vim /etc/ansible/site.yml---
- hosts: cxkremote_user: rootroles:- httpd
- hosts: wybremote_user: rootroles:- mysql4.2.3 運行Ansible-Playbook??
cd /etc/ansible
ansible-playbook site.yml4.3?Roles模塊舉例——LAMP
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/php/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -ptouch /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/php/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml4.3.1?編寫httpd模塊
(1)編寫yml文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/tasks/main.yml- name: install apacheyum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start apacheservice: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started?(2)定義變量
vim /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/vars/main.yml
#可以定義在全局變量中,也可以定義在roles角色變量中,一般定義在角色變量中
pkg: httpd
svc: httpd4.3.2 編寫Mysql模塊
(1)編寫yml文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml- name: install mysqlyum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start mysqlservice: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started(2)定義變量
vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/vars/main.ymlpkg:- mariadb- mariadb-server
svc: mariadb4.3.3 編寫Php模塊
(1)編寫yml文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/tasks/main.yml- name: install phpyum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start php-fpmservice: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started(2)定義變量
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/vars/main.ymlpkg:- php- php-fpm
svc: php-fpm4.3.4 編寫Roles實例并啟動
vim /etc/ansible/site.yml---
- hosts: wybremote_user: rootroles:- httpd- mysql- phpcd /etc/ansible
ansible-playbook site.yml五、 Ansible常用命令小結
5.1.ansible-doc
ansible-doc -h Usage: ansible-doc [options] [module...]
#該指令用于查看模塊信息,常用參數有兩個-l 和 -s ,具體如下
ansible-doc -l
#列出所有已安裝的模塊ansible-doc -s command
#查看具體某模塊的用法,這里如查看command模塊5.2 ansible-galaxy
ansible-galaxy -h Usage: ansible-galaxy [init|info|install|list|remove] [--help] [options] ...
#ansible-galaxy指令用于方便的從https://galaxy.ansible.com/ 站點下載第三方擴展模塊,我們可以形象的理解其類似于centos下的yum、python下的pip5.3 ansible-playbook
通過讀取playbook 文件后,執行相應的動作
5.4 ansible-pull
該指令使用需要談到ansible的另一種模式——pull 模式,這和我們平常經常用的push模式剛好相反,其適用于以下場景:你有數量巨大的機器需要配置,即使使用非常高的線程還是要花費很多時間
5.5 ansible-vault
ansible-vault主要應用于配置文件中含有敏感信息,又不希望他能被人看到,vault可以幫你加密/解密這個配置文件,屬高級用法。主要對于playbooks里比如涉及到配置密碼或其他變量時,可以通過該指令加密,這樣我們通過cat看到的會是一個密碼串類的文件,編輯的時候需要輸入事先設定的密碼才能打開。這種playbook文件在執行時,需要加上 –ask-vault-pass參數,同樣需要輸入密碼后才能正常執行。



)




)
)
)



)


![[Java EE] 文件IO(一):文件概念與文件系統操作](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Java EE] 文件IO(一):文件概念與文件系統操作)

